Web UI automation using Selenium
Automate web UI testing with Python and Selenium
Pycon India 2018
5th Oct 2018
Bhoomika Agarwal
- LinkedIn Learning Instructor
- Data Science Enthusiast
- Poet
- Developer at SAP Labs
Abhiram Ravikumar
- Mozilla Tech Speaker
- Open Source evangelist
- Data Science Enthusiast
- LinkedIn Learning Instructor
- Developer at SAP Labs
Facilitators

Contents
- Why do we need to automate testing
- Automated testing
- Python Selenium bindings
- Locating elements on a page
- Navigating through pages
- Waits
- Best practices
- Recap
Why do we need to automate testing?
- Decreased cost and time of testing
- Enable continuous delivery through round-the-clock testing
- Ensure regression testing
- Increased test coverage
- Cross-device testing made easy
Automated Testing
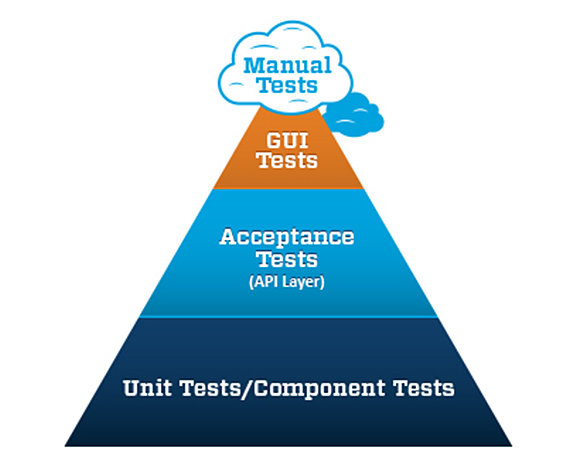
Mike Cohn's test automation pyramid
Cost
Quality
Time
So, where does Python fit in?


unittest
Selenium bindings for Python
- Web UI Automation means the automatic execution of the actions performed in a web browser window
- Selenium automates browsers
- Selenium WebDriver is the one that can automate all these tasks.
-
Used to scale tests to multiple browsers and environments using the selenium grid


Selenium bindings for Python
- Installing Selenium
- Simple test script
#Python selenium bindings installation
pip install selenium
#Test script
from selenium import webdriver
import time
driver= webdriver.Firefox()
driver.get('http://seleniumhq.org')
time.sleep(2)
driver.close()Locating elements
- Uses the id tag to locate elements in a page
-
The HTML ‘id’ attribute specifies a unique id for a HTML element
-
The rules for the ‘id’ attribute are-
1. At least one character
2. No space characters
3. Case sensitive
4. Unique
#Find element by ID
login_form = driver.find_element_by_id('loginForm')Locating by id
Locating elements
- Uses the name tag to locate elements in a page
- Multiple elements might share a name
-
Usually used in forms to reference the element when data is submitted.
# Find username and password by name
username = driver.find_element_by_name('username')
password = driver.find_element_by_name('password')
#Returns login
continue = driver.find_element_by_name('continue')Locating by name
Locating elements
- Used when you don’t have a suitable id or name attribute for the element
-
XPath uses path expressions to identify and navigate nodes in an XML document
- Can be used in absolute or relative terms
#locate the login form element
login_form_absolute = driver.find_element_by_xpath("/html/body/form[1]")
login_form_relative = driver.find_element_by_xpath("//form[1]")
login_form_id = driver.find_element_by_xpath("//form[@id='loginForm']")
#locate the username element
username = driver.find_element_by_xpath("//form/input[@name='username']")
username = driver.find_element_by_xpath("//form[@id='loginForm']/input[1]")
username = driver.find_element_by_xpath("//input[@name='username']")Locating by xpath
Locating elements
- Use the class tag to find elements
-
These classnames are used to point to a class in a style sheet
#Find by class name
content = driver.find_element_by_class_name('content')
Locating by class
Page Interaction
- Finding an element on a page
- Interacting with the element
#Finding an element
search = driver.find_element_by_name('q');
#Interacting with the element
search.clear();
search.send_keys("pycon");
search.send_keys(Keys.RETURN);
Filling forms
- Selecting and deselecting options
- All options
- Submitting a form
from selenium.webdriver.support.ui import Select
#Selecting options
select= Select(driver.find_element_by_name('numReturnSelect'))
select.select_by_index(4)
select.select_by_visible_text("200")
select.select_by_value("250")
#Deselecting options
select.deselect_all()
#All options
options = select.options
#Submitting
submit_button = driver.find_element_by_name('continue')
submit_button.submit();Drag and Drop
- Select the source and destination element
- Drag and drop using ActionChains
- Drag and drop by Offset and from source to target
from selenium.webdriver import ActionChains
action_chains= ActionChains(driver)
#Locate source element
source= driver.find_element_by_id('draggable')
#Locate target element
target = driver.find_element_by_id('droppable')
#Drag and drop by offset
action_chains.drag_and_drop_by_offset(source, 100, 100).perform()
#Drag and drop from source to target
action_chains.drag_and_drop(source, target).perform()
Waits
- The elements in a webpage may be loaded at different time intervals due to AJAX calls
-
While locating elements on a page, the locate function will raise a ‘ElementNotVisibleException’ if the element has not been loaded into the DOM at that point of time.
-
Waiting adds a time interval between actions performed by the WebDriver
-
2 types- explicit and implicit
Waits - Implicit
- Polls the DOM for a certain amount of time when trying to find an element or elements if they are not immediately available.
The waiting time is specified in seconds
from selenium import webdriver
driver = webdriver.Firefox()
driver.implicitly_wait(10) # seconds
driver.get("http://somedomain/url_that_delays_loading")
myDynamicElement = driver.find_element_by_id("myDynamicElement")
Waits - Explicit
- Pause until a certain condition has been satisfied
-
Use a combination of the classes WebDriverWait and Expected Condition to add explicit waits.
try:
element = WebDriverWait(driver, 10).until(
EC.presence_of_element_located((By.ID, "myDynamicElement"))
)
finally:
driver.quit()Waits - Conditions
- title_is
- title_contains
- visibility_of
- presence_of_all_elements_located
- text_to_be_present_in_element
- text_to_be_present_in_element_value
- frame_to_be_available_and_switch_to_it
- invisibility_of_element_located
- element_to_be_clickable - it is Displayed and Enabled.
- element_located_selection_state_to_be
- alert_is_present
Best Practices
- Figure out what works best for you
- Variables naming convention [ _ and ()]
- Separating action and intent
- there is no single 'best' approach
- agile, iterative, incremental approach
- keep selenium up to date
- Practice
- Hack around
Recap
- The need for automated testing
- Mike Cohn's test automation pyramid
- Python Selenium bindings
- Locating elements by id, name, xpath and class
- Navigating through pages - Page interaction, filling forms, drag and drop
- Waits - implicit and explicit

Thank You!
Questions?
bhoomika10@gmail.com
abhi12ravi@gmail.com
Web UI automation using Selenium
By Bhoomika Agarwal
Web UI automation using Selenium
Automate Web UI testing using Python Selenium
- 1,111



