Studying DNA-6mA in Paramecium tetraurelia with PacBio sequencing






Guillaume DELEVOYE
E. Meyer Lab
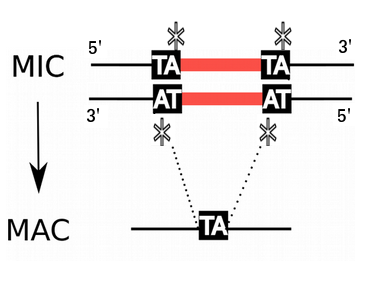
P. tetraurelia: Genomic architecture
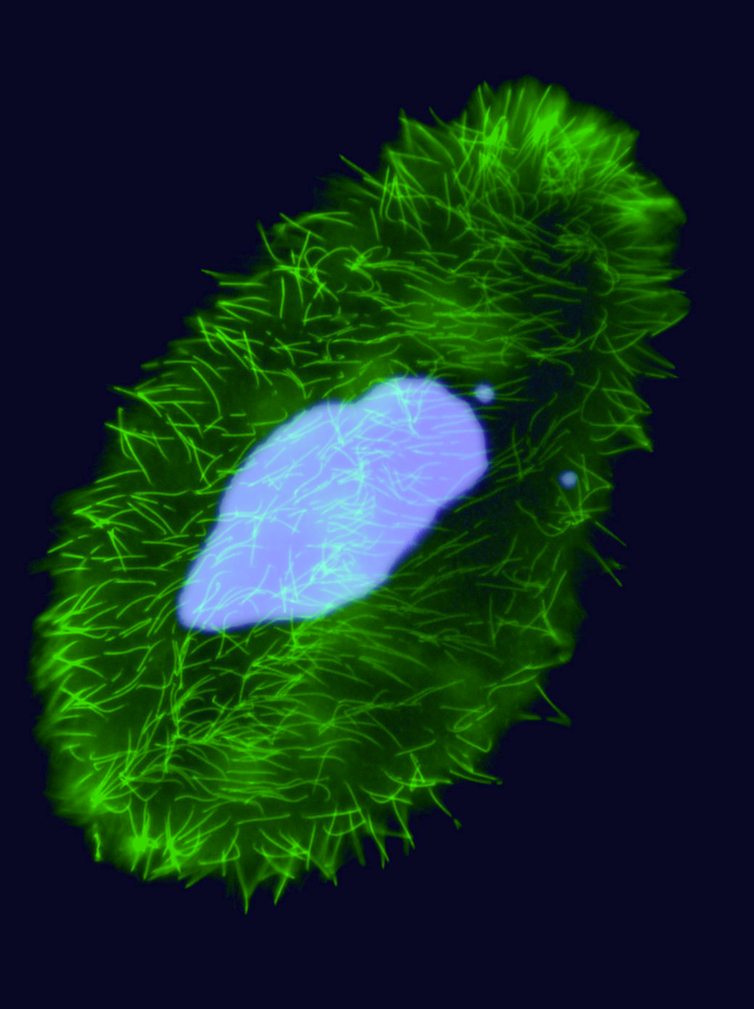
Unicellular eucaryote with 3 nuclei:
-
2xMIC nuclei (2n)
- Germline nucleus
-
Contains: TE & IES
- No transcription outside meiosis
-
1xMAC nucleus (up to 800n)
- Somatic nucleus
- Amplified and "fixed" version of the MIC
- Free from TE and IES
- Transcriptionnally active
DNA ratio: 1 MIC for 200 MAC
+ DIfficult to purify the MIC DNA
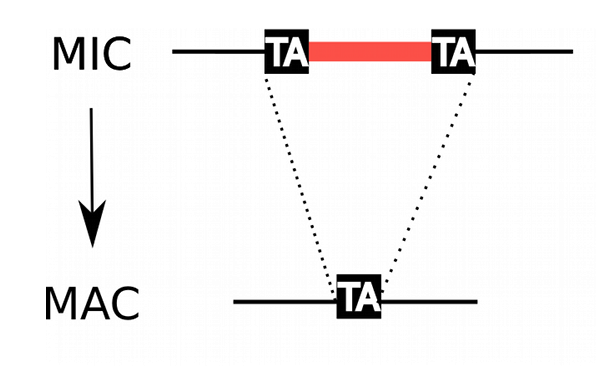
Profiling the IESs
- Non-coding
- Excised after sexual processes
- Remnant of TE ?
- Most recent IES are very short (< 27bp), and are the majority of IESs
45.000 Unique sequences
How are IESs recognized ?
(1/2)
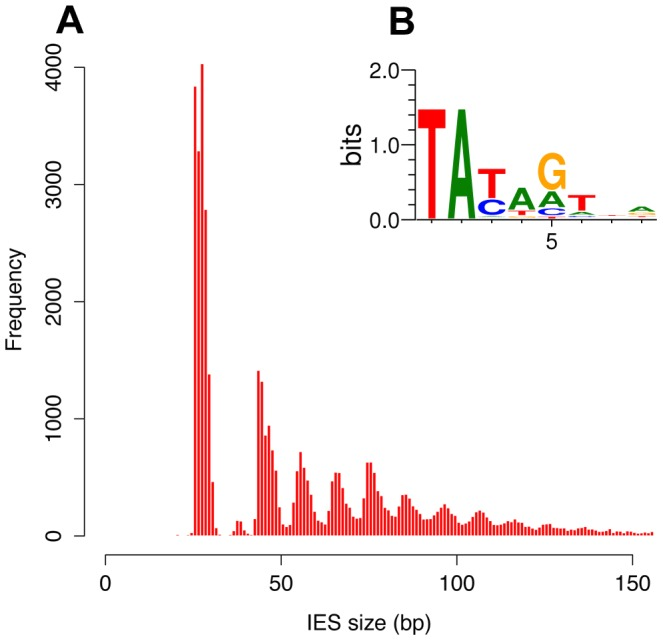
- 100% TA-Bounded
-
Weak consensus TAYAG
- Degenerated TC1-Mariner TE insertion site
- Not sufficient
- Periodic size distribution
30% of IESs only are small-ncRNA dependant (shown by DICER-like2-3 silencing)
- What about the majority remaining ?
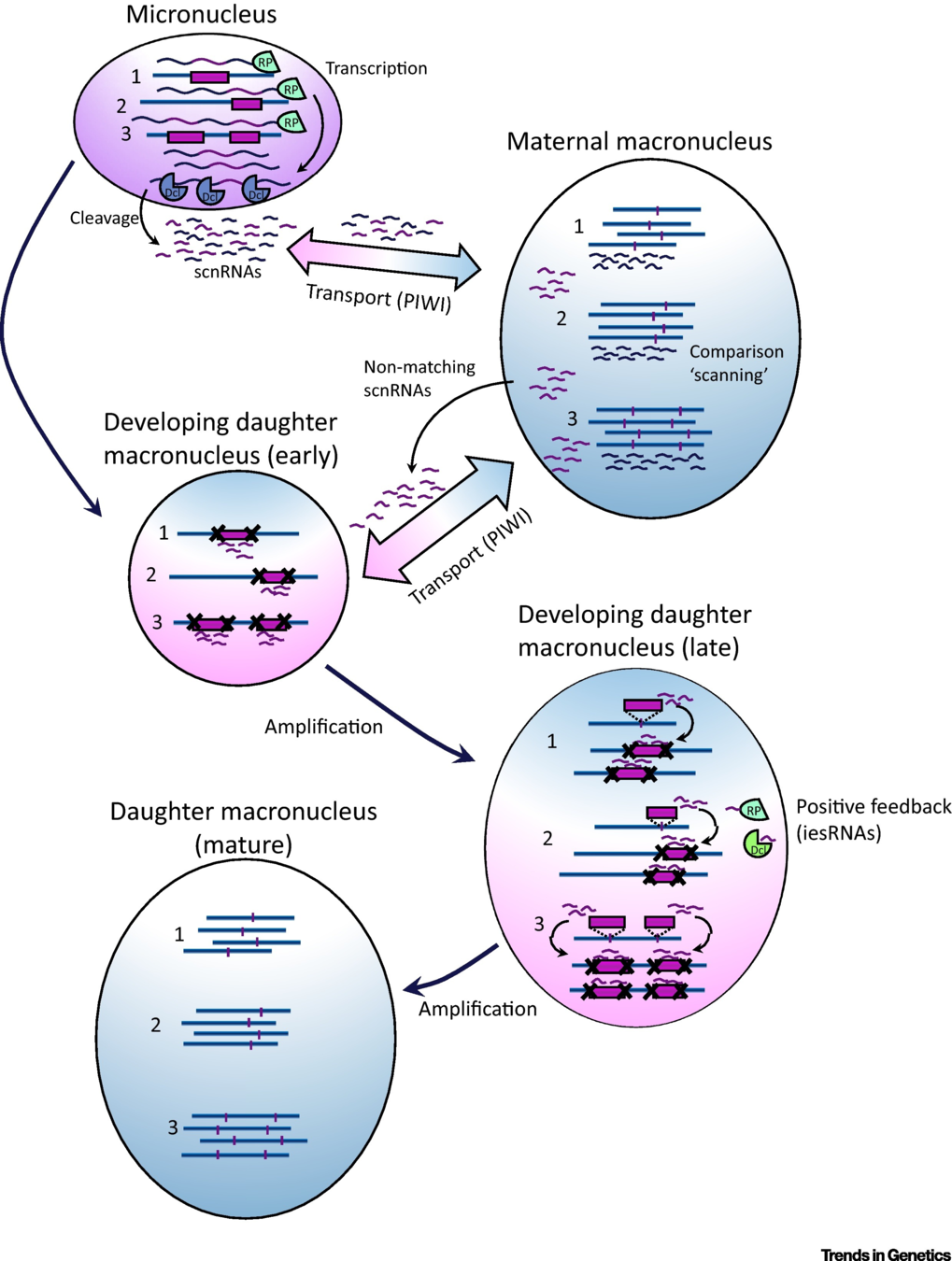
How are IES recognized ? (2/2)
The sc-RNA pathway
IES recognition:
The DNA methylation hypothesis
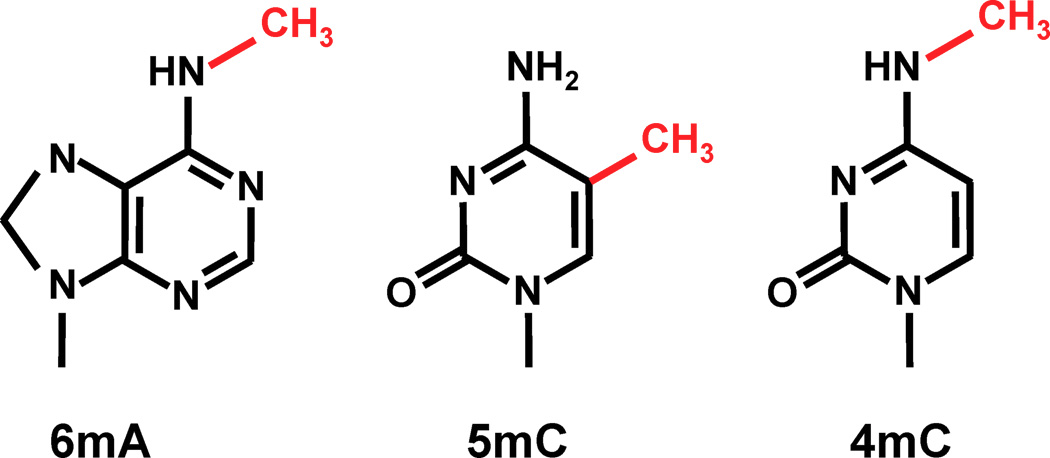
6mA likely to be abundant in Paramecium:
-
Suspected 2.5% in the MAC of P. aurelia by Cummings et Al (1975)
-
Also documented 6mA in the MIC
-
-
Detected methylation by SMRT in the MAC in our lab
-
Detection by SMRT in the MAC by Sandra Duharcourt's lab
- Detection in Oxytricha by L. Landweber et Al (2019)
- no 5mC, 4mC in the MAC a priori


2) In the new forming MAC
1) Constant pattern in the MIC
Transcient ?
PacBio SMRT principle
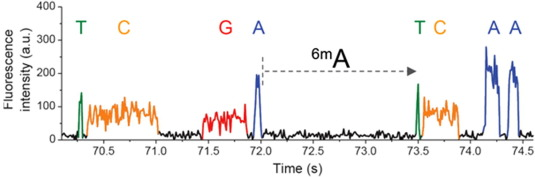
Methylation analysis needs local coverage> 25X
- Kinetic signature of n6mA
- InterPulse Duration (IPD)
-
Compared
- either to WGA
- or Trained model (ML - "in-sillico control") - SImulation from context of nucleotides
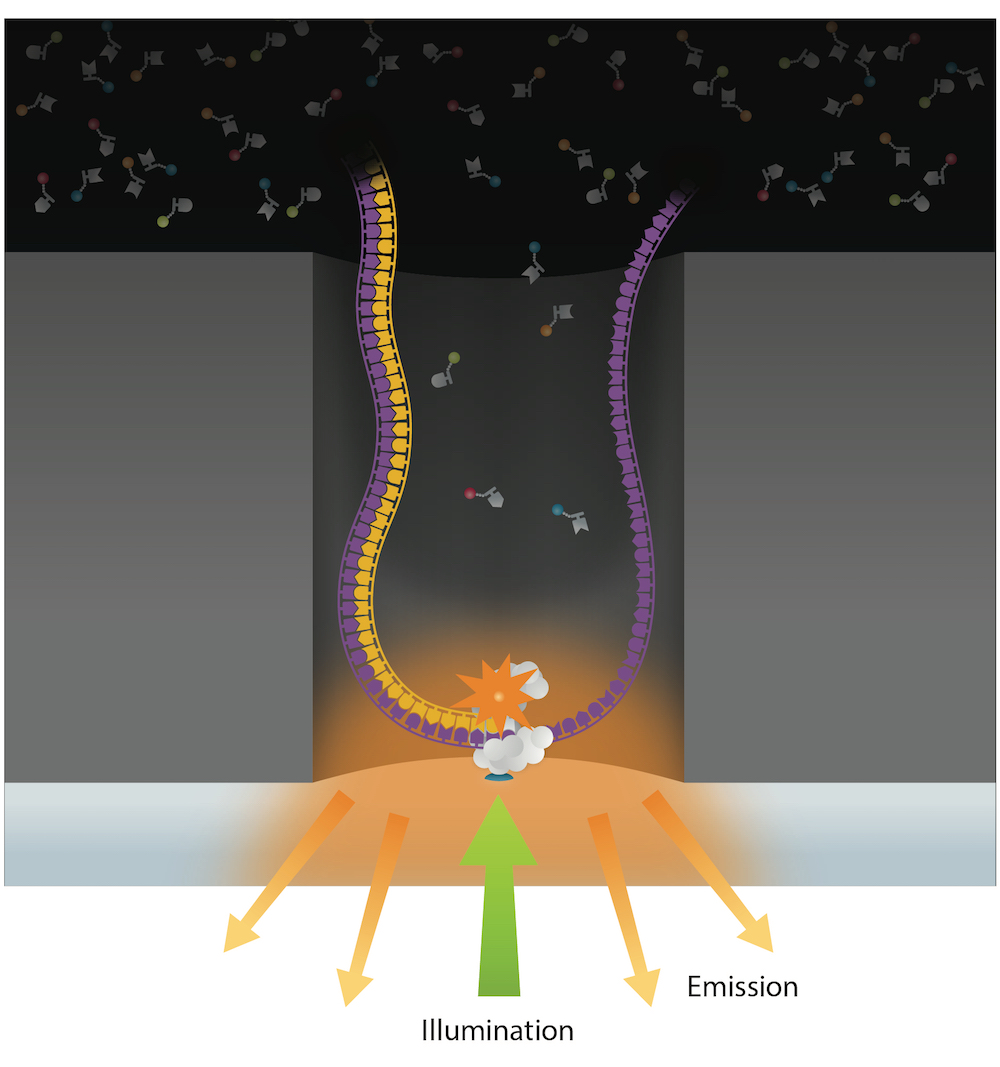
Reads up to 80 kbp
- We use the isn-sillico model
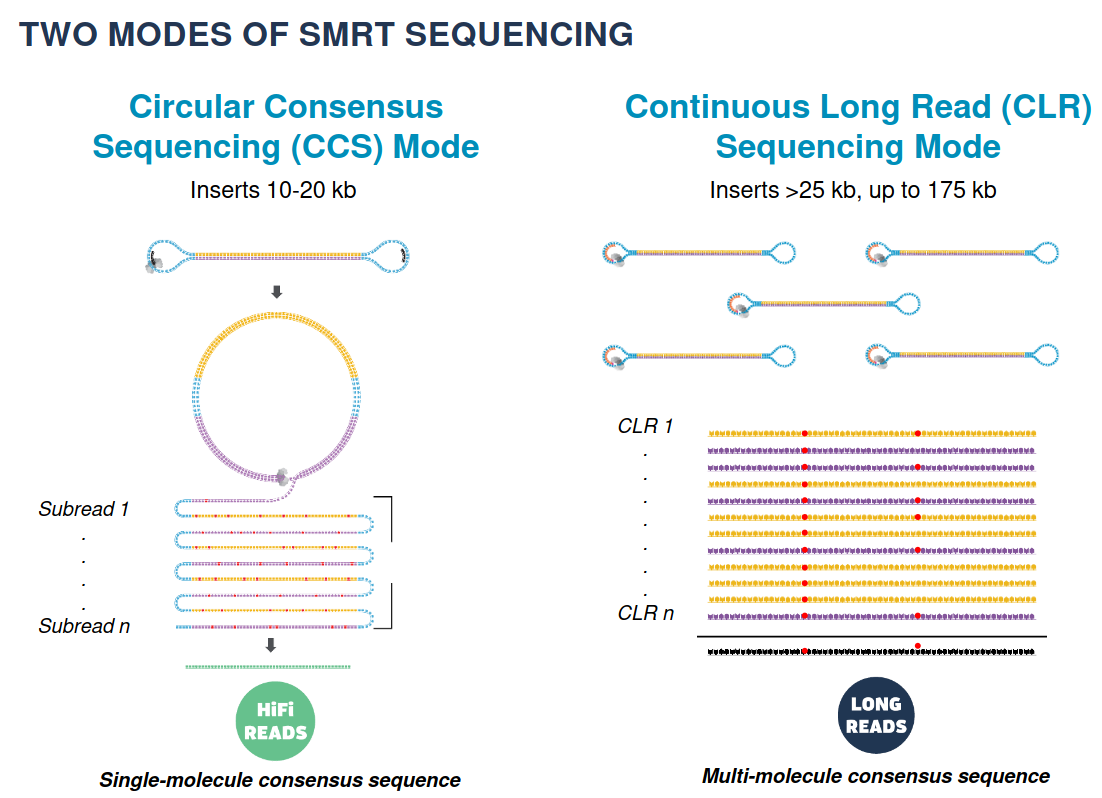
ENLEVER 10-20 KB
Methylase candidates
Candidates:
- 7 "DPPW motif IV" genes
- NM4, NM9, NM10
- Another family: MT1a, MT1b, MT2
2) PacBio sequencing with short inserts | 6mA ++
Also at hand:
- Vegetative WT cells (HTVEG)
- Vegetative cells with a silencing of a control gene (MAB)
- Cells that started autogamy (HT2 - 2 hour* , HT6 - 6 hour*)
1) Grouped silencings by sequence homology
* t0 is defined as the time where 50% of cells entered meiosis
Step 1: Consensus
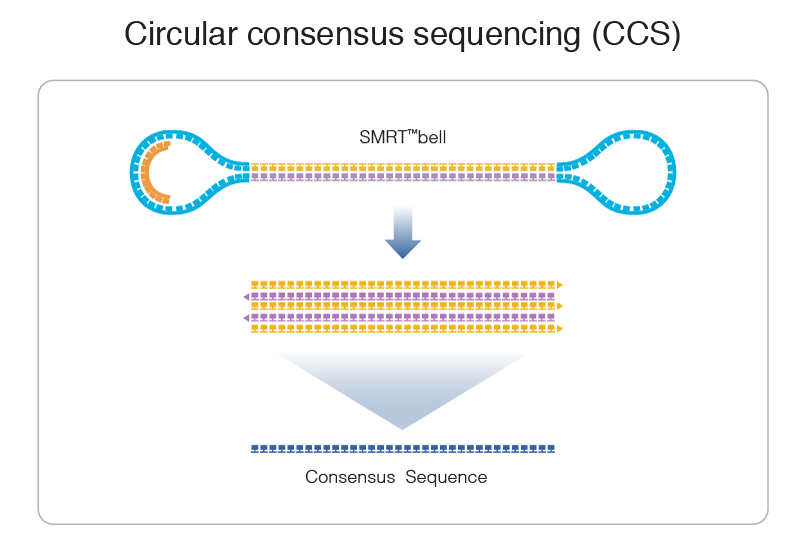
99% accuracy
Max
75% accuracy

Because our inserts are circular and shorts, we can make CCS of high accuracy despite a 15% error-rate in the subreads
Changer : 15% d'erreur
Step 2: Sorting (1/2)
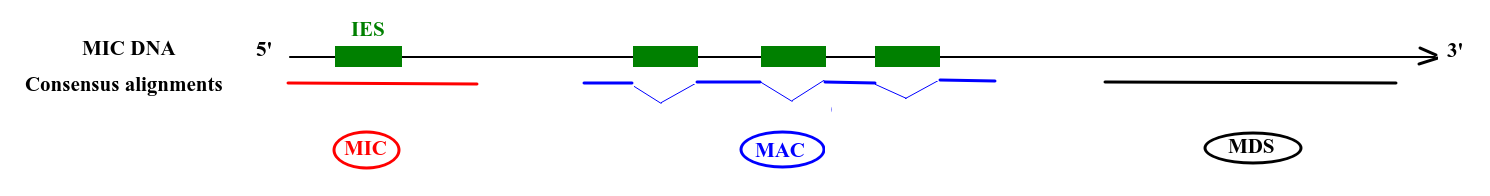
Deduced origin
MIC DNA
Alignment of consensus

TA
TA
TA
Step 2: Sorting (2/2)
- Quite rare
- When it happens, can be amplified up to 400x
- We addressed it by removing separating "True IESs" and "others"
- Filtering based on the number of reads mapped on each IES, in 4 replicated vegetative samples
A few words about IES retention in the MAC:
ADDRESSED UP TO 400X --> NON
Step 3 : DNA methylation analysis
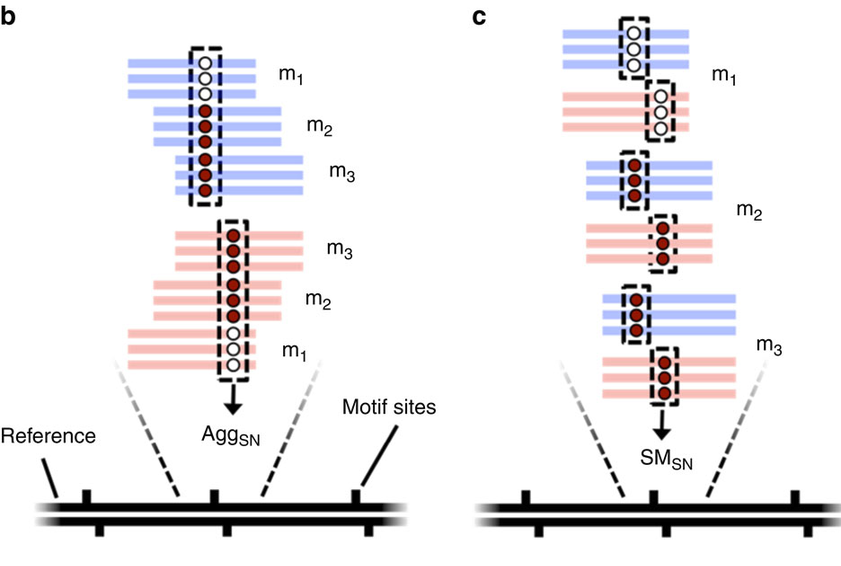
- Single-molecule
- Single-nucleotide resolution
- "SMsn" approach
- "SMsn" approach
- Independant yet pairable analysis on both strands
Some more details:
the random sampling approach

Deduced origin
MIC DNA
Alignment of consensus
Only a few remaining: ~ 10 to ~200 sequences
100% should carry a methylation pattern in our first work hypothesis
-
1 out of 200 comes from the MIC
-
1/6 of MIC inserts will carry an IES
-
1/2 of IESs will be removed by our safety filtering
-
(Eliminate potential retention)
-
(Eliminate potential retention)
- ~7-10% of the remnants are small RNA dependant (and most of them are only partly dependant)
PLOIDIE : Pas ~100% mais 99.5%
préciser proportion de séquences
Final categories
- MDS
- = "MAC" for 99% of sequences
- MAC_IES
- "true" MAC_IES (never seens retained)
- other MAC_IES (sometimes retained)
- MIC
- Other MIC specific (TE, repeated sequences)
- MAC (TA Junction)
- Overlap a TA junction of excision
- rDNA
- mtDNA
-
Other:
- Contaminants
- Alternative excision boundaries ("LOWID")
- low identity consensus ("Trash")
"genome"
Total Paramecium
Total sequencing
Orders of magnitude
- 1M holes available in the sequencer
- ~30% will have enough subreads to generate a CCS
At the end of the day:
100K to 250K reads with decent and exploitable consensus
~ 1.000 pure MIC + ~ 100-200 MIC with IES
Among the remainings we also find:
- Misligations and chimeric reads
- Adapter missed by the sequencer
- Exceptionnaly low identity subreads
- Contaminant, etc
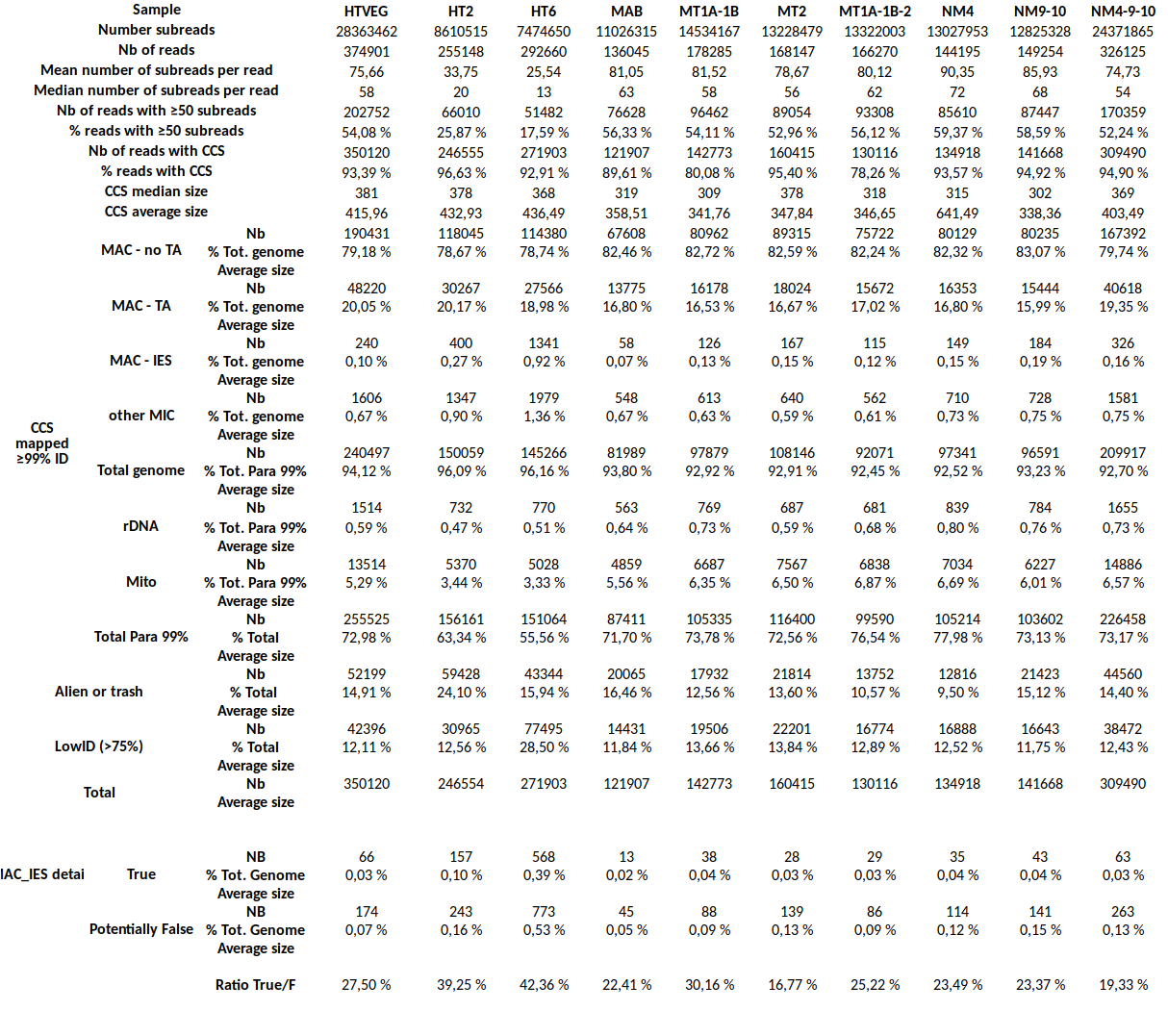
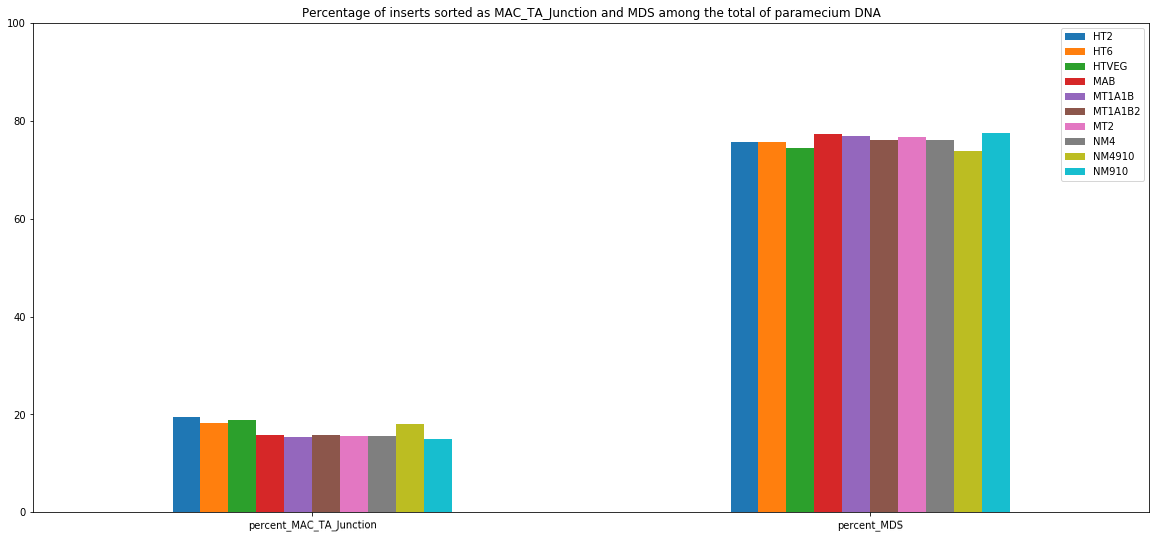
MDS and MAC_TA_Junction represent a vast majority
MIC specific and IES are as rare as expected
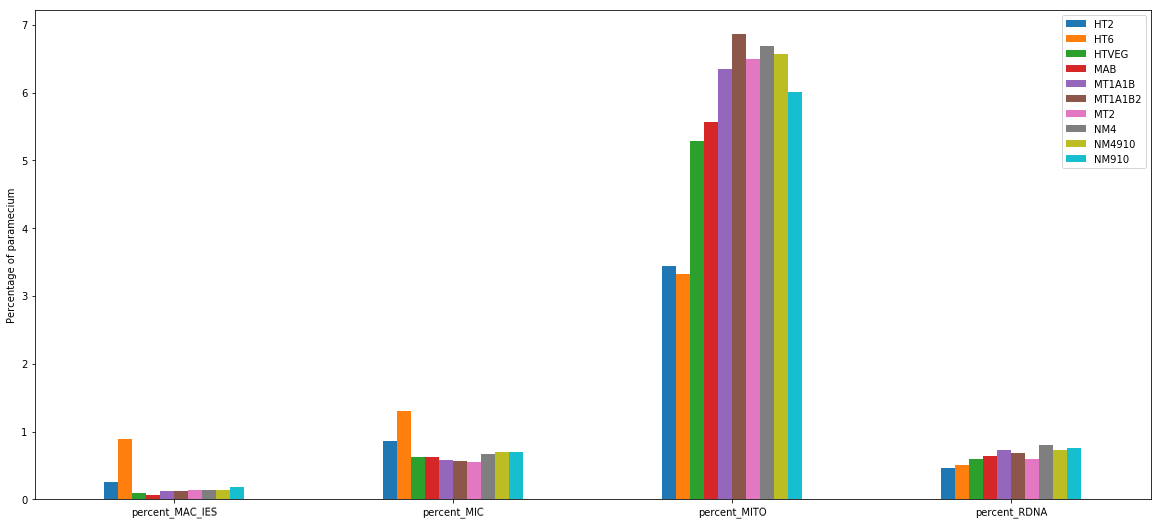
+ Applying the retention filter divides the number of "MAC_IES" approximately by 50%
Detecting m6A in details
Detection of n6mA
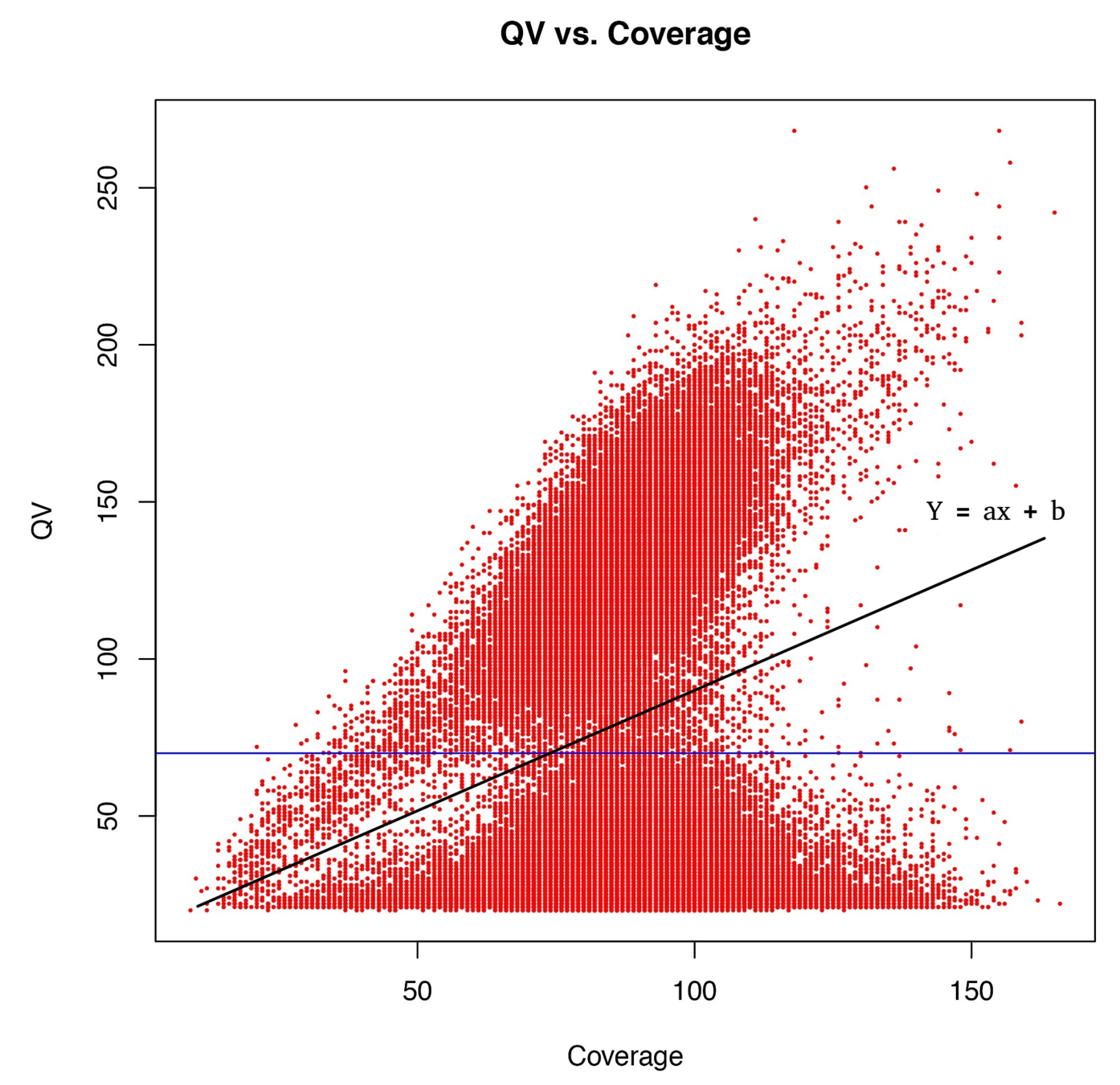
"positive detection"
=
score > linear thershold, function of coverage
How good is it ??
Définir QV
ipdRatio
Detecting m6A optimally
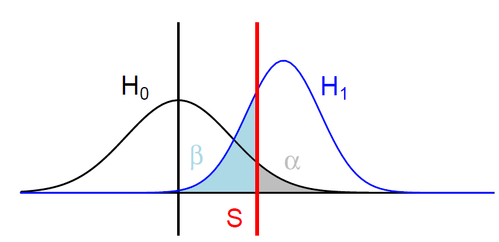
H0: ipdRatio of umethylated-Adenines
H1: ipdRatio of 6mA
S: Threshold on the pvalue
--> Specificity
--> Sensitivity
$$\alpha$$
$$1 - \beta $$
Adenine
6mA
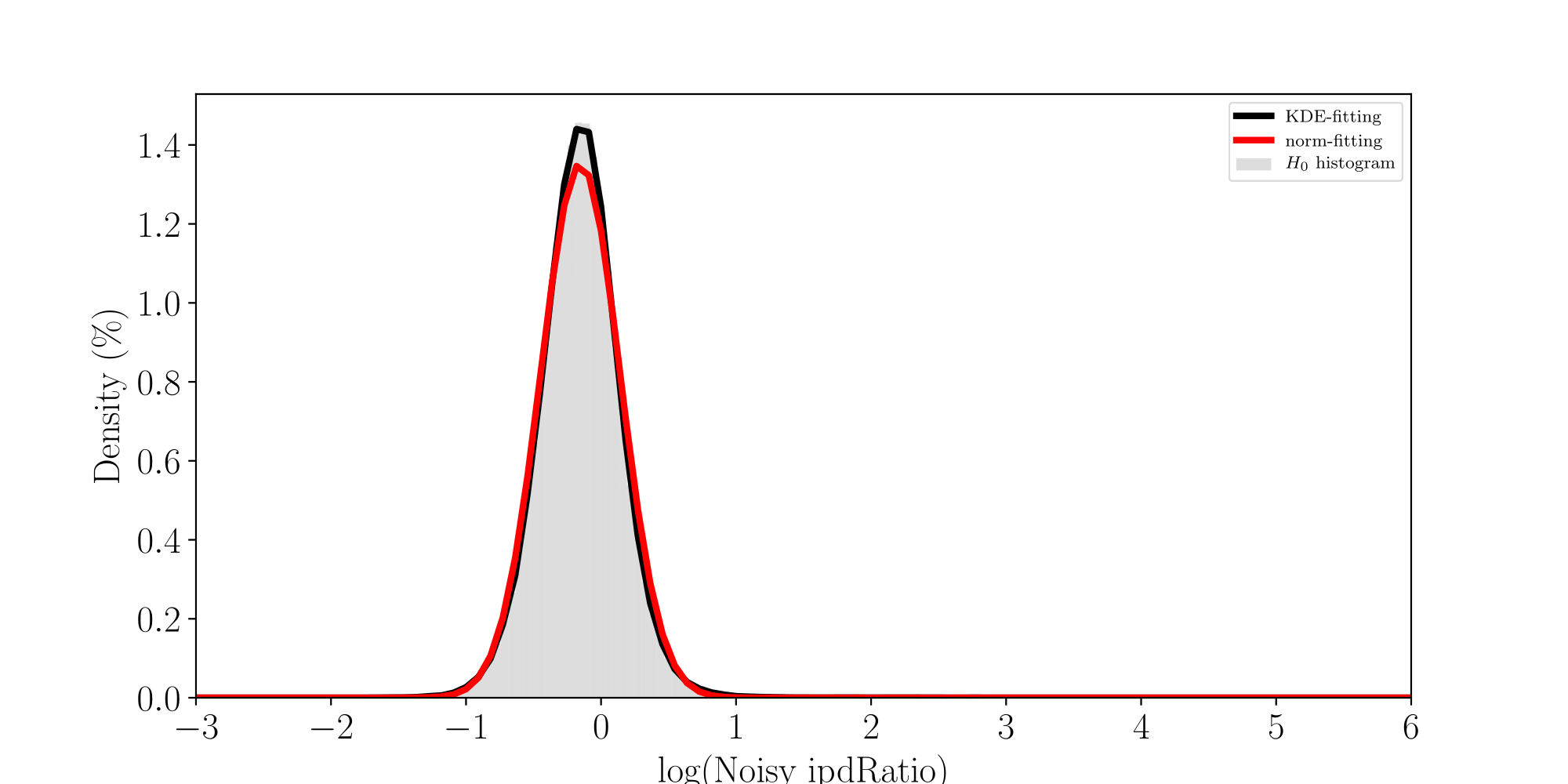
ln(ipdRatio) ~ N(0,1)
log(ipdRatio)
A pvalue is just the likelihood that log(ipdRatio) is in the tail of H0 when H0 is true
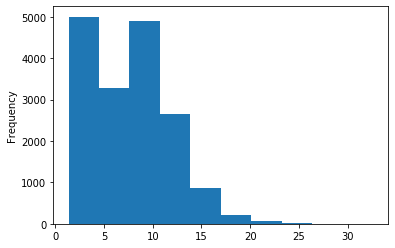
How log(ipdRatios) look in E.coli
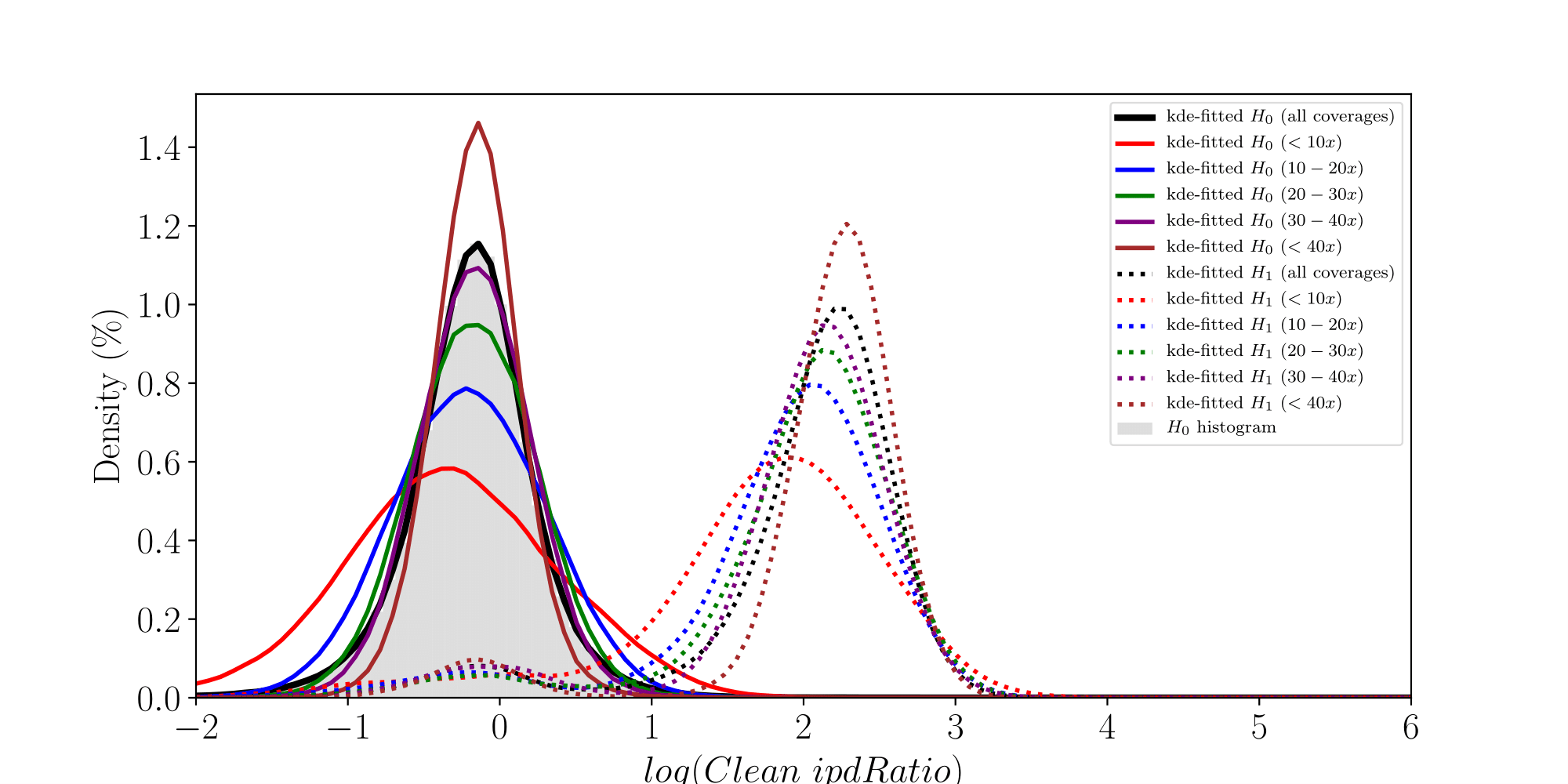
Separability raises with coverage, which is expected
PacBio pvalues do have some biological meaning
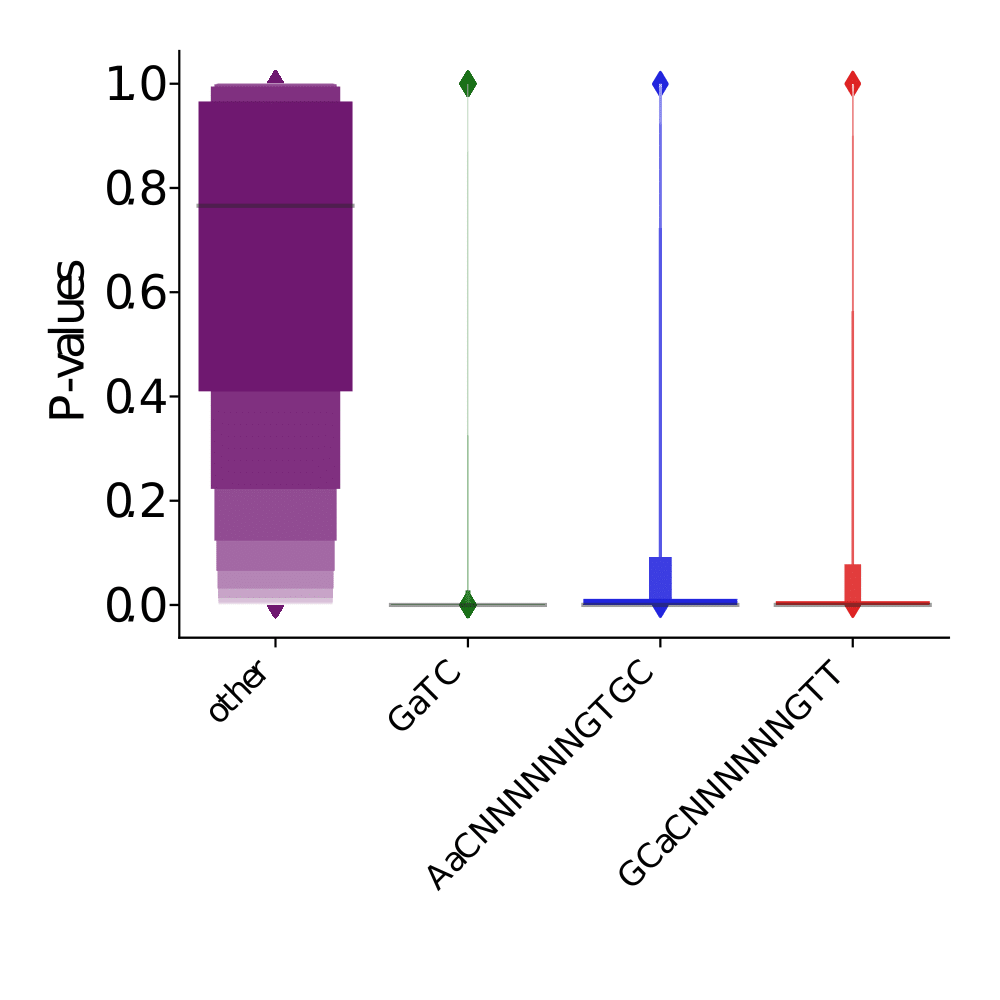
PacBio pvalues do have a meaning...
...but are not ideally distributed
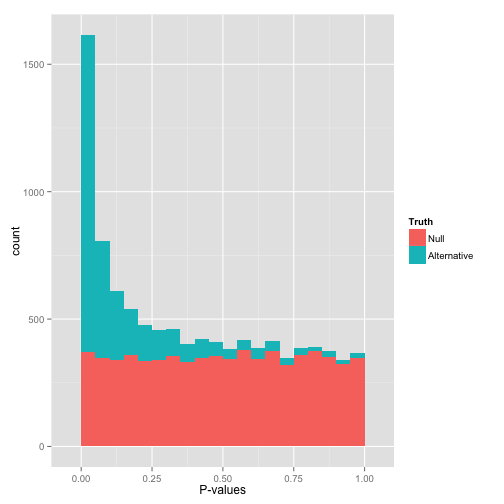
Ideal pvalues
--> Allows magic !
PacBio's
- Allow estimation of
- Allows optimal, adaptative FDR control
$$\pi_{0}, \pi_{1}$$
- Just don't
-
Obvious point n°1:
- log(ipdRatio < 1) -> -inf
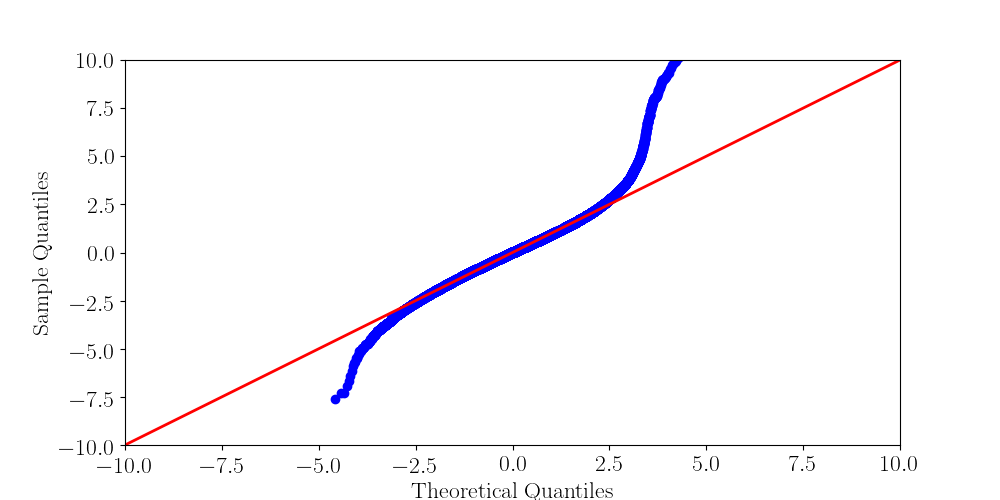
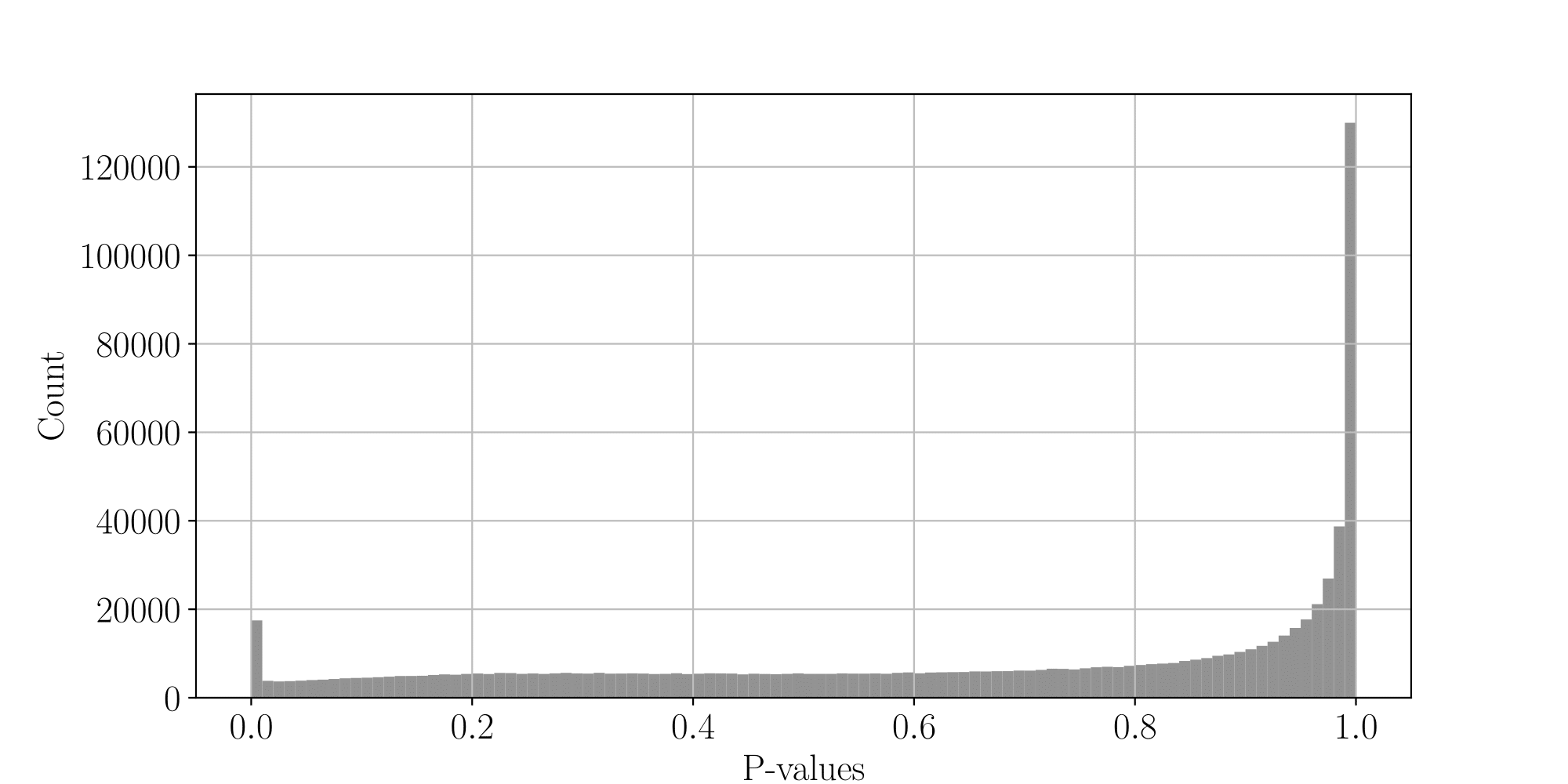
Normality assumptions under H0 are broken under high coverages
- The higher the coverage, the worse (here, >40x)
-
Will cause bell-shaped pvalues under null
- Hidden phenomena on the previous curve
Normality assumption matters
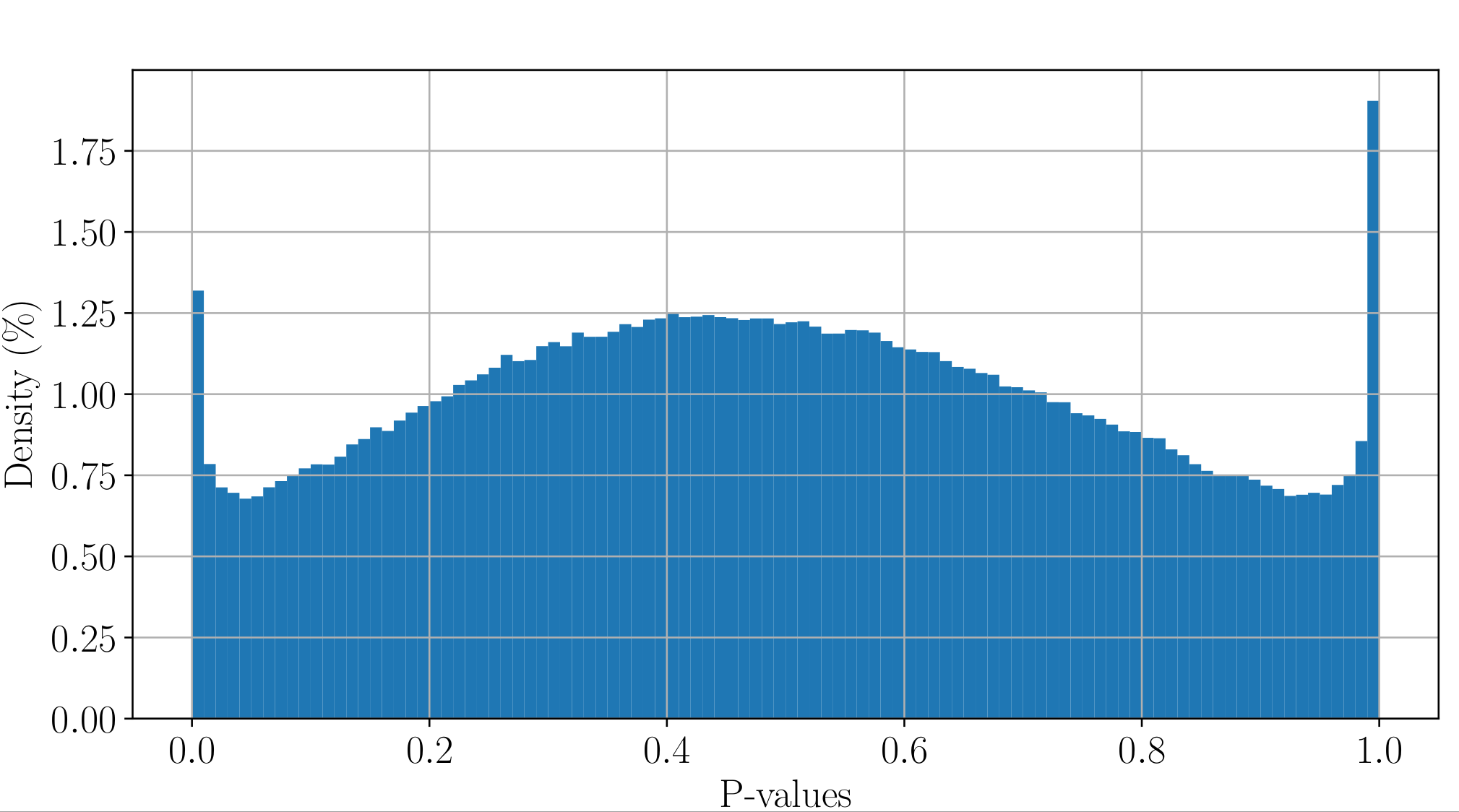
All Adenines' pvalues [E.coli] coverage > 40X
Other PBio's scores for m6A
For n6mA, PacBio produces:
-
A modification score --> Slowing of the polymerase
- pvalue against H0 only (the one we presented earlier)
-
An identification score --> Kinetic signature of a modification
-
loglikelihood between H0 and H1 (H1 = Other modifications or secondary peaks)
-
loglikelihood between H0 and H1 (H1 = Other modifications or secondary peaks)

They are PHRED-transformed p-values of two different statistical tests, that rely on the mean of the IPDs
PHRED scores
The scores (Qv) are PHRED-transformed p-values
Typical covscore plot
Modification score / coverage
Using flat threshold on modification score = Hudge lack of power
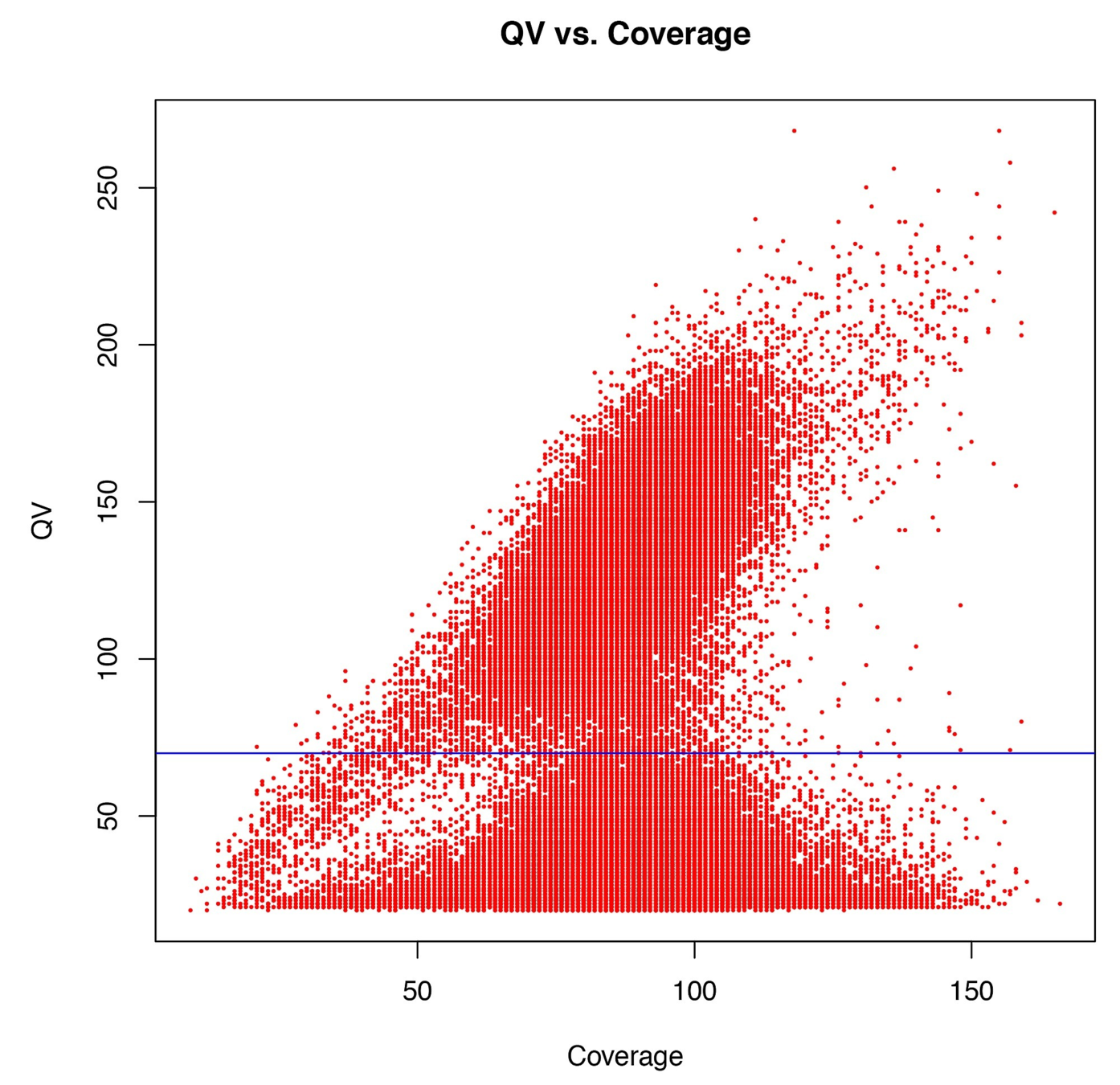
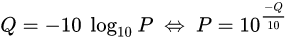
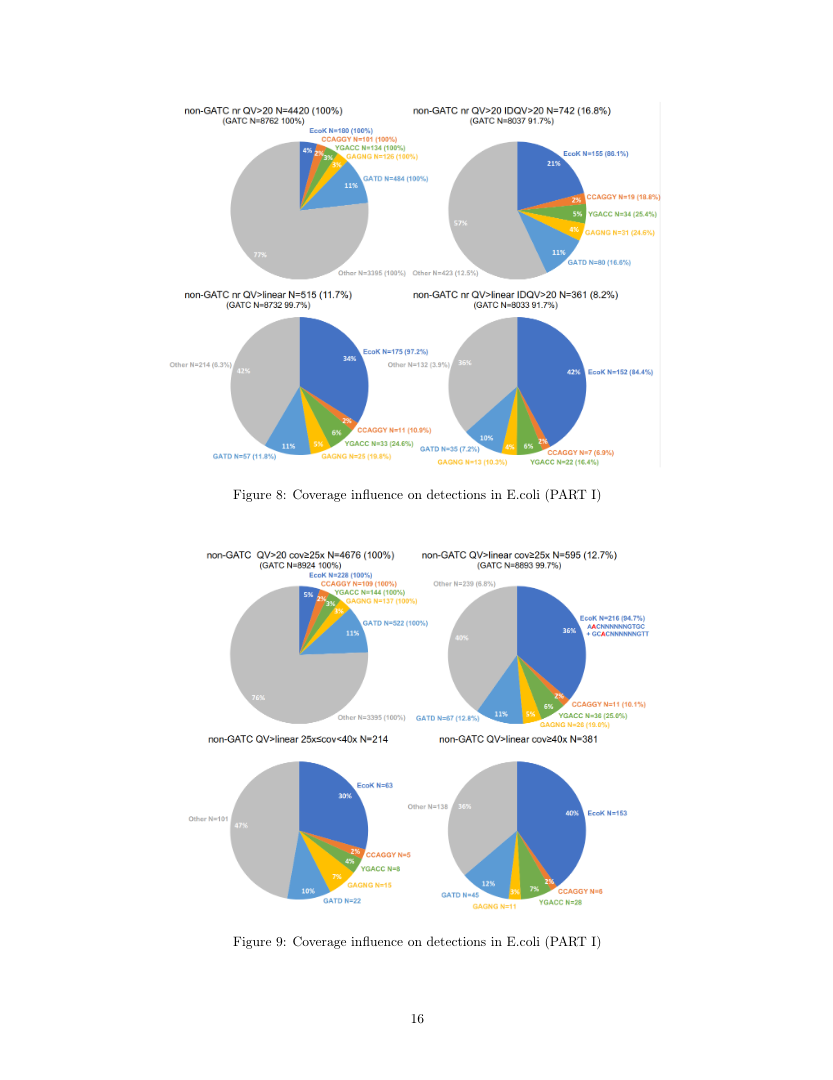
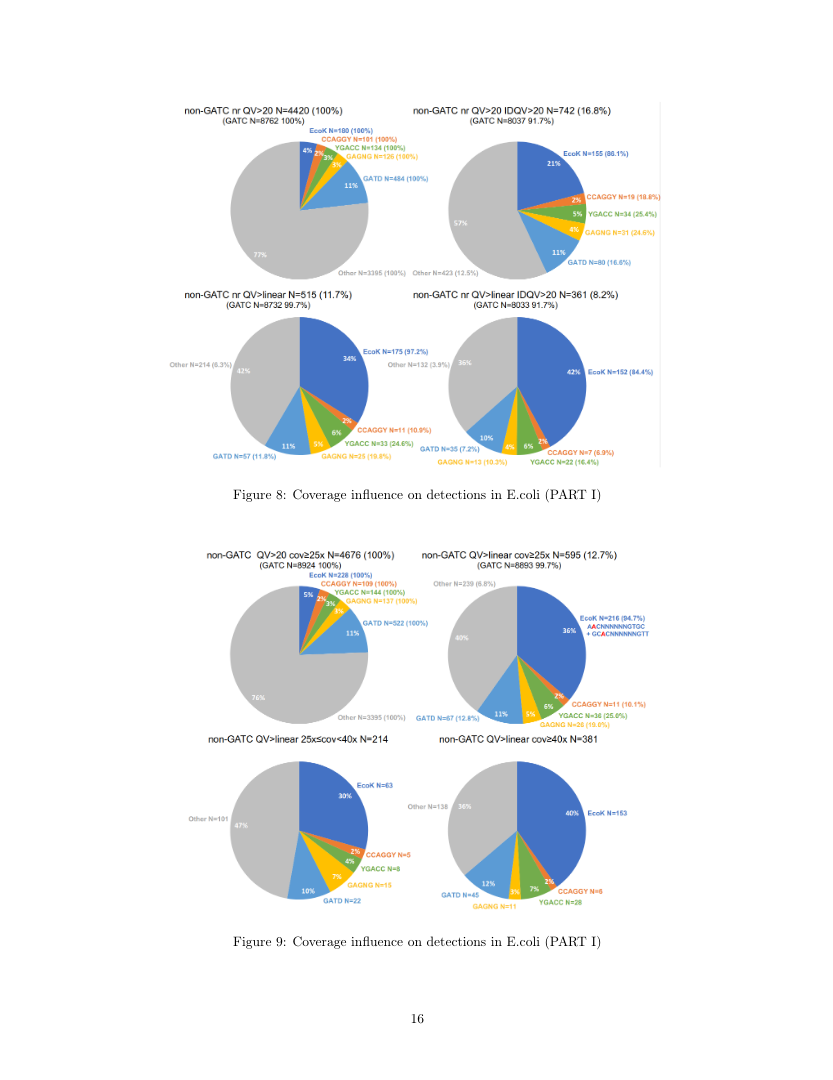
Using E.coli as ground truth
E.coli:
- Feeds paramecium: contaminants+++
-
In theory
- GATC
- EcoK
- Few others
- ... All contain n6mA on both strands
- Outside of GATC and EcoK: very low levels of m6A
Long story short
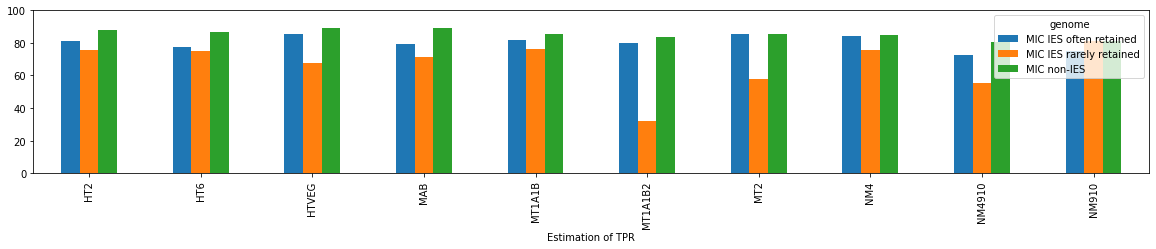
How good (or bad) is our method ?
$$Se = P(D^+|M) ~ 92\%$$
$$Sp = P(D^-|NM) ~ 99.9\%$$
...But only If we suppose that:
- All GATC and EcoK carry symmetrical n6mA
- No other motif contains n6mA
- GATC/EcoK will display similar scores as other motifs (--> +/- True)

How to be sure about our Se and Sp ?
- We can't
- We don't need to
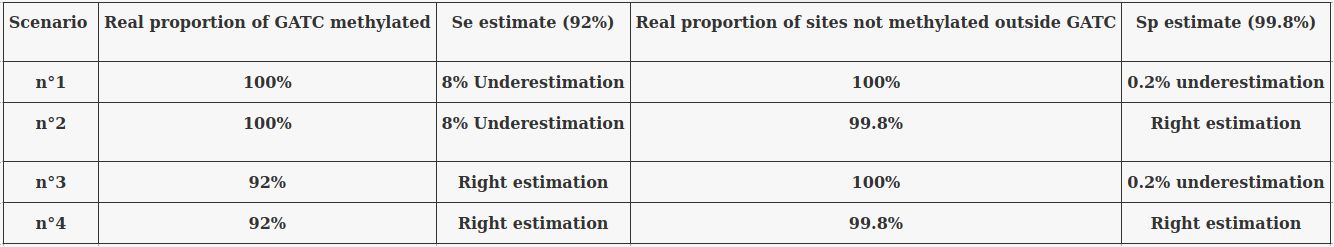
The 4 scenarii for Se and Sp
- We don't care about Se and Sp
- We care about the fact that eventual mis-estimations of them doesn't really change anything
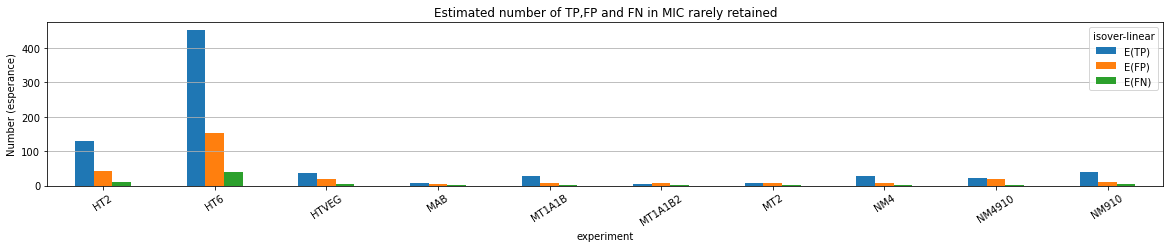
Finding unbiased estimators for and FDR
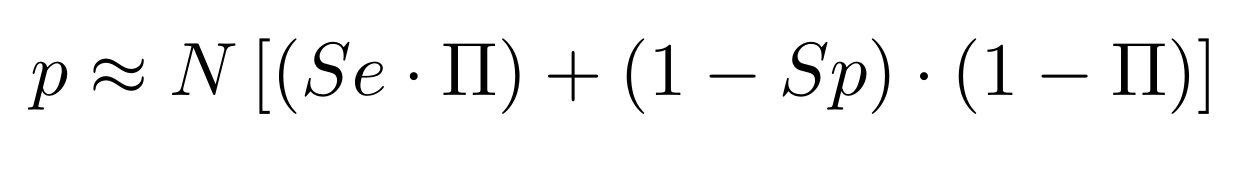
If p number of positive detections among N tests:
p = FP + TP
$$\pi$$
So,
Which means
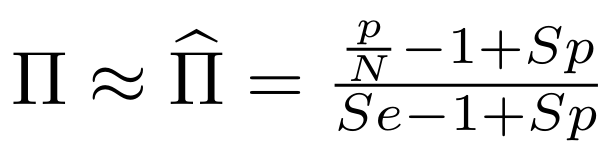
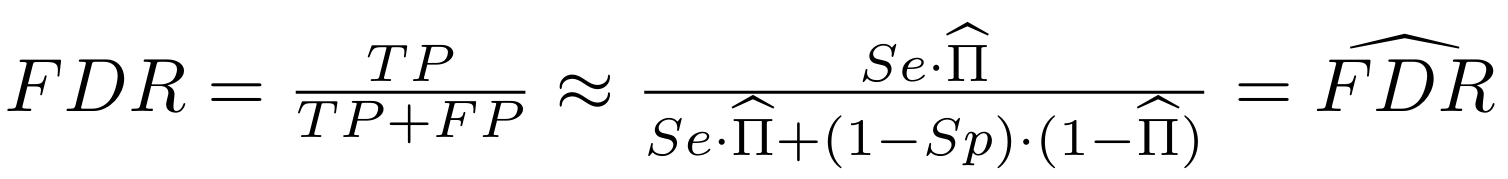
And:
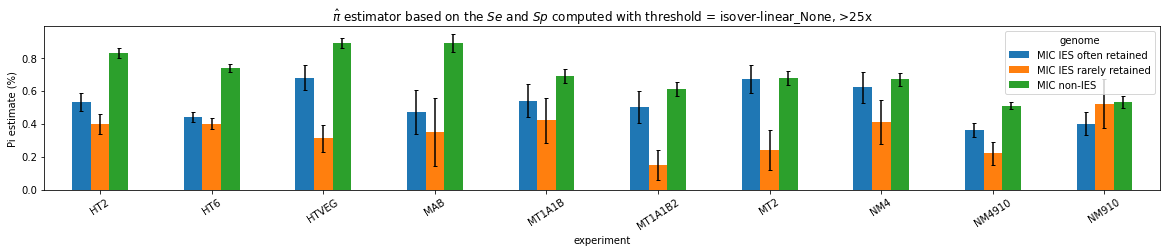
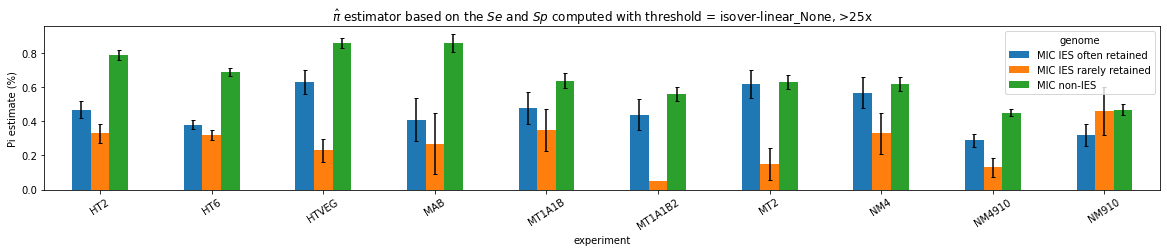
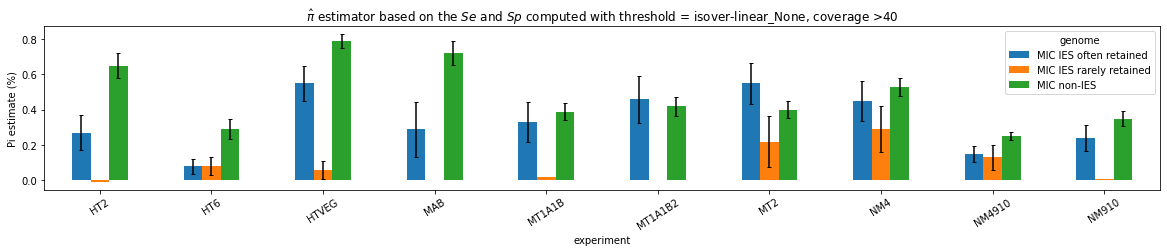
What it gives in Paramecium
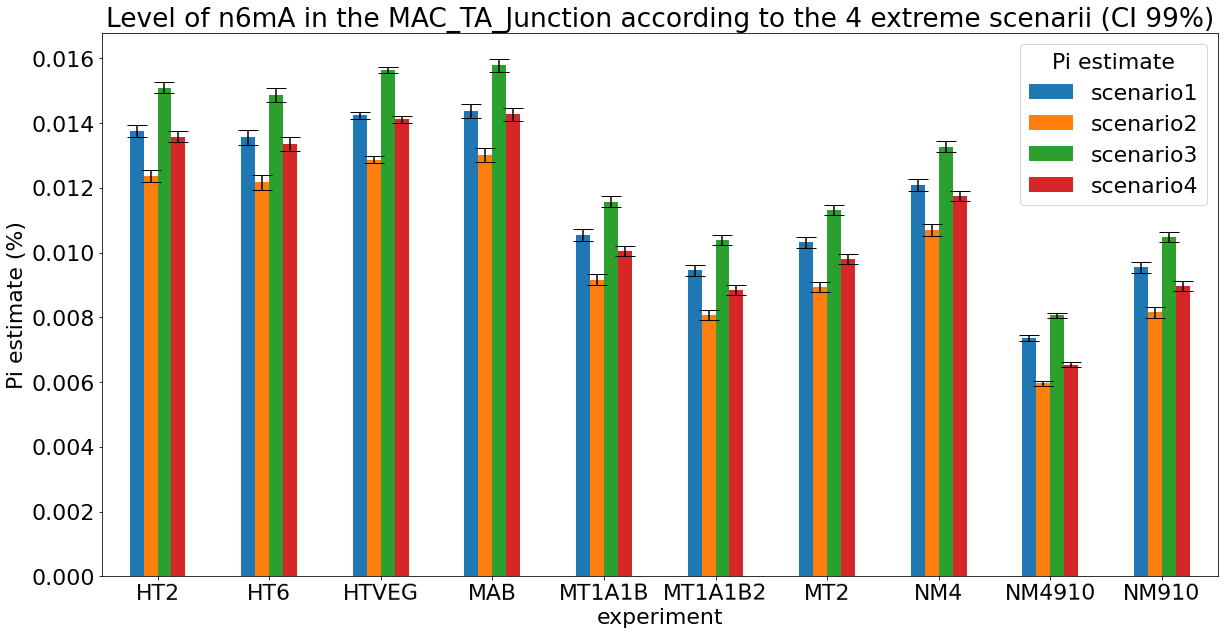
Debiased levels of m6A in the MAC_TA inserts
Details in MAC HTVEG
-
~95% of the methylation locates in AT dinucleotides in the MAC
-
True in any condition
-
-
75% of the methylation in an AT dinucleotide is actually symetrically modified
Kept in MIC and MAC
All conditions
95% --> C'est faux ?
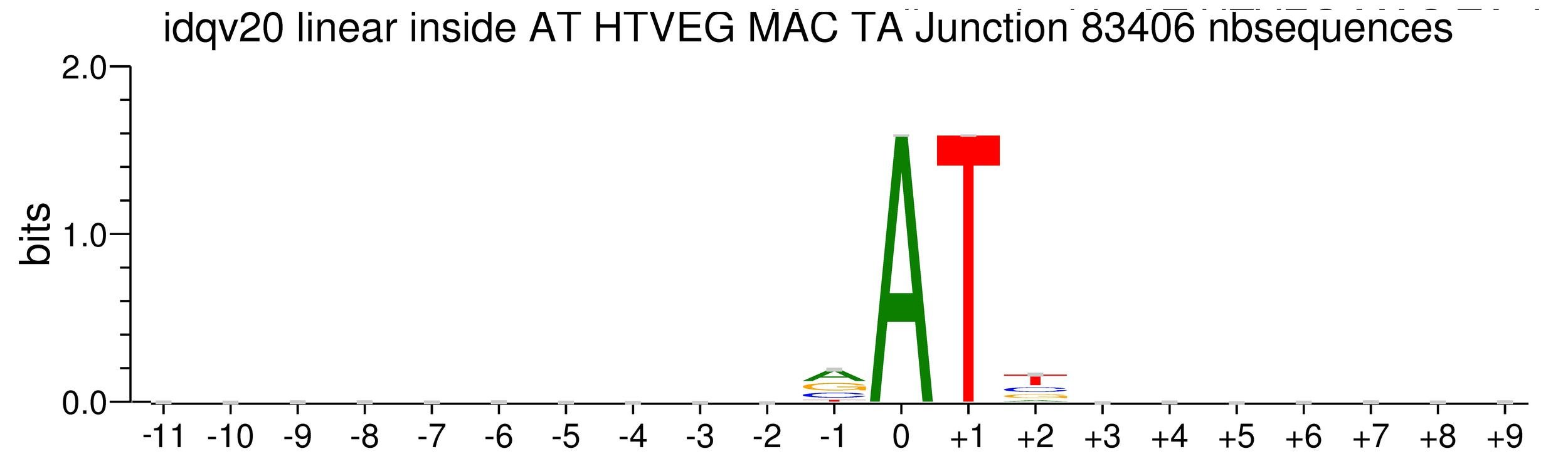
MAC_TA outside of AT sites
Detections outside AT sites are likely to be at least partly true positives
Present in all samples
Never erased
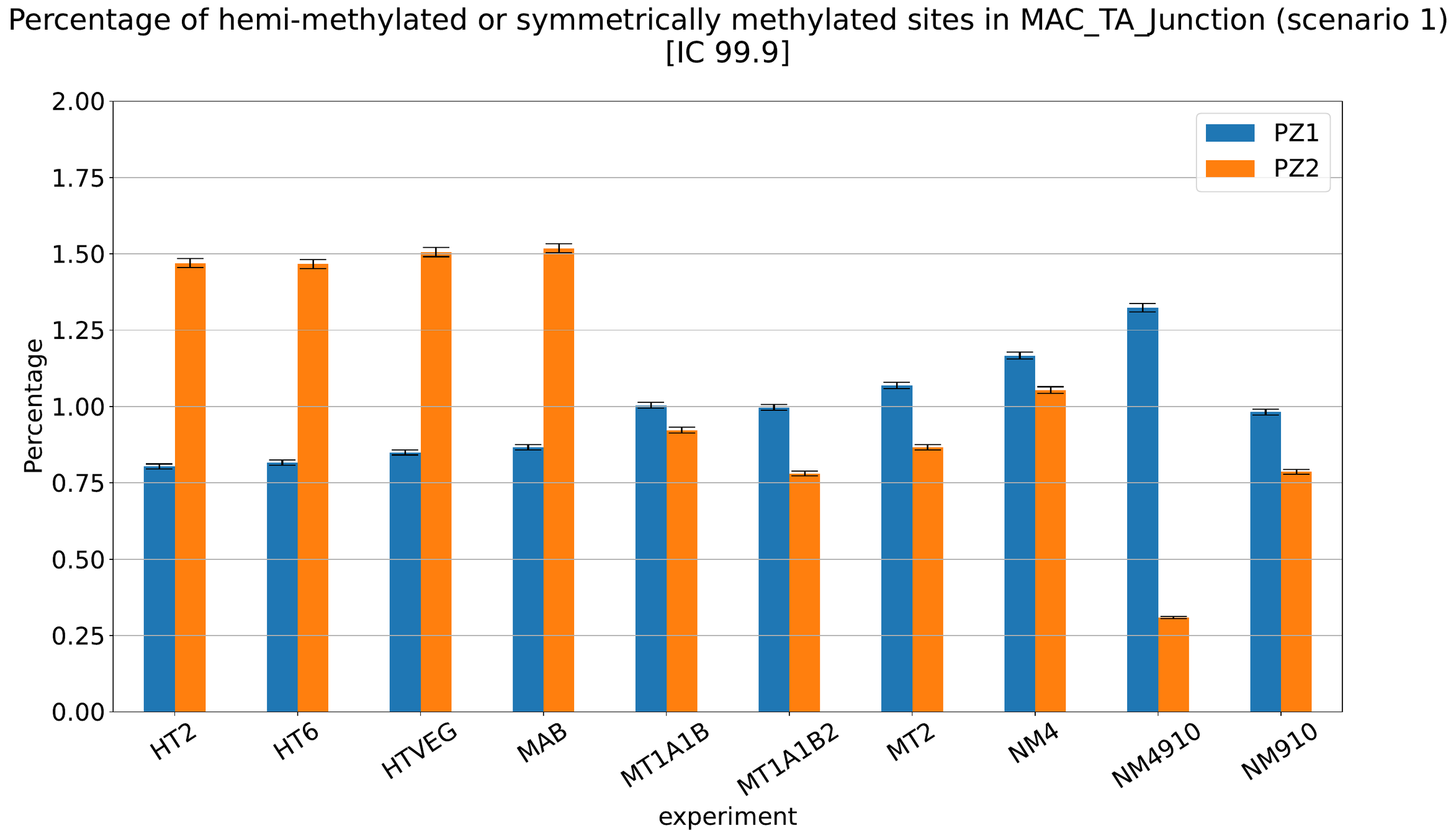
Conclusion: We are either in scenario 1 or 3
(Sp largely underestimated)


This allows us to announce...
- It is very, very likely that 1.4 to 1.6% of Adenines in the MAC are n6mA
-
~0.1% of the adenines located outside of AT sites might be n6mA too
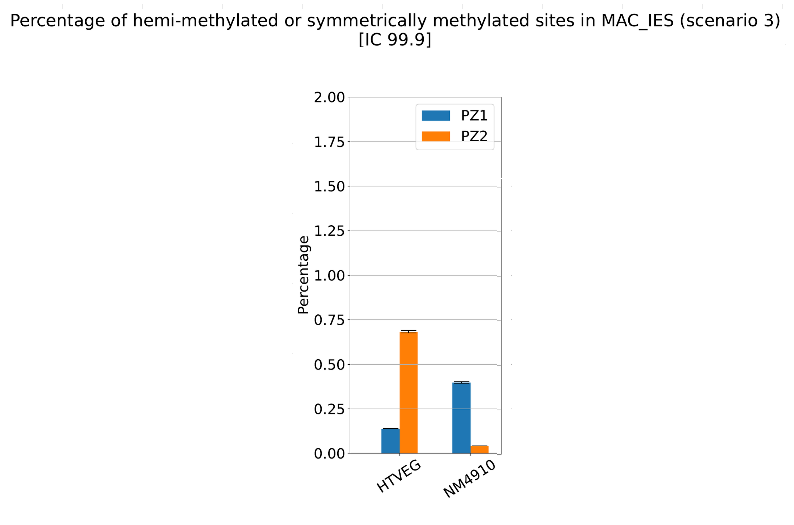
The problem of hemi-methylation
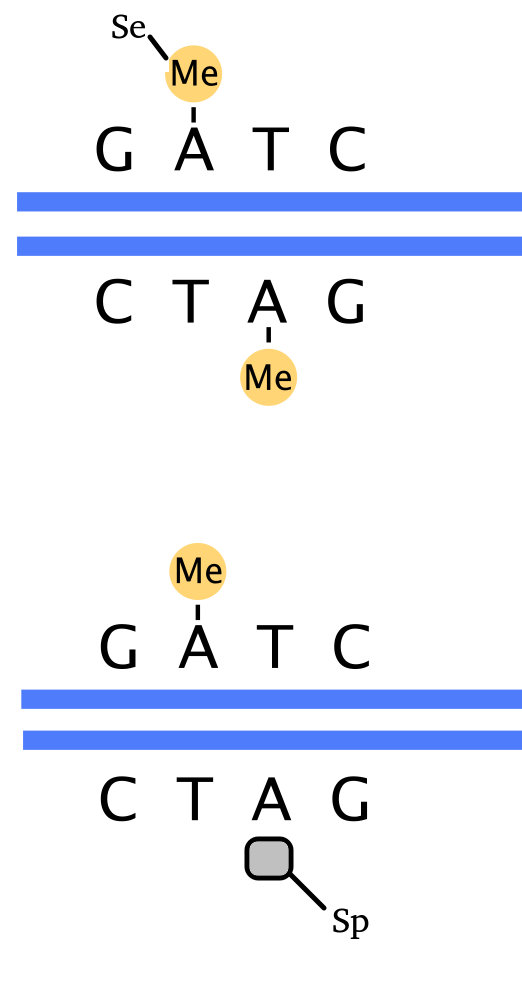
How can we estimate P(M=i | D=j) ?
Methodological development to correct hemi-methylation detection
Let FD1 and FD2 be resp:
- Fraction of hemi-methylated AT sites
-
Fraction of sym-methylated AT sites
PZ0, PZ1, PZ2: unbiased estimators of non, hémi, symetrically methylated AT sites
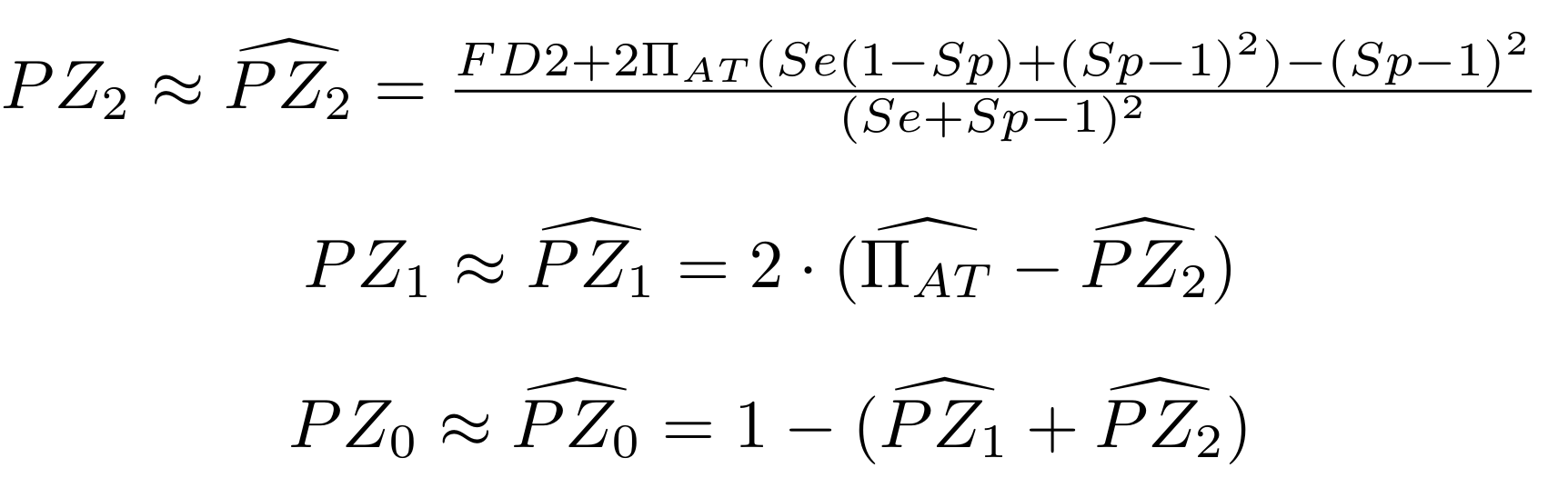
Then:
With
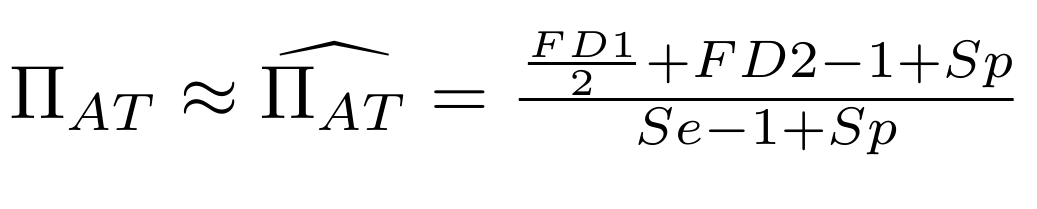
Methodological development to correct hemi-methylation detection (2/2)
We can also find the number of hemi-methylated sites being detected as such, and the proportion of sites detected as hemi-methylated that are really hemi-methylated. This is possible because we now approximately know PZ0, PZ1 and PZ2, and P(D|Z) is easy to determine:

Then, P(Z|D) can be determined through Bayes theorem using P(D|Z), P(Z) and P(D) (which are all known)
P(Z=1|D=1)
is our case of interest
What it gives in Paramecium
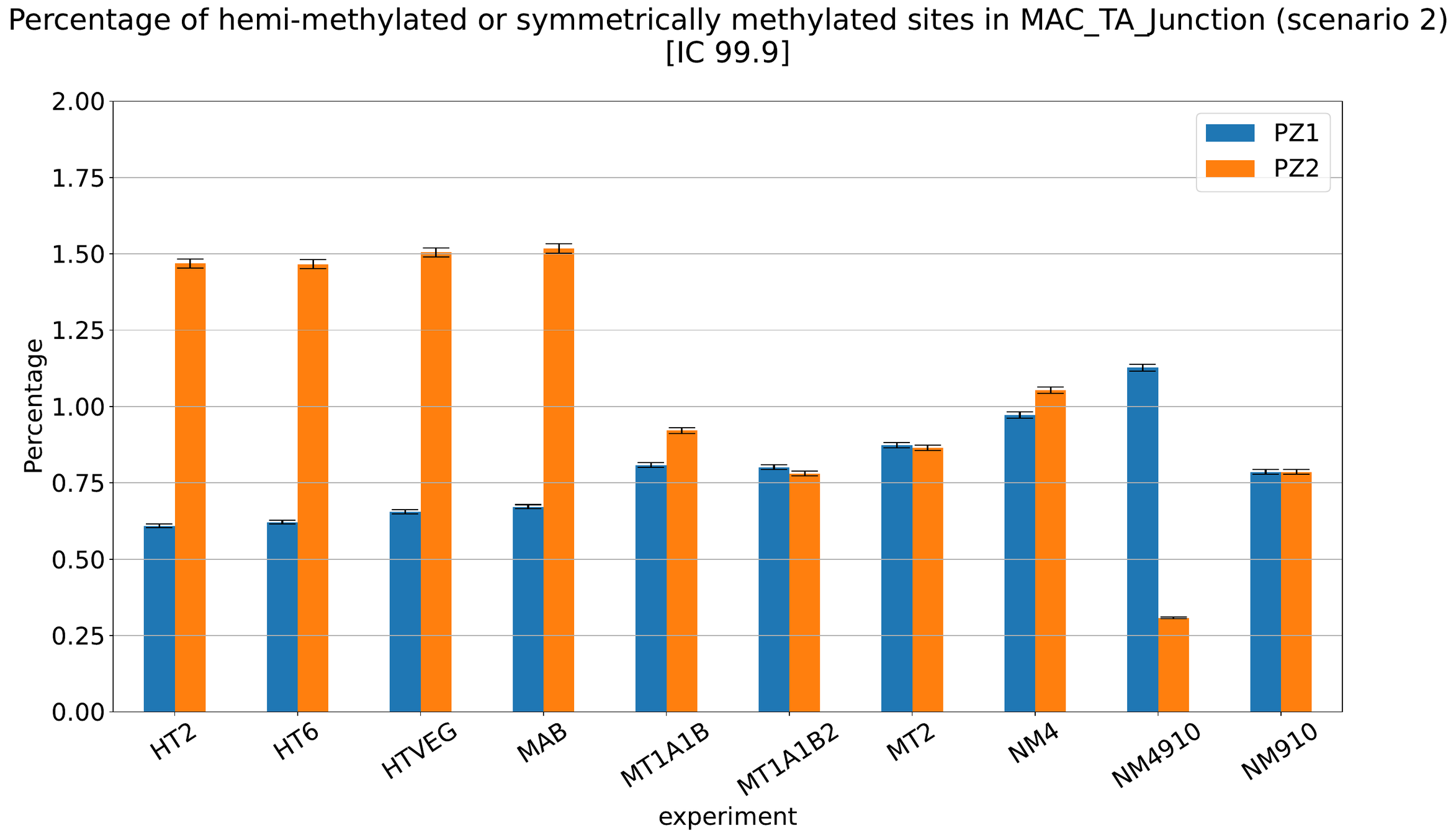
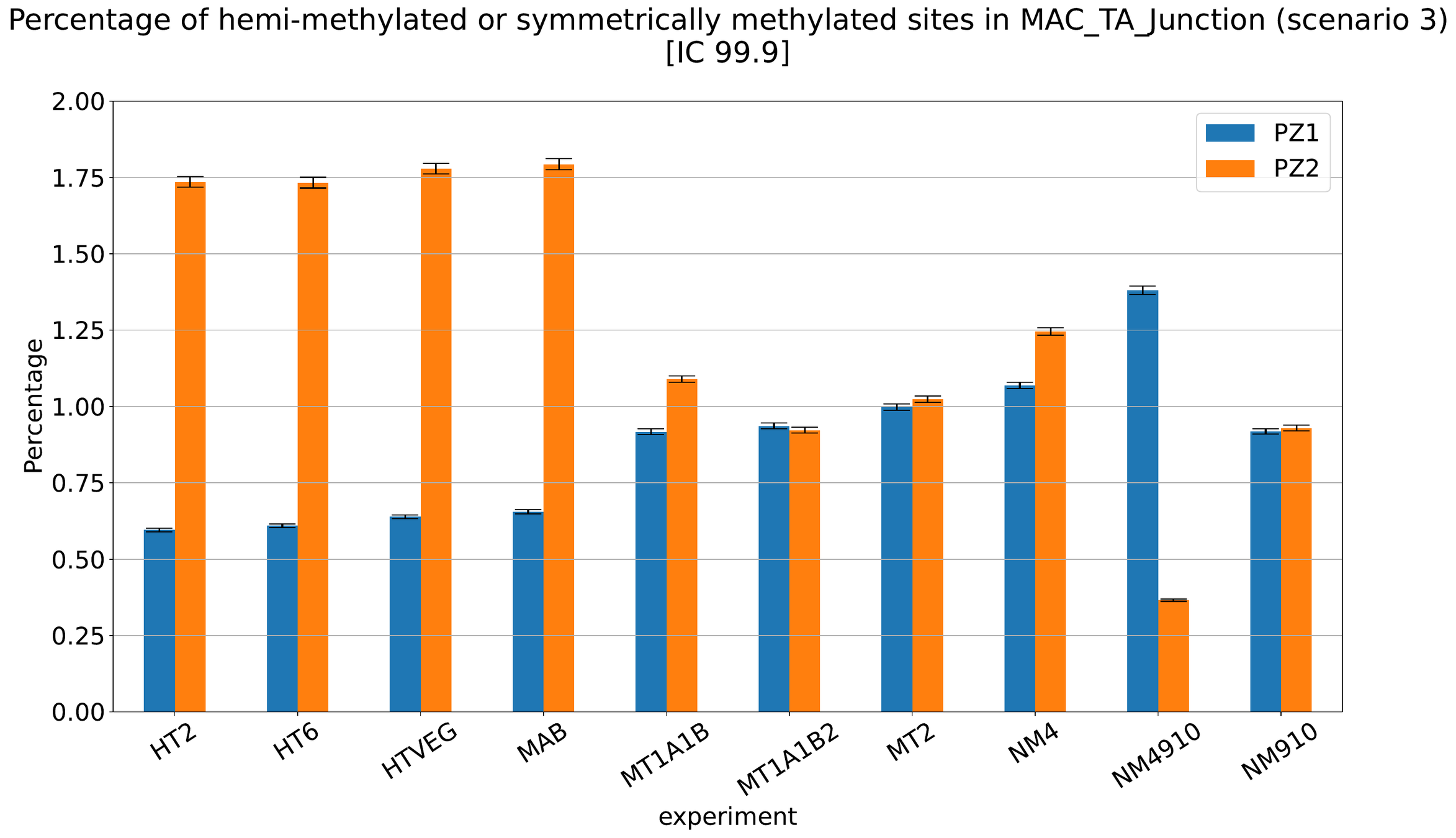
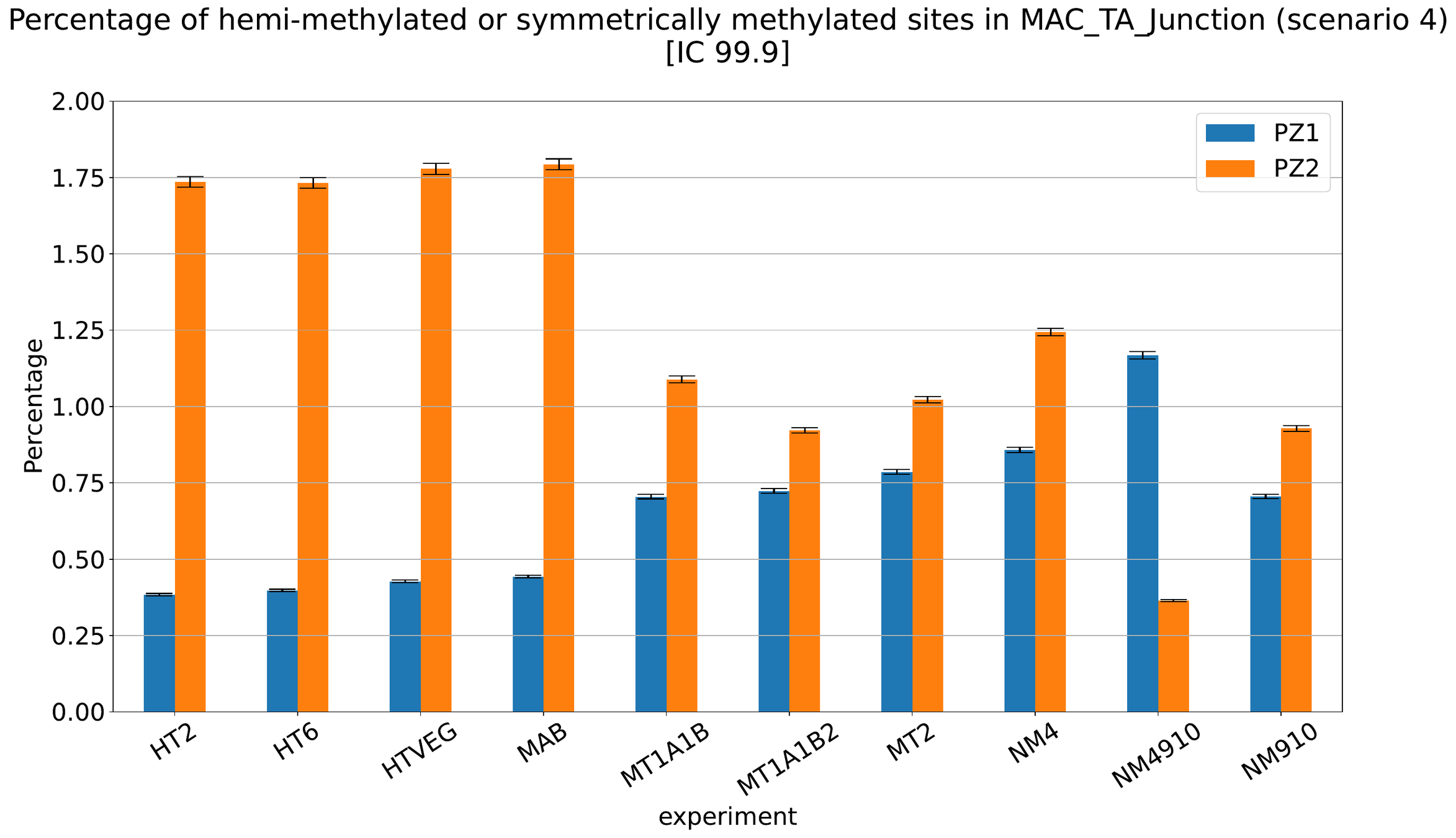
Debiased Hemi-methylation in MAC_TA
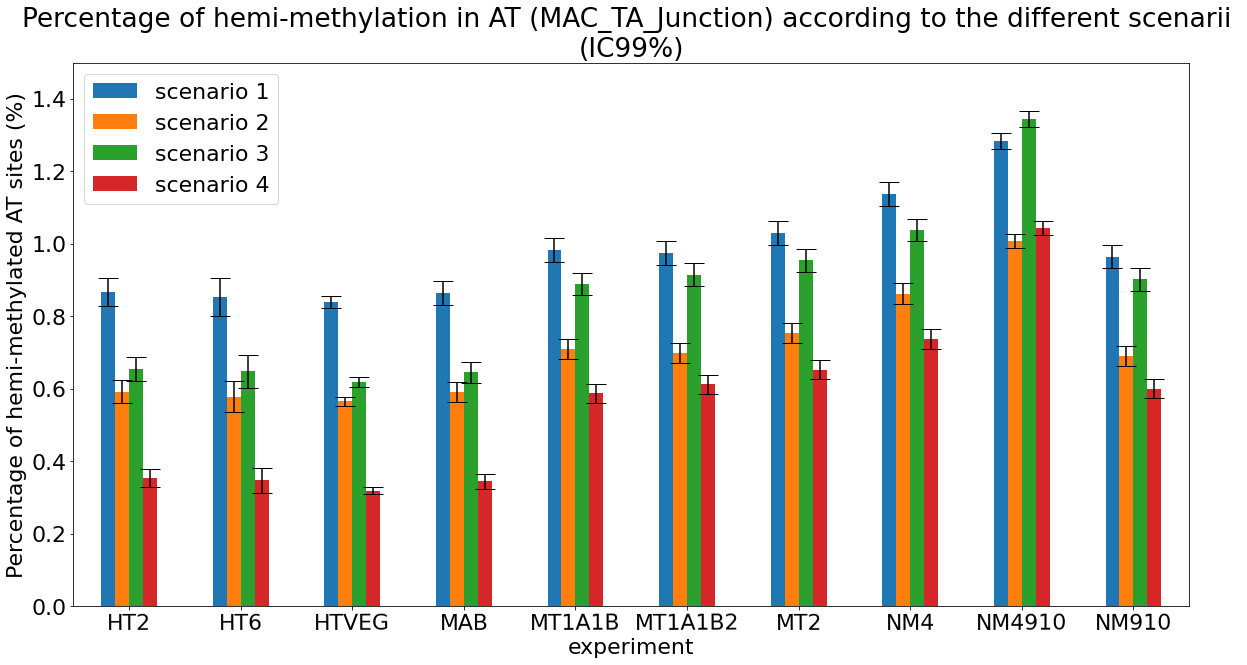
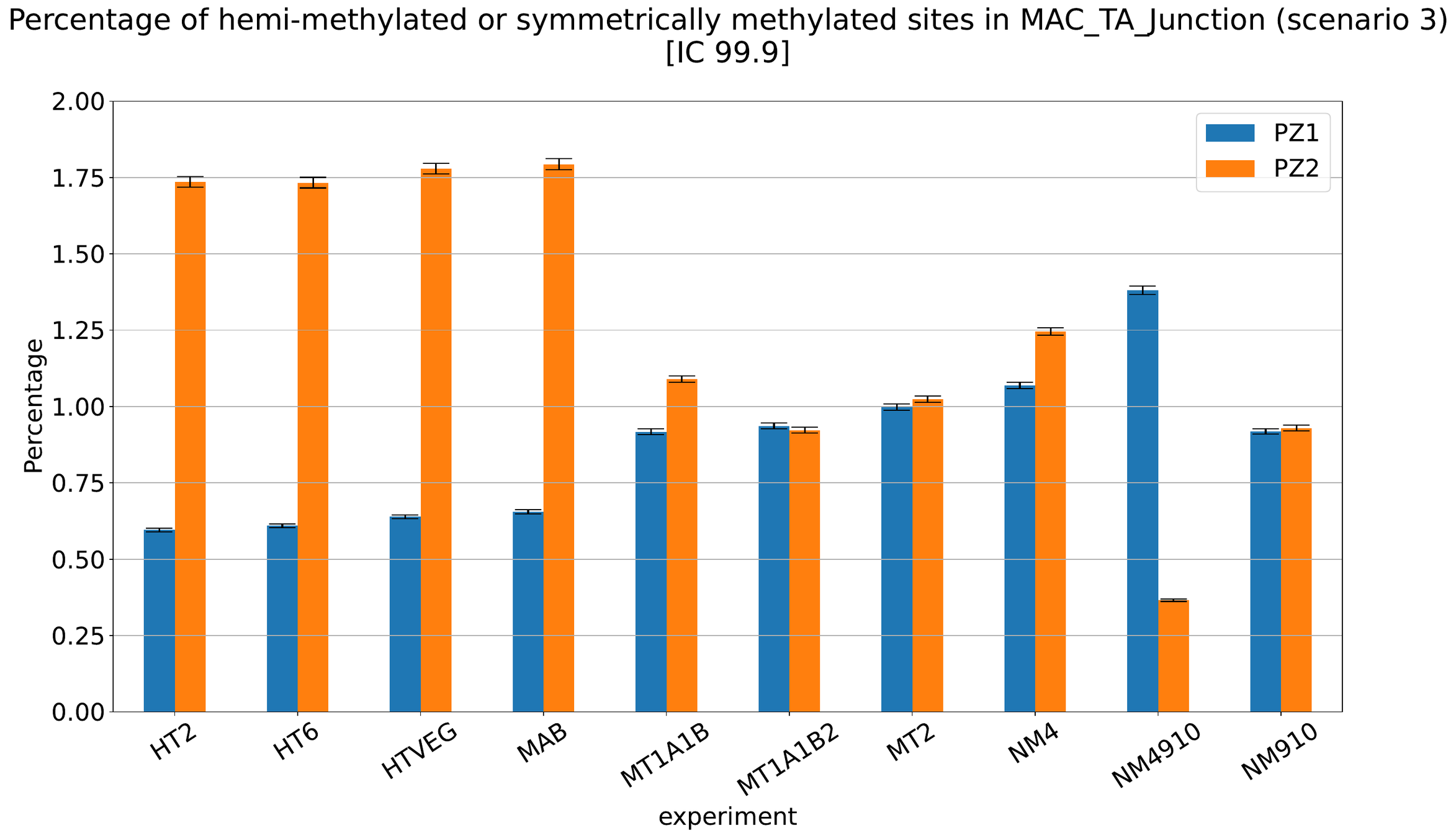
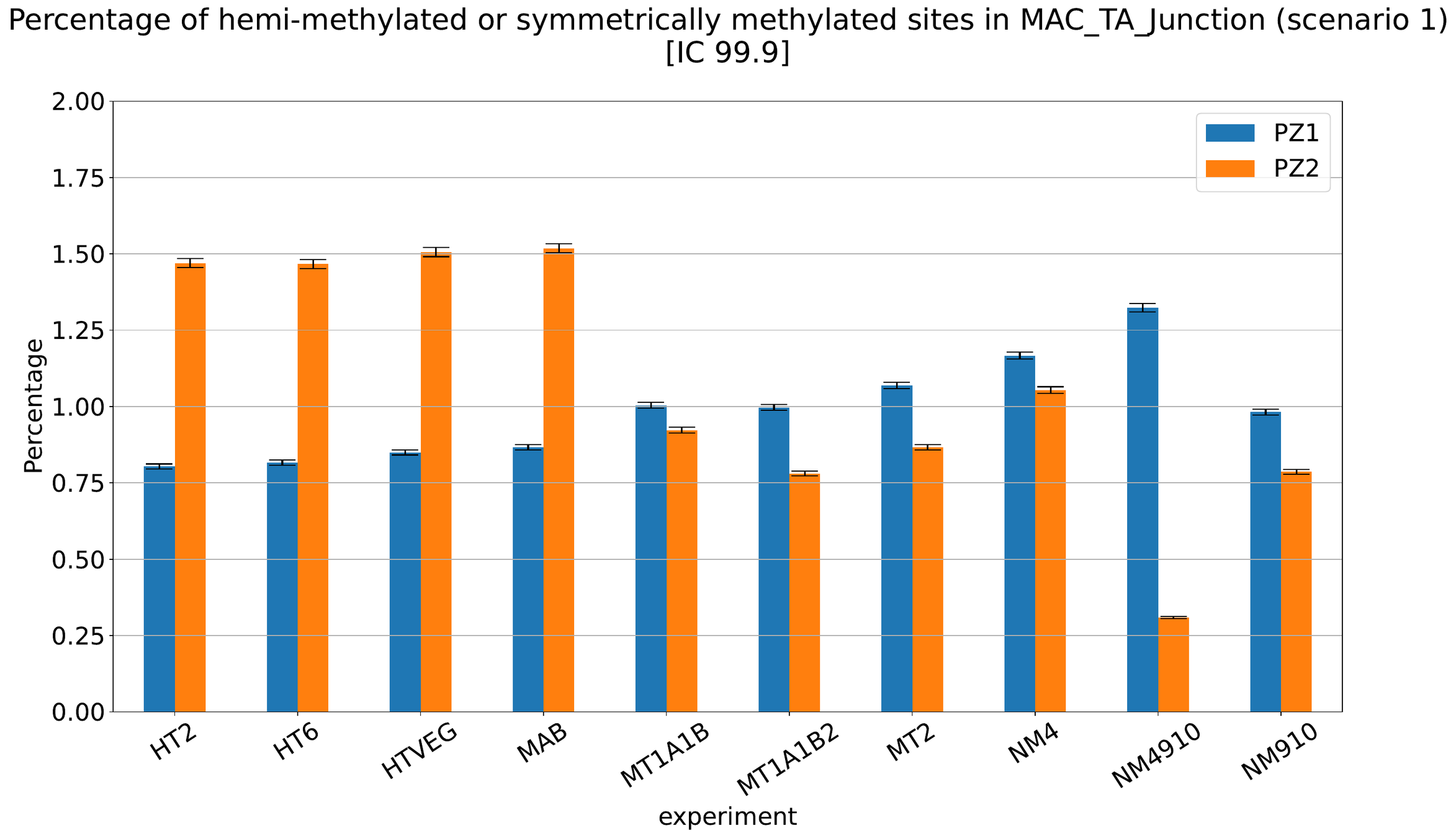
No FP
Some n6mA are missed
Perfect detections
Same conclusion !


No FP
Some n6mA are missed
Perfect detections
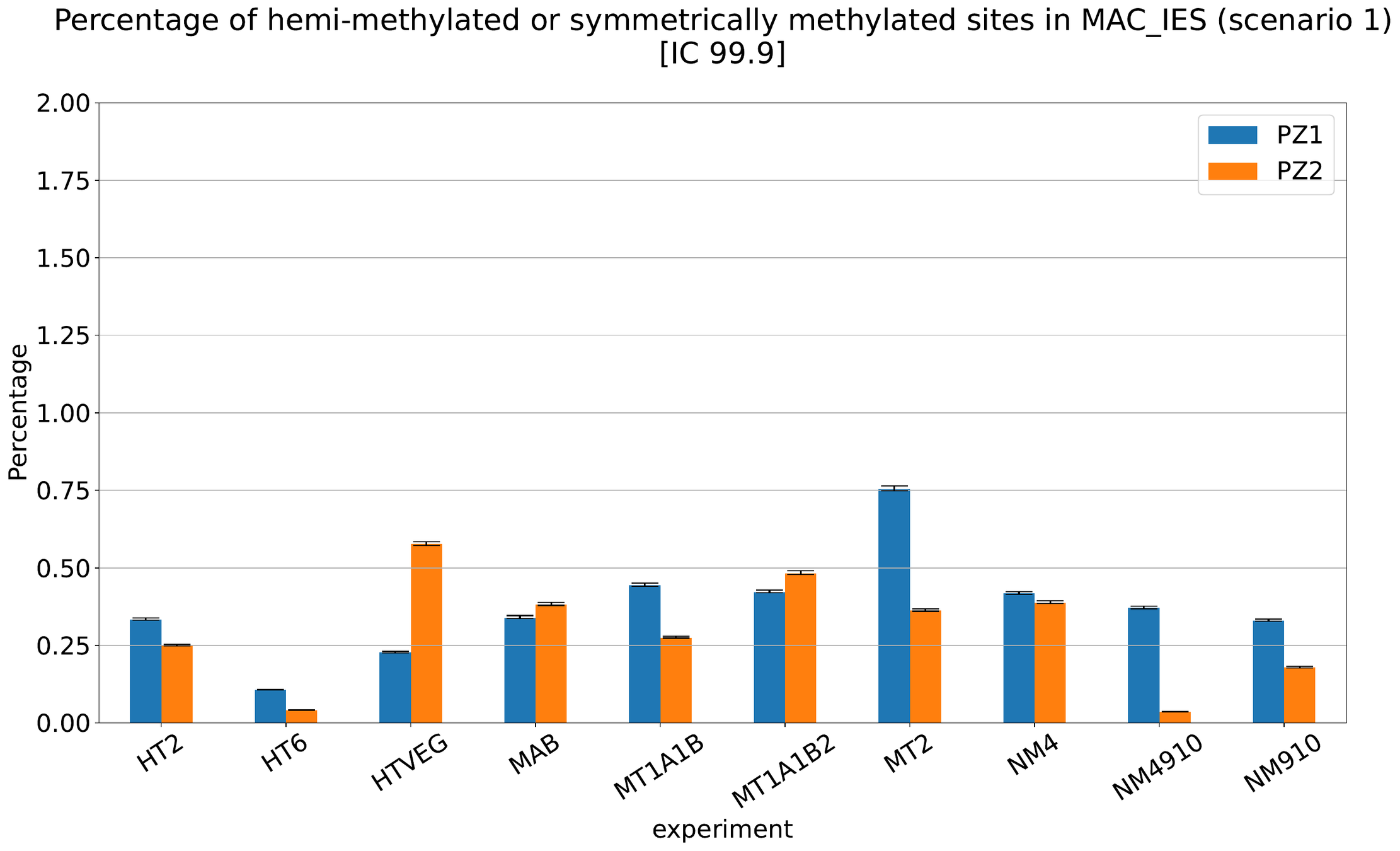
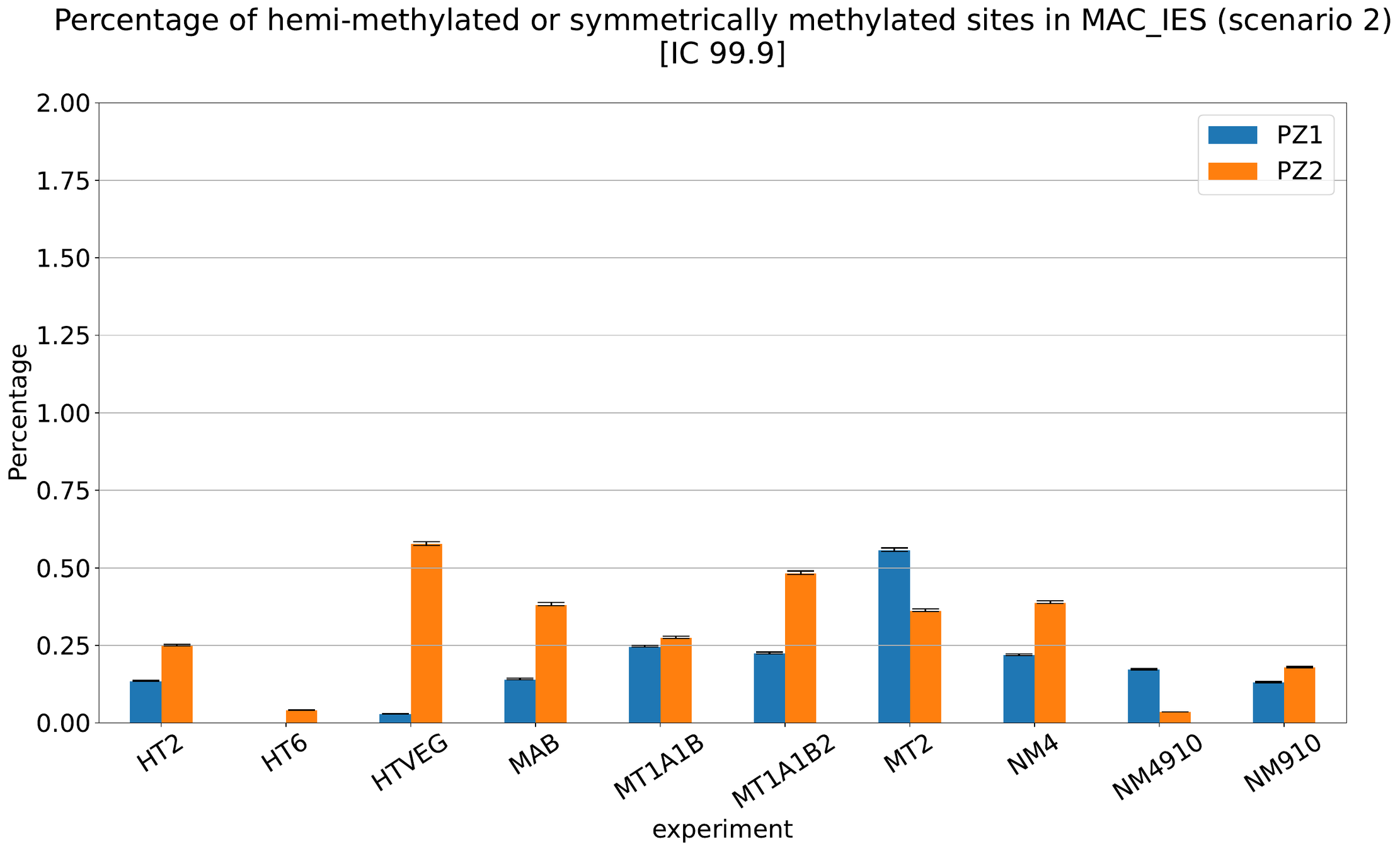
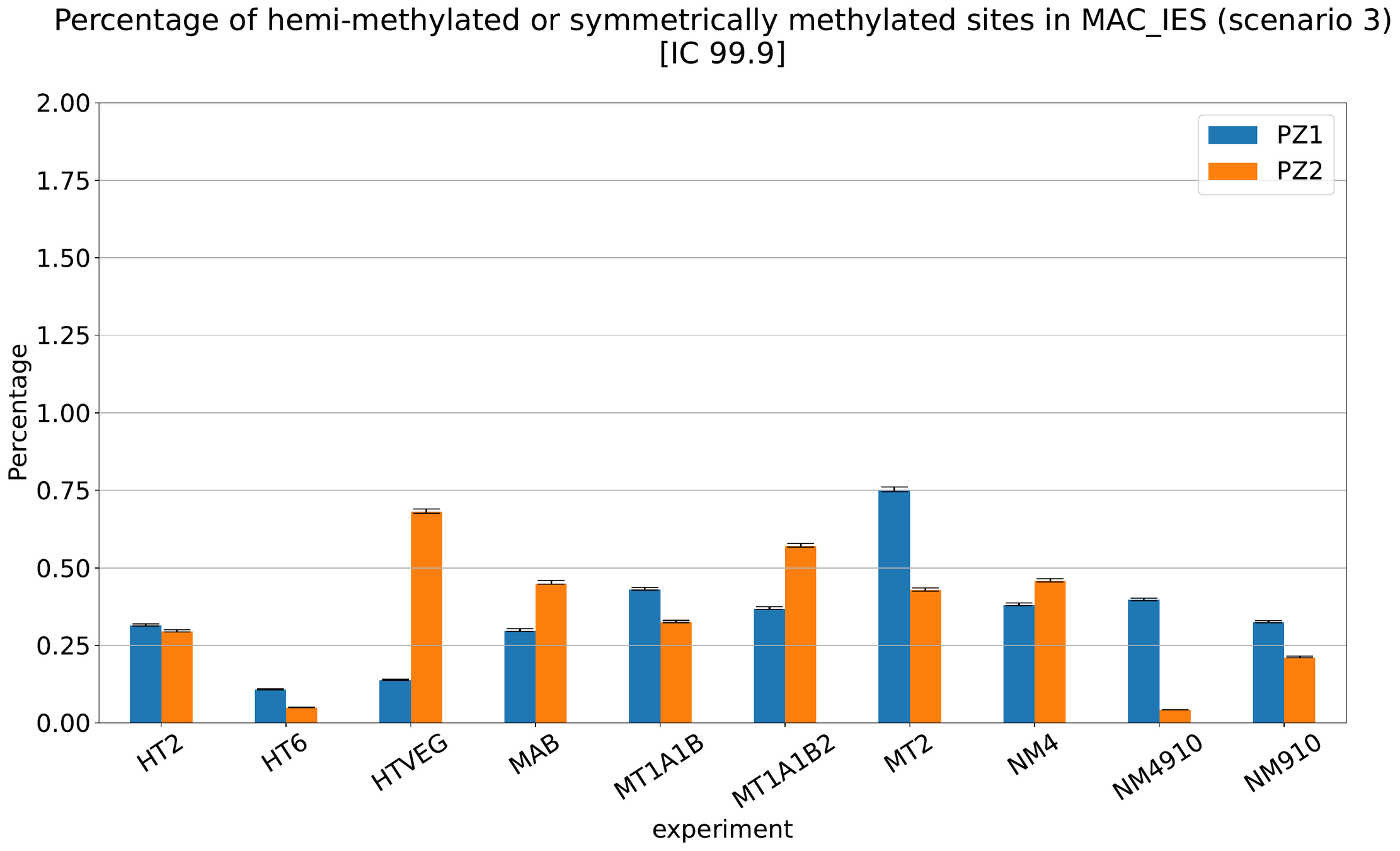
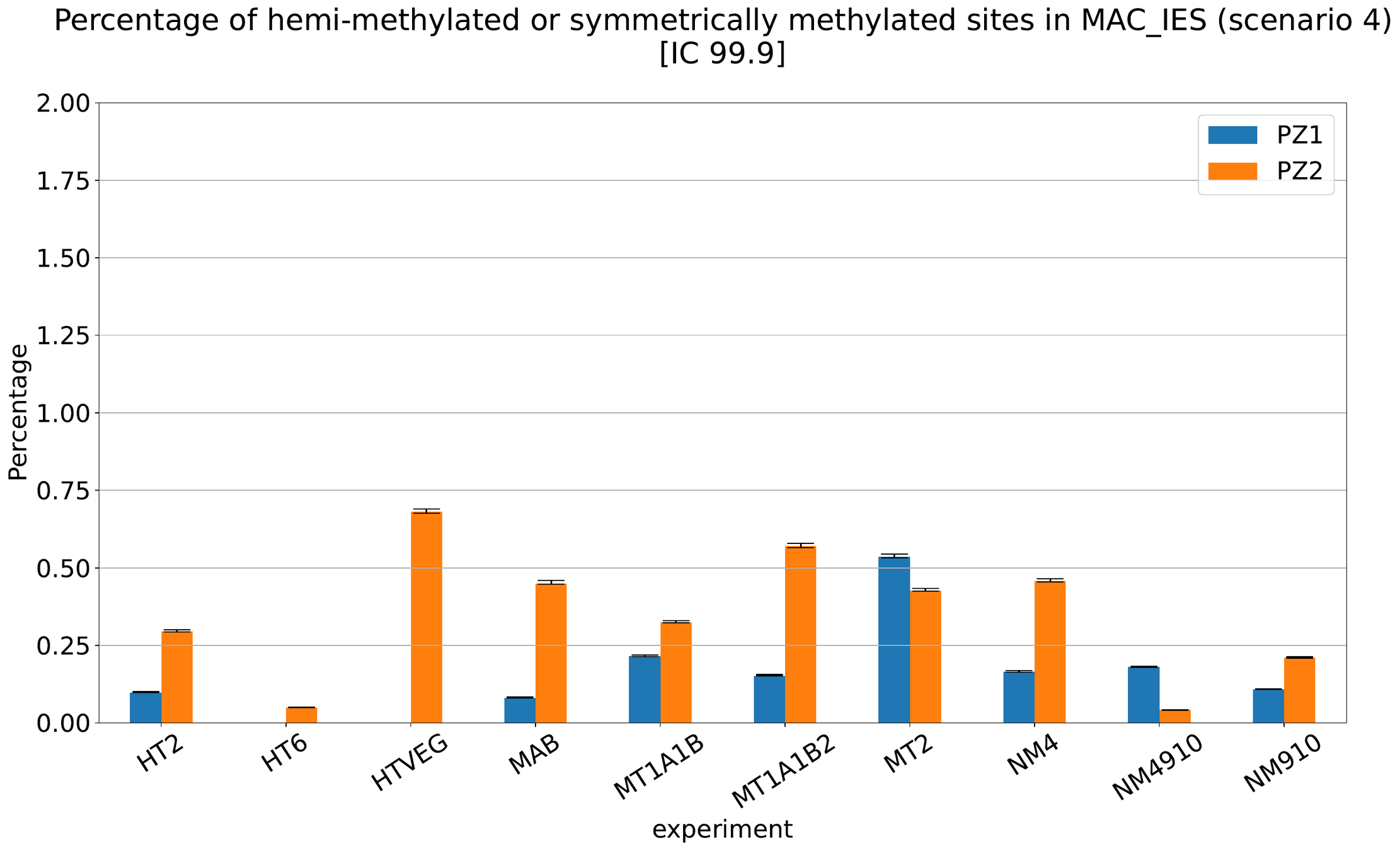
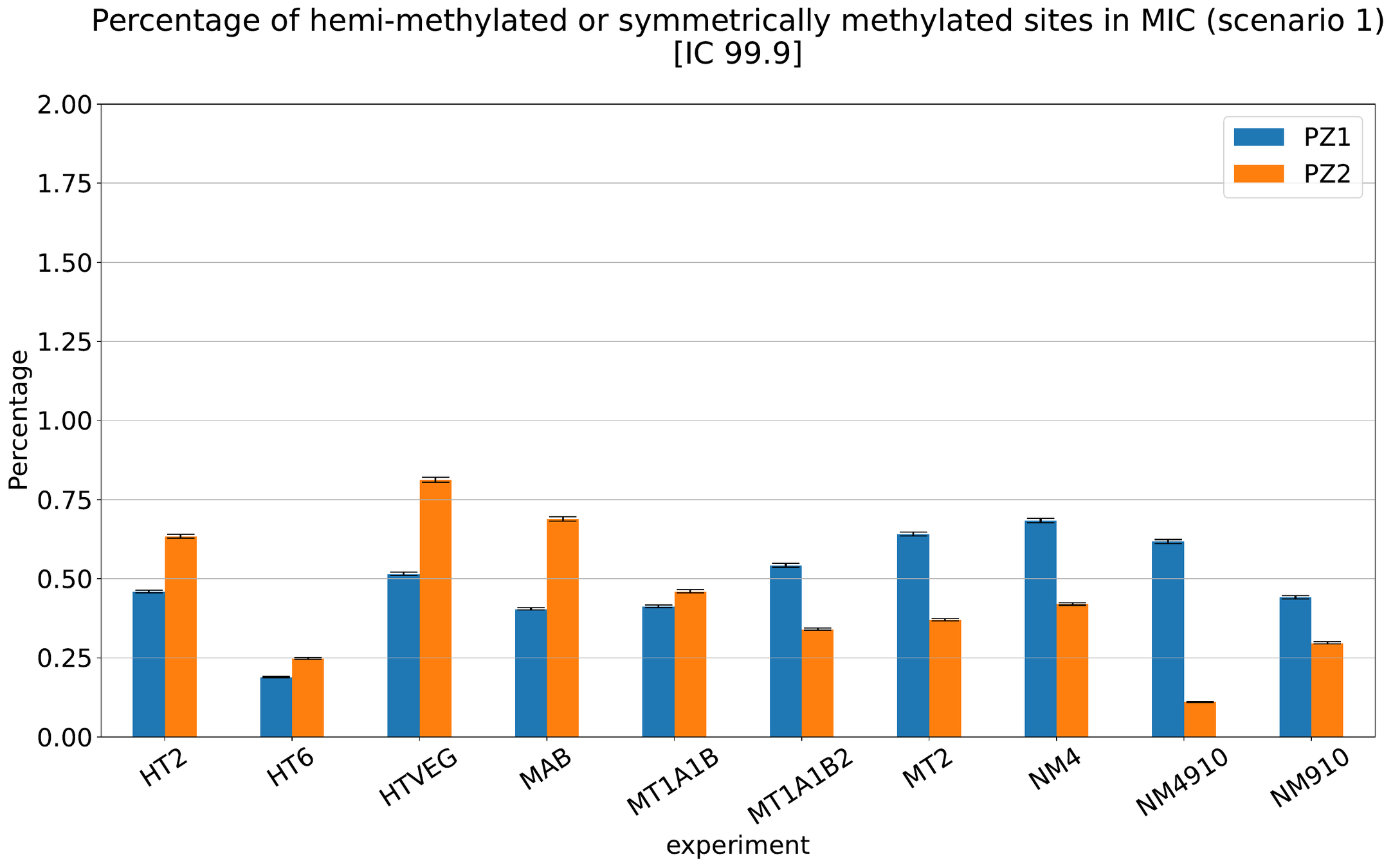
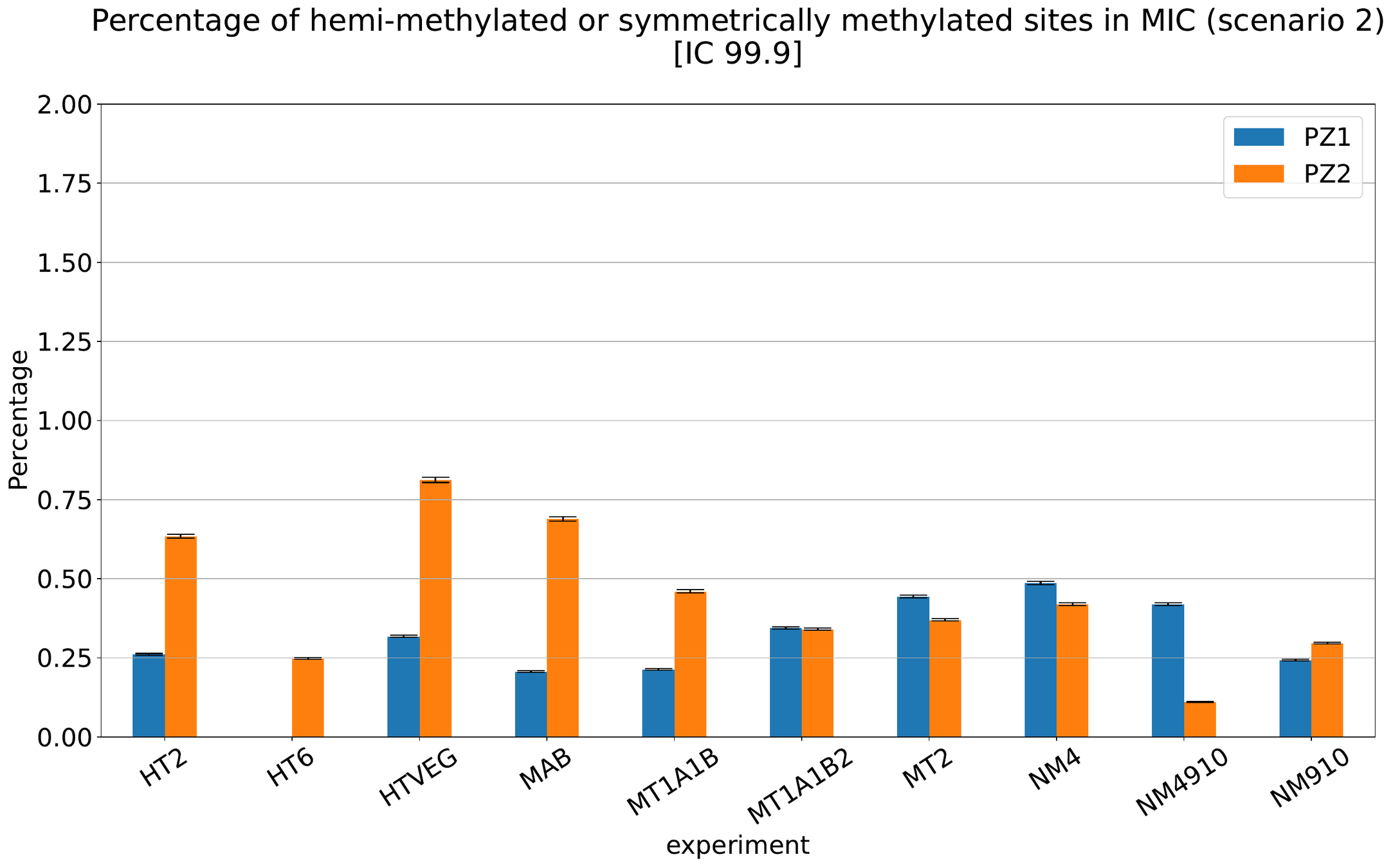
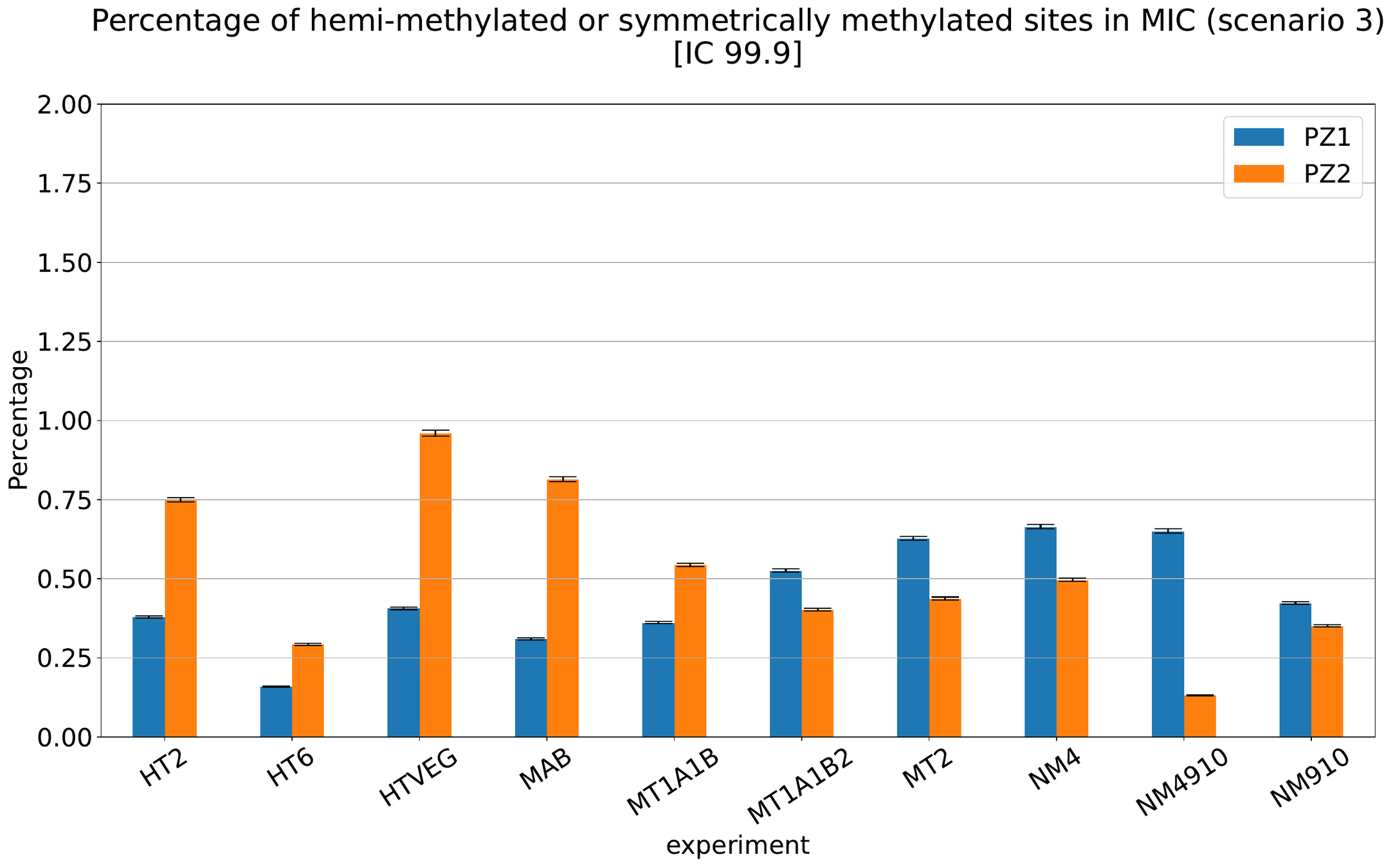
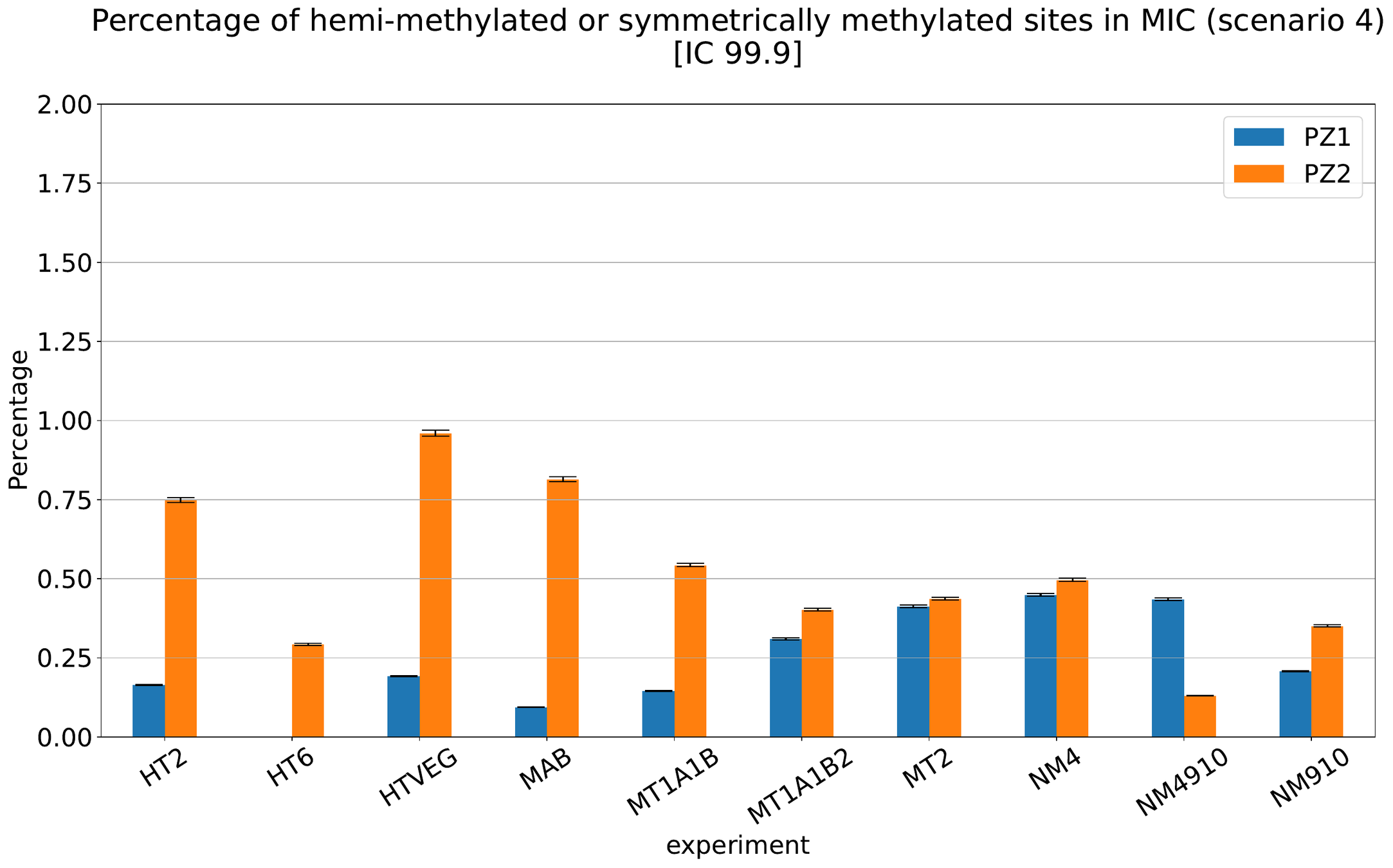
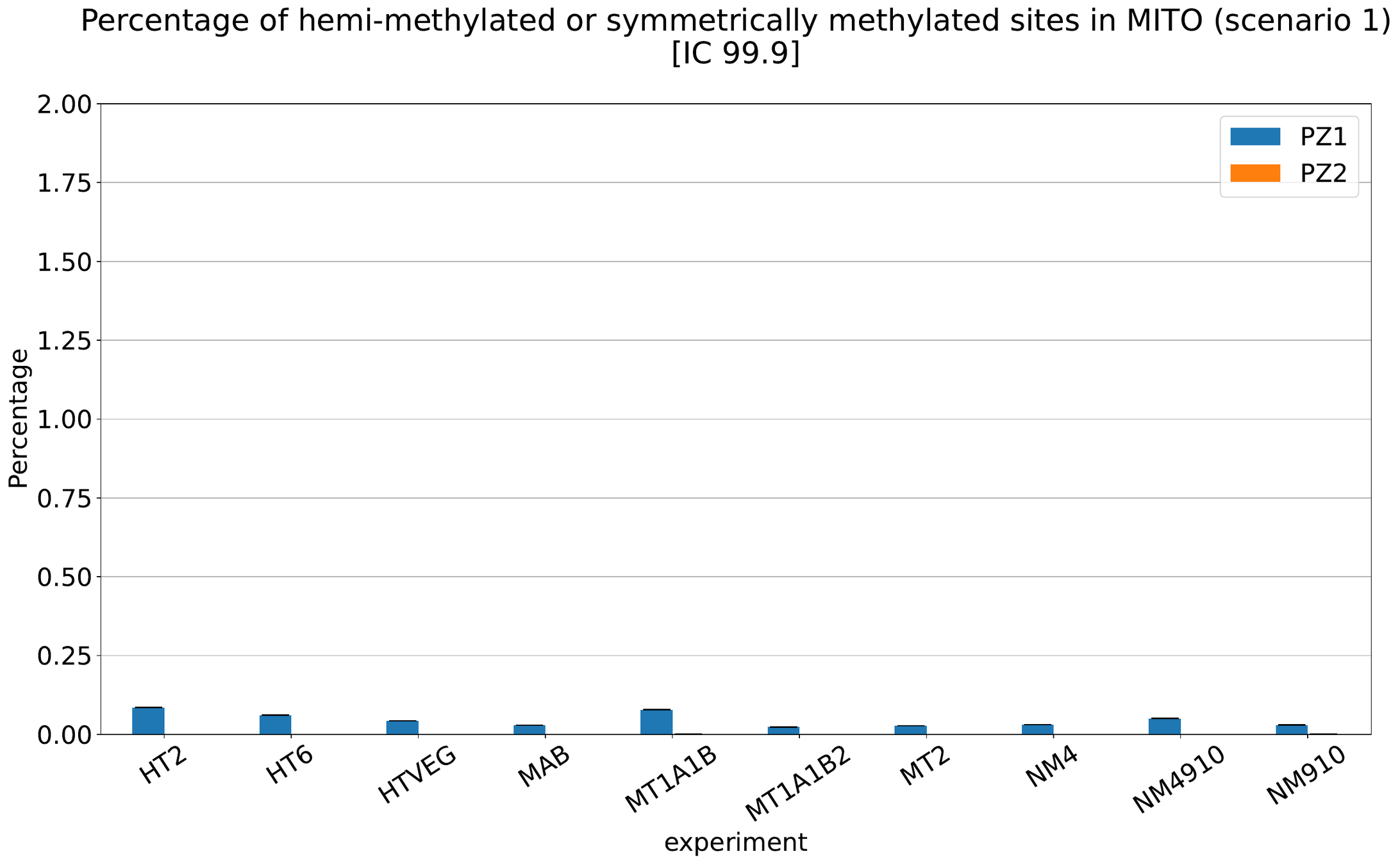
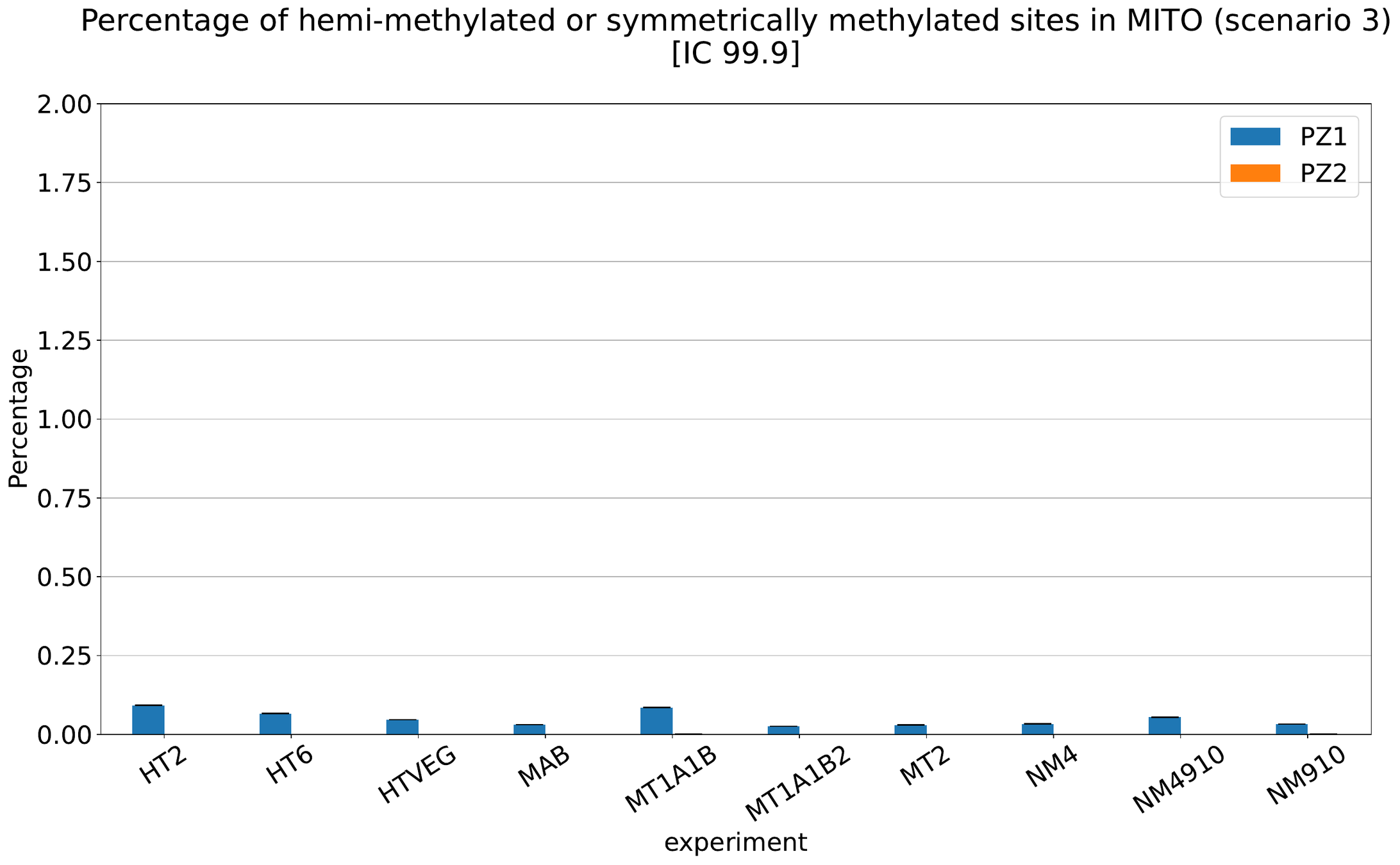
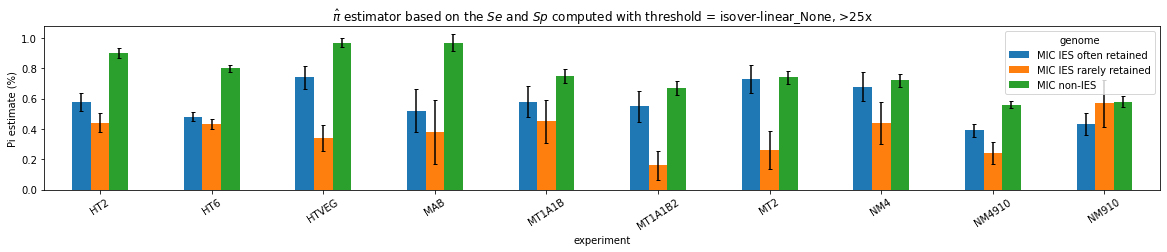
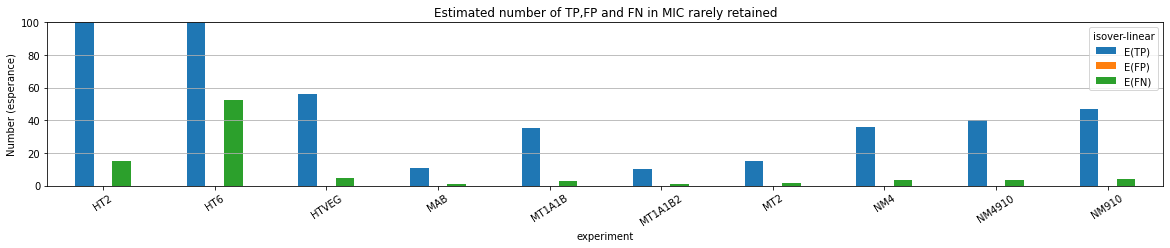
What about IESs ?
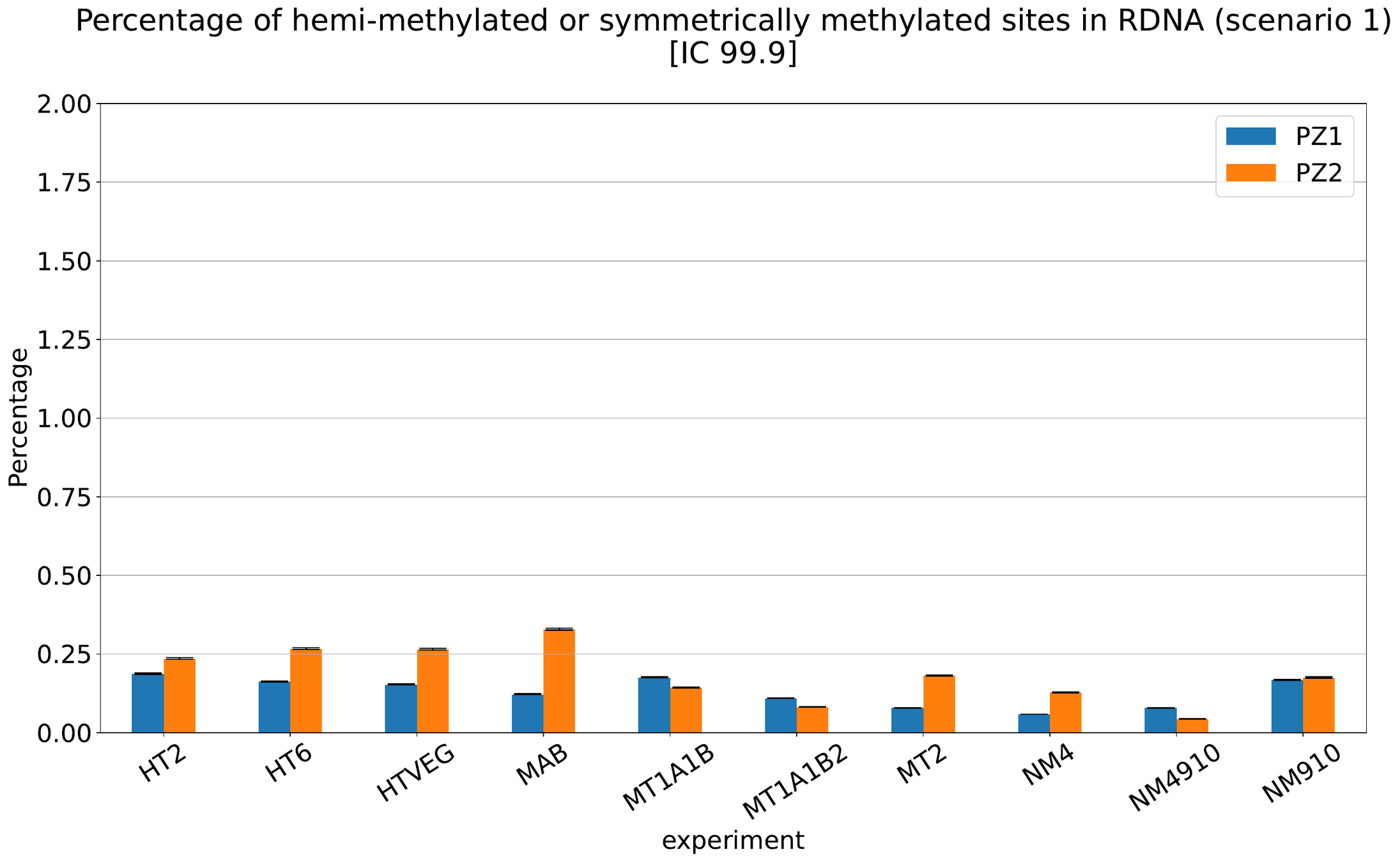
MAC IES (scenario 1 - perfection)
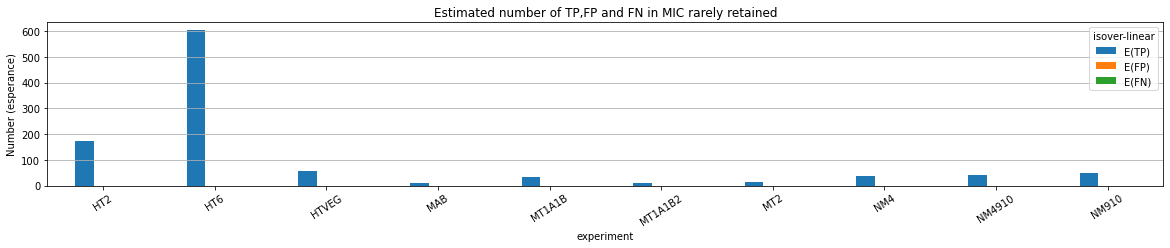
~ 0.4% in the vegetative MIC
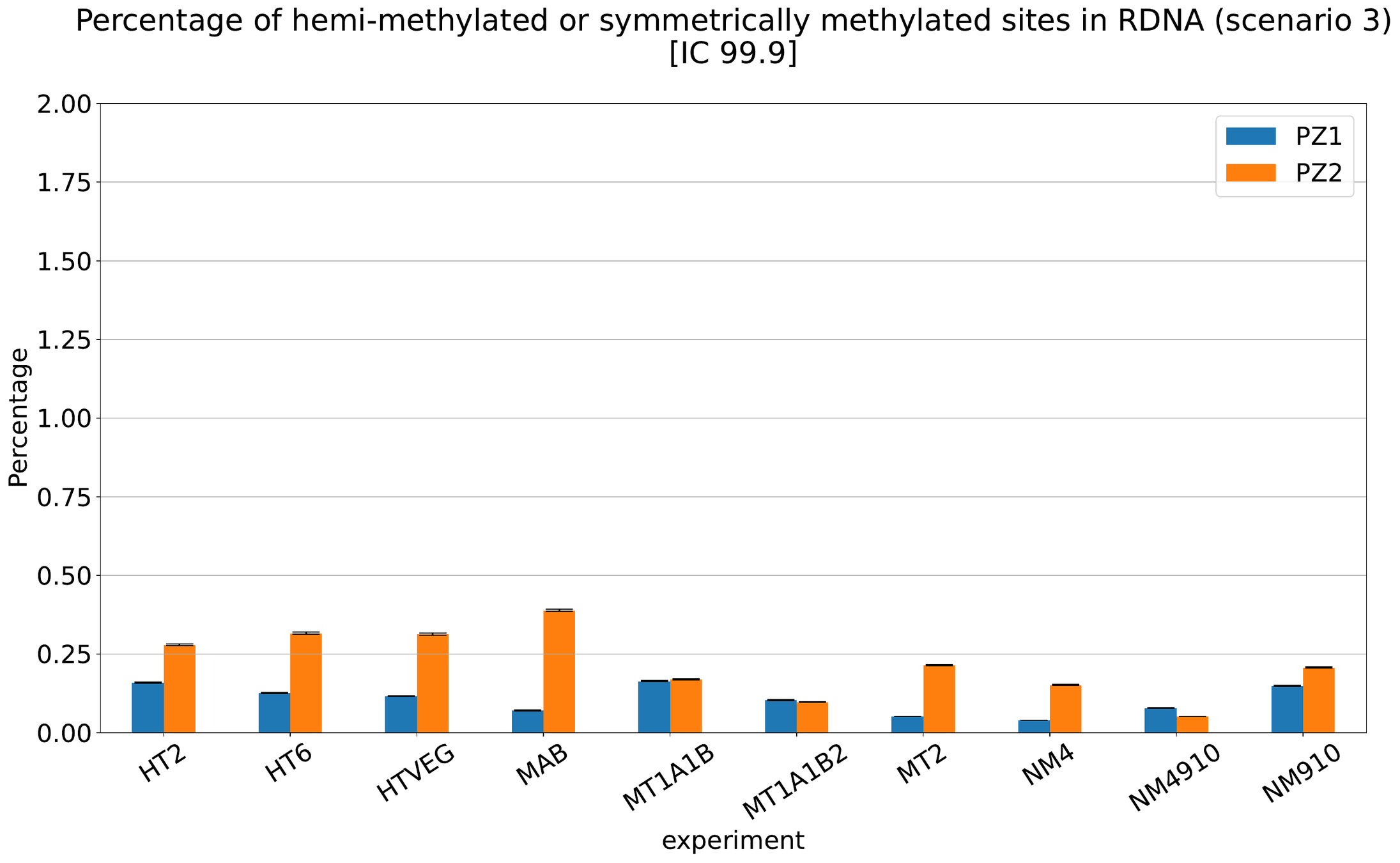
MAC IES (scenario 3)
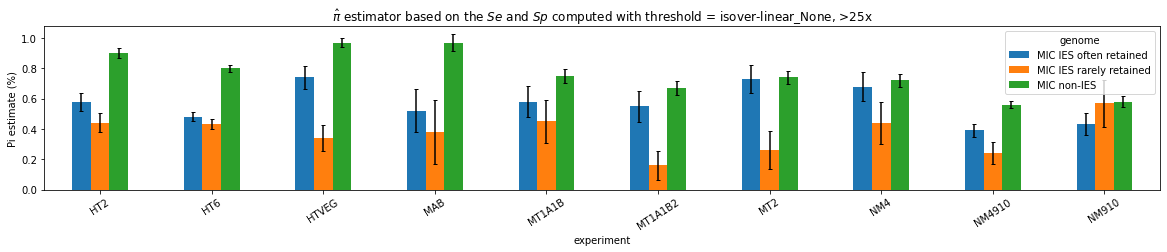
- A few missed
- No FP
~ 0.4% in the vegetative MIC
Should we get excited or not about those 0.4% ?
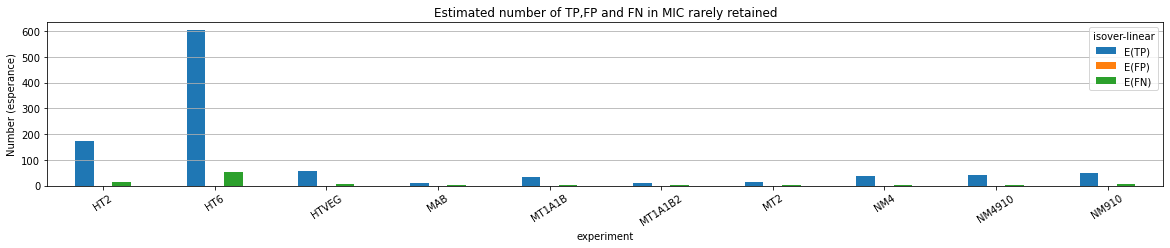
The repartition of n6mA accross molecules

Number n6mA
If we look at some of them:
* Located in AT
* Symetrical, except in NM4-9-10
Some/Many sequences are probably comming from the MAC
However,
It's still possible that Scan-RNA IES are 100% methylated, even if all other sequences with n6mA actually come from the MAC
About pure MIC sequences ?
Still ongoing
Conclusion
In the vegetative MAC
- Confirmation of previous studies
- New robust motif outside AT sites
Effects of NM4-9-10 on hemi-methylation in the MAC :
- This tells an interesting story about the NM family, and the possible deposition mechanisms of n6mA
In the vegetative MIC
- Impossible for now to know whether there is n6mA or not
- If there is, it must be far lesser than in the MAC
During autogamy
We didn't even start to investigate
Perspectives
I have plenty perspectives in mind we can discuss, but I'd be glad to hear your ideas about it too :)

Additional
Title Text
Title Text
Title Text
Title Text
Title Text
Title Text
Title Text
Subtitle
Title Text
Subtitle
Title Text
Title Text
Title Text
Title Text
Title Text
Title Text
Subtitle
Title Text
MAC IES (scenario 4)
MAC IES (scenario 3)
n6mA in the MIC (preliminary)
Pure MIC sequences: Cannot yet be trusted (error in the pipeline)
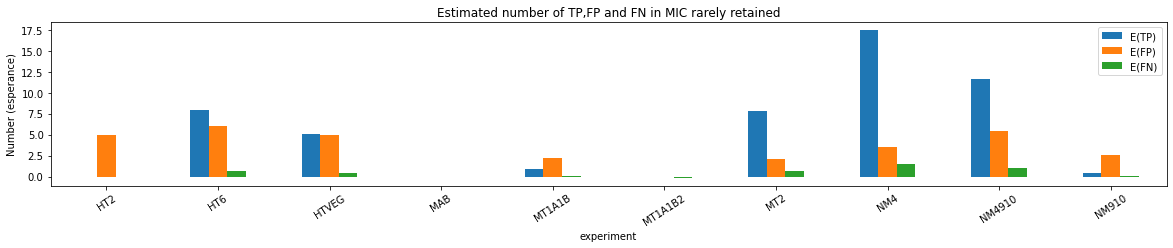
Coverage >= 40X made us lose too many materials, should restart with >=20X
2.1 Retroingineering
The capping of IPDs
-
modelPrediction is the predicted IPD value by the model in a given context of nucleotides at this position
-
globalIPD is the mean of all the IPD values of the read.
-
localIPD represents all IPDs that have been mapped at a given position in the genome, including those from other sequences
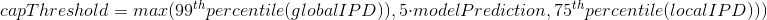
Conclusion on the capping
- Isn't coded as advertized by PacBio
- The way it's implemented for AggSN is problematic and doesn't really make sense
- Paradoxally, it should be more relevant for our approach than for the default one
- We expect no methylation to be undetected due to the capping
Laura landwebehr 2020
Oxytrichia trifallax
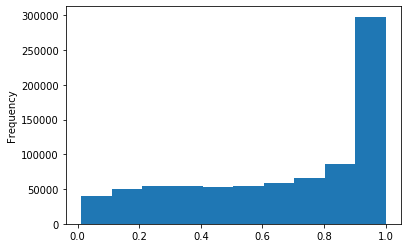
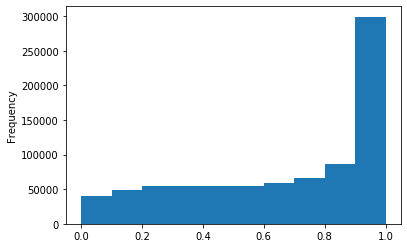
p values (A)
p-values (A score >20)
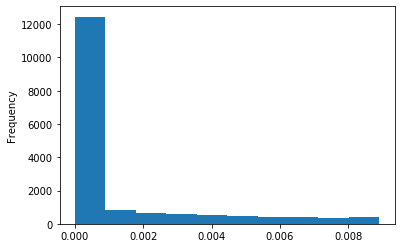
Out GATC score < 20
Out GATC
ipdRatio score 20
ipdRatio idv20/score20
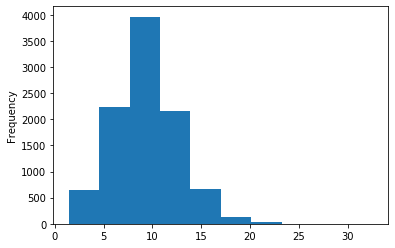


A outAT score 20 isQv20 (812 seq)
A outAT score20 idQv20 + Strong BH correction (176 seq)
ipdRatio out GATC before filtering BH vs after (qv20/idqv20)
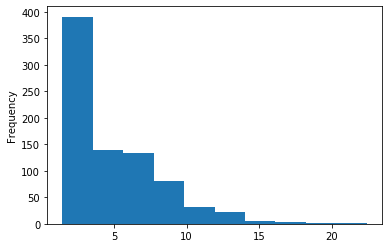
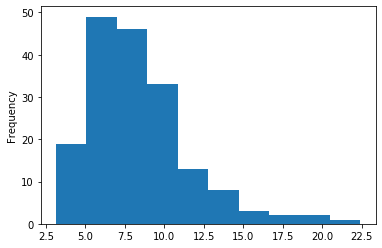
In GATC

ANR meeting
By biocompibens
ANR meeting
28/02/19
- 105



