Role of DNA methylation in the genomic rearrangements in P. tetraurelia




PhD Defense
DELEVOYE Guillaume
09/06/2022
Supervisor : Dr MEYER Eric
Jury members : Dr DUHARCOURT Sandra, Dr CHEN Chunlong, Dr DURET Laurent
Introduction
P. tetraurelia



Studying ciliates
A 350 years old story



A. van Leeuwonhoek (1668)
"Animalcules"
Pasteur (1862)
Spontaneous generation
HS Jennings (~ 1900)
Paramecium as a model
T. Sonneborn (1937)
Non-mendelian inheritance
of sexual type
in Paramecium

Carol Greider & Elizabeth Blackburn (1985)
Nobel prize (telomeres in Tetrahymena)

Teams of E. Meyer and S. Duharcourt (2014)
Sexual type determined not by DNA but maternal RNAs, in Paramecium
There is more...
-
First known organisms that do not use the "universal" genetic code
- Paramecium (Caron and Meyer 1985)
- Tetrahymena (Preer et al. 1985)
-
Histone Acetlyases (HAT)
- Tetrahymena (Brownell et al. 1996)
-
Self-splicing introns (ribozymes)
- Tetrahymena
- Tubulin post-translational modifications
> The genome-wide programmed rearrangements <
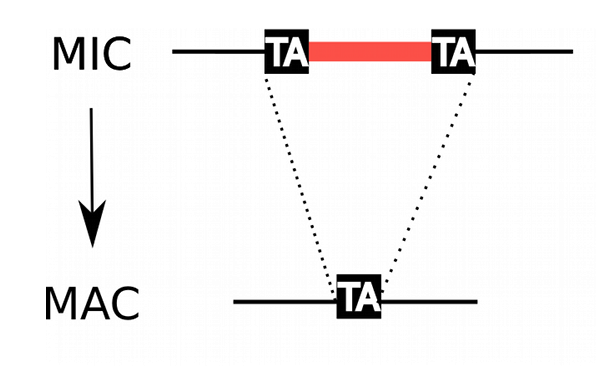
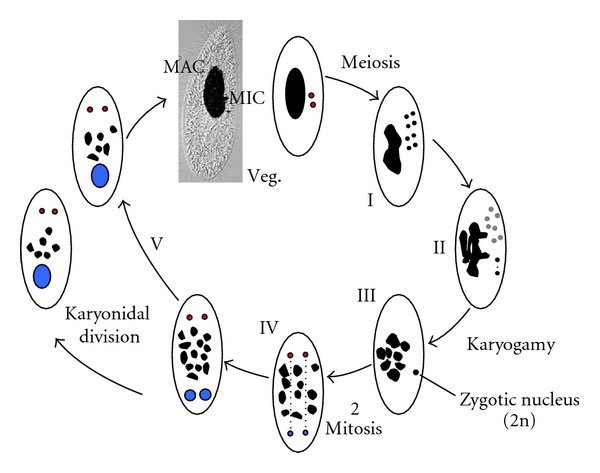
P. tetraurelia: Nuclear dimorphism
Unicellular eucaryote with 3 nuclei:
-
2xMICronuclei (2n)
- Germline nucleus
- Contains: Transposons + Repeated sequences + 49.260 Internal Excised Sequences (IES)
- No transcription outside meiosis
DNA ratio: 1 MIC for 200 MAC
-
1xMACronucleus (800n)
- Somatic nucleus
-
Derived from the MIC genome
- Amplified
- Free from TEs; repeated sequences and IESs
- Transcriptionnally active
- Rebuilt after each sexual process, under the control of the maternal MAC (hence frequent non-mendelian inheritance)
Programmed rearrangements
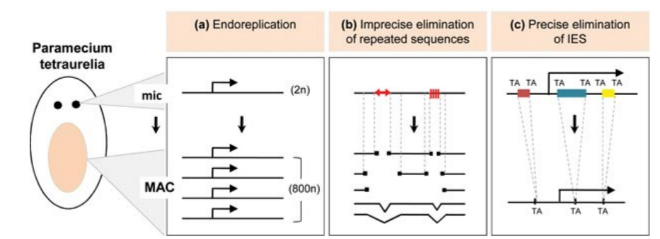
After sexual processes, a new MAC is formed, with important genome re-arrangements
Results in a MAC DNA almost purely made of coding sequences
Coyne et al. 2012
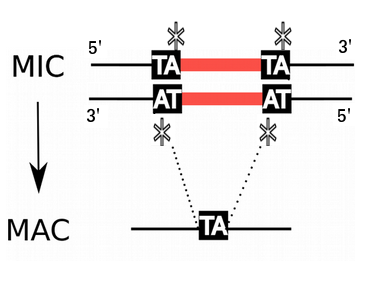
Profiling IESs (1/2)
- Non-coding
- Remnants of Tc1/Mariner
-
All excised by Pgm
- Excised with a single-nucleotide precision
-
Life or death issue
- Genes interrupted
- IES excision is exapted for the sexual type
- Size shrinks with age
- Most IES are very short (26-150bp)
49.260 unique sequences
O. Arnaiz et al 2012
PiggyMac (Pgm)
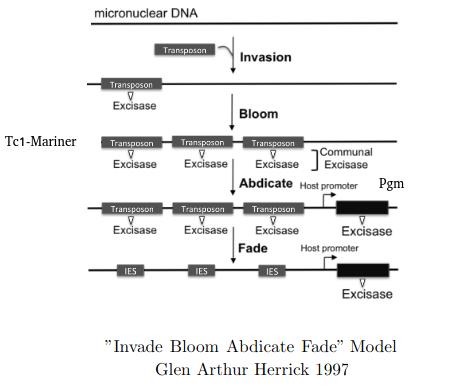
"Invade Bloom Abdicate Fade" model
Adapted from Glen Arthur Herrick 1997
100%
Profiling IESs (2/2)
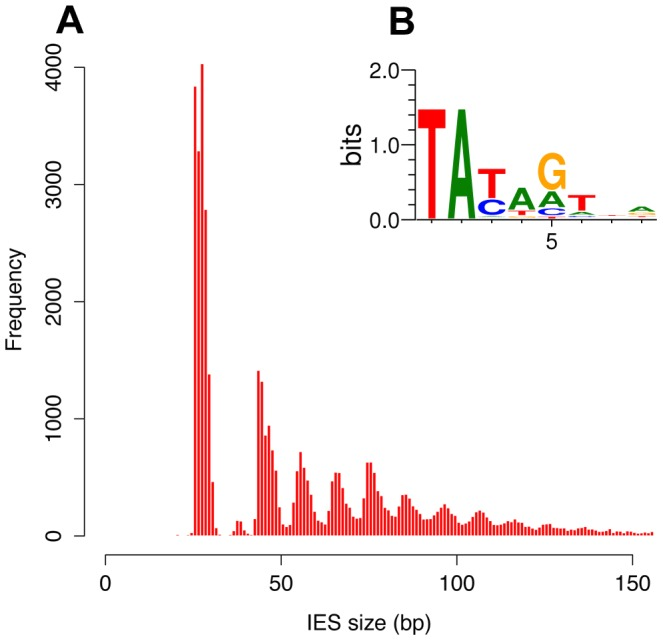
- 100% TA-Bounded
-
Weak consensus TAYAG
- ~ Tc1/Mariner
- Periodic size distribution ~10
O. Arnaiz et al. 2012
Not sufficient to distinguish IESs from the rest of the genome
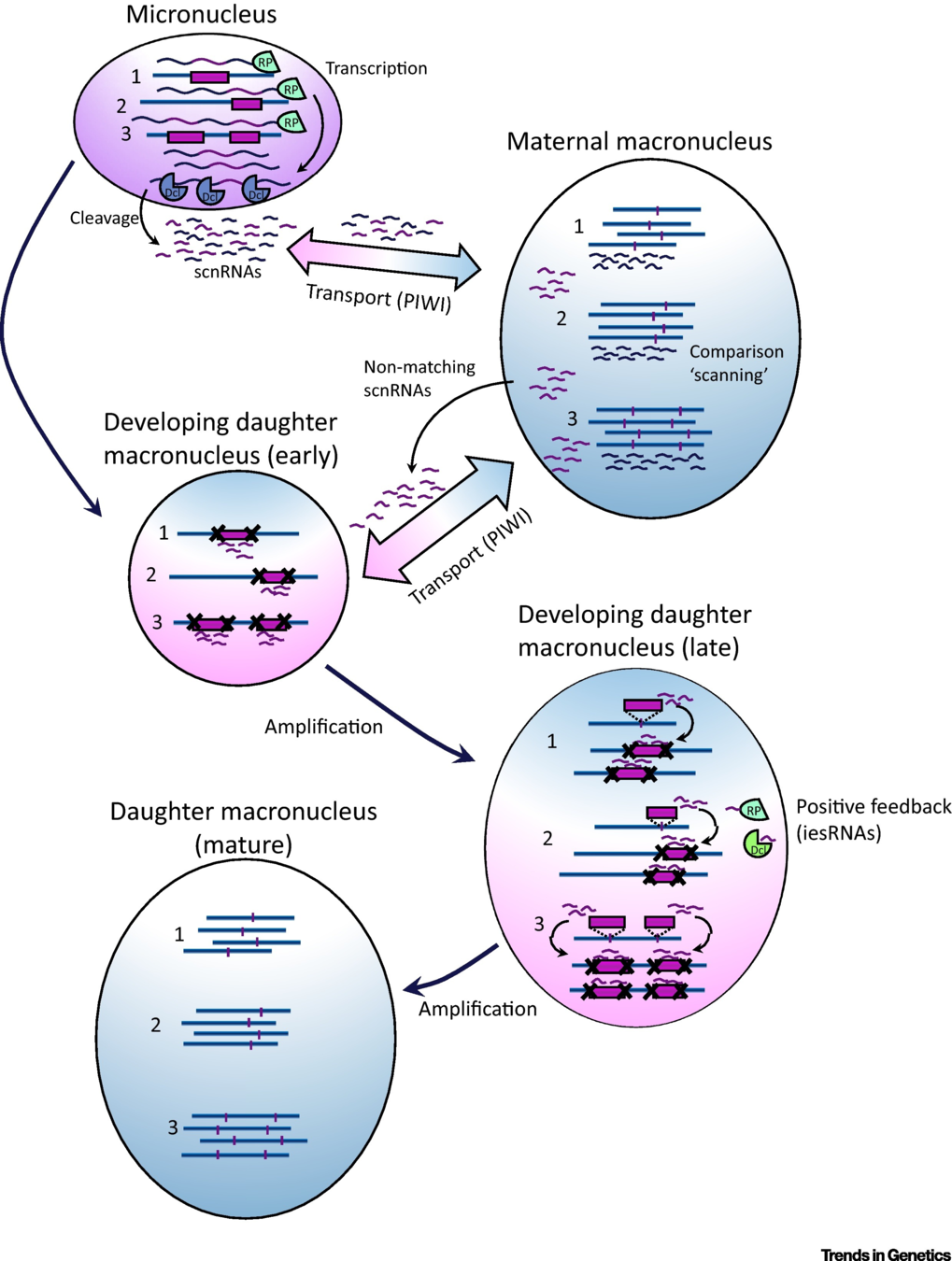
IES recognition: scnRNA pathway
S. E. Allen and M. Nowacki - 2017
If not in the maternal MAC : Recognized and excised
Problematic
Problematic
Inactivation of scnRNA and iesRNA pathways:
- ~30% of IESs are retained
- Their retention is not even complete
- Oldest = More independent to small RNAs
- IES features = insufficient to explain the recognition
All IESs may be recognized through the small RNAs
... but is there a redundant system for the oldest/shortest ones ?
Problematic ~ Self VS non-self recognition
Hypothesis : DNA methylation


5e base <-> PERMANENT
The DNA methylation hypothesis
-
2.1-2.5% in the MAC and MIC of P. aurelia (Cummings et al. 1975)
-
Detection by SMRT in the MAC (A. Hardy et al. 2020)
- 0.8% and 1.6% of adenines
- 81.5% are located in AT sites
- Enriched downstream the Transcription Start Sites (TSS)
- Detection in Oxytricha by L. Landweber et al. (2019)


N6-methyladenine (6mA) abundant in Paramecium:
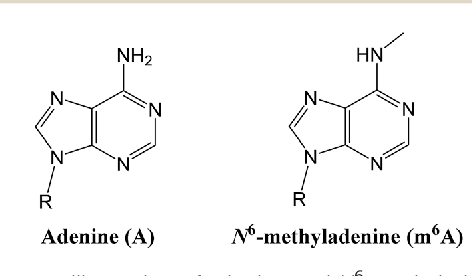
?
Other:
- 4mC ?
- No 5mC in the MAC
If maintained in the whole cell cycle in the MAC
Could explain :
- Conservation through replication
- Single-nucleotide precision
% tetrahymena oxytricha
Tetrahymena : pas de 6mA dans le MIC
Faire remarquer que palindrome
Lien méthylase de maintenance (pour discussion)
CpG DNMT1
- voir si place & temps
Transcient ?
Other possible role of DNA modifications
DNA modifications could also play a role in the new MAC in formation (transiently)
Part of the scnRNA pathway
[ QUITTE A ... ] scRNA génèrent la méthylation pour guider plus précisément ?
Pas scnRNA
The DNA methylation hypothesis

And many other possibilities...

Méthylase de maintenance (si palindromique)
Methylase candidates

- In 2015, DAMT-1 in C. elegans (6mA) - Preer et al.
-
MTA-70 domain of DAMT-1 identified in P. tetraurelia too
- Silenced by RNA interference (Grouped by homology)
- Reduction of 6mA (southwestern blot)
> Sequenced with PacBio SMSN sequencing



WT Veg
Control
silencing
T=2h
T=6h




RNA interference






Candidate methylases
Reduction 6mA
Southwesternblot
Total DNA
1:200 MIC !!!
LISTER ECHANTILLONS
Première méthylase != première 6mA
Southwestern : 90%. Pk pas nous ?
MTA1 -- orthologue 4-9-10
MTA9 -- Pas catalytique chez Tetrahymena [..] --> MT1A1B2
Notes
Subtitle
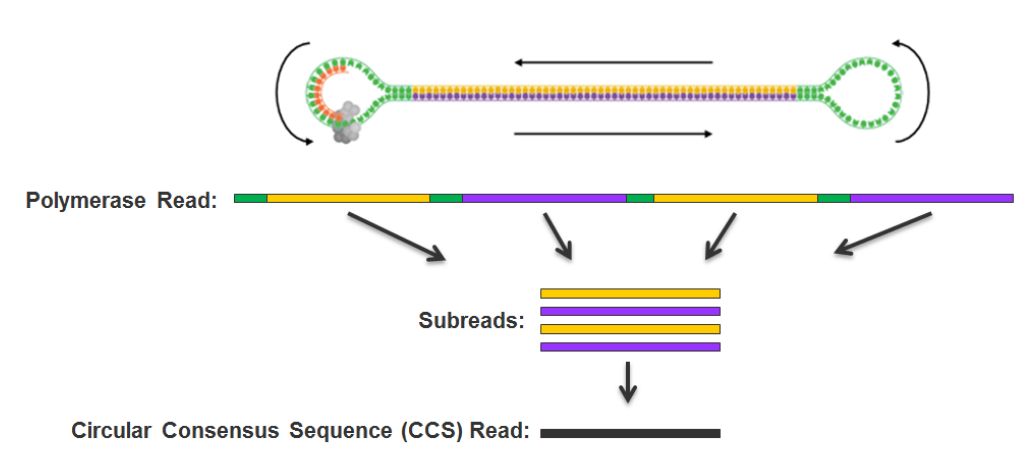
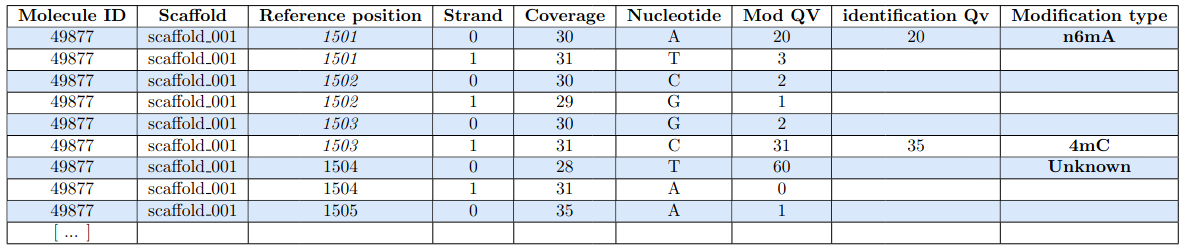
PacBio SMSN sequencing
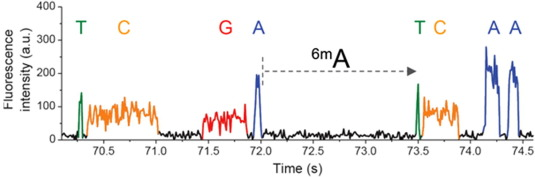
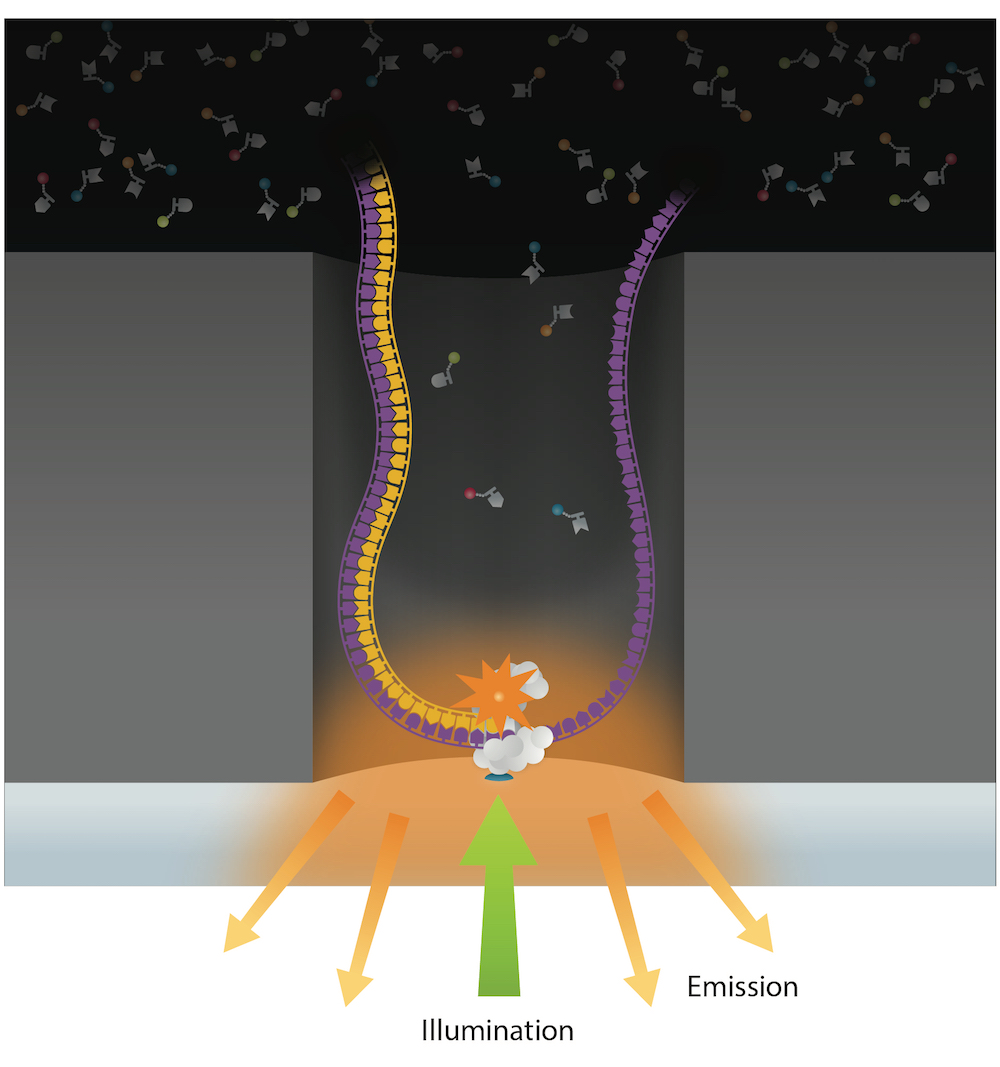
$$ipdRatio= \frac{MeanIPD_{experience}}{unmethylated\ control}$$
~ 85% accuracy
~ 100% accuracy
Kinetic signatures
Global principle
Nucleotide context
DNA modifications
depending
on
6mA
12 nucleotides dans le canal
1 séquence de 12 = une vitesse
Four variants of PacBio

Only SMSN + in-sillico are compatible with our strategy
No analysis pipeline existed
> 25 measures
SMSN : Same molecule
Measured multiple times
AggSN : Aggregation of
distinct molecules
$$ipdRatio= \frac{MeanIPD_{experience}}{unmethylated\ control}$$
Whole Genome Amplified DNA (WGA)
Machine-learning
"in-sillico"
Overview
- Identify MIC vs MAC molecules
- Analyze methylation
- No pipeline !
- Implement and test it
- No pipeline !
- 6mA MAC
- 6mA MIC
Isolate the MIC
molecules
The random sampling strategy
IES
Other MIC
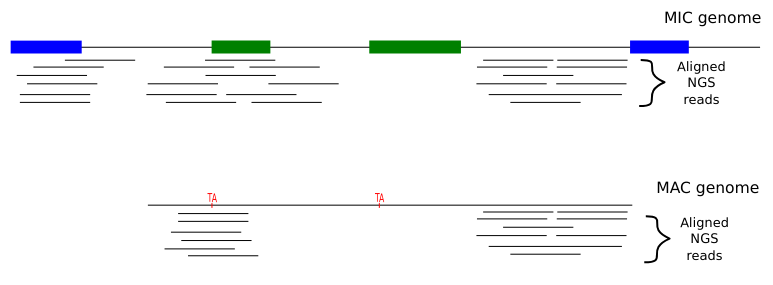
Other MIC
IES
Mac Destinated Sequences (MDS)
MAC
TA Junction
-
We work on total DNA :
- ~ 1 molecule out of 200 comes from the MIC
-
Sometimes the physical origin of the molecule can be guessed
- ~ 100% accurate PacBio consensus (CCS) !
- MIC regions that are far from the IESs and the MIC-specific sequences cannot be studied
Parler petits inserts
Expected number of IES+ sequences
-
1 molecule out of 200 comes from the MIC
- A bit less due to contaminants
- ~ 1/6 of MIC inserts will carry an IES
-
# of PacBio consensus (CCS) per sample :
- > 150.000 (multiplexed)
- ~ 350.000 PacBio CCS (not multiplexed)
That is,
-
Expected ~100 to 300 IES+ sequences per experiment
- Got 49 to 310
Orders of magnitude :

This is not much, but if we are right 100% of the scnRNA independent IESs could be methylated
Raw numbers of PacBio consensus (CCS) per sample and category
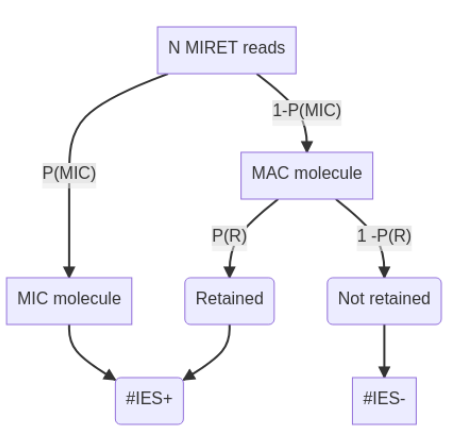
IES retention
- IESs are sometimes retained in the MAC
P(R)
1 - P(R)
-
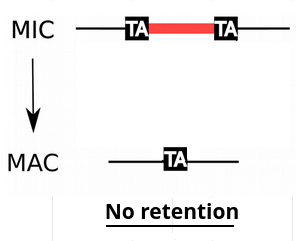
Quantification: "IES Retention Score" (IRS)
- MIRET : Cyril Denby Wilkes, Olivier Arnaiz, Linda Sperling 2016, eg:
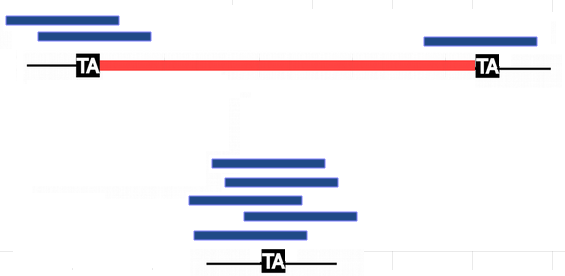
5 reads IES -
1 read IES +
2 reads IES +
$$IRS_L = \frac{2}{2+5} \approx 27\%$$
$$IRS_R = \frac{1}{1+5} \approx 16\%$$
The higher the IRS, the higher the retention.
IES retention
Pitfall
e.g
MIC = 4n, MAC = 800n, R = 0.005 , N = 100 NGS reads
$$\mathbb{E}(IRS)= 0$$
$$P(MIC|IES+) = 50\%$$
No !
Even a low IRS can be problematic for us !
When the N is small (~100), it's just impossible to see small retention levels
Due to the MAC ploidy, even the slightest retention leads to $$P(MIC|IES^+) < P(MAC|IES^+)$$
Let's just keep all IESs with an IRS = 0 ?


IES retention
Proposed approach




??
Le faire pour chaque IES
Implicitement (amalgamé : Dépend de l'IES plus que du réplicat)
IES retention
Four options to estimate R :


Hamiltonian
Monte-carlo
Inverse
transform
(calculus)
Reject sampling
Monte-carlo
Bayesian approaches
(credible intervals)
Frequentist approach
(confidence interval)
Computation time
Hard to implement
Expected to give similar results
$$\mathbb{E}(IRS) = P(MIC) + P(R) \cdot P(MAC) $$
IES retention
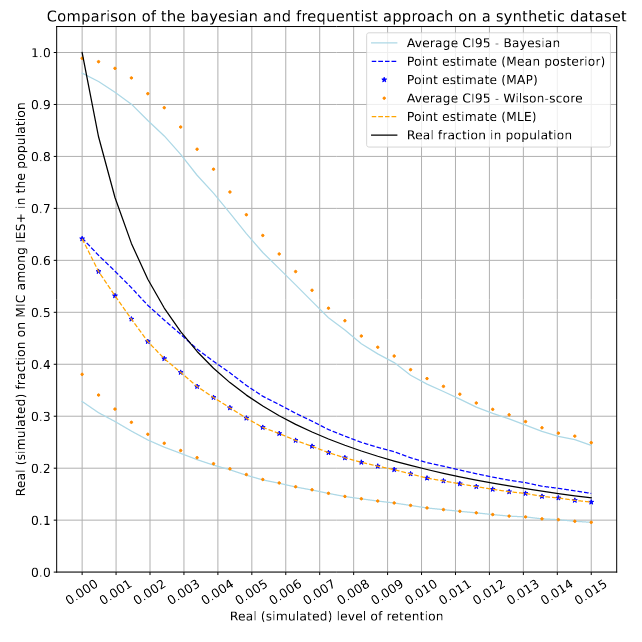
- The 3 bayesian methods are equivalent
- Bayesian ~ Frequentist
- True value in confidence/credible interval 95% of times
Comparison / Benchmarks
$$P(MIC|IES+) \in [9.5\% - 93.7\%], \alpha = 5\%$$

Problem : The size of confidence intervals is very big
- e.g 150 NGS reads, 0 IES+
For most IESs, we will simply not be able to tell wether it comes from the MAC or the MIC


IES retention
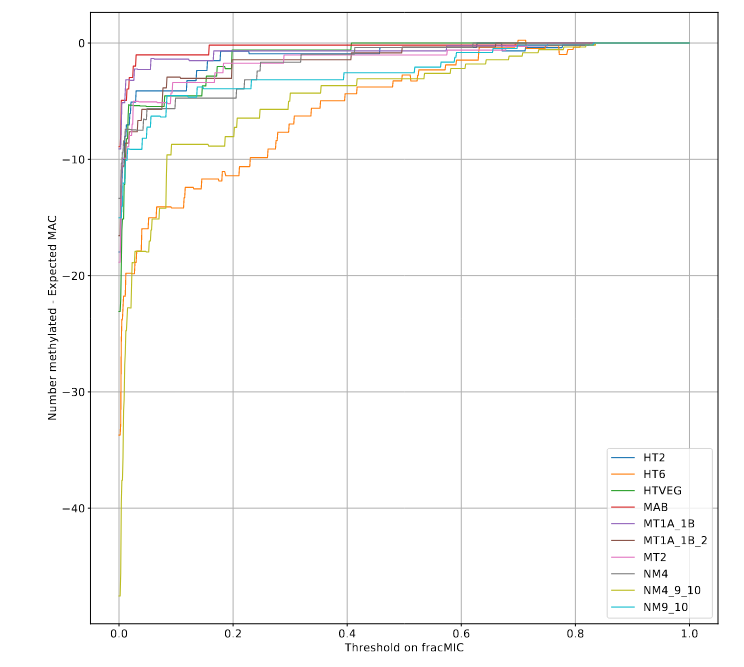
Workaround : Pooling samples

Rare picture of Eric, doing so archeology to find more samples to pool and gain coverage (circa 2022, colourized)
MITO --> Mettre pour conclure 50% retenu quand IES
Implicitement (amalgamé : Dépend de l'IES plus que du réplicat)
Dire explicitement que ce sont des séquen_ages d'ADN total de cellules végétatives
ENLEVER L'HISTOGRAMME
Mac ploidy : 800n ?
If MAC ploidy = 800n than without retention :
$$E(IRS) = \frac{4}{800+4} \approx 0.005$$
If retention :
$$E(IRS) >> \frac{4}{800+4}$$
Something is odd !
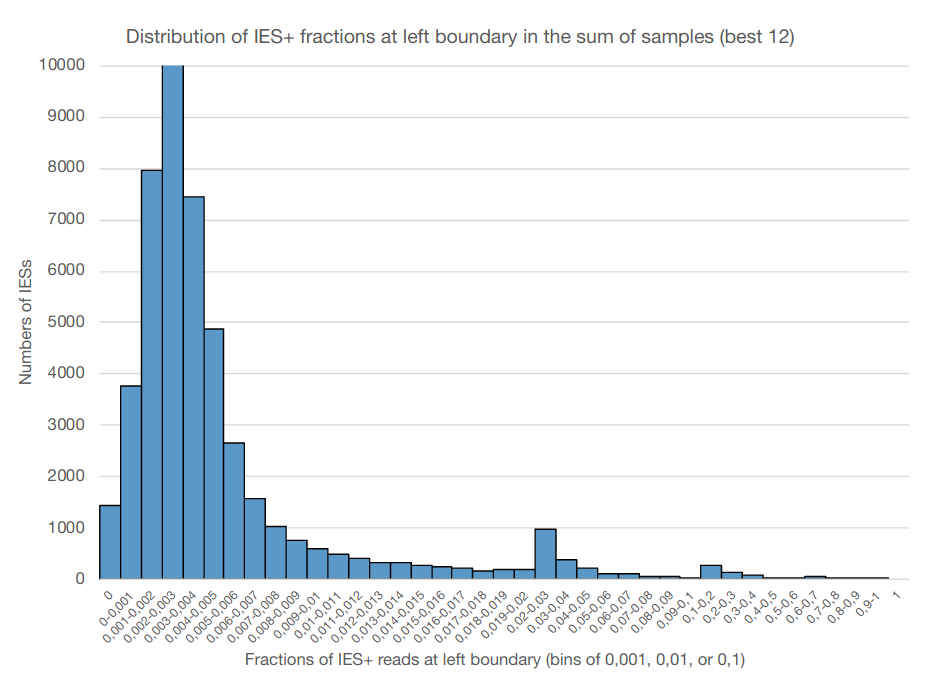
0.002-0.003
Mac ploidy ... At least 1600n ?
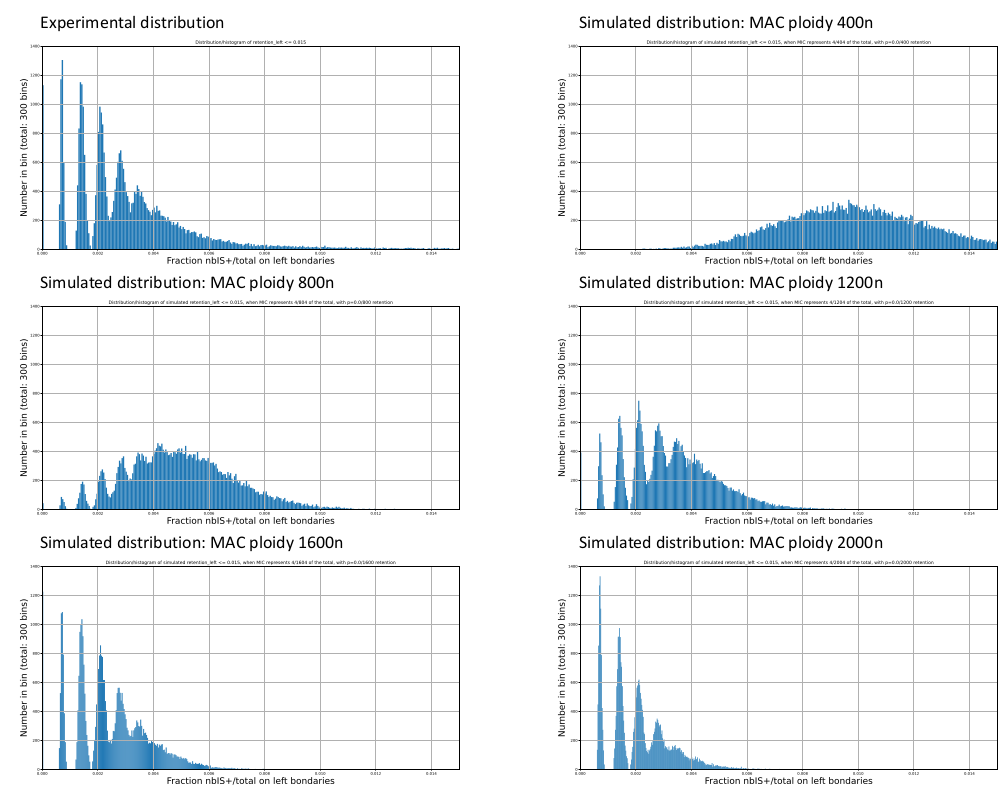
Mac ploidy ... At least 1600n ?
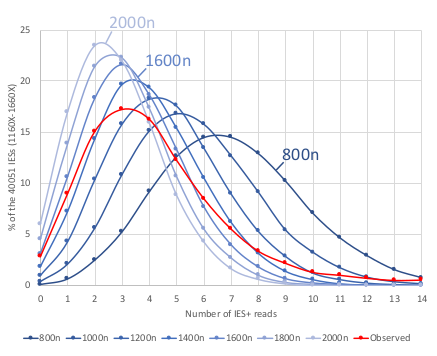
IES retention
Pooling samples is not sufficient !
On average, we will have only very vague estimates of P(MIC|IES+) !
Computed with Kmac = 1600n
SMSN pipeline
A few months of plumbing later...
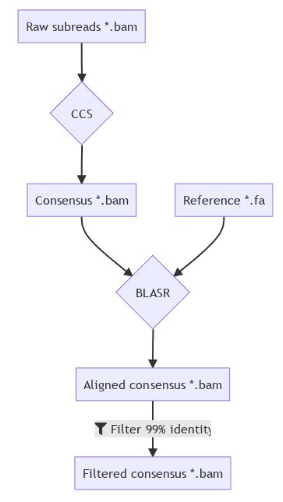
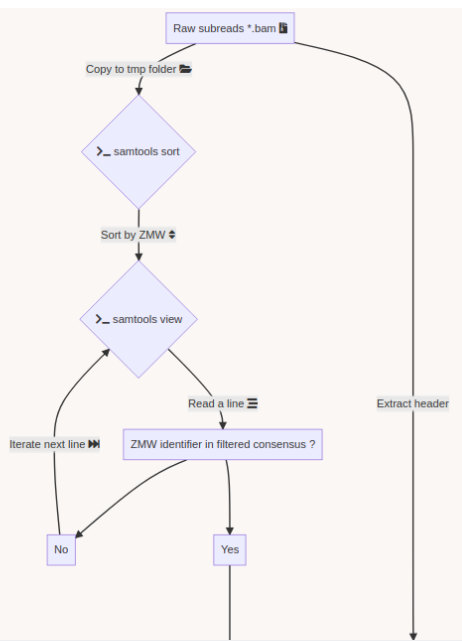

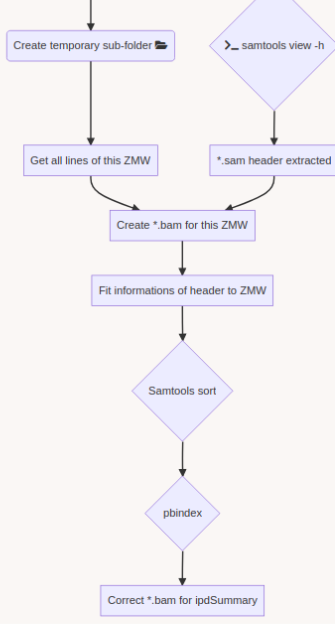
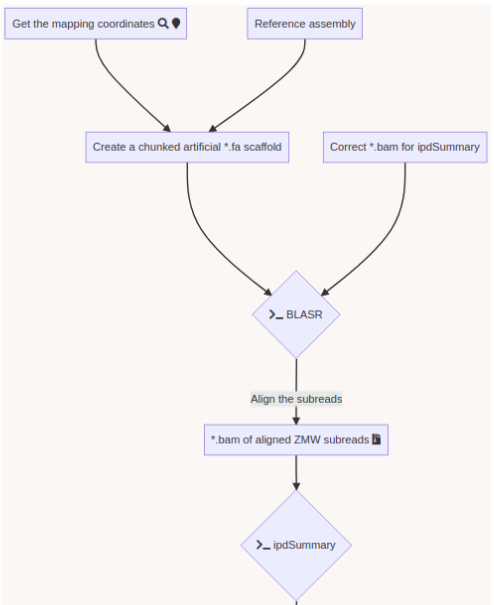






Using E. coli DNA
-
Nearly 100% 6mA (symmetrical):
- GATC +++
- EcoK
-
A few others
-
Depends a lot of the strain
-
Depends a lot of the strain
-
Nearly 0% 6mA :
- Everything else
E.coli is used to feed paramecium (contaminants)
DOnc on peut l'utiliser pour tester le pipeline
ipdRatio in E. coli (1/2)
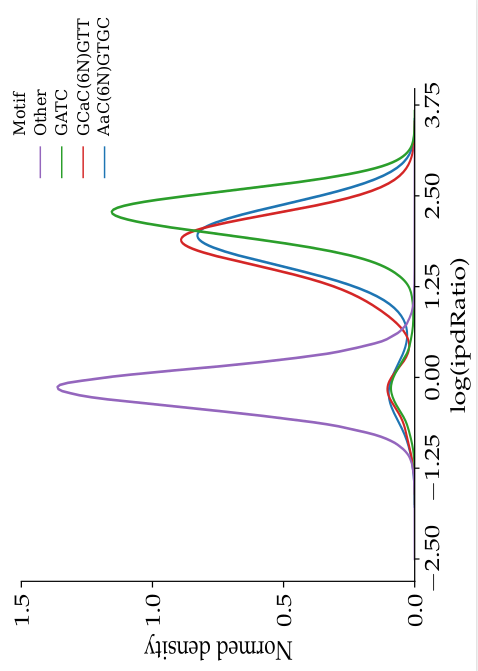
- The nucleotides we expect to be methylated have a high ipdRatio
- Slight changes between motifs
- Some exceptions : really not-methylated ?
ipdRatio in E. coli (2/2)
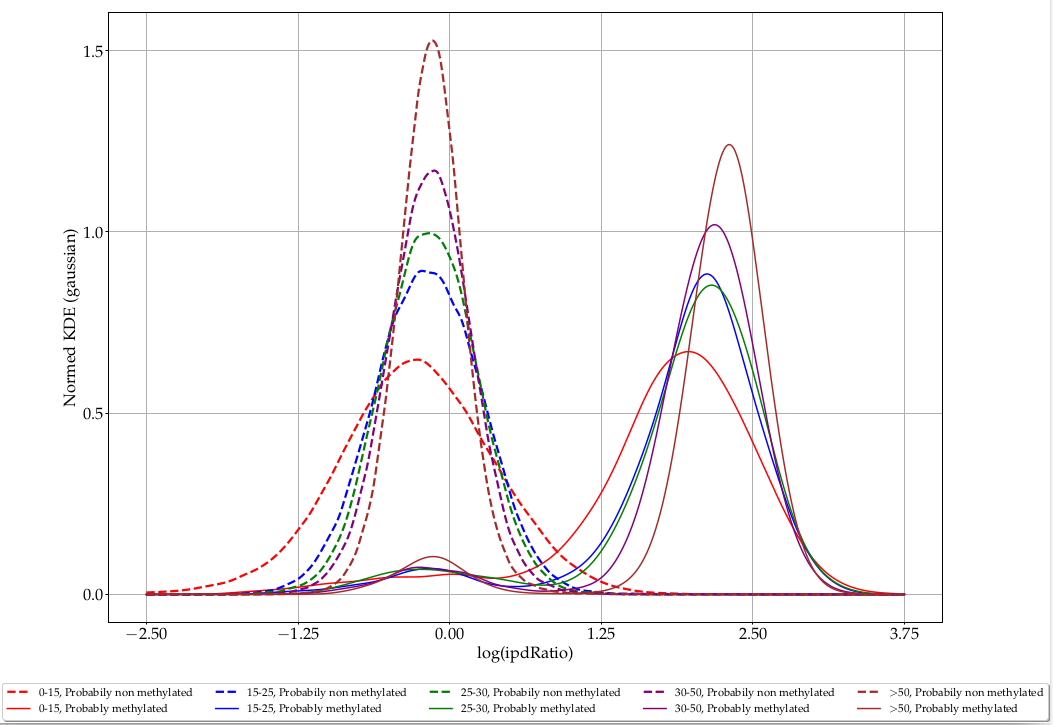
Separability and coverage are correlated
How to binarize the ipdRatio ?
Either a nucleotide is methylated, or it is not :
- We need to use a threshold on the ipdRatio to call modified nucleotides
- This threshold has to take account of the coverage effect
- No optimal solution anyway
Our pragmatical solution : An arbitrary linear threshold
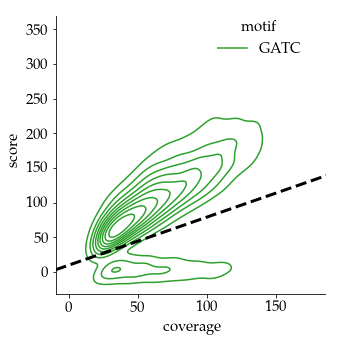
Benchmark (6mA)
- ~92% of 6mA in EcoK and GATC
- ~99.8% of non-6mA elsewhere
If we make the simplification that all GATC/EcoK sites are methylated and that 6mA is only present there :
$$Sensitivity = P(D|M)$$
$$Se = 92\%$$
But :
-
Some GATC/EcoK are unmethylated
- The real Se is actually better than 92%
-
A few amount of 6mA outside of GATC/EcoK site
- The real Sp is actually better than 99.8%
- Se = 92% and Sp = 99.8% are worst case estimates
$$Specificity = P(\overline{D}|\overline{M})$$
$$Sp = 99.8\%$$
Benchmark
(other modifications)
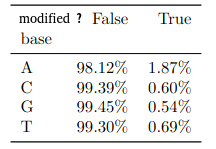
PacBio sequencing was already known for its propensity to generate false positives for 4mC (K. O’Brown et al. 2014)
- It is very likely that most of these detections are false positives
Qv30
Est-ce que c'est pareil pour du PCR amplifié ?
DNA modifications
In the MAC
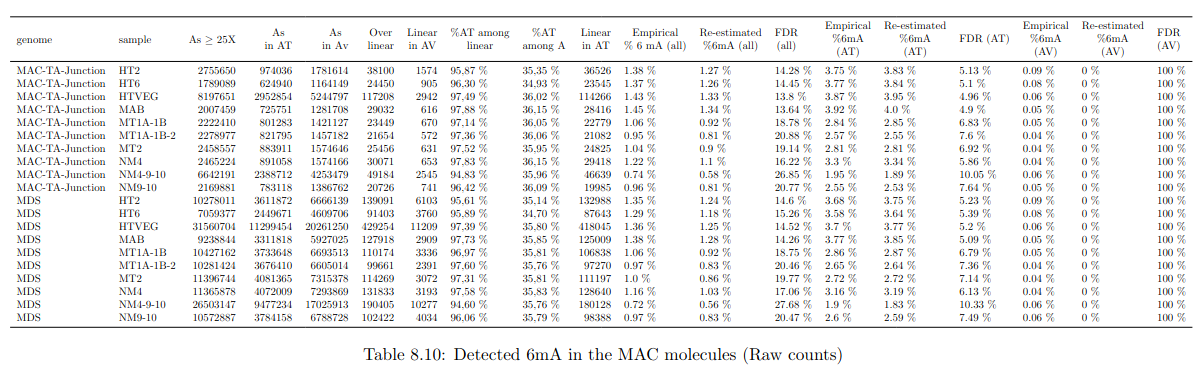
Hallmarks in HTVEG
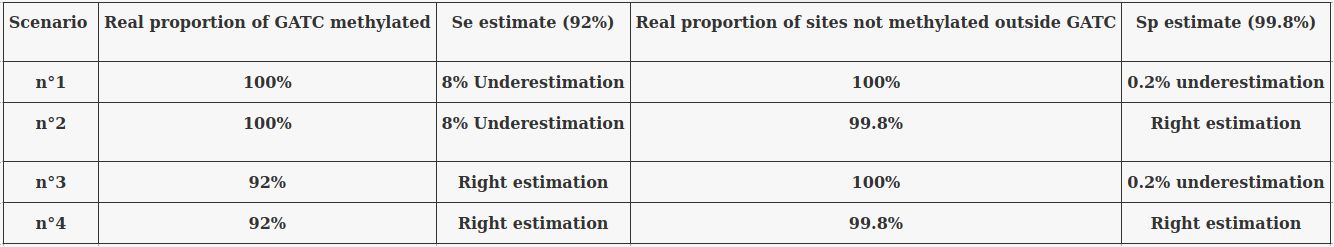
• Between 1.25% and 1.45% of 6mA in the MAC
• Between 97.39 and 100% of them are located in
AT sites
Taking account of the uncertainty of Se and Sp :
Problem : Some results will vary greatly depending on Se and Sp !
En faisant les corrections
The 4 scenarii for Se and Sp
- We don't care about Se and Sp
- We care about the fact that eventual mis-estimations of them doesn't really change anything
Mettre couleurs
Parfait
Sous évaluation
Sur évaluation
Quelques confusions
Global level of 6mA in the MAC
-50% NM4+9+10
>> Bulk of 6mA in the MAC
Other candidates too
Pareil que chez Tetrahymena
Role of our candidates
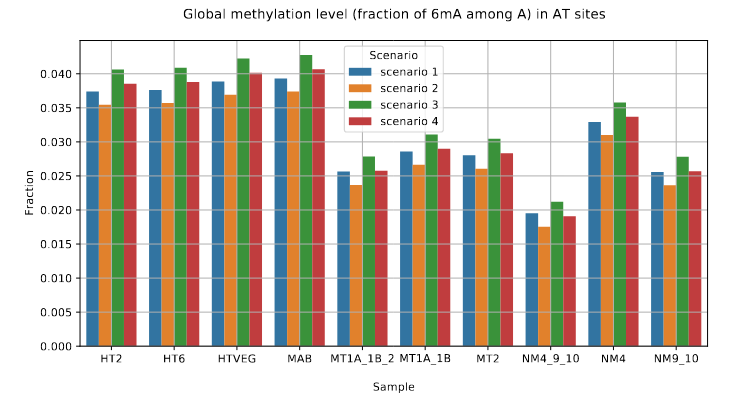
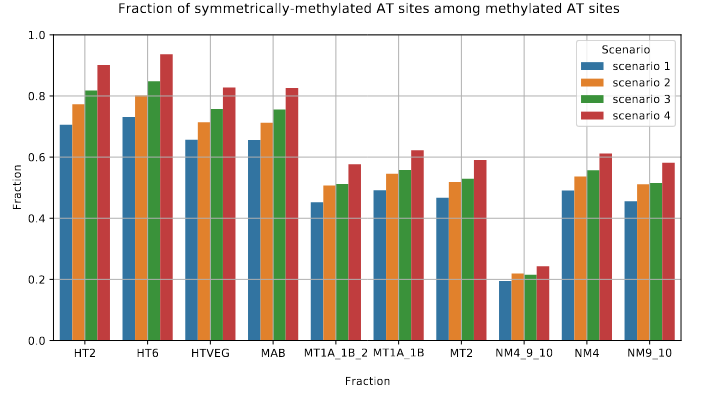
Symmetrical methylation of hemi-methylated AT sites
Raise of hemi-methylation, whose intensity depends importantly on how well Se and Sp are well estimated or not
Role of our candidates
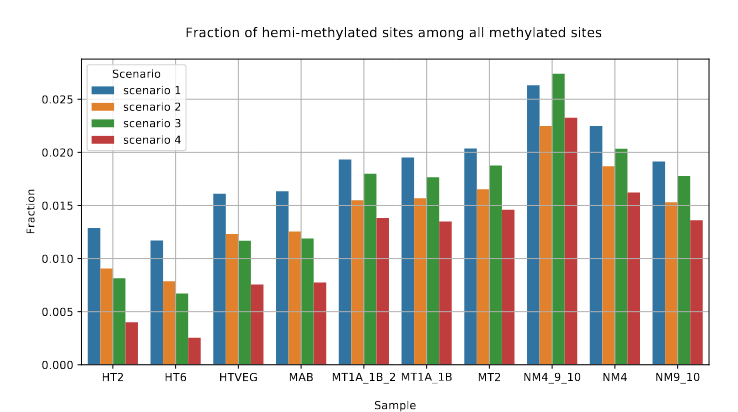
De novo methylation of unmethylated AT sites
Role of our candidates
The capacity to make symmetrical methylation is never abolished completely
Outside of AT sites
Predicted FDR : 100%
But likely detection outside of AT sites too
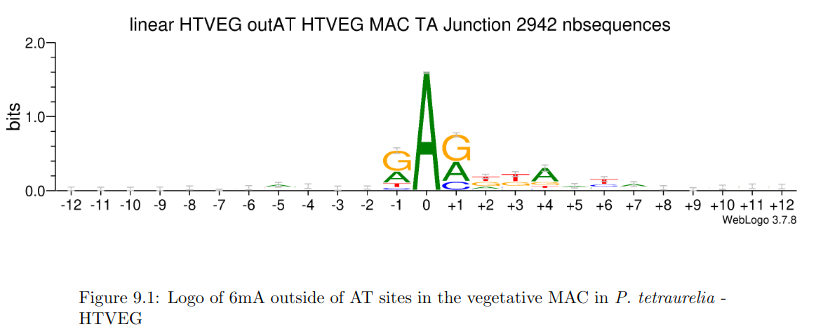
AGAA and GAGG motif
are documented as methylated sites (6mA) in C. el-
egans too (Greer et al. 2015)
DNA modifications
In the MIC
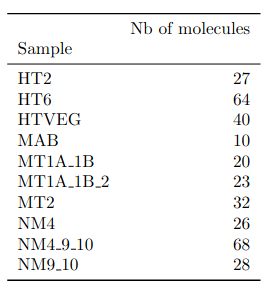
A ruthless data shrinkage
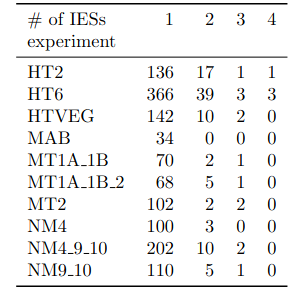
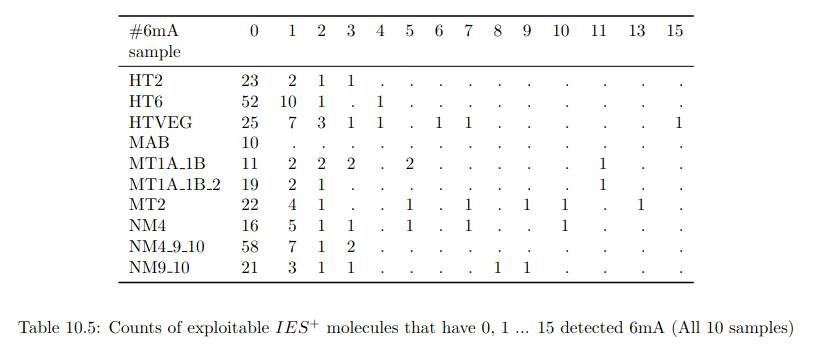
Number of molecules with at least one exploitable adenine
- several IESs
- variable MAC regions
- extremity outliers
REGIONS VARIABLES !!!!!!!!
P(MIC|IES+) among the surviving molecules
The vast majority of IES+ molecules come actually... From the MAC !!!
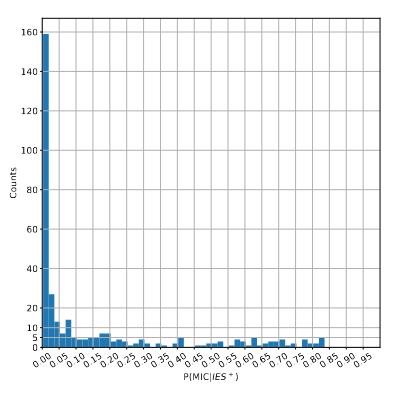
A few MAC molecules concentrate the majority of 6mA (1/2)
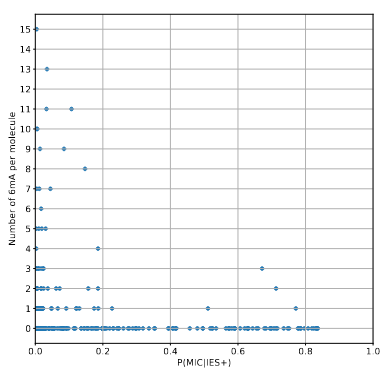
A few MAC molecules concentrate the majority of 6mA (2/2)
We can never exclude the hypothesis that 6mA comes from the MAC

The 4 scenarii for Se and Sp
- We don't care about Se and Sp
- We care about the fact that eventual mis-estimations of them doesn't really change anything

Finding unbiased estimators for and FDR
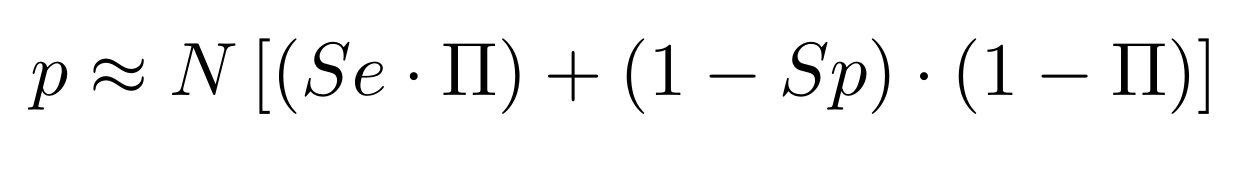
If p number of positive detections among N tests:
p = FP + TP
$$\pi$$
So,
Which means
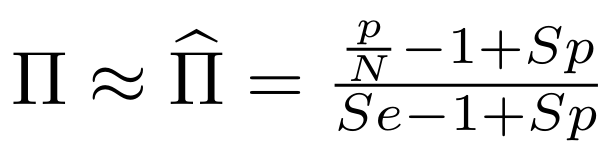
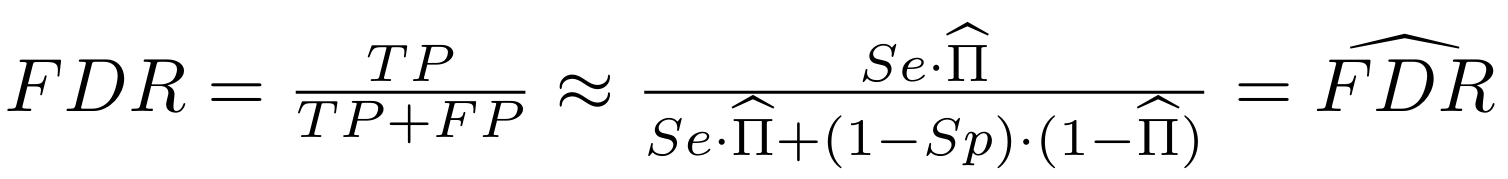
And:
What it gives in Paramecium
Methodological development to correct hemi-methylation detection (1/2)
Let FD1 and FD2 be resp:
- Fraction of hemi-methylated AT sites
-
Fraction of sym-methylated AT sites
PZ0, PZ1, PZ2: unbiased estimators of non, hémi, symetrically methylated AT sites
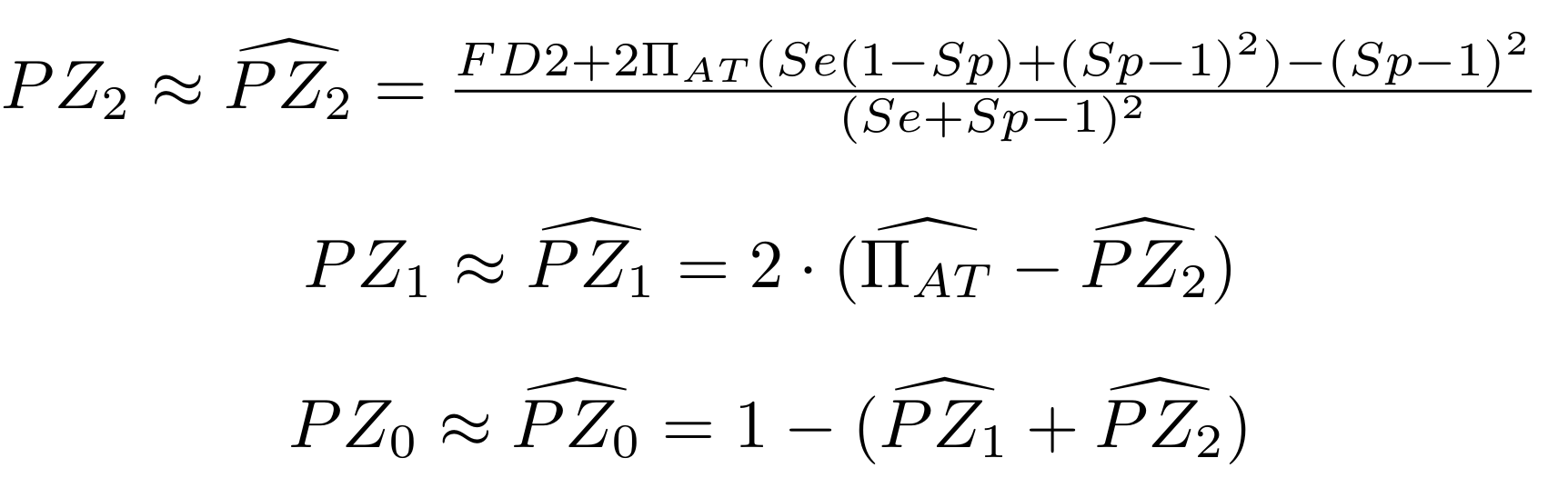
Then:
With
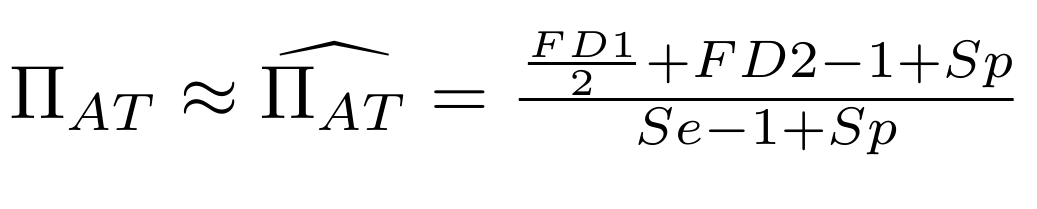
Methodological development to correct hemi-methylation detection (2/2)
We can also find the number of hemi-methylated sites being detected as such, and the proportion of sites detected as hemi-methylated that are really hemi-methylated. This is possible because we now approximately know PZ0, PZ1 and PZ2, and P(D|Z) is easy to determine:

Then, P(Z|D) can be determined through Bayes theorem using P(D|Z), P(Z) and P(D) (which are all known)
P(Z=1|D=1)
is our case of interest
What it gives in Paramecium
2.1 Retroingineering
The capping of IPDs
-
modelPrediction is the predicted IPD value by the model in a given context of nucleotides at this position
-
globalIPD is the mean of all the IPD values of the read.
-
localIPD represents all IPDs that have been mapped at a given position in the genome, including those from other sequences
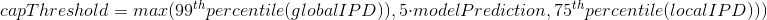
Conclusion on the capping
- Isn't coded as advertized by PacBio
- The way it's implemented for AggSN is problematic and doesn't really make sense
- Paradoxally, it should be more relevant for our approach than for the default one
- We expect no methylation to be undetected due to the capping
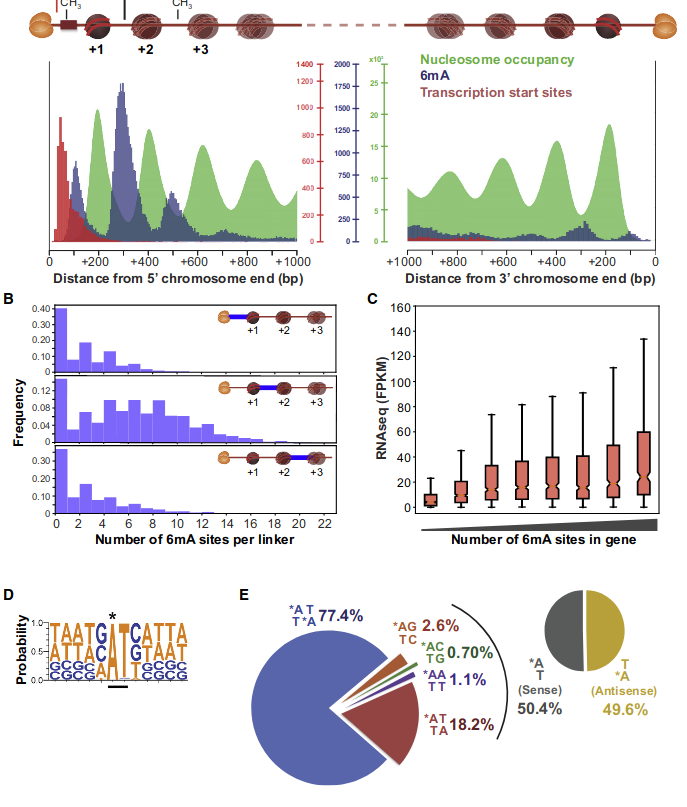
Laura landwebehr 2020
Oxytrichia trifallax


A outAT score 20 isQv20 (812 seq)
A outAT score20 idQv20 + Strong BH correction (176 seq)
PhD defense (short)
By biocompibens
PhD defense (short)
28/02/19
- 110



