Role of DNA methylation in the genomic rearrangements in P. tetraurelia




PhD Defense
DELEVOYE Guillaume
09/06/2022
Supervisor : Dr MEYER Eric
Jury members : Dr DUHARCOURT Sandra, Dr CHEN Chunlong, Dr DURET Laurent
Introduction
Part 1 : Transposable Elements (TEs)
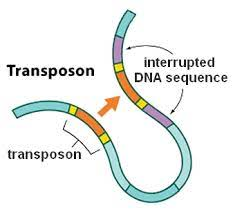
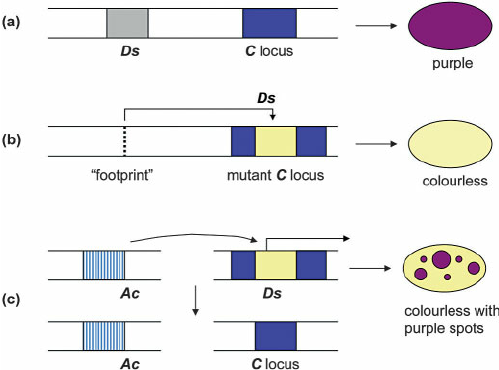
1948 : Jumping genes

Barbara McClintock discovers the As/Dc elements in maize

Nobel prize (1983)
Ds jumps in presence of Ac (non-autonomous)
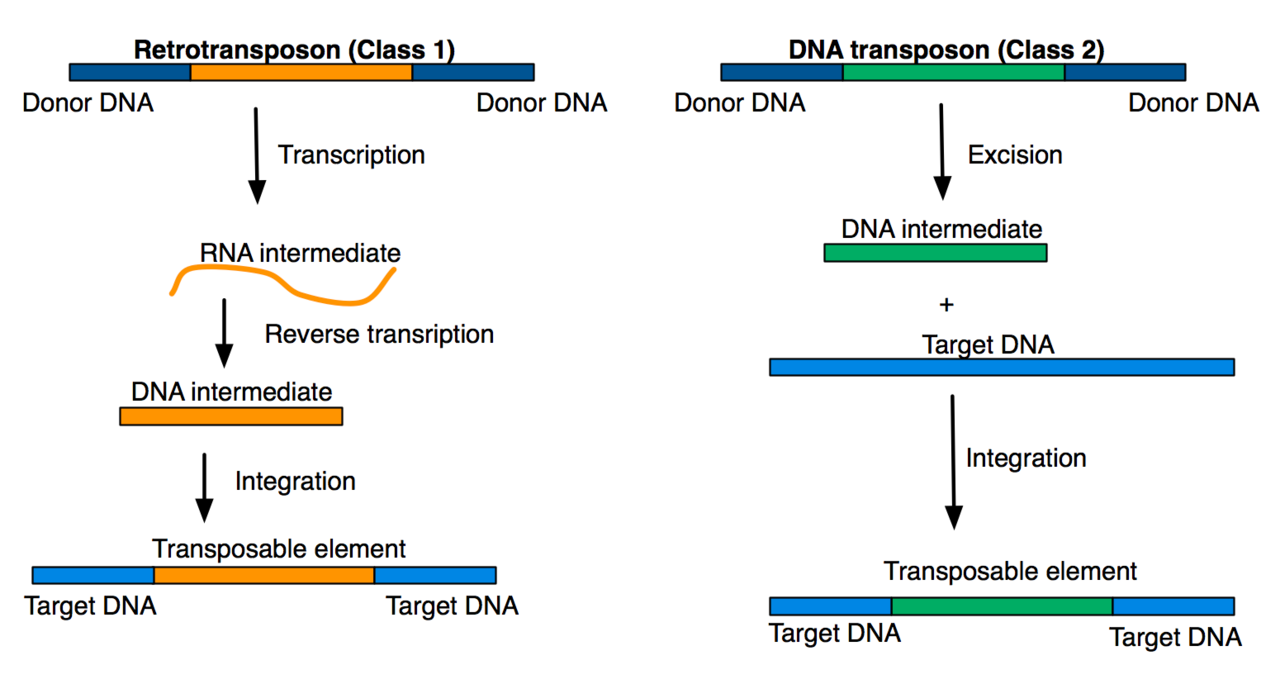
Historical classification
(Finnegan)
"Copy paste" versus "Cut and paste"
Historical understanding
Junk/Selfish DNA
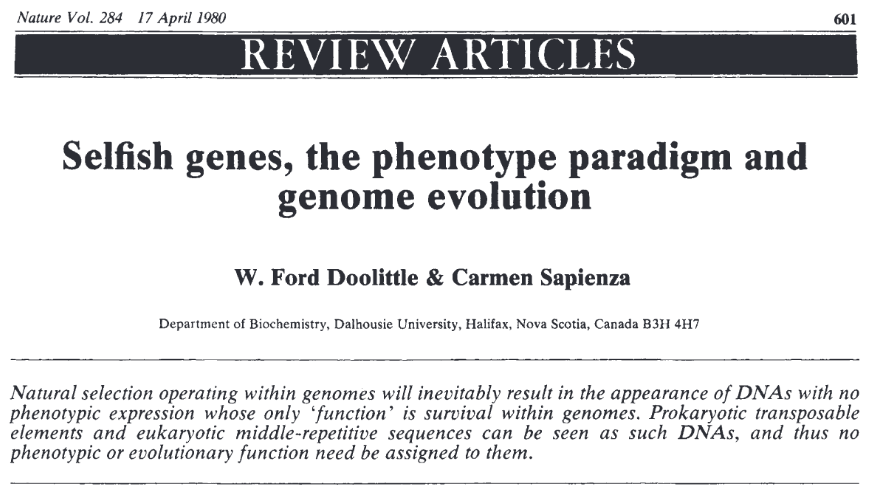

TEs were first considered as :
-
"Selfish DNA"
- They do not perform any "function" for their host
-
Neutral or mildly deleterious
- That is, evolutionary burdens
TEs are conserved not because they provide an additional fitness to their host, but despite the fact that they don't. This is the non-phenotypic selection.
Doolittle, Orgel, Crick and Sapienza (1980)
The same day in Nature journal
Modern taxonomy
Wicker et al. 2007
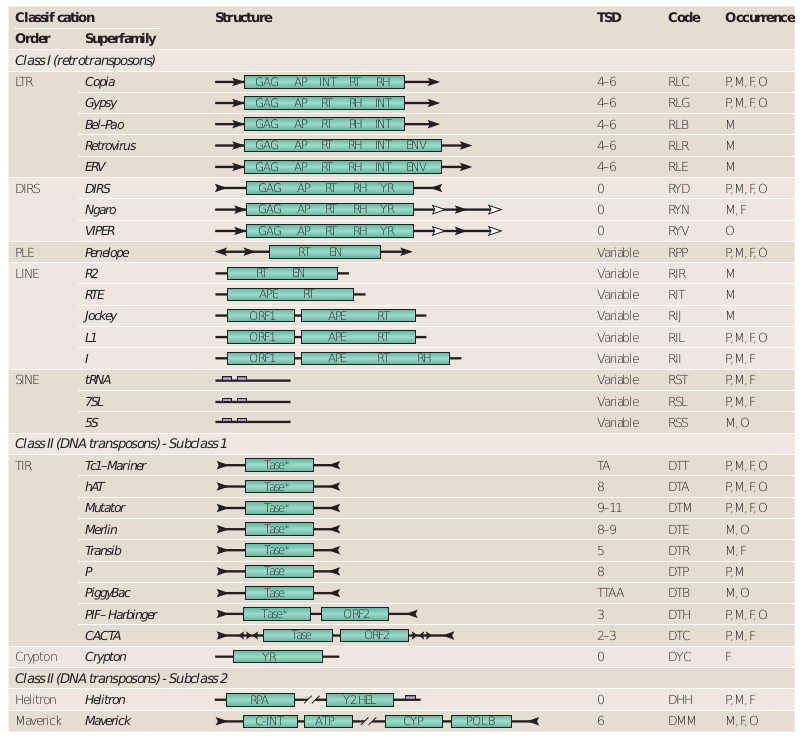
- 3 classes
- 9 orders
- 29 superfamilies
Based on:
- Mechanistic / Enzymatic criteria
- Structural data
The cut-paste versus copy-paste comparison turned out to less relevant over time
TEs are ubiquitous
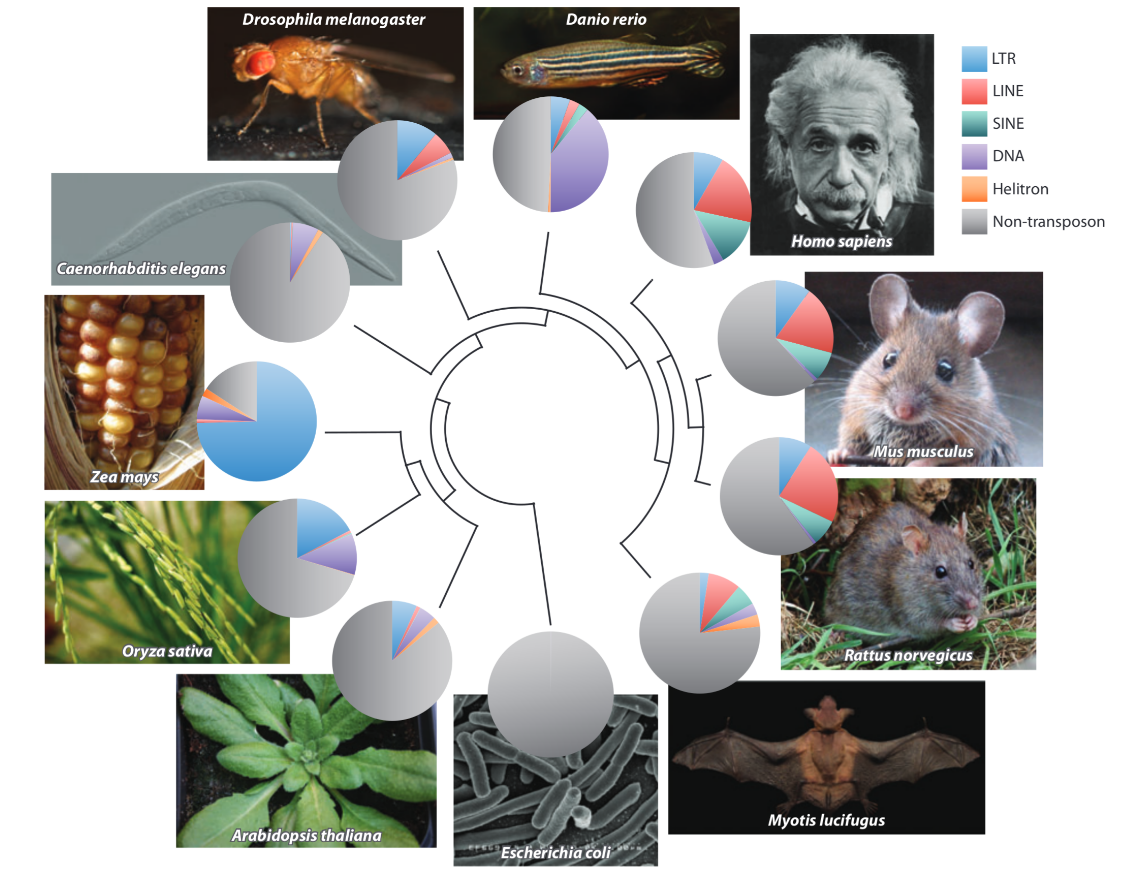
Modern understanding
- TEs Generate selection :
- Purifying: growth rate = Genome-wide invasion
- Adaptative: Exon shuffling, transcription regulation ++,
exaptation (e.g Rag1 & Rag2 in mammals), etc.
- Are transferred vertically (++) and horizontally (HTT)
- Several thousands known HTT
- P-element invaded Drosophilia worldwide in less than 100 years !
- Are present in all cellular organisms
- Probably exist since the ~ begining of the cellular life
The paradigm is currently shifting from "Junk DNA" to "Major actors of evolution".
$$\sim2^N$$

Regulation mechanisms

> Any particulary vulnerable organisms has been wiped out in the past
> Logical conclusion : All remaining life forms have some kind of resilience towards TEs.
> All virulent TEs have wiped out their host (and disappeared with them)
Many epigenetic regulations exist :
- 5-methylcytosine (5mC) silences TEs in H. Sapiens
- 6mA in Drosophila
- piRNA in animals
- 5mC and H1 Histone methylation in Arabidopsis
- ...
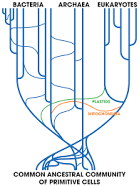
P. tetraurelia has an original way of dealing with TEs
Introduction
Part 2 : P. tetraurelia


Studying ciliates
A 350 years old story



A. van Leeuwonhoek (1668)
"Animalcules"
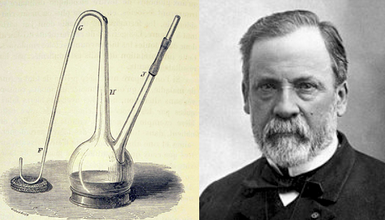
Pasteur (1862)
Spontaneous generation
HS Jennings (~ 1900)
Paramecium as a model
T. Sonneborn (1937)
Non-mendelian inheritance
of sexual type
in Paramecium

Carol Greider &
Elizabeth Blackburn
Telomeres (1985) - Nobel prize

Meyer and Duharcourt (2014)
Sexual type is inherited via maternal RNAs, in Paramecium
There is more...
-
First known organisms that do not use the "universal" genetic code
- Paramecium (Caron and Meyer 1985)
- Tetrahymena (Preer et al. 1985)
-
Histone Acetlyases (HAT)
- Tetrahymena (Brownell et al. 1996)
-
Self-splicing introns (ribozymes)
- Tetrahymena
- Tubulin post-translational modifications
> The genome-wide programmed rearrangements <
P. tetraurelia: Nuclear dimorphism
Unicellular eucaryote with 3 nuclei:
-
2xMIC nuclei (2n)
- Germline nucleus
- Contains: TEs + 49.260 Internal Excised Sequences (IES)
- No transcription outside meiosis
-
1xMAC nucleus (up to 800n)
- Somatic nucleus
- Amplified version of the MIC
- Free from TEs and IESs
- Transcriptionnally active
- Rebuilt from a MIC after each sexual process, under the control of the maternal MAC (hence frequent non-mendelian inheritance)
DNA ratio: 1 MIC for 200 MAC
Programmed rearrangements
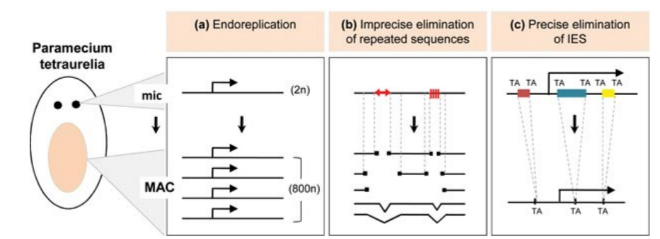
A new MAC is formed from a MIC, with important genome re-arrangements
Results in a MAC DNA almost purely made of coding sequences
Coyne et al. 2012
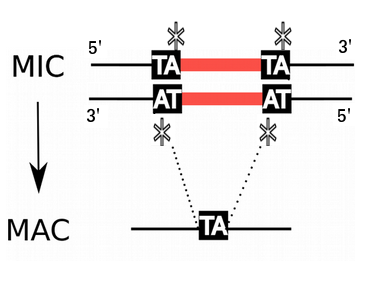
Profiling IESs (1/2)
- Non-coding
- Excised after sexual processes with a single-nucleotide precision
-
Relationship with TEs :
- IESs = Degenerated remnants of Tc1/Mariner elements
- Excised by a domesticated PiggyBac transposase (Pgm)
- Most recent IES are very short (< 27bp), and are the majority of IESs
49.260 unique sequences
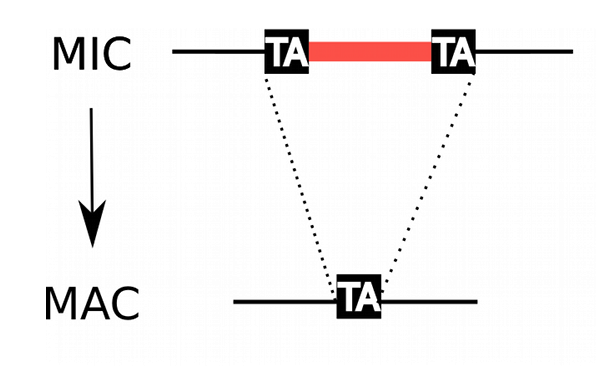
O. Arnaiz et al 2012

PiggyMac (Pgm)
Profiling IESs (2/2)
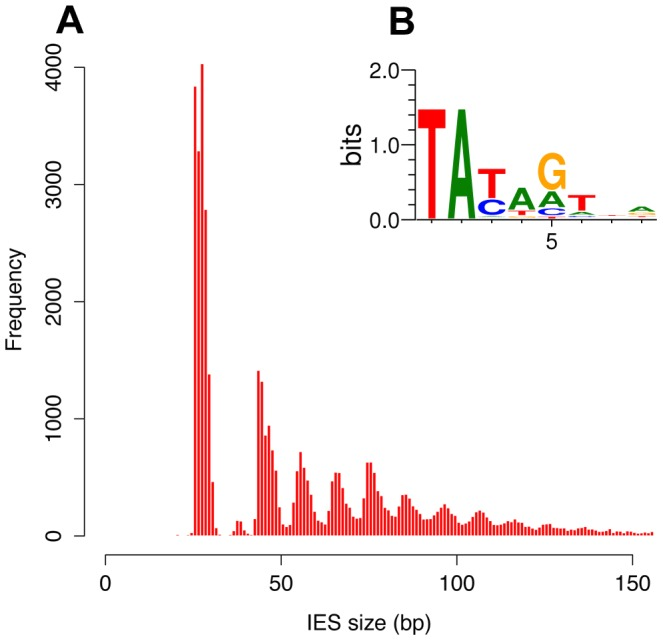
- 100% TA-Bounded
-
Weak consensus TAYAG
- Degenerated TC1-Mariner TE insertion site
- Periodic size distribution
O. Arnaiz et al. 2012
This is not sufficient for the cell to distinguish IESs from the rest of the genome
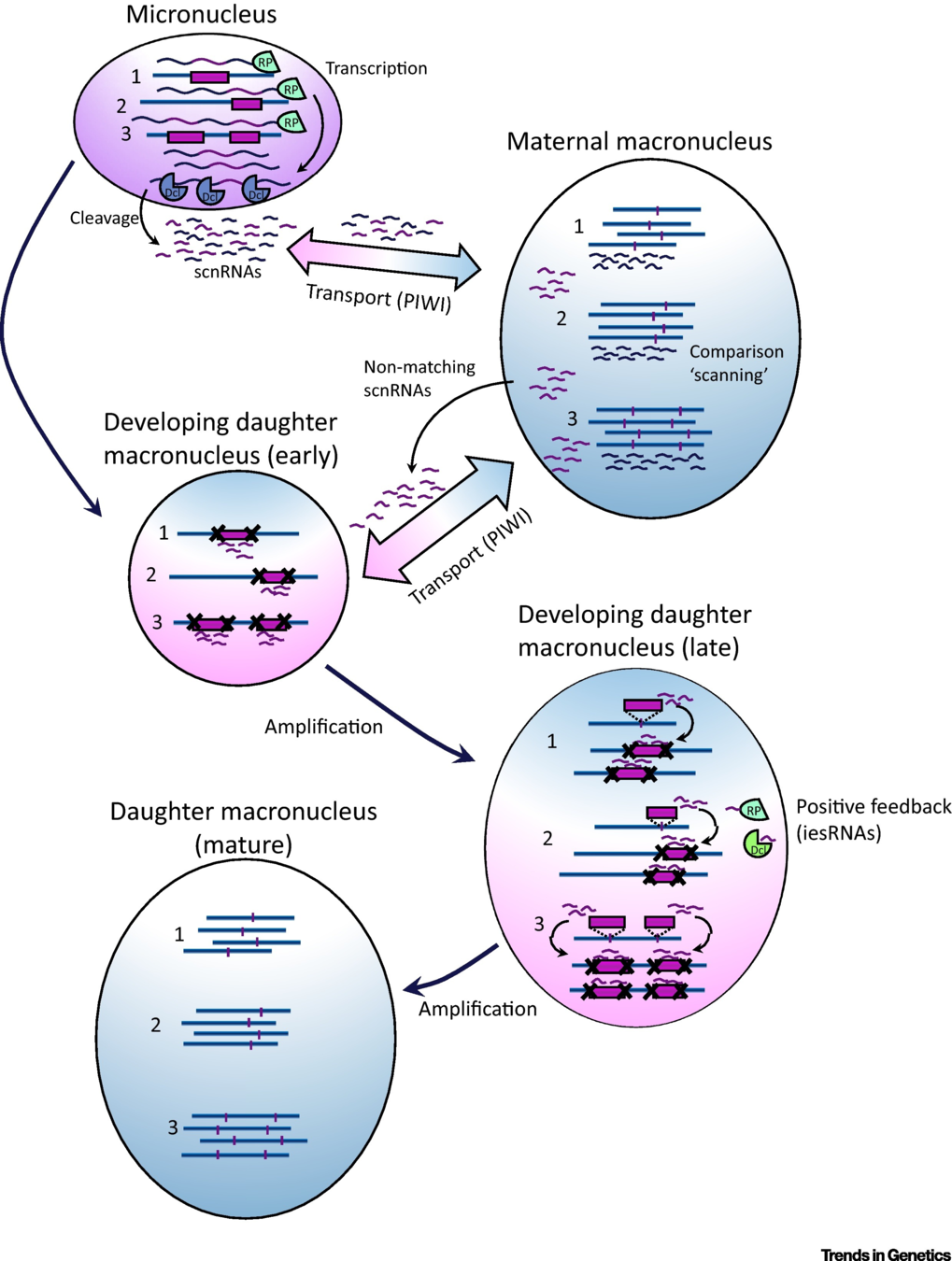
IES recognition: sc-RNA pathway
E. Allen and M. Nowacki - 2017
Problematic
Problematic in a nutshell
-
~30% of IESs only are small-ncRNA dependant
- What about the majority remaining ?
-
How does the cell recognize IESs ?
- Especially, the scnRNA independent ones
- ~ Self VS non-self recognition
- MIC/MAC ploidy ratio = Challenge +++
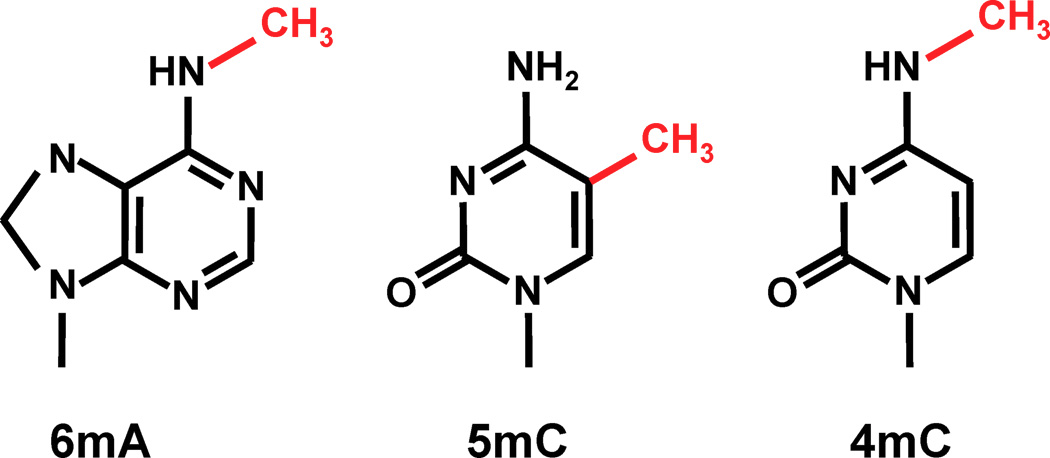
The DNA methylation hypothesis
6mA abundant in Paramecium:
-
2.5% in the MAC and MIC of P. aurelia (Cummings et al. 1975)
- Detection by SMRT in the MAC (Hardy et al.)
- Detection in Oxytrichia by L. Landweber et al. (2019)
- no 5mC, 4mC in the MAC a priori


2) In the new forming MAC
1) Constant pattern in the MIC
Transcient ?
The DNA methylation hypothesis


And many other possibilities...
Methylase candidates

- In 2015, DAMT-1 in C. elegans (6mA) - Preer et al.
-
MTA-70 domain of DAMT-1 identified in P. tetraurelia too
- Silenced by RNA interference (Grouped by homology)
- Sometimes, reduction of 6mA (southwestern blot)
| Silencing | Objective | Target of interest | Location of interest |
| None | WT methylation (MIC and MAC) | 6mA + ? | MIC and MAC |
| Control gene | Control | 6mA + ? | MIC and MAC |
| None | Pattern right before the excision ? | 6mA + ? | new forming MAC |
| None | Pattern right before the excision ? | 6mA + ? | new forming MAC |
| NM4 | Bulk of 6mA | 6mA | MAC ++ |
| NM9 + NM10 | Bulk of 6mA | 6mA | MAC ++ |
| NM4 + NM9 + NM10 | Bulk of 6mA | 6mA | MAC ++ |
| MT1A | Permanent pattern erased ? | ? | MIC |
| MT1A + MT1B | Permanent pattern erased ? | ? | MIC |
| MT1A + MT1B + MT2 | Permanent pattern erased ? | ? | MIC |
> Sequenced with PacBio SMSN sequencing
Objectives and overview
-
Code the analysis pipeline
- Benchmark it (E. coli)
-
Sort what comes physically from the MAC and MIC
- Take acount of IES retention
- Re-estimation of the MAC ploidy ~ O(1600n)
-
Analyze the DNA modifications in the MAC
- Statistical pitfall when studying hemi-methylation
- Analyze the DNA modifications in the MIC
- Conclude on the role of our methylase candidates
- Conclude on the role of DNA methylation in the recognition of the small-ncRNA independent IESs
Methods vs Application
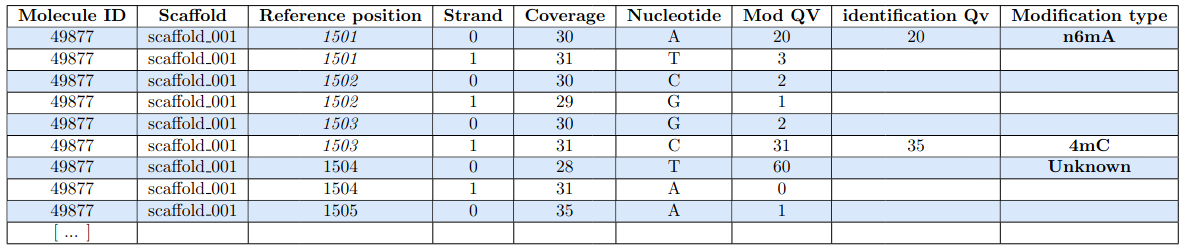

Methodological results
Part I : Analysis pipeline
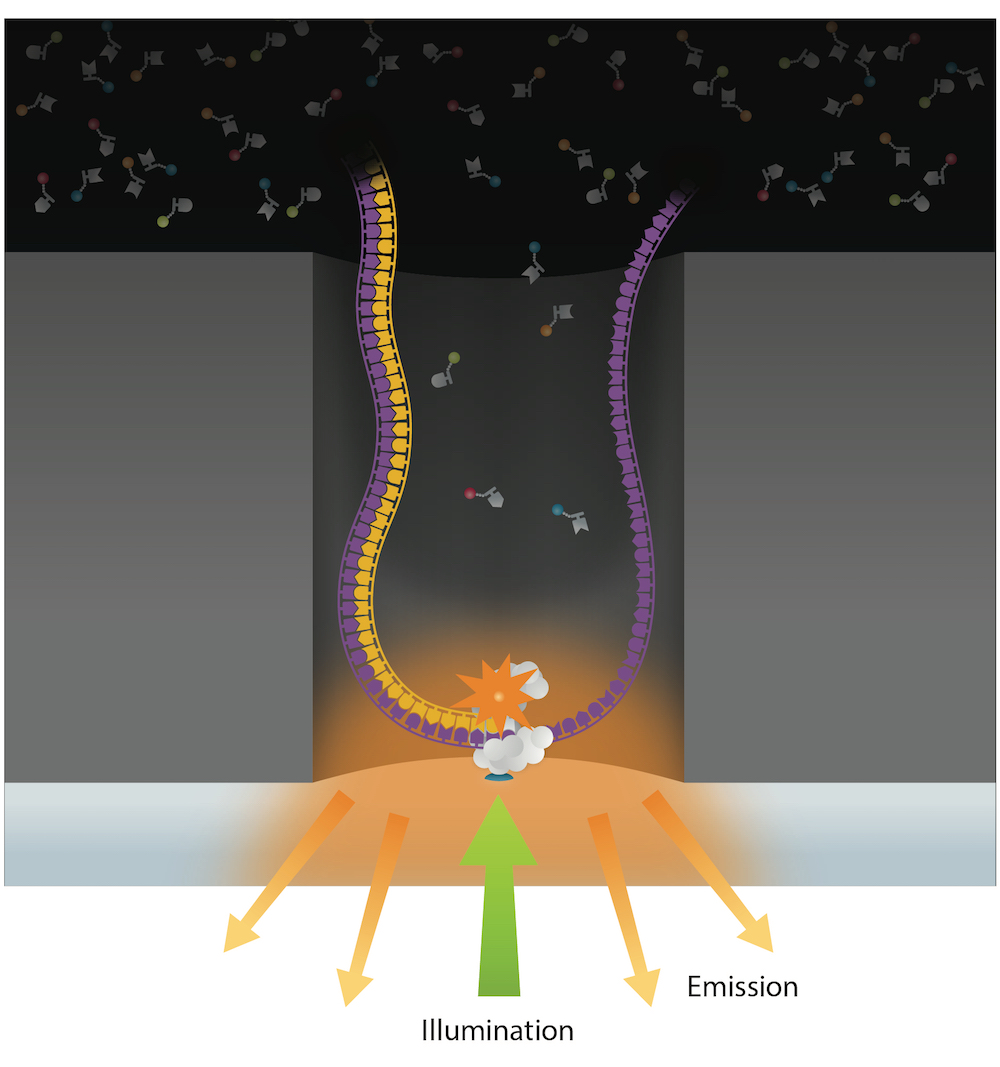
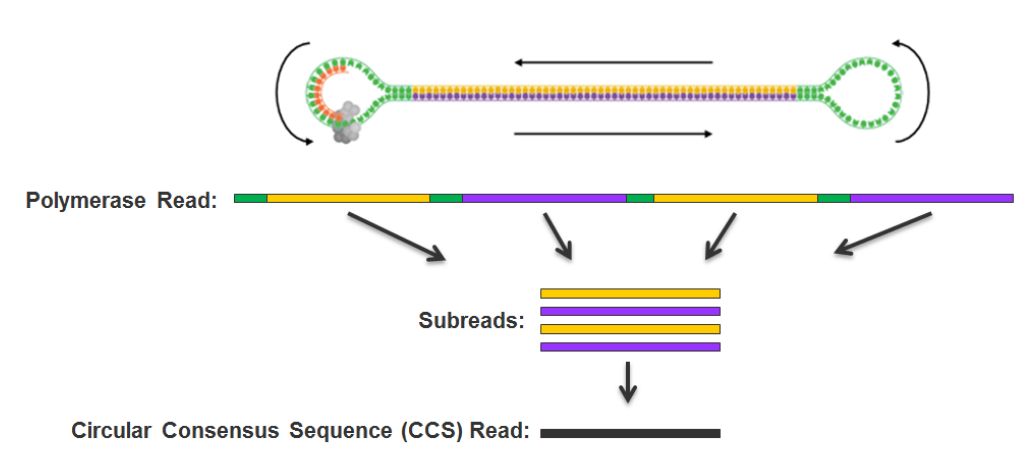
PacBio SMSN sequencing
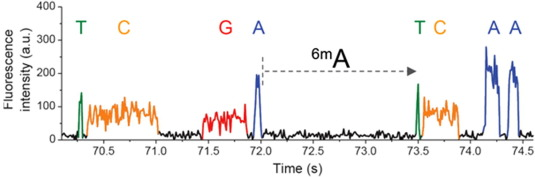
$$ipdRatio= \frac{MeanIPD_{experience}}{unmethylated\ control}$$
~ 85% accuracy
~ 100% accuracy
Slowing around modified nucleotides (~ time x100)
Global principle
PacBio SMSN sequencing
Expected output

An analysis for each nucleotide, on each strand, of each molecule (SMSN = Single-Molecule Single Nucleotide)
Possible detection : 4mC, 5mC, 6mA, "other"
SMSN-seq is like mixing milk and cereals : There are two ways of doing it
$$ipdRatio= \frac{MeanIPD_{experience}}{control}$$

A) Control = Whole Genome Amplified (WGA) DNA
- Real-world values
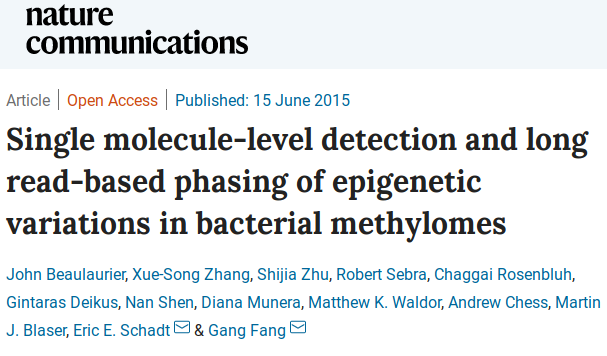
- Analysis pipeline exists (J. Beaulaurier et al. 2015)
B) Control = Machine-learning (nucleotide context)
- Invented values
- No pipeline exists






Then

First
a.k.a The best way ™

Then

First



A few months of plumbing later...
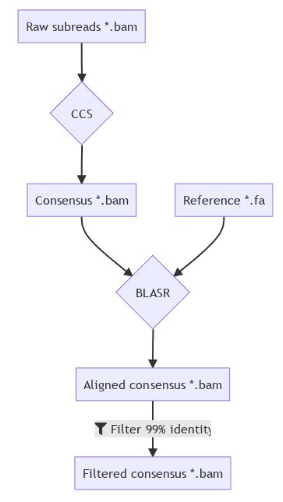
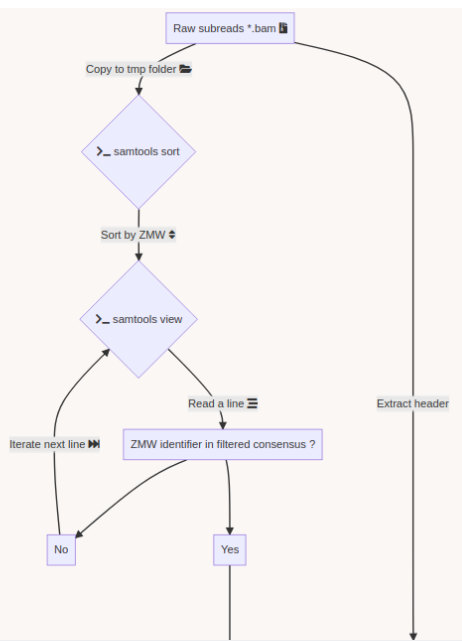

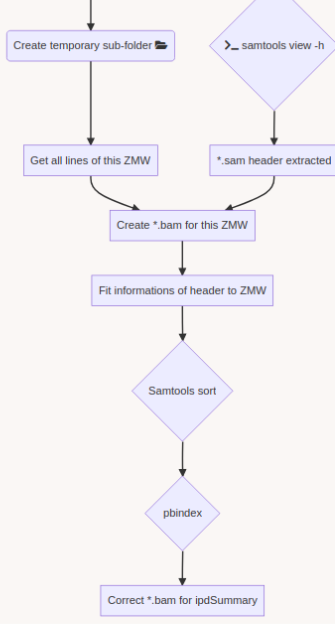
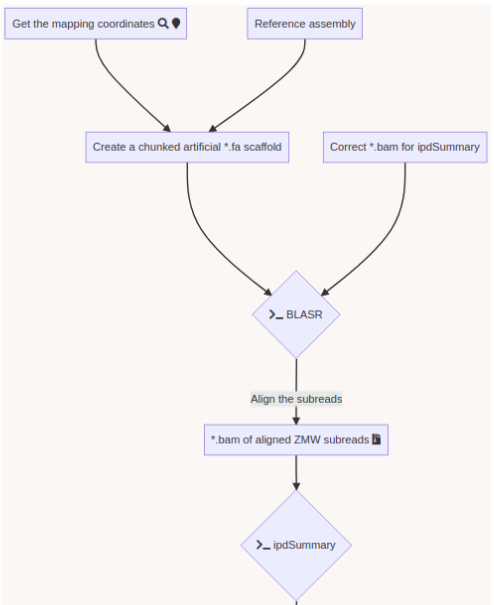








Using E. coli DNA

-
Nearly 100% 6mA (symmetrical):
- GATC +++
- EcoK
-
A few others
-
Depends a lot of the strain
-
Depends a lot of the strain
-
Nearly 0% 6mA :
- Everything else
E.coli is used to feed paramecium (contaminants)
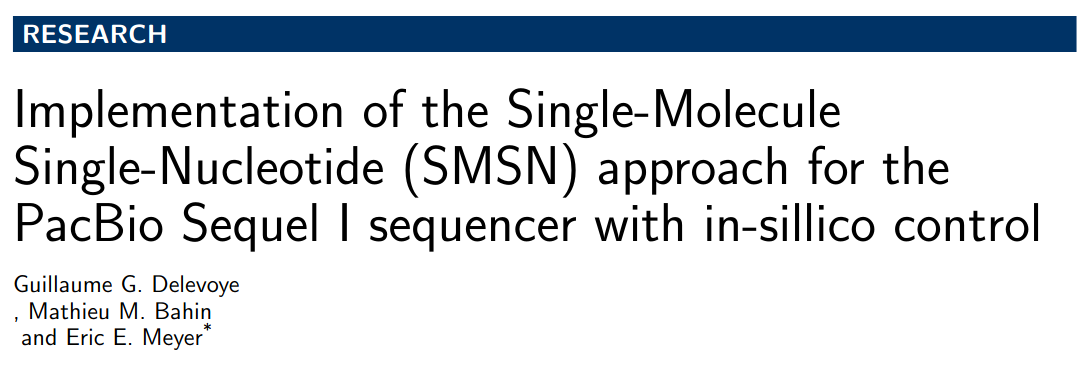
ipdRatio in E. coli (1/2)
- The nucleotides we expect to be methylated have a high ipdRatio
- Some exceptions : False negative or really not-methylated ?
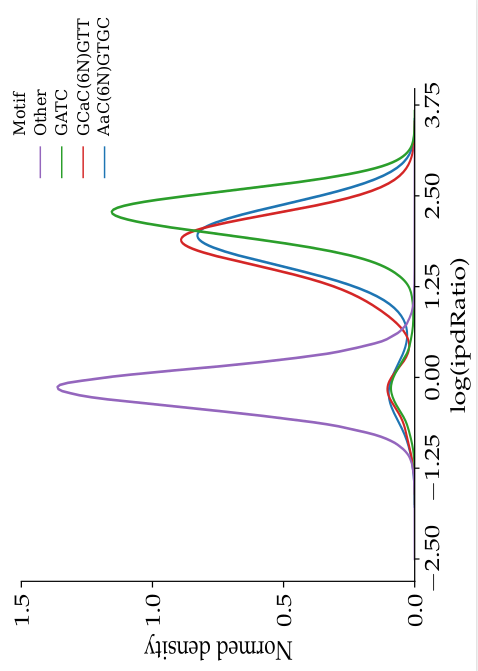
ipdRatio in E. coli (2/2)
Separability and coverage are correlated
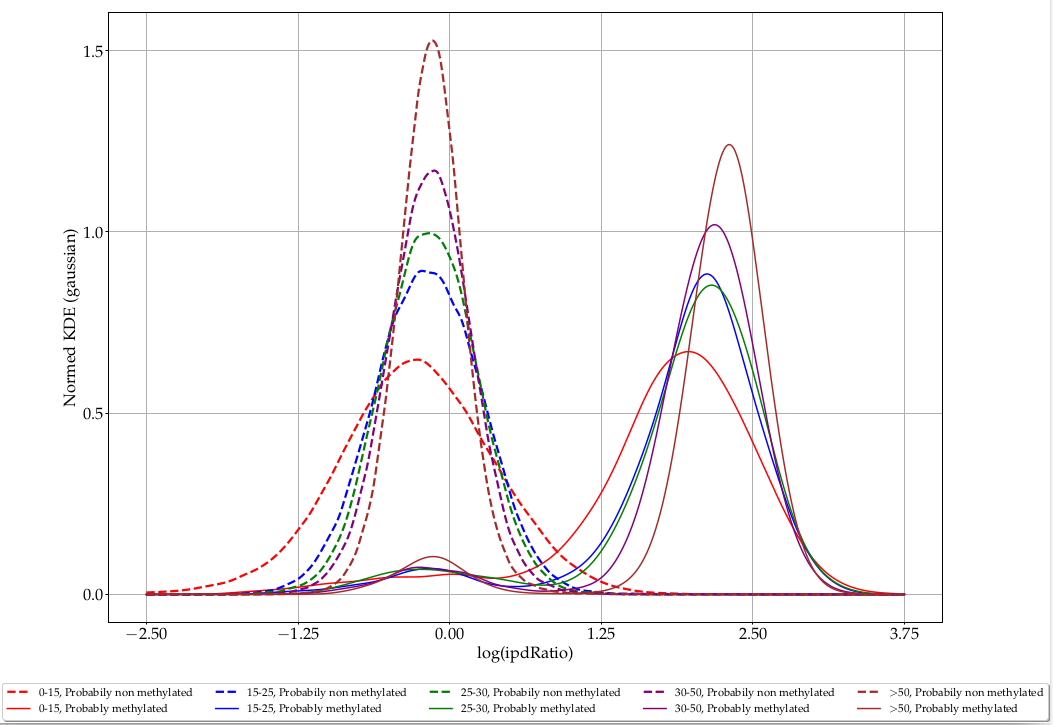
How to binarize the ipdRatio ?
Either a nucleotide is methylated, or it is not :
- We need to use a threshold on the ipdRatio to call modified nucleotides
- This threshold has to take account of the coverage effect
- No optimal solution anyway
Our pragmatical solution : An arbitrary linear threshold
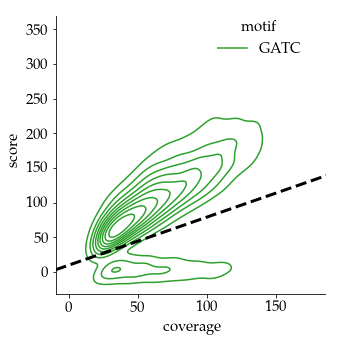
Benchmark (6mA)
- ~92% of 6mA in EcoK and GATC
- ~99.8% of non-6mA elsewhere
If we make the simplification that all GATC/EcoK sites are methylated and that 6mA is only present there :
$$Sensitivity = P(D|M)$$
$$Se = 92\%$$
But :
-
Maybe some GATC/EcoK are tuly unmethylated
- In this case, the real Se is actually better than 92%
-
Maybe there is a few amount of 6mA outside of GATC/EcoK site
- In this case, the real Sp is actually better than 99.8%
- Se = 92% and Sp = 99.8% are worst case estimates
$$Specificity = P(\overline{D}|\overline{M})$$
$$Sp = 99.8\%$$
Benchmark
(other modifications)
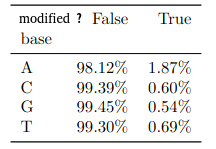
PacBio sequencing was already known for its propensity to generate false positives for 4mC (K. O’Brown et al. 2014)
- It is very likely that most of these detections are false positives
Objectives and overview
-
Code the analysis pipeline
- Benchmark it (E. coli)
-
Sort what comes physically from the MAC and MIC
- Take acount of IES retention
- Re-estimation of the MAC ploidy ~ O(1600n)
-
Analyze the DNA modifications in the MAC
- An important statistical pitfall when studying hemi-methylation
- Analyze the DNA modifications in the MIC
- Conclude on the role of our methylase candidates
- Conclude on the role of DNA methylation in the recognition of the small-ncRNA independent IESs
Methods vs Application



Methodological results
Part II : Sorting + IES retention
The random sampling strategy
IES
Other MIC
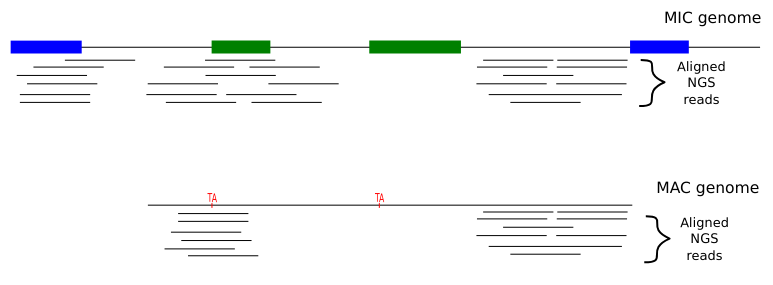
Other MIC
IES
Mac Destinated Sequences (MDS)
MAC
TA Junction
-
We work on total DNA :
- ~ 1 molecule out of 200 comes from the MIC
- Sometimes the physical origin of the molecule can be guessed
- MIC regions that are far from the IESs and the MIC-specific sequences cannot be studied
Expected number of IES+ sequences
-
1 molecule out of 200 comes from the MIC
- A bit less due to contaminants
- ~ 1/6 of MIC inserts will carry an IES
-
# of PacBio consensus (CCS) per sample :
- > 150.000 (multiplexed)
- ~ 350.000 PacBio CCS (not multiplexed)
That is, ~100 to 300 IES+ sequences per experiment
- We got 49 to 310
- If our hypothesis is true, 100% of them are methylated
Orders of magnitude :
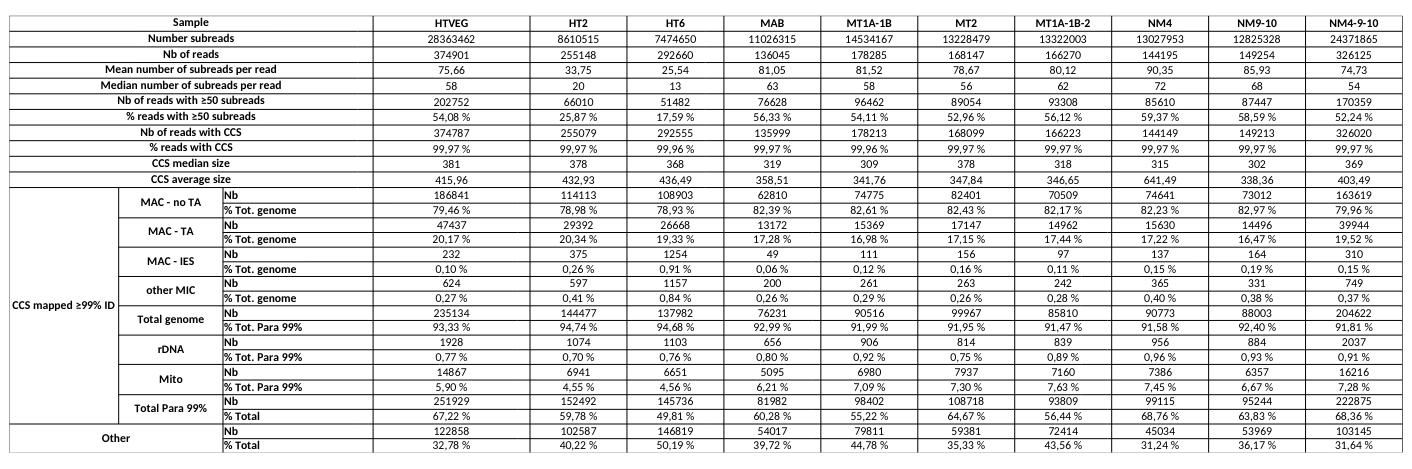
IES retention
Methodological results
Part III : The MAC ploidy
Is the MAC ploidy 800n ?
MAC ploidy
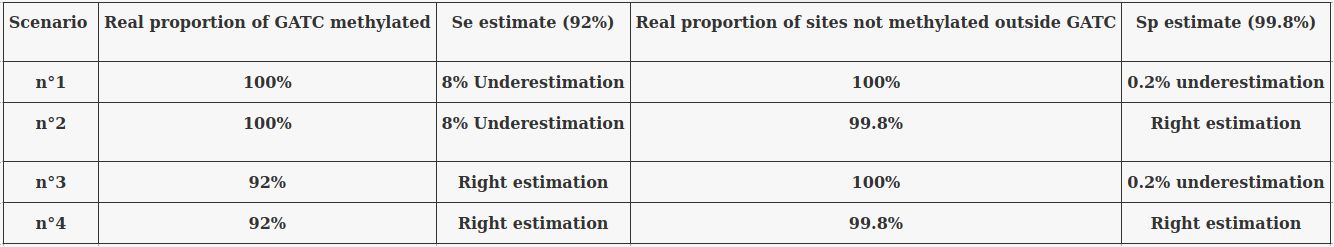
The 4 scenarii for Se and Sp
- We don't care about Se and Sp
- We care about the fact that eventual mis-estimations of them doesn't really change anything
Finding unbiased estimators for and FDR
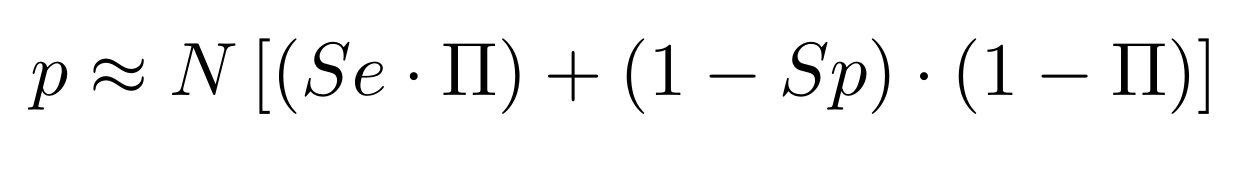
If p number of positive detections among N tests:
p = FP + TP
$$\pi$$
So,
Which means
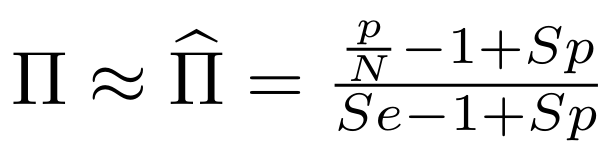
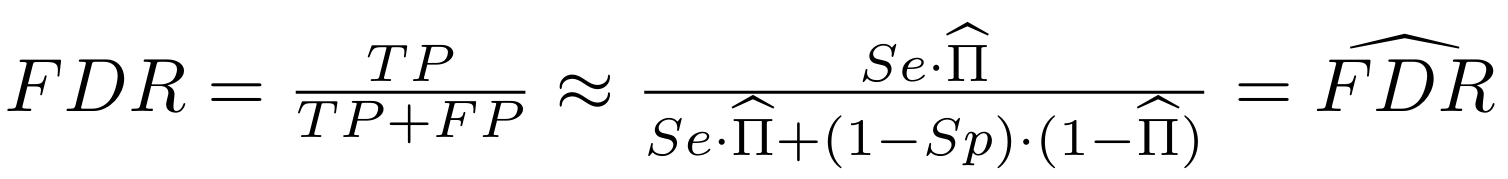
And:
What it gives in Paramecium
Methodological development to correct hemi-methylation detection (1/2)
Let FD1 and FD2 be resp:
- Fraction of hemi-methylated AT sites
-
Fraction of sym-methylated AT sites
PZ0, PZ1, PZ2: unbiased estimators of non, hémi, symetrically methylated AT sites
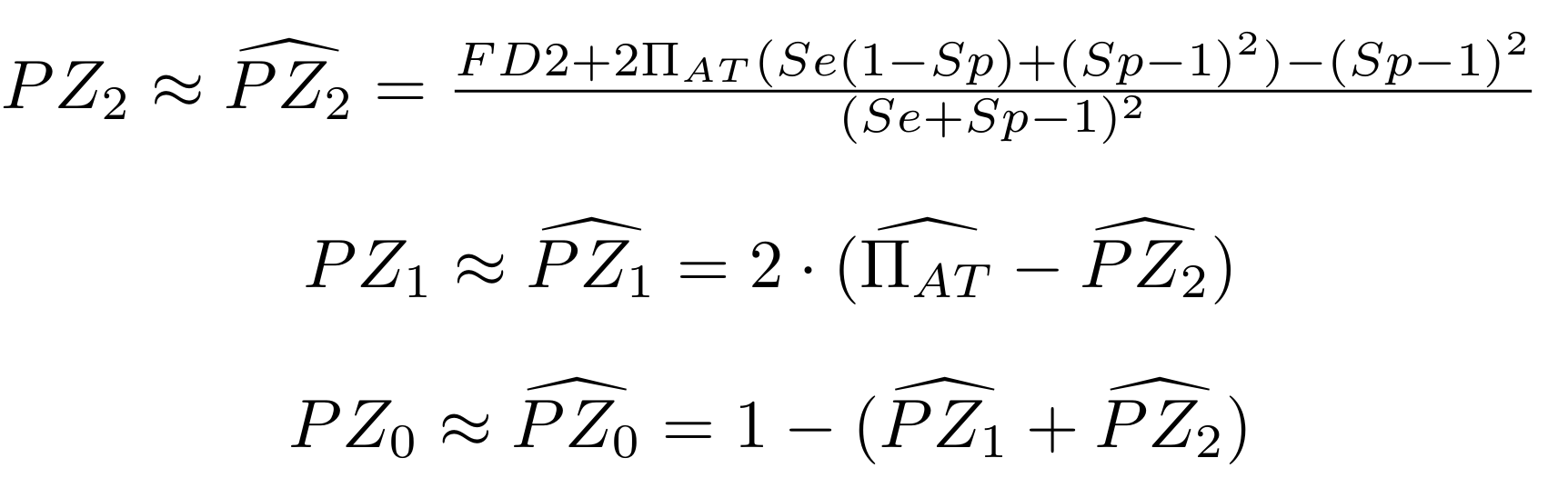
Then:
With
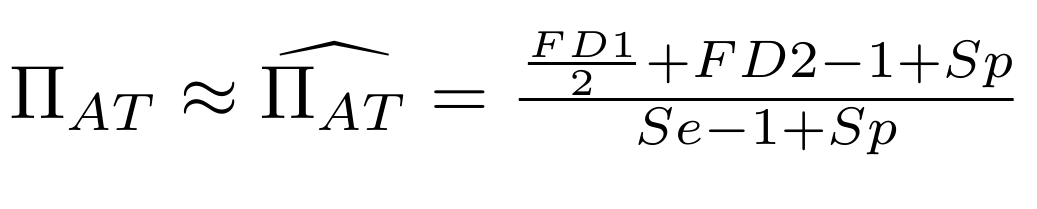
Methodological development to correct hemi-methylation detection (2/2)
We can also find the number of hemi-methylated sites being detected as such, and the proportion of sites detected as hemi-methylated that are really hemi-methylated. This is possible because we now approximately know PZ0, PZ1 and PZ2, and P(D|Z) is easy to determine:

Then, P(Z|D) can be determined through Bayes theorem using P(D|Z), P(Z) and P(D) (which are all known)
P(Z=1|D=1)
is our case of interest
What it gives in Paramecium

2.1 Retroingineering
The capping of IPDs
-
modelPrediction is the predicted IPD value by the model in a given context of nucleotides at this position
-
globalIPD is the mean of all the IPD values of the read.
-
localIPD represents all IPDs that have been mapped at a given position in the genome, including those from other sequences
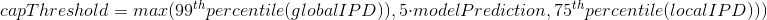
Conclusion on the capping
- Isn't coded as advertized by PacBio
- The way it's implemented for AggSN is problematic and doesn't really make sense
- Paradoxally, it should be more relevant for our approach than for the default one
- We expect no methylation to be undetected due to the capping
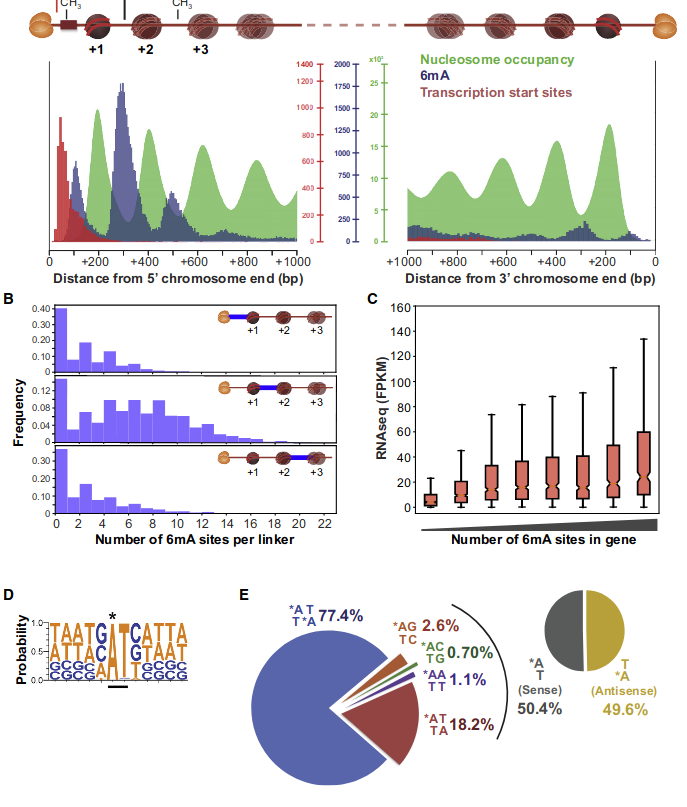
Laura landwebehr 2020
Oxytrichia trifallax


A outAT score 20 isQv20 (812 seq)
A outAT score20 idQv20 + Strong BH correction (176 seq)
PhD defense (long)
By biocompibens
PhD defense (long)
28/02/19
- 104



