Role of DNA methylation in the genomic rearrangements in P. tetraurelia




PhD Defense
DELEVOYE Guillaume
09/06/2022
Supervisor : Dr MEYER Eric
Jury members : Dr DUHARCOURT Sandra, Dr CHEN Chunlong, Dr DURET Laurent
Introduction
P. tetraurelia
P. tetraurelia: Nuclear dimorphism
Unicellular eucaryote (ciliate) with 3 nuclei:
-
2xMICronuclei (2n)
- Germline nucleus
- Contains: Transposons + 49.260 Internal Excised Sequences (IES)
- No transcription outside of meiosis
DNA ratio: 1 MIC for 200 MAC
-
1xMACronucleus (800n)
- Somatic nucleus
-
Derived from the MIC genome
- Amplified
- Free from TEs and IESs
- Transcriptionnally active
- Rebuilt after each sexual process
Programmed rearrangements
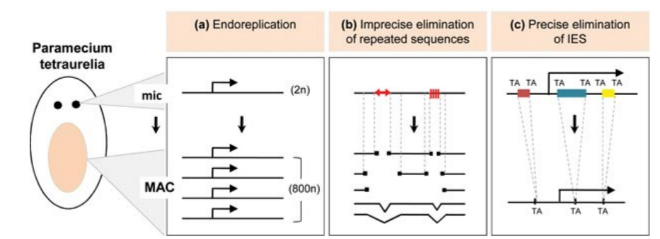
After sexual processes, a new MAC is formed, with important genome re-arrangements
Results in a MAC DNA almost purely made of coding sequences
Coyne et al. 2012
Profiling IESs (1/2)
- Non-coding
- Remnants of Tc1/Mariner ?
-
All excised by Pgm
- Excised with a single-nucleotide precision
- Life or death issue : Genes interrupted
-
IES excision was exapted many times
- e.g The mating-type !
- Size shrinks with age, most IESs are very short (26-150bp)
49.260 unique sequences
O. Arnaiz et al 2012
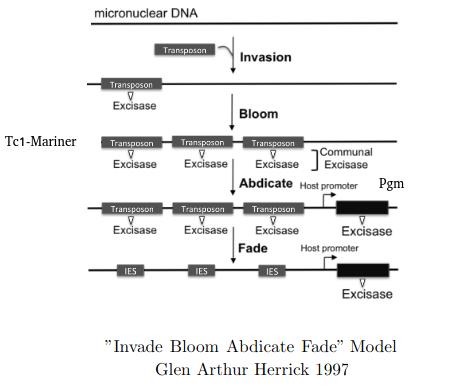
"Invade Bloom Abdicate Fade" model
Adapted from Glen Arthur Herrick 1997
Excision = 100% PiggyMac (Pgm)
Profiling IESs (2/2)
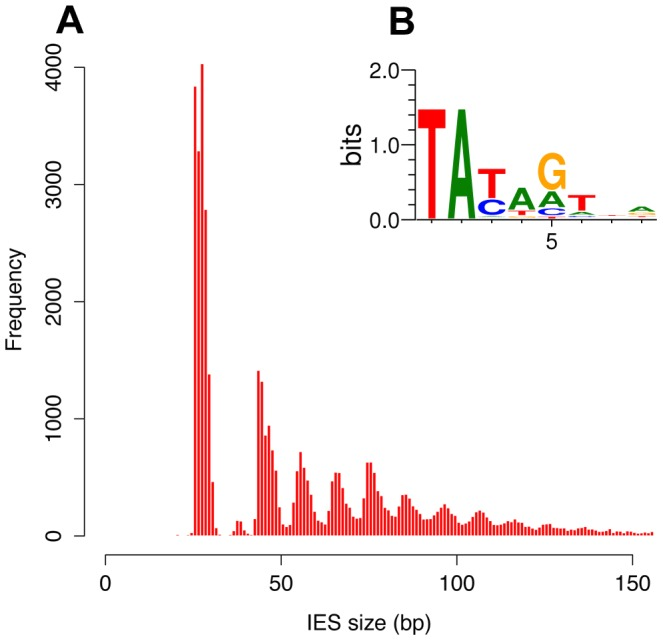
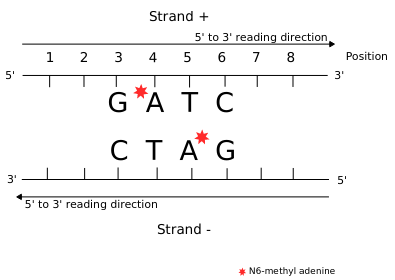
- 100% TA-Bounded
-
Weak consensus TAYAG
-
~ Tc1/Mariner
-
~ Tc1/Mariner
- Periodic size distribution ~10bp
O. Arnaiz et al. 2012
Not sufficient to distinguish IESs from the rest of the genome
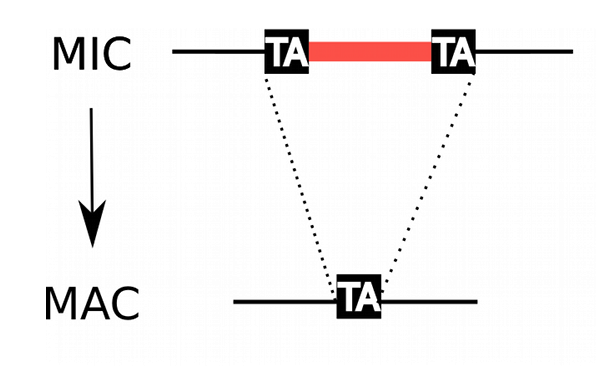
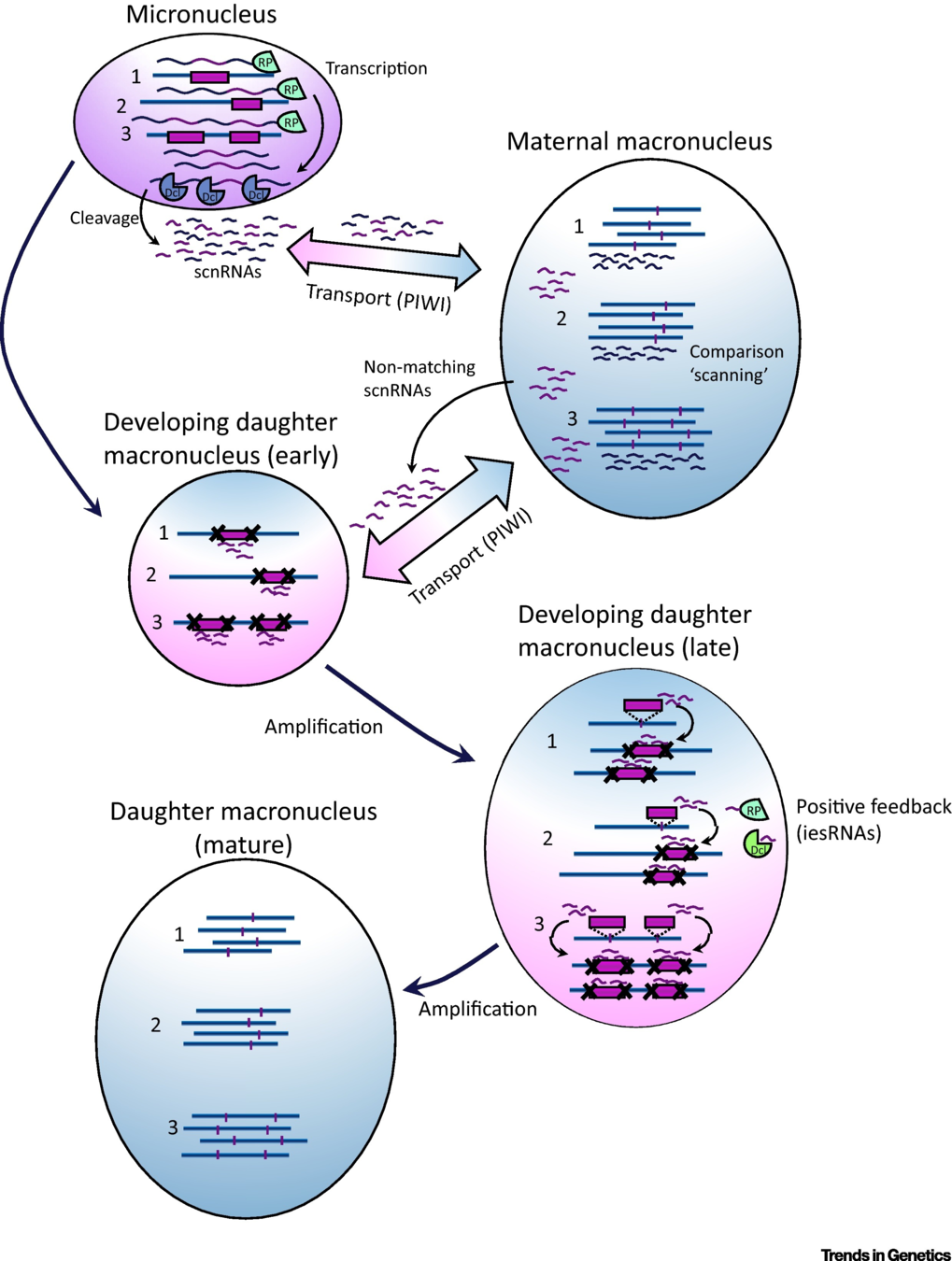
IES recognition: scnRNA pathway
S. E. Allen and M. Nowacki - 2017
If not in the maternal MAC : Recognized and excised
Problematic
Problematic
Inactivation of scnRNA and iesRNA pathways:
- ~30% of IESs are retained
- Their retention is not even complete
- Oldest = More independent to small RNAs
- IES features = insufficient to explain the recognition
All IESs may be recognized through the small RNAs
... but is there a redundant system for the oldest/shortest ones ?
Problematic ~ Self VS non-self recognition
Hypothesis : Role of DNA modifications

Two possible roles of DNA methylation
DNA modifications could play a role :
- In the recognition of IESs +++
- i.e : It is permanently present in the MIC
- In their excision
-
i.e : It is transiently present in the new forming MAC, right when the IESs are excised.
- ~ Actor of the scnRNA pathway
-
i.e : It is transiently present in the new forming MAC, right when the IESs are excised.

Hypothesis


The fifth element
-
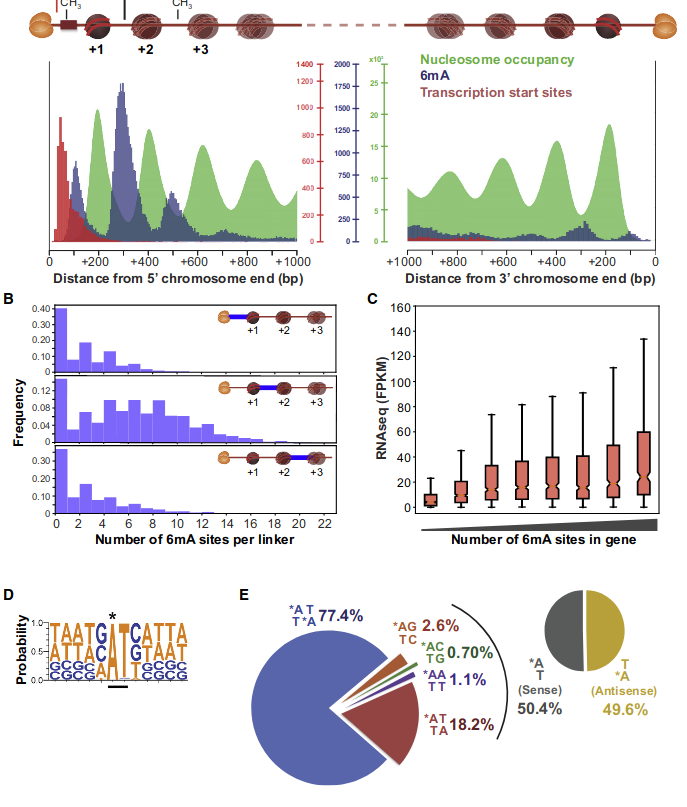
2.1-2.5% in the MAC and MIC of P. aurelia (Cummings et al. 1975)
-
Detection by SMRT in the MAC (A. Hardy et al. 2020)
- 0.8% and 1.6% of adenines
- 81.5% are located in AT sites
- Enriched downstream the Transcription Start Sites (TSS)
- In other ciliates :
- AT sites ++ and TSS ++ :
- Oxytricha by L. Landweber et al. (2019)
- Tetrahymena (No 6mA in MIC)
- AT sites ++ and TSS ++ :

... Could be N6-methyladenine (6mA)
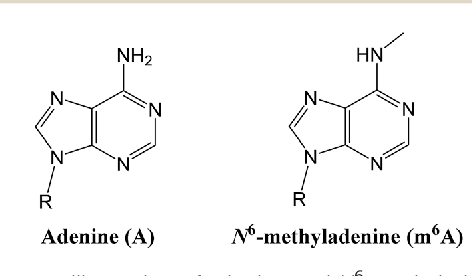
?
Other:
- 4mC ?
- No 5mC in the MAC

Police-sketch of the methylation pattern
If the pattern allows the recognition of IESs, it must allow :
- Single-nucleotide precision
- Distinction between a TA of an IES, from another TA elsewhere
- Conservation through replication
A typical example : DNMT1-Like system
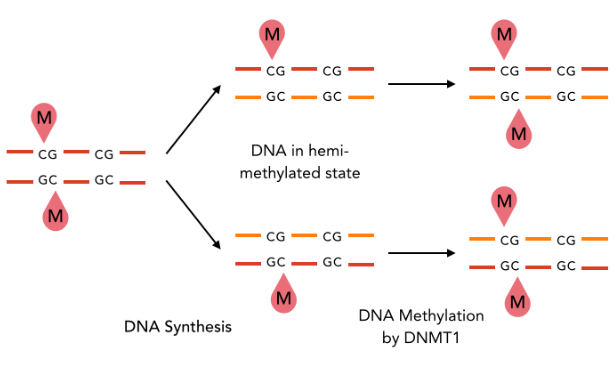
The DNA methylation hypothesis

Examples of possible patterns
And many other possibilities...

Maintenance
through replication ?

Single-nucleotide precision OK
Maintenance through replication : OK if DNMT1-Like


Single-nucleotide precision ?
Experimental approach
Long before I arrived in the lab !
Methylase candidates
-
DAMT-1 in C. elegans (6mA) Greer et al. 2015
- MTA-70 domain of DAMT-1 identified in P. tetraurelia too

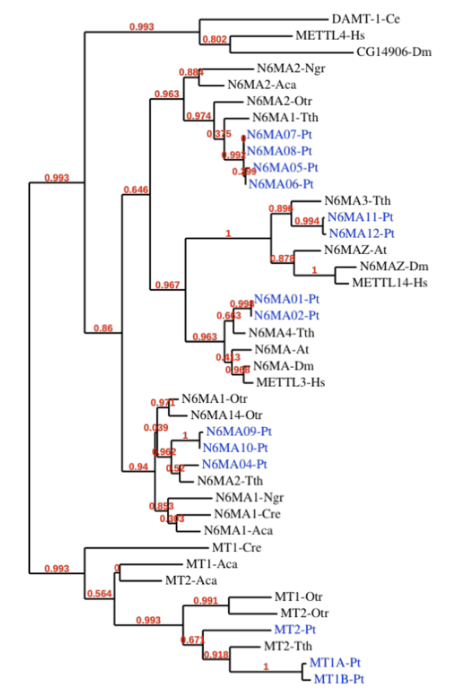
Expr. Sexual events (Collaborators)
RNA methyltransferases ?
Our 6 proteins
- NM4
- NM9
- NM10
- MT1A
- MT1B
- MT2
Sequencing strategy



WT Veg
Control
silencing
T=2h
T=6h




RNA interference






Candidate methylases
Reduction 6mA
Southwesternblot
up to 90%
Total DNA
1:200 MIC !!!
Protocol :
- Sequence vegetative and autogamous cells
- Silence the methylase candidates by RNA interference
- Sequence with PacBio SMRT sequencing
Autogamy
PacBio SMRT sequencing
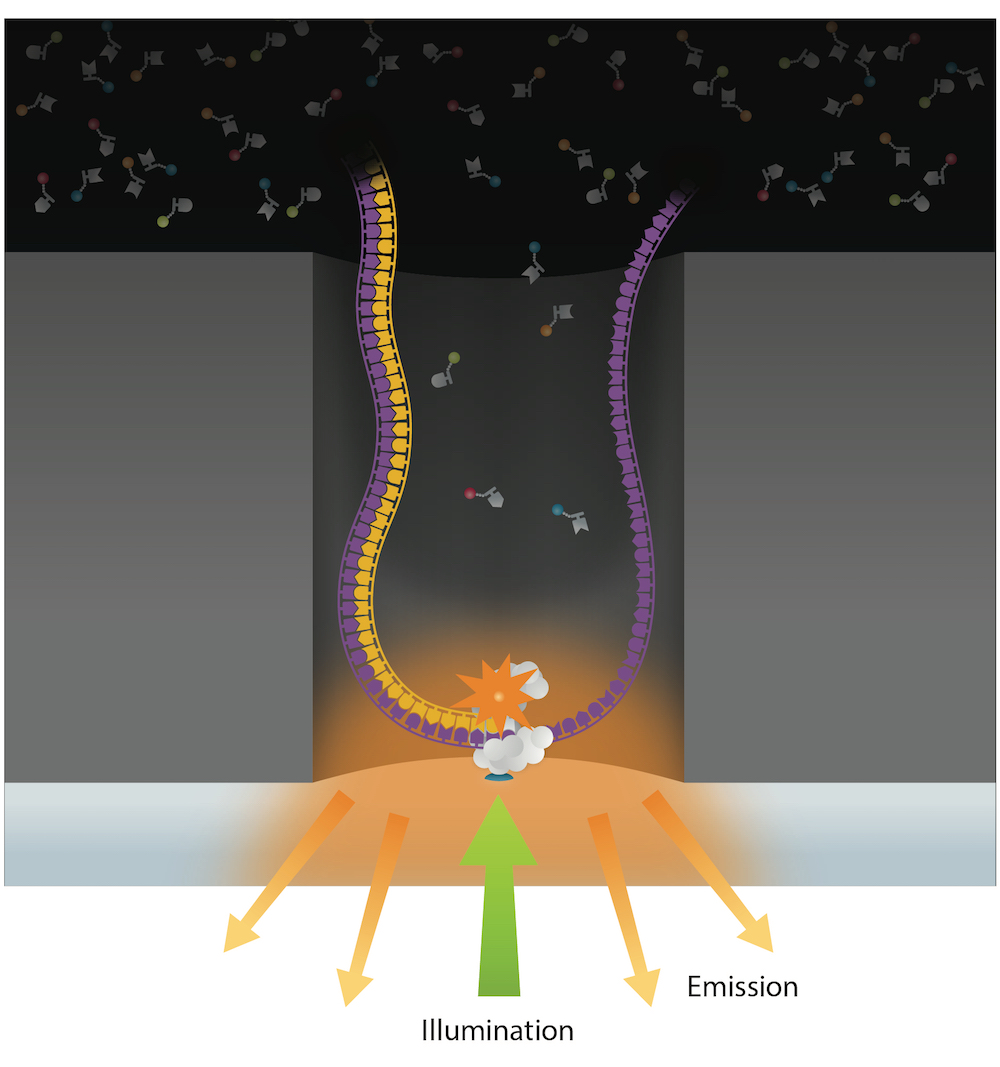
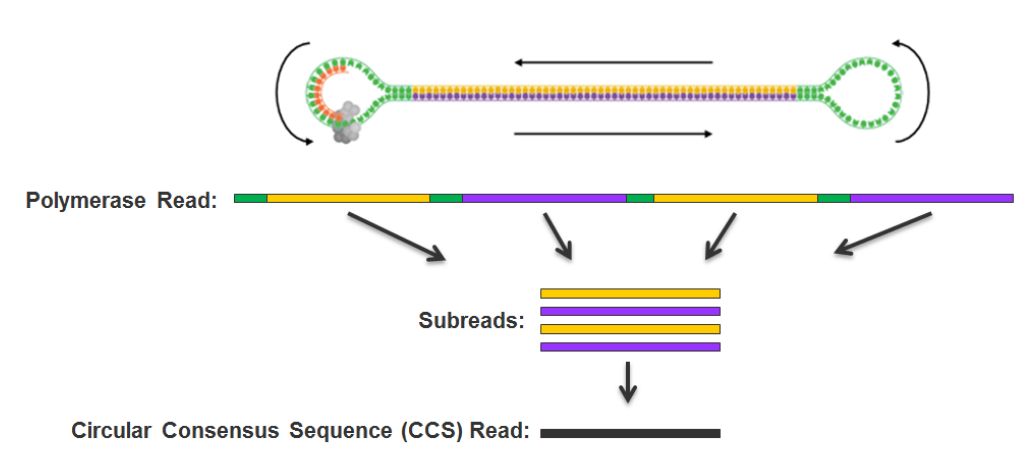
~ 85% accuracy
~ 100% accuracy
if many passes
10 – 15 kb
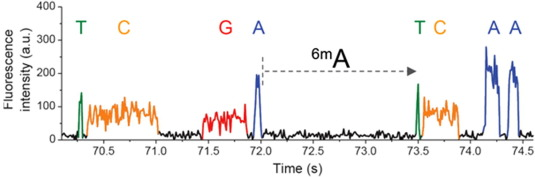
IPD
Nucleotide context (-3/+8nt)
Kinetic signatures
Depends on
DNA modifications
ipdRatio
$$ipdRatio= \frac{MeanIPD_{experience}}{unmethylated\ control}$$
(Relevant if >25 measures)

IPD
Two types of control :
- PCR
- In-silico (machine-learning)
Ideal approach
- Purify MIC DNA
-
Make libraries of long inserts from it
- Several kb
- Sequence it with PacBio SMRT
- Compare with PCR of full MIC genome
e.g

~O(20) to ~O(100) molecules
[...]
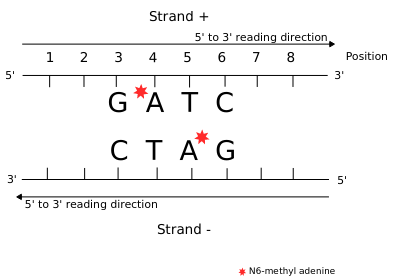
- Position n°7260 in the genome
- Strand +
- 52 molecules methylated out of 100
Problem = Purification of MIC DNA
(min. 25X)
Transcient ?
- Fish IES+ molecules in a sea of MAC molecules
- Short inserts (~350bp)
- Same molecule sequenced multiple times
Random sampling strategy

each molecule
~O(20) to ~O(100) measures
(MIC)
Workaround : work on total DNA instead
- Molécule n°49256
- Nucléotide n°7, strand + (Adénine)
- ipdRatio : 20x
But purifying the MIC is problematic
(min. 25X)

Look at methylation (only) around (some) IESs
in-silico control required
My job starts here !
NM4.bam
NM9_10.bam
MT1A_1B.bam
MT1A_1B_2.bam
MT2.bam
HTVEG.bam
MAB.bam
HT2.bam
HT6.bam
NM4_9_10.bam
Challenge = Sorting + No pipeline
The guiding thread
- Identify MIC vs MAC molecules
- DNA methylation detection :
- No pipeline !
- Implementation and test
- 6mA MAC
- 6mA MIC

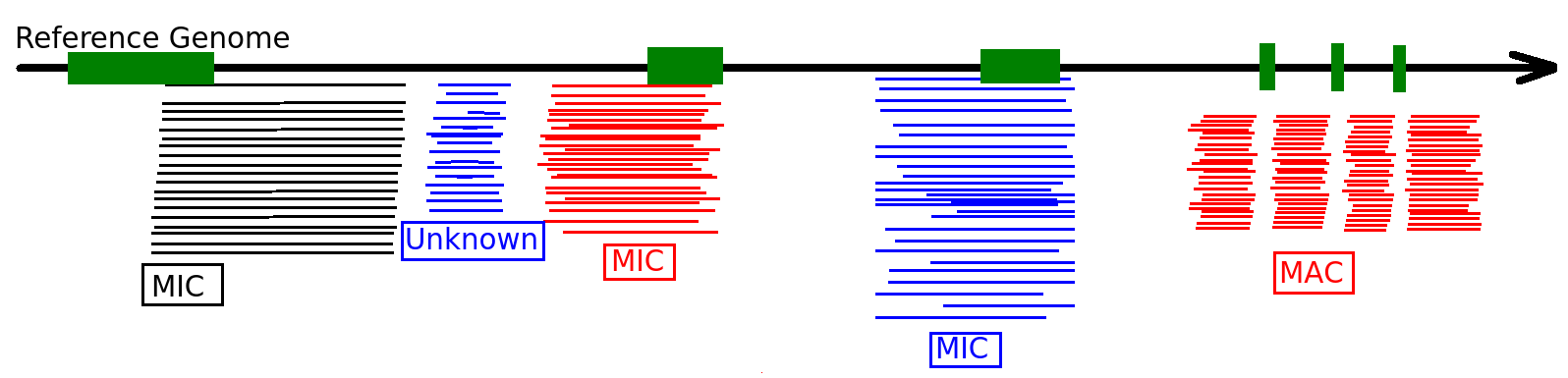
Identify MIC vs MAC molecules
Sorting (overview)

~ 85% accuracy
~ 100% accuracy
10 – 15 kb
~350bp
Alignment
MAC
MAC+IES
MIC
The random sampling strategy
IES
Other MIC
Other MIC
IES
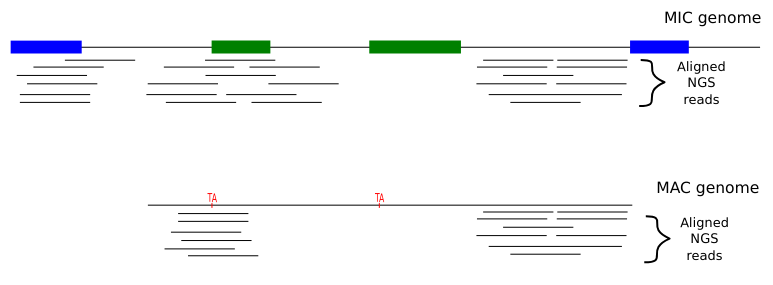
Mac Destinated Sequences (MDS)
MAC
TA Junction
-
Most sequences are Mac Destinated Sequences (MDS) : We cannot guess their nuclear origin
- A vast majority of them (>99.5%) comes from the MAC
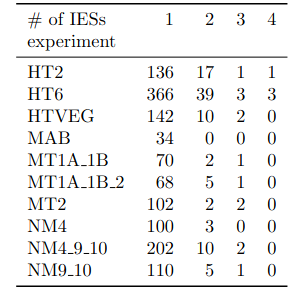
Expected number of IES+ sequences
-
1 molecule out of 200 comes from the MIC
- A bit less due to contaminants
- ~ 1/6 of MIC inserts will carry an IES
-
# of PacBio consensus (CCS) per sample :
- > 150.000 (multiplexed)
- ~ 350.000 PacBio CCS (not multiplexed)
That is,
-
Expected ~100 to 300 IES+ sequences per experiment
- Got 49 to 310
Orders of magnitude :

This is not much, but if we are right 100% of the scnRNA independent IESs could be methylated
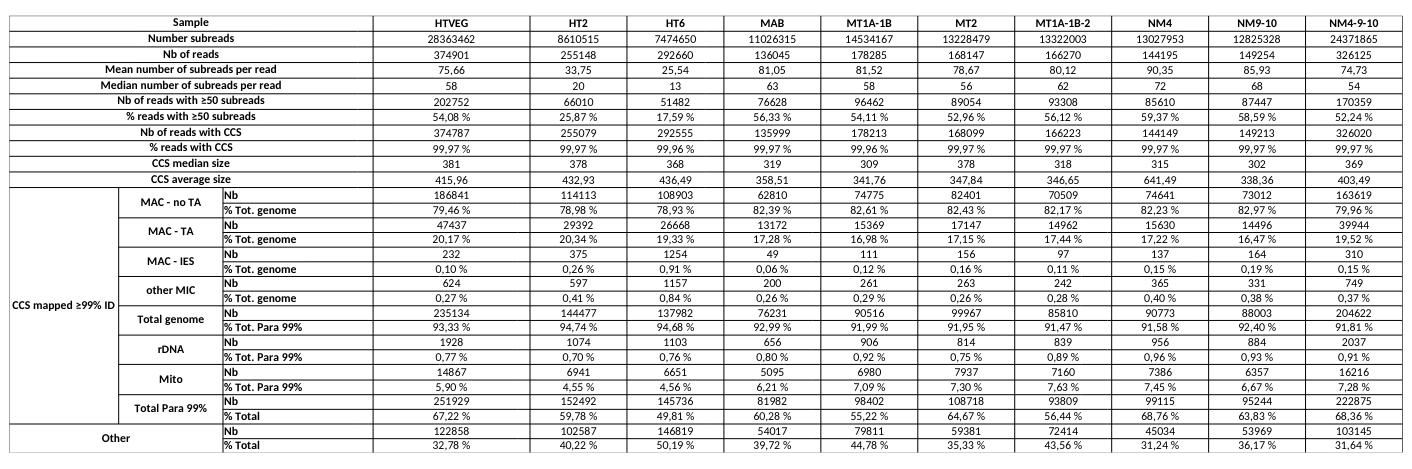
Raw numbers of PacBio consensus (CCS) per sample and category
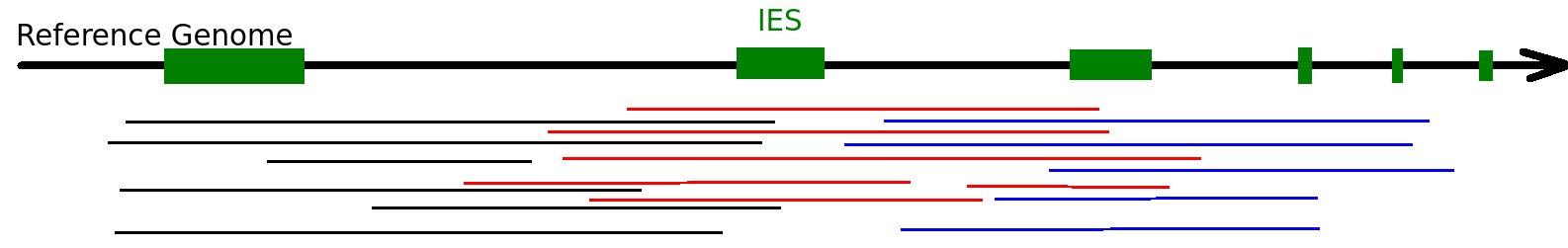
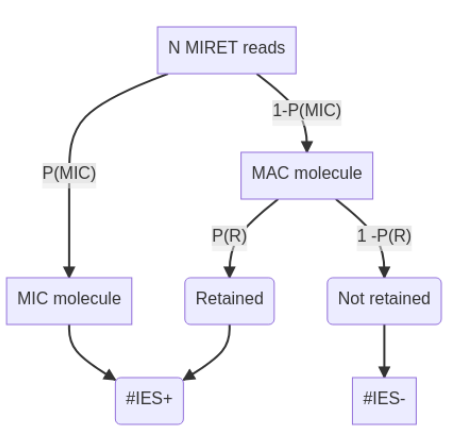
IES retention
- IESs are sometimes retained in the MAC
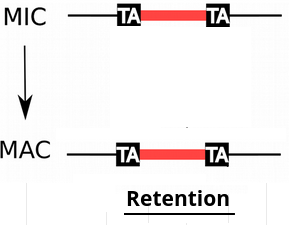
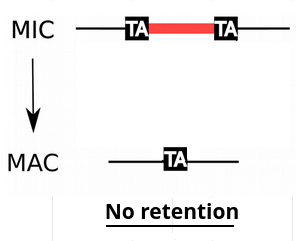
P(R)
1 - P(R)
-
Quantification: "IES Retention Score" (IRS)
- MIRET : Cyril Denby Wilkes, Olivier Arnaiz, Linda Sperling 2016, eg:
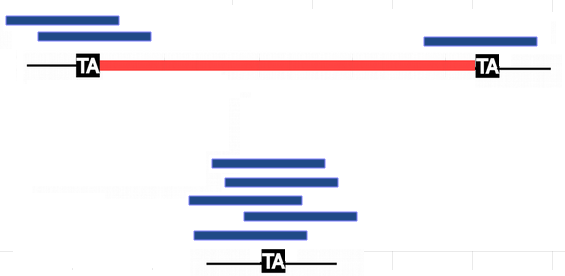
5 reads IES -
1 read IES +
2 reads IES +
$$IRS_L = \frac{2}{2+5} \approx 27\%$$
$$IRS_R = \frac{1}{1+5} \approx 16\%$$
The higher the IRS, the higher the retention.
Danger !
IES retention
Pitfall
e.g
MIC = 4n, MAC = 800n, R = 1/200 = 0.005 , N = 100 NGS reads
$$\mathbb{E}(IRS)= 0$$
$$P(MIC|IES+) = 50\%$$
No !
Even a low IRS can be problematic for us !
When the N is small (~100), it's just impossible to see small retention levels
Due to the MAC ploidy, even the slightest retention leads to $$P(MIC|IES^+) < P(MAC|IES^+)$$
Let's just keep all IESs with an IRS = 0 ?


IES retention
Proposed approach




??
-
Possible to compute R for each IES
- Use it to compute P(MIC|IES+)
- Give a confidence interval to both R and P(MIC|IES+)
IES retention
Comparison / Benchmarks
$$P(MIC|IES+) \in [9.5\% - 93.7\%], \alpha = 5\%$$
Problem : The size of confidence intervals is very big
- e.g 150 NGS reads, 0 IES+
For most IESs, we will simply not be able to tell wether it comes from the MAC or the MIC
IES retention
Workaround : Pooling samples

Rare picture of Eric, doing some archeology to find more samples to pool and gain coverage (circa 2022, colorized)
- 12 vegetative samples
- Coverage reached : 1160 - 1660X !
- Implicit assumption : R is mostly IES-dependent
Mac ploidy : 800n ?
If MAC ploidy = 800n than without retention :
$$E(IRS) = \frac{4}{800+4} \approx 0.005$$
If retention :
$$E(IRS) >> \frac{4}{800+4}$$
Something is odd !
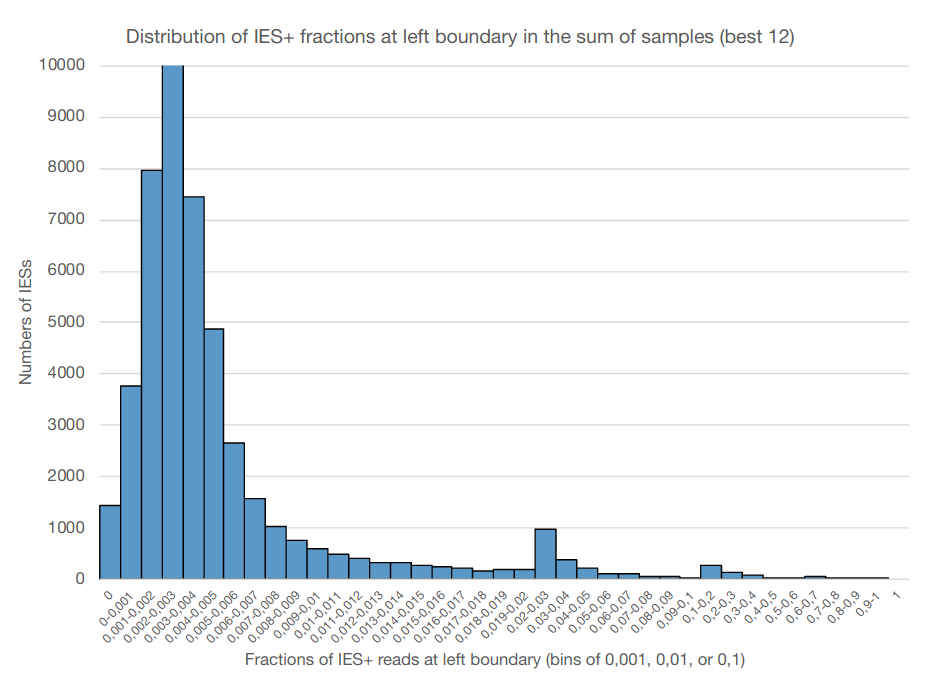
0.002-0.003

Mac ploidy ... At least 1600n ?
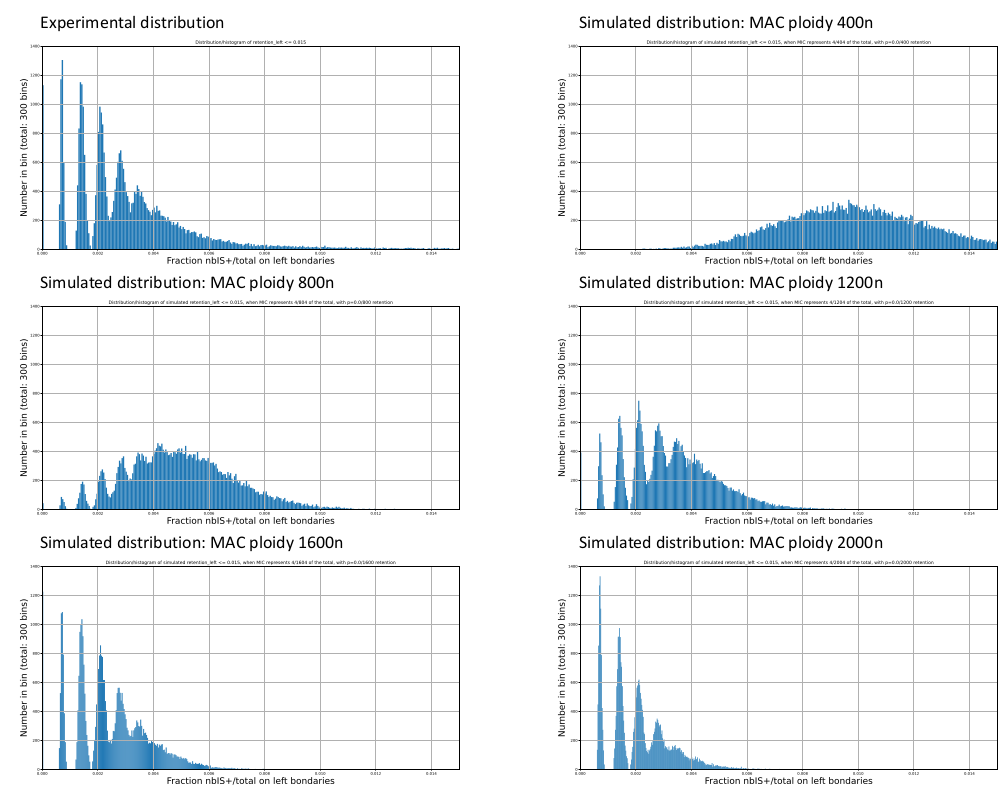

Mac ploidy ... At least 1600n ?
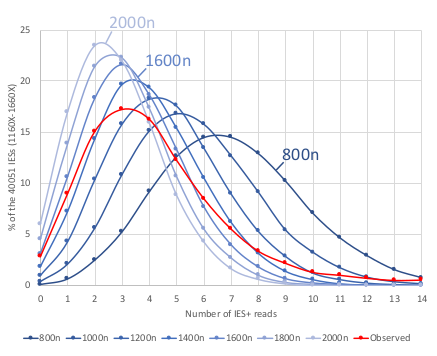

For our calculus, we used K = 1600n
Numerical application
When using :
- Kmac = 1600n
- 12 vegetative samples to quantify R and P(MIC|IES+)
- ...
On average, we will still have only very vague estimates of P(MIC|IES+) !
On average on all the IESs without retention :
$$R = 0 \implies P(MIC|IES^+) \in [33\% - 100\%]$$
CONCLUSION :
Numerical application
On a fake dataset (simulated retention)
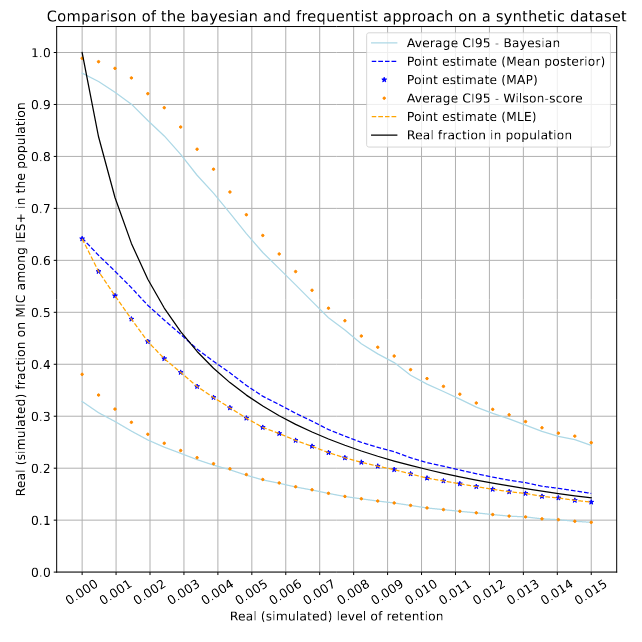
Real retention R (simulated)
P(MIC|IES+)
Summary
Can we identify the MIC sequences ?
- Very hard to have a correct estimate of P(MIC|IES+)
- When we will, it will mostly be for heavily retained IESs anyway
-
With even the slightest retention :
- Only works for IESs, not other MIC
- Only works when the ploidy is well caracterized
> We should expect lots of our MIC data to be impossible to use
$$R > 0 \implies P(MIC|IES^+) \approx 0$$
The guiding thread
-
Identify MIC vs MAC molecules
-
DNA methylation detection :
- Implementation and test of an analysis pipeline
- 6mA MAC
- 6mA MIC

(+ Found a new way to quantify IES retention)

(+ re-estimated the MAC ploidy)

DNA methylation analysis pipeline
A few months of plumbing later...

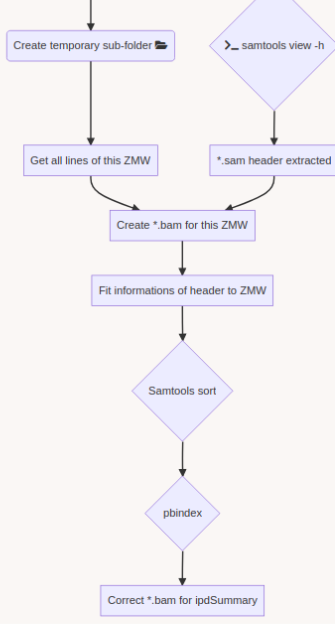
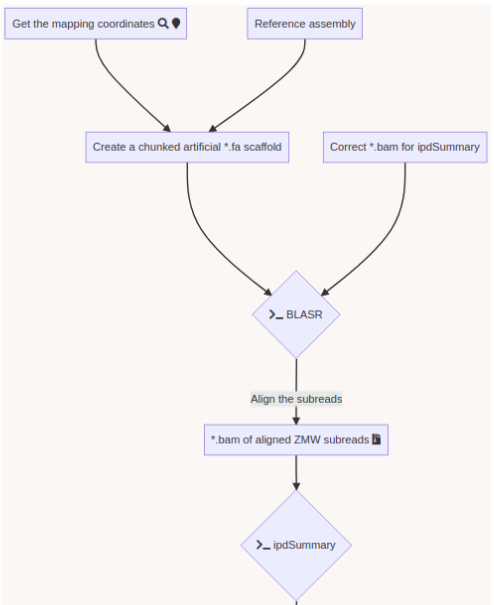



Outputs scores :
"ipdRatio": 2, 1, 4...
"ModificationQv" : 0, 30, 25...
"identificationQv": 1, 0, 50...
When do we call a nucleotide methylated ?
Pipeline output



Using E. coli DNA
-
Nearly 100% 6mA (symmetrical):
- GATC +++
- EcoK
-
A few others
-
Depends a lot of the strain
-
Depends a lot of the strain
-
Nearly 0% 6mA :
- Everything else
E.coli is used to feed paramecium (contaminants)
> Can be used to benchmark our pipeline's ability to detect 6mA
ipdRatio in E. coli
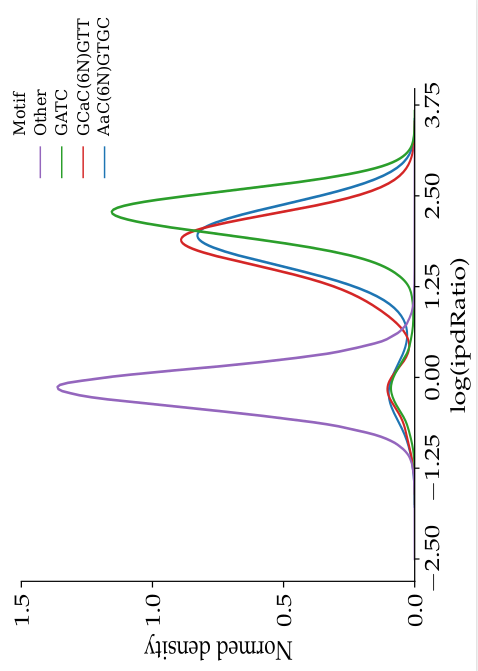
- The nucleotides we expect to be methylated have a high ipdRatio
- Slight changes between motifs
- Some exceptions : really not-methylated ?
Motif effect
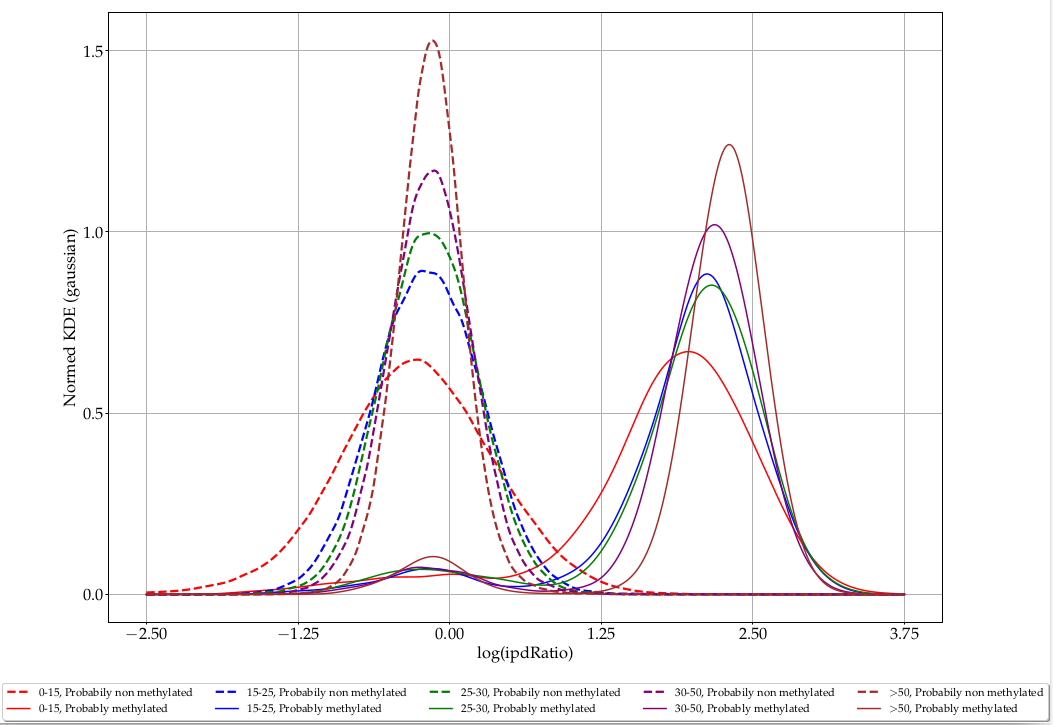
Coverage
L. methylated
L. unmethylated
> 50
35-50
25-35
15-25
0-15
ipdRatio in E. coli
Coverage effect
How to binarize the ipdRatio ?
Either a nucleotide is methylated, or it is not :
- We need to use a threshold on the ipdRatio to call modified nucleotides
- This threshold has to take account of the coverage effect
- No optimal solution anyway
Our pragmatical solution : An arbitrary linear threshold
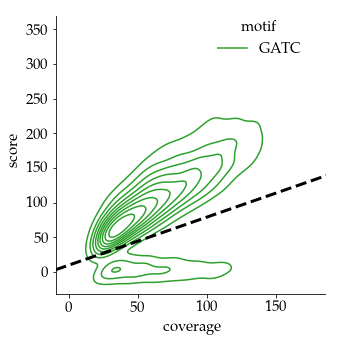
Benchmark (6mA)
- ~92% of 6mA in EcoK and GATC
- ~99.8% of non-6mA elsewhere
If we make the simplification that all GATC/EcoK sites are methylated and that 6mA is only present there :
$$Sensitivity = P(D|M)$$
$$Se = 92\%$$
But :
-
Some GATC/EcoK are unmethylated
- The real Se is actually better than 92%
-
A few amount of 6mA outside of GATC/EcoK site
- The real Sp is actually better than 99.8%
- Se = 92% and Sp = 99.8% are worst case estimates
$$Specificity = P(\overline{D}|\overline{M})$$
$$Sp = 99.8\%$$
Remark on hemi-methylation
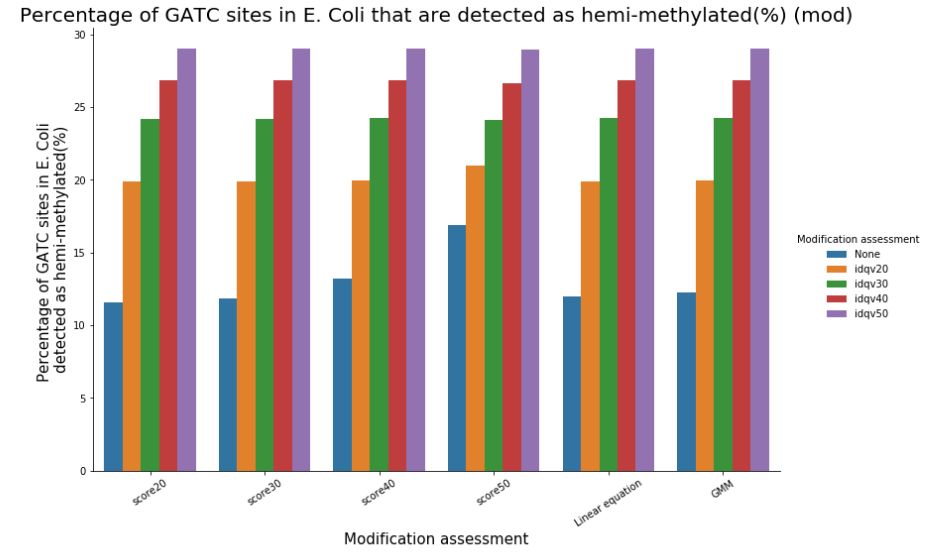
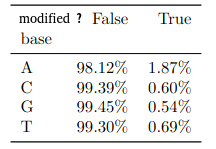
We can easily have more than 50% of so-called hemi-methylated sites that are actually not hemi-methylated
Quantifying hemi-methylation is tricky if $$Se < 100\%\ and\ Sp\ < 100\%$$
Benchmark
(other modifications)
PacBio sequencing was already known for its propensity to generate false positives for 4mC (K. O’Brown et al. 2014)
Qv30
- Either false positives, or a Nature paper
- "Killer experiment": See with amplified DNA
- For now, we ignored it
Analysis Pipeline
summary
Great to detect 6mA
Other ??
Potential problems when quantifying hemi-methylation
The guiding thread
-
Identify MIC vs MAC molecules
-
DNA methylation detection :
- Implementation and test of an analysis pipeline
- 6mA MAC
- 6mA MIC

(+ Found a new way to quantify IES retention)

(+ re-estimated the MAC ploidy)

DNA modifications
In the MAC
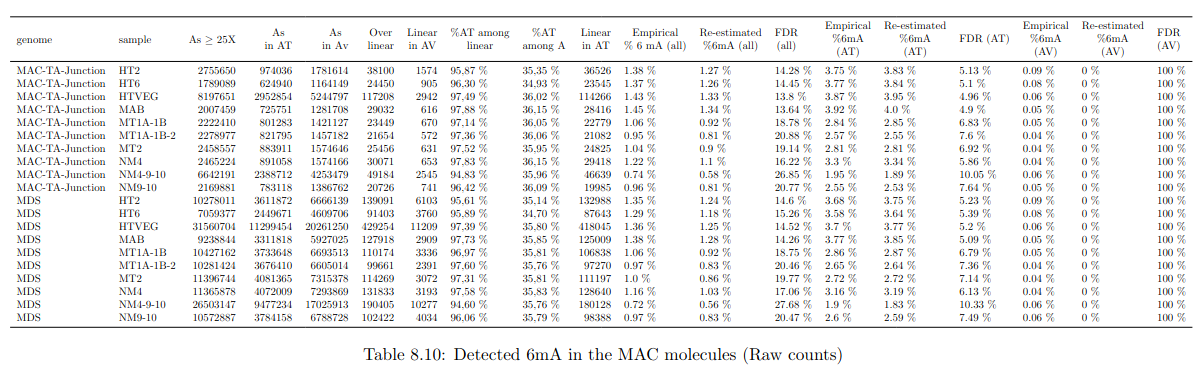
Hallmarks in HTVEG
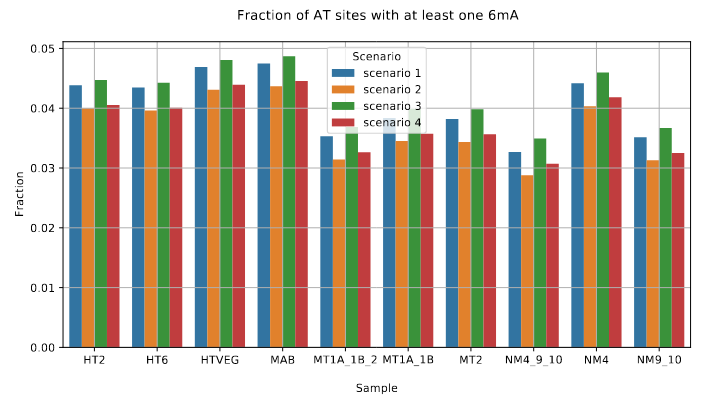
• Between 1.25% and 1.45% of 6mA in the MAC
• Between 97.39 and 100% of them are located in
AT sites
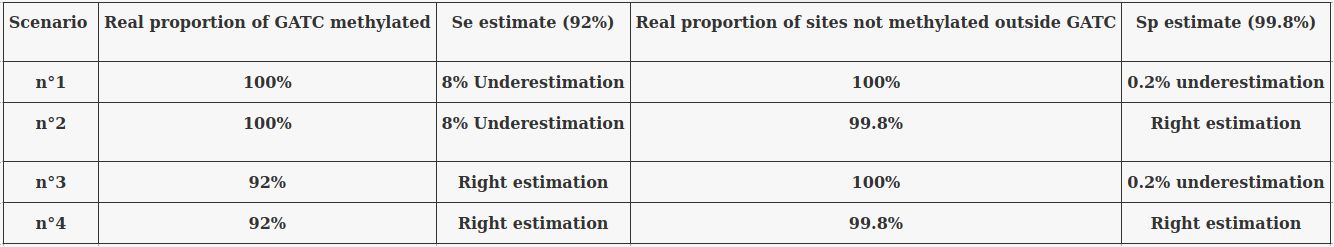
Taking account of the uncertainty of Se and Sp :
Problem : Some results will vary greatly depending on Se and Sp !
The 4 scenarii for Se and Sp
- We don't care about Se and Sp
- Only thing that matters : Does it impact the result ?
| Se | Sp | Interpretation | Scenario Number |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100% | 100% | Perfect | 1 |
| 100% | 99.8% | Sometimes it misses | 2 |
| 92% | 100% | Sometimes it invents | 3 |
| 92% | 99.8% | A few confusions here and there | 4 |
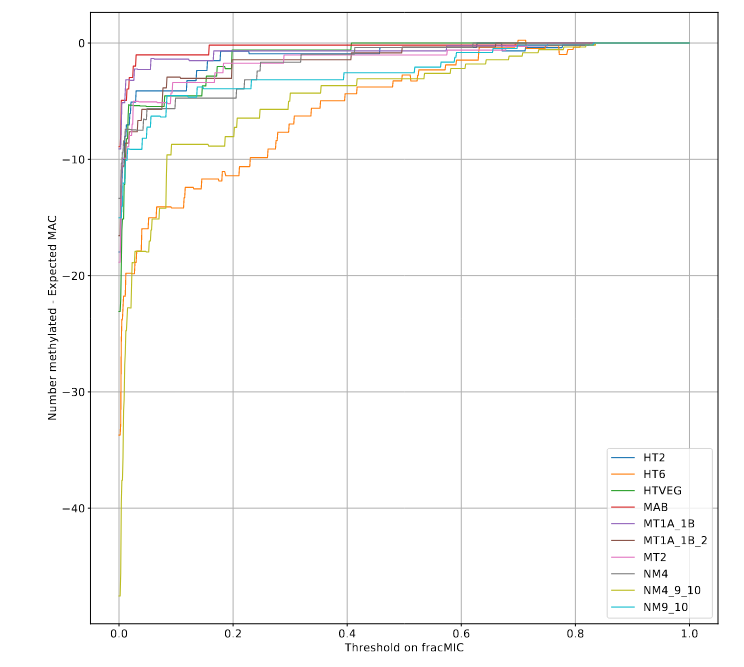
Global level of 6mA in the MAC
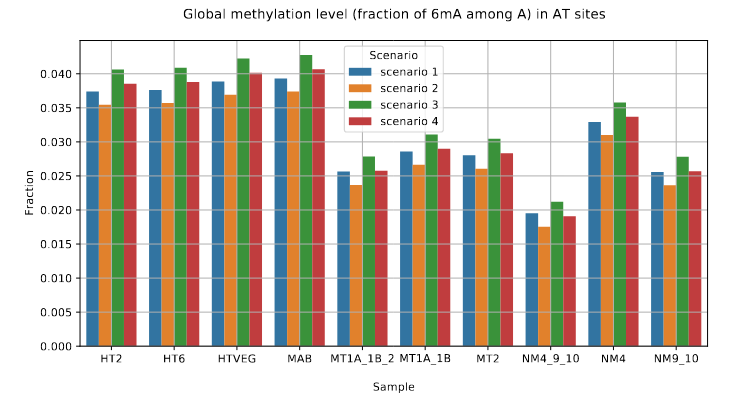
> Implied in the bulk of 6mA in the MAC
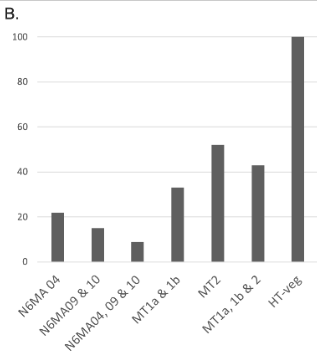
Reduction of 6mA
P. tetraurelia
Mitochondrial
Total BET
-80 to -90% NM proteins
-60 to 70% MT proteins
We expected -90%
Get only -50% ??

Less than predicted by southwestern blot
Role of our candidates
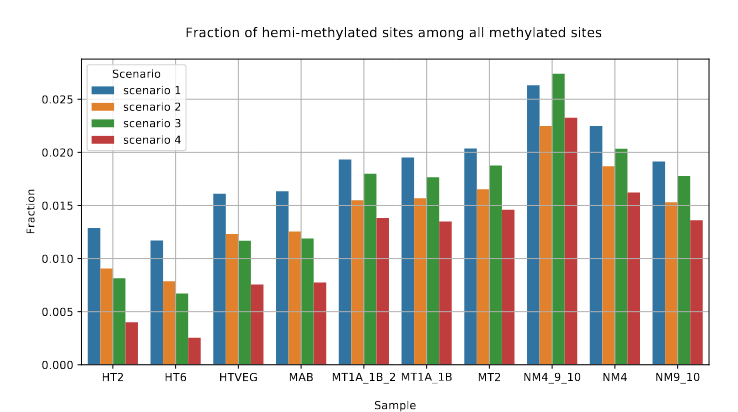
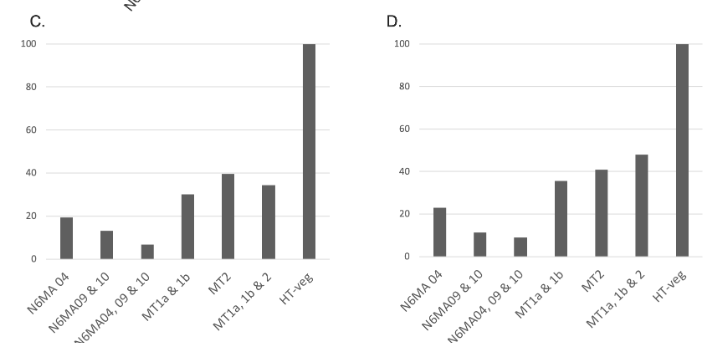
Raise of hemi-methylation, whose intensity depends importantly on how well Se and Sp are well estimated or not
Fraction of AT sites that are hemi-methylated
Role of our candidates
Role of our candidates
The capacity to make symmetrical methylation is never abolished completely
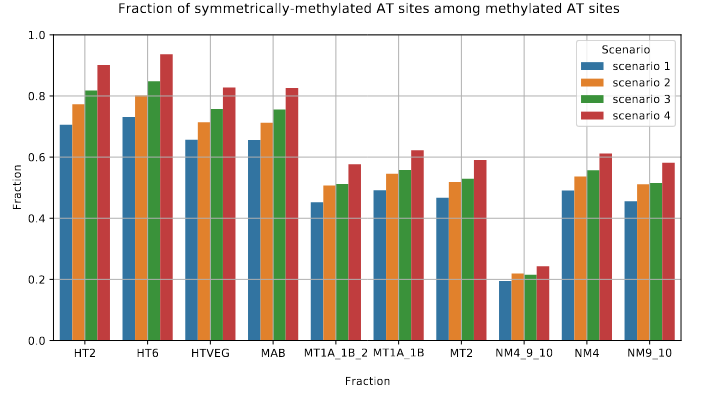
Role of our candidates
De novo methylation of unmethylated AT sites :
Unchanged NM4.
Drops everywhere else
Proposed interpretation/Hypothesis
Role of our candidates


All weakly implied except NM4 (not implied)
All strongly implied
Never abolished
Function = Symmetry +++
Outside of AT sites
Predicted FDR : 100%
But likely detection outside of AT sites too
never erased
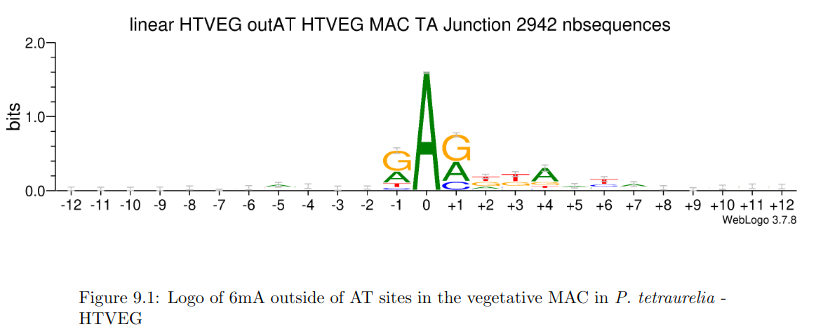
AGAA and GAGG motif
are documented as methylated sites (6mA) in C. el-
egans too (Greer et al. 2015)
The guiding thread
-
Identify MIC vs MAC molecules
-
DNA methylation detection :
- Implementation and test of an analysis pipeline
- 6mA MAC
- 6mA MIC

(+ Found a new way to quantify IES retention)

(+ re-estimated the MAC ploidy)

DNA modifications
In the MIC
A ruthless data shrinkage
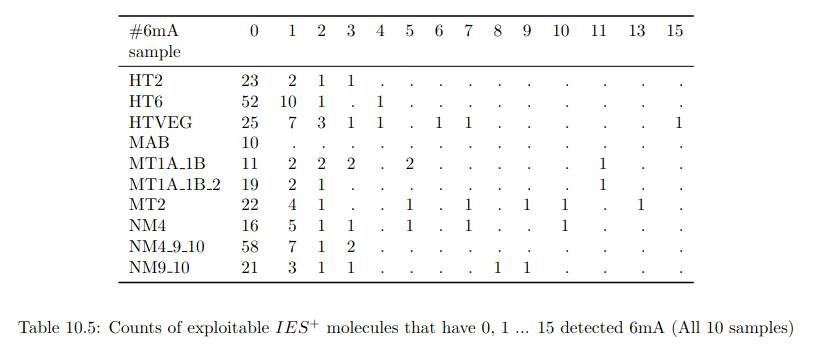
Number of molecules with at least one exploitable adenine
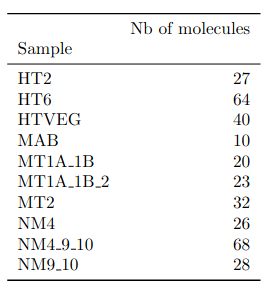
- several IESs
- variable MAC regions
- extremity outliers
Is our calculus valid for several IESs ?
Remaining with computable P(MIC|IES+)
P(MIC|IES+) among the surviving molecules
The vast majority of IES+ molecules come actually... From the MAC !!!
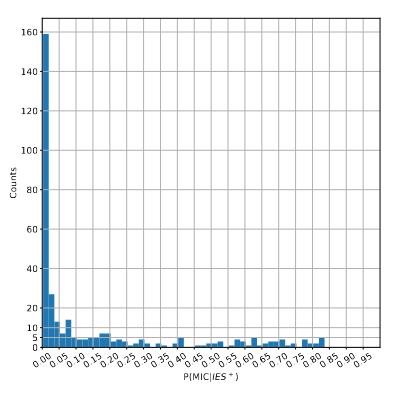
A few MAC molecules concentrate the majority of 6mA
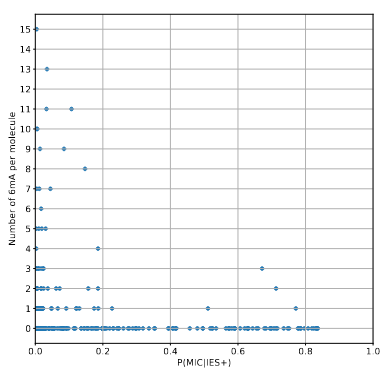
A few MAC molecules concentrate the majority of 6mA (2/2)
We can never exclude the hypothesis that 6mA comes from the MAC
Conclusion on the MIC
- We cannot confirm of invalidate the hypothesis that there is 6mA in the MIC
- Therefore, we cannot conclude about the role of 6mA as a permanent marker of IESs in the MIC of P. tetraurelia
Summary
Methodological developments :
- Analysis pipeline
- Retention / P(MIC|IES+)
- MAC ploidy > 1600n
- [ Hemi-methylation ]
On our MAC data :
- Methylase candidates = active in the bulk of methylation in the MAC
- Symmetrical methylation of AT sites + a few de novo hemi-methylation
- AGAA / GAGG outside of AT sites
On our MIC data:
We cannot exclude the hypothesis that all 6mA comes from the MAC
Perspectives
-
P(MIC|IES+) when > 1 IES ?
- Could invalidate the hypothesis definitely
-
Deeper analysis of HT2 and HT6
- P(MIC|IES+) is irrelevant here
- Still possible to find 6mA or other modifications around the IES very transiently
- Check 6mA / TSS
-
Hemi-methylation :
- TSS ?
- Maintained through replication ?
On these data :
For the future :
- MIC purification +++
- Nanopore ?
- Partial purification ?
- The random sampling is doomed to fail in P. tetraurelia
MERCI !
Team Meyer
Team Genovesio
SPIBENS
Les infos et admin.
Jury: Chunlong, Sandra, Eric, Laurent
Comité de thèse: Linda, Mireille, Chunlong
La communauté paramécie
Les petites mains derrière les données
Mes collègues de pause
Toi public
Mentions spéciales contributions directes :
Eric Meyer
France Rose
Mathieu Bahin
O. Arnaiz
Leandro



MTA1 -- orthologue 4-9-10
MTA9 -- Pas catalytique chez Tetrahymena
[..] --> MT1A1B2
Pas 6mA tetrahymena MIC
MTA1 -- orthologue 4-9-10
MTA9 -- Pas catalytique chez Tetrahymena
[..] --> MT1A1B2
Pas 6mA tetrahymena MIC
The 4 scenarii for Se and Sp
- We don't care about Se and Sp
- We care about the fact that eventual mis-estimations of them doesn't really change anything
Finding unbiased estimators for and FDR
If p number of positive detections among N tests:
p = FP + TP
$$\pi$$
So,
Which means
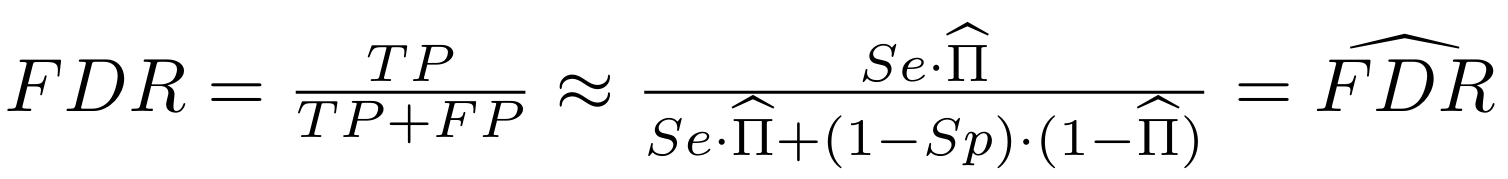
And:
What it gives in Paramecium
Methodological development to correct hemi-methylation detection (1/2)
Let FD1 and FD2 be resp:
- Fraction of hemi-methylated AT sites
-
Fraction of sym-methylated AT sites
PZ0, PZ1, PZ2: unbiased estimators of non, hémi, symetrically methylated AT sites
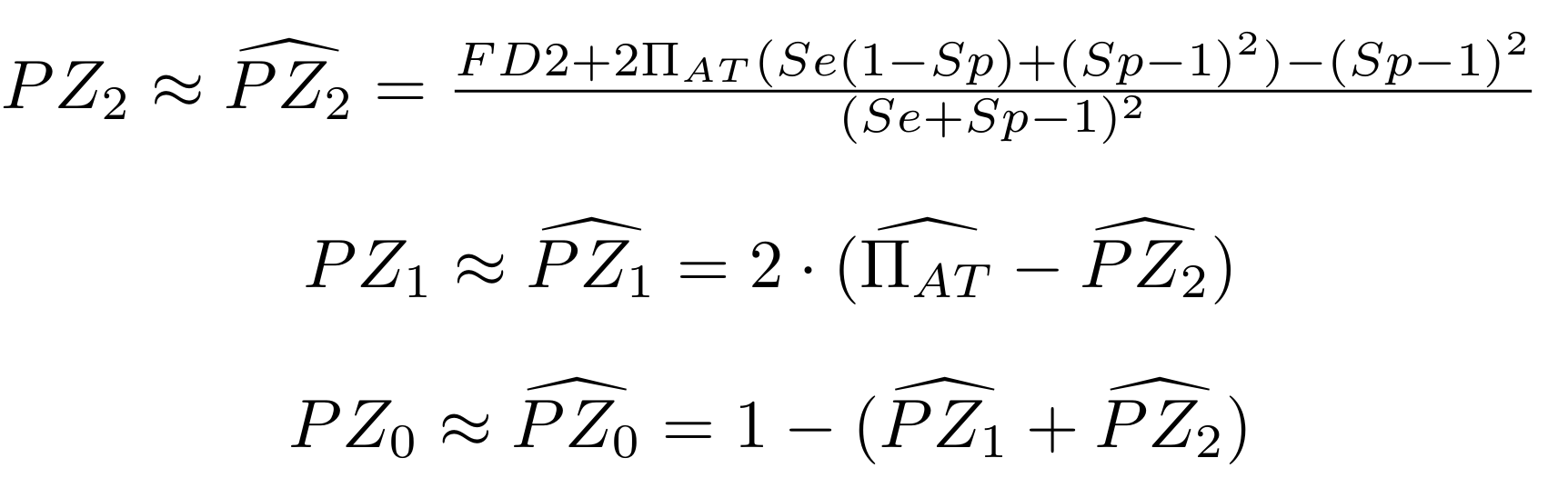
Then:
With
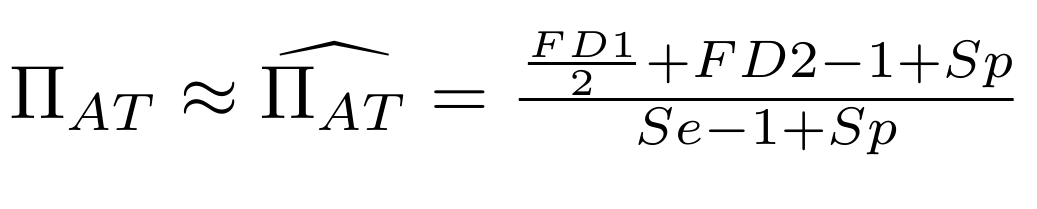
Methodological development to correct hemi-methylation detection (2/2)
We can also find the number of hemi-methylated sites being detected as such, and the proportion of sites detected as hemi-methylated that are really hemi-methylated. This is possible because we now approximately know PZ0, PZ1 and PZ2, and P(D|Z) is easy to determine:

Then, P(Z|D) can be determined through Bayes theorem using P(D|Z), P(Z) and P(D) (which are all known)
P(Z=1|D=1)
is our case of interest
What it gives in Paramecium
2.1 Retroingineering
The capping of IPDs
-
modelPrediction is the predicted IPD value by the model in a given context of nucleotides at this position
-
globalIPD is the mean of all the IPD values of the read.
-
localIPD represents all IPDs that have been mapped at a given position in the genome, including those from other sequences
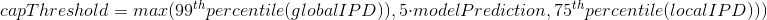
Conclusion on the capping
- Isn't coded as advertized by PacBio
- The way it's implemented for AggSN is problematic and doesn't really make sense
- Paradoxally, it should be more relevant for our approach than for the default one
- We expect no methylation to be undetected due to the capping
Laura landwebehr 2020
Oxytrichia trifallax


A outAT score 20 isQv20 (812 seq)
A outAT score20 idQv20 + Strong BH correction (176 seq)
PhD defense - DDay
By biocompibens
PhD defense - DDay
28/02/19
- 111



