Studying DNA methylation in Paramecium with PacBio sequencing






Eric Meyer - Mathieu BAHIN
The team

Bahin Mathieu
Bioinformatics

Eric Meyer
Biology - Parameciology
Suzanne Marques (PhD student), Veronique Tanty (IE - PhD student),
Sophie Malinski (MCU)
Eric's Team:
Introduction
P. tetraurelia: Genomic architecture
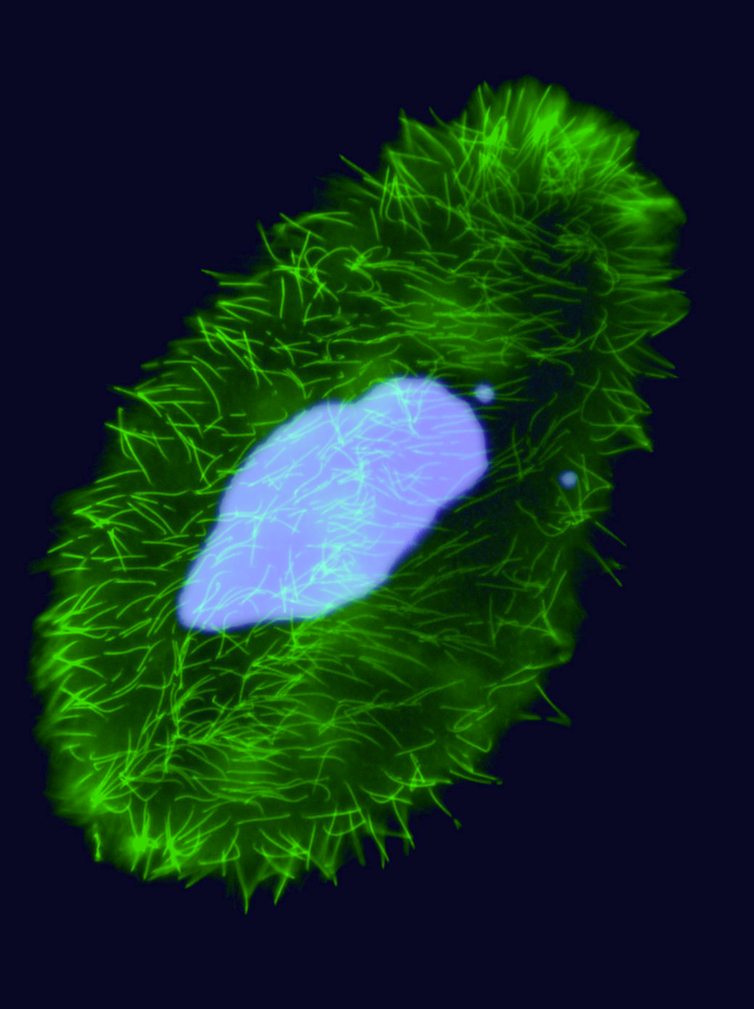
Unicellular eucaryote with 3 nuclei:
-
2xMIC nuclei (2n)
- Germline nuclei
-
Contains: TE & IES
- No transcription
-
1xMAC nucleus (up to 800n)
- Somatic nucleus
- Amplified and "fixed" version of the MIC
- Free from TE and IES
- Transcriptionnally active
DNA ratio: 1 MIC for 200 MAC
+ DIfficult to purify the MIC DNA
Up to 0.120 mm
Profiling the IESs
-
Non-coding sequences
- ~ 45.000
- Inserted within genes
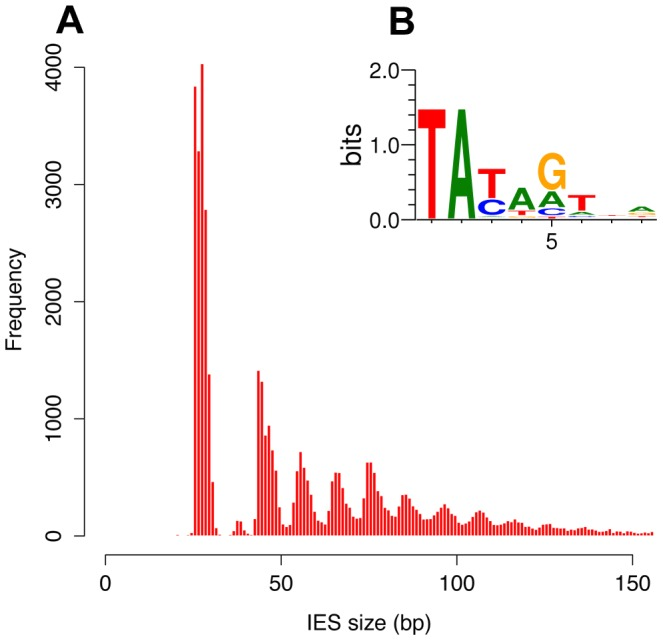
- Most recent IES are very short (~30bp)
- Remnant of TE ?
- ~ 100% TA-Bounded
-
Weak consensus at the boundaries
- PibbyBac transposase ?
- How are they recognized ?
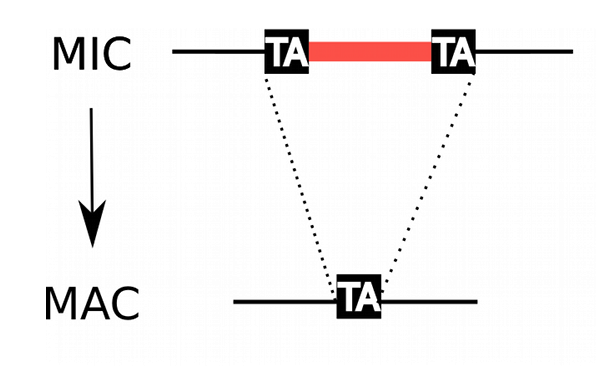
IES
Internal Excised Sequences
IES recognition ?
The ScanRNA pathway ?
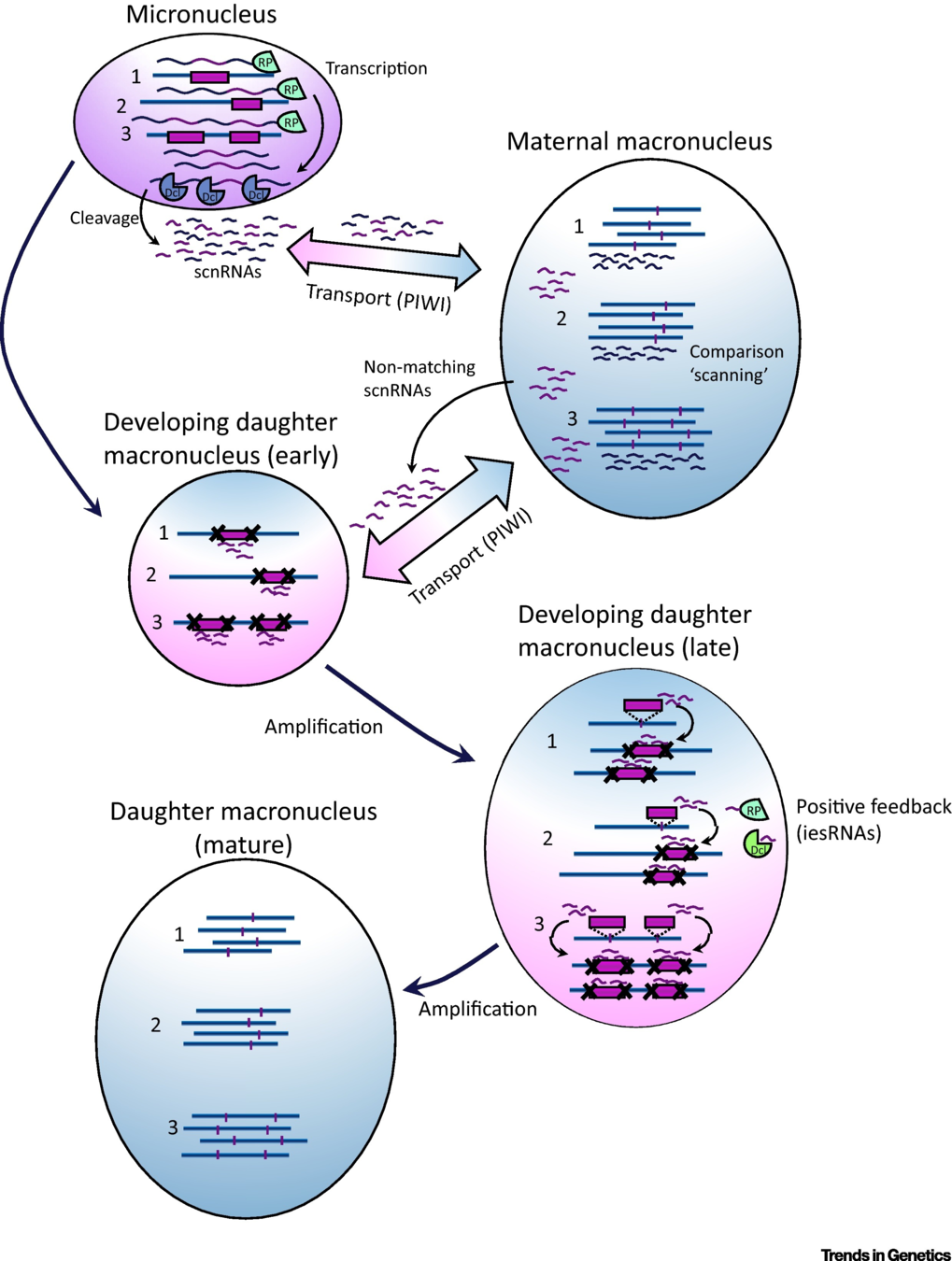
10% of IES are scanRNA dependant.
30% of IES are small-RNA dependant (shown by DICER-like silencing)
- What about the majority remaining ?
PhD Project
One big question remains: How does the cell recognize the Scan-RNA independant IES ?
2 independant hypothesis:
- Some motifs or specific nucleotide composition might differenciate these IES from the rest of the genome
- Those sequences can be permanently marked in the MIC by a DNA methylation pattern
Which epigenitic modification could we look at ?
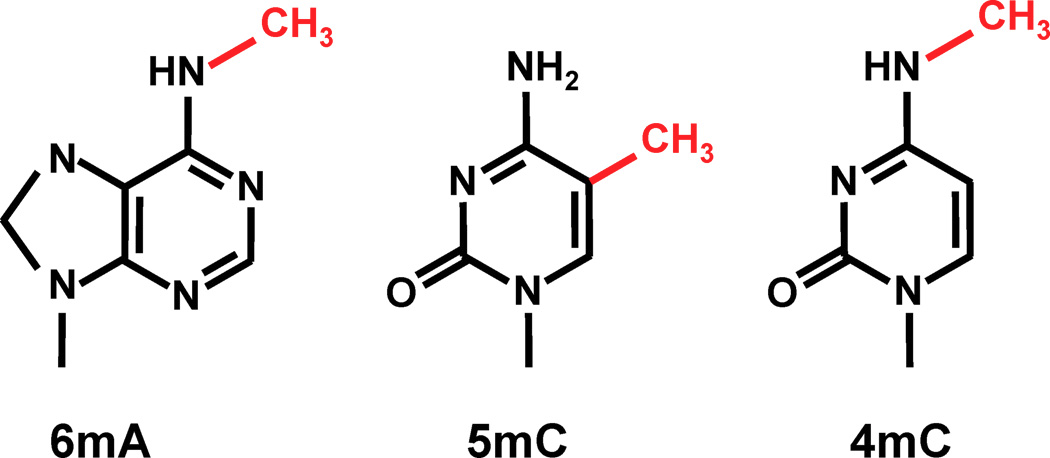
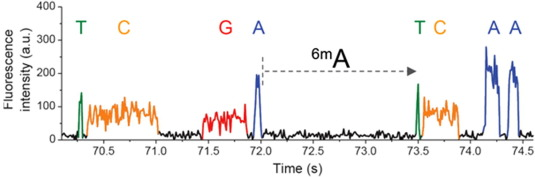
n6mA is one the the 3 most frequent known methylations in DNA
6mA likely to be abundant in Paramecium:
-
Suspected 2.5% in P. aurelia by Cummings et Al (1975)
- Detected methylation by SMRT in the MAC in our lab (unpublished data)
- Detection by SMRT in the MAC by Sandra Duharcourt's lab (unpublished)
- Detection in Oxytrichia by L. Landweber et Al (2019)
25x 250x 25x
Materials and methods
Identify methylase candidates
- Identification of potential n6mA DNA methyltransferases
RNA silencing
Candidates:
- 7 "DPPW motif IV" genes
- NM4, NM9, NM10 studied in our lab
- others are studies by collaborators
- And another family: MT1a, MT1b, MT2
PacBio SMRT sequencing
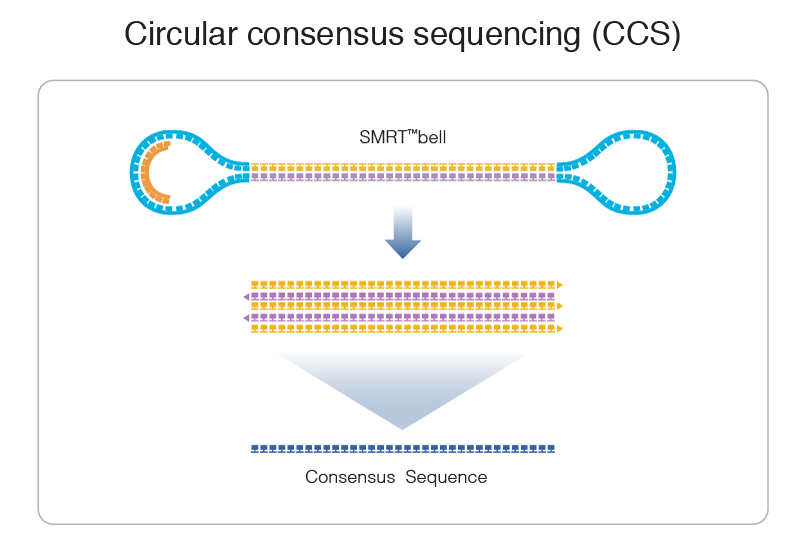
99% accuracy
Max
85% accuracy
Methylation analysis needs local coverage> 25X
- IPD are captured and compared either with WGA or Trained model (ML - "in-sillico control")
- Allows detection of suspect downturns of polymerase (function of the -3/+8 nt context)
Reads up to 80 kbp
Analysis of methylation
Two-different approaches
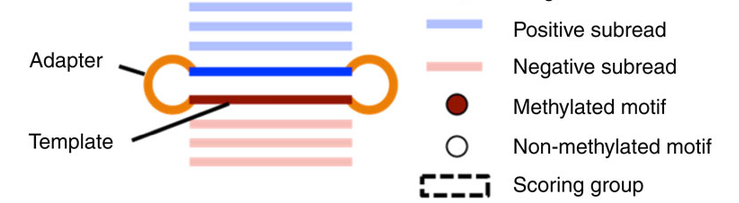
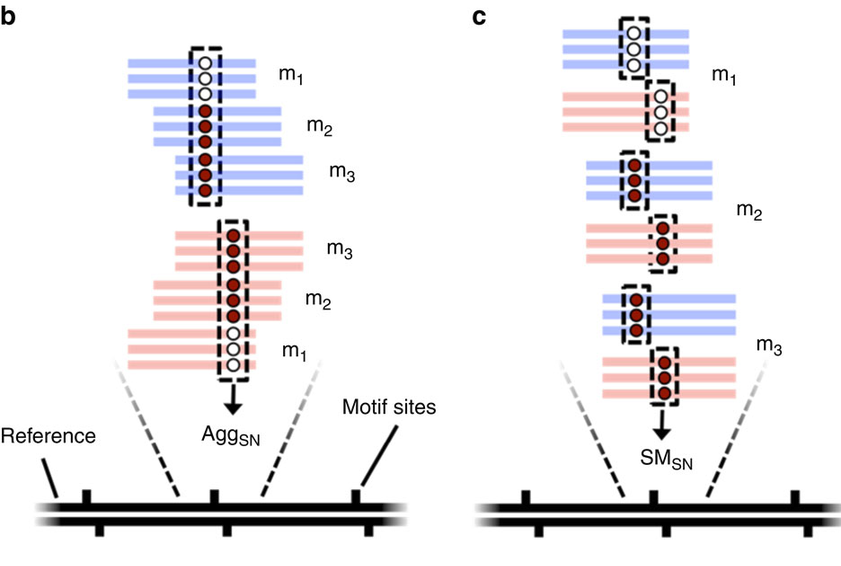
Pooled analysis of different molecules (default - Aggregation)
Analyze every molecule independantly from the others
(Needs shorter inserts - multiple passes)
Beaulaurier et Al 2015
Higher resolution
Strategy:

SMsn

1:200 (MIC/MAC)
Random sampling

PacBio SMRT
150K to 300K inserts of 350bp
80kb reads (> 100X)
- 1 out of 200 comes from the MIC
- 1/6 of MIC inserts will carry an IES
- 1/2 of IESs are just wrongly excised
- 30% of the remnants are scanRNA dependant
Only a few remaining: ~ 10 to ~50 sequences
100% should carry a methylation pattern
Available data at day0
PacBio sequencing
- Short insert strategy (SMSN)
- No WGA data
Wild type:
- Vegetative Cell (HTVEG)
- During autogamy (after 2h - HT2)
-
During autogamy (after 6h - HT6)
-
Asynchronous cultures / Quite blurred state
-
Asynchronous cultures / Quite blurred state
Silencing of methylase candidates:
-
Si/MAB (identified since then - probably a histone methylase)
-
MT proteins:
- Si/MT2
- Si/MT1A-1B
-
Si/MT1A-1B-2
-
NM proteins:
- Si/NM4-9-10
- Si/NM9-10
- Si/NM4
Also: AggSN of PGM32
1. Sorting of the sequences
Sort the sequences
-
High number of passes accuracy >99.9%
- Possible to determine where it comes from:
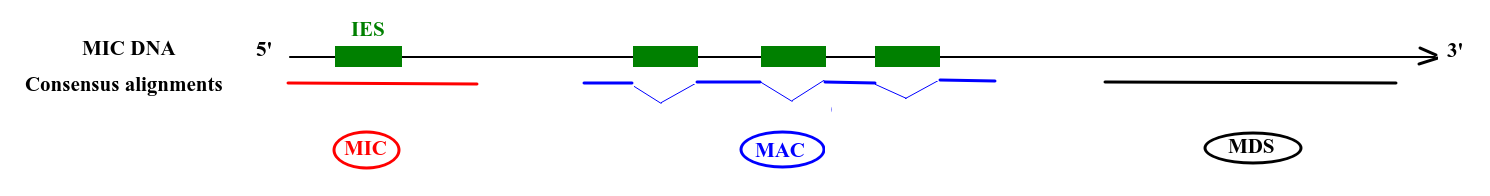
Deduced origin
MIC DNA
Alignment of consensus
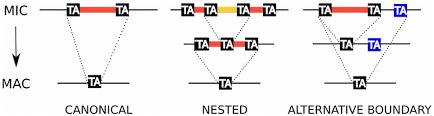
- MAC sequences clearly identified only if overlapTA of junction
- otherwise = MDS
Categories of sorting
- MDS
- = "MAC" for 99% of sequences
- MAC_IES
- "true" MAC_IES (never seen retained)
- other MAC_IES (sometimes retained)
- MIC
- Other MIC specific (TE, repeated sequences)
- MAC (TA Junction)
- Overlap a TA junction of excision
- rDNA
- mtDNA
-
Other:
- Contaminants
- Alternative excision boundaries ("LOWID")
- low identity consensus ("Trash")
"genome"
Total Paramecium
Total sequencing
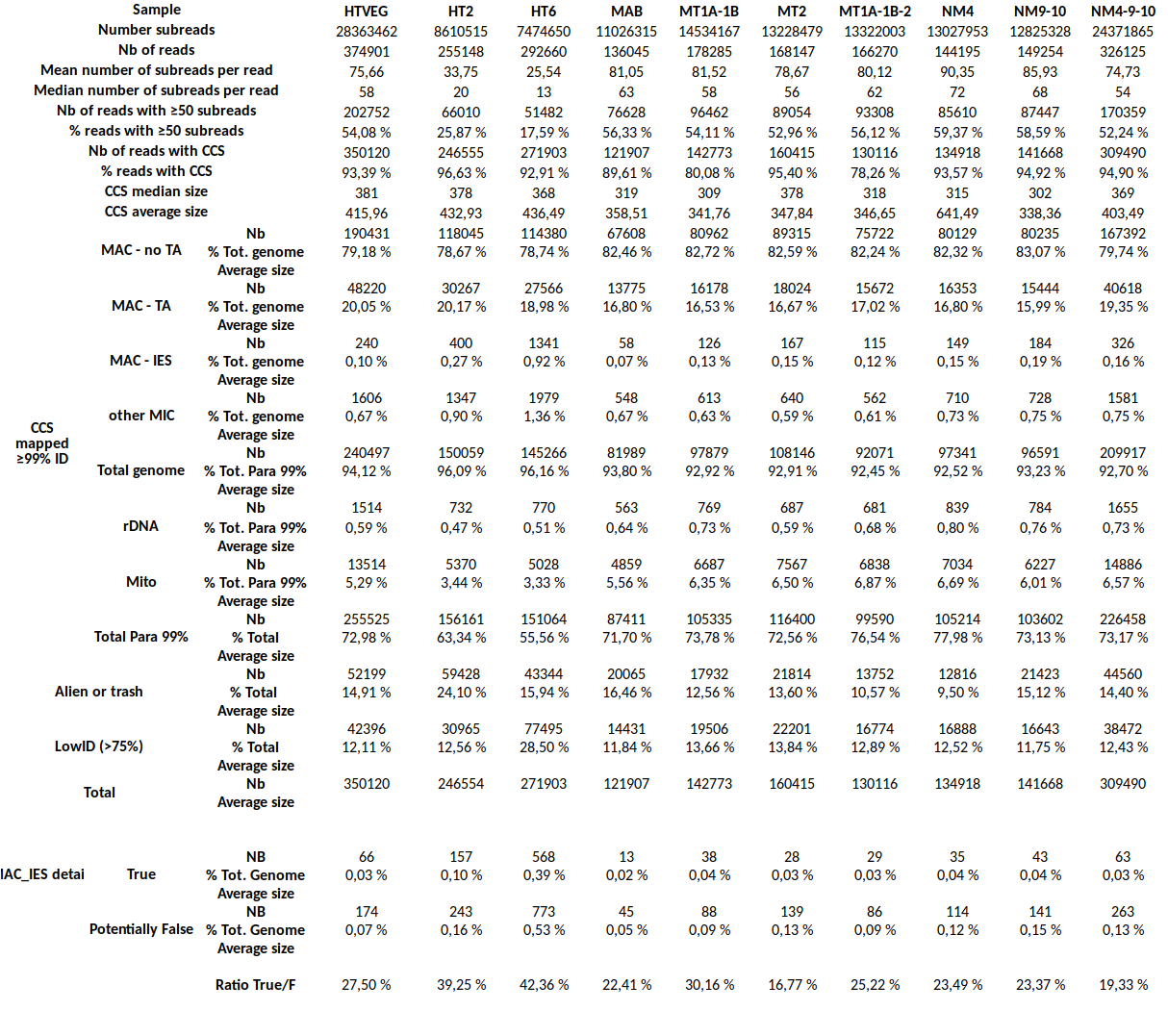
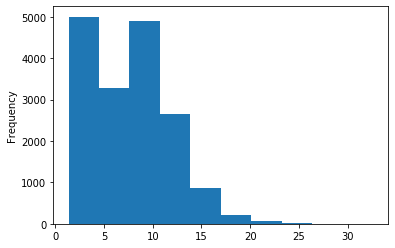
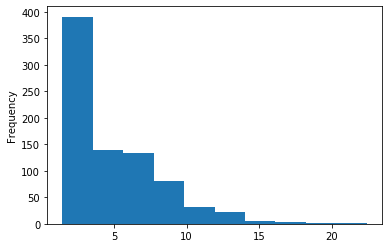
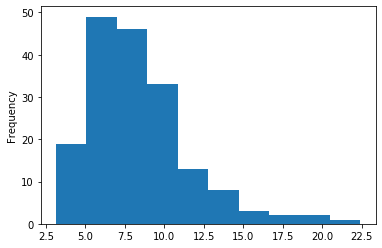
Output example
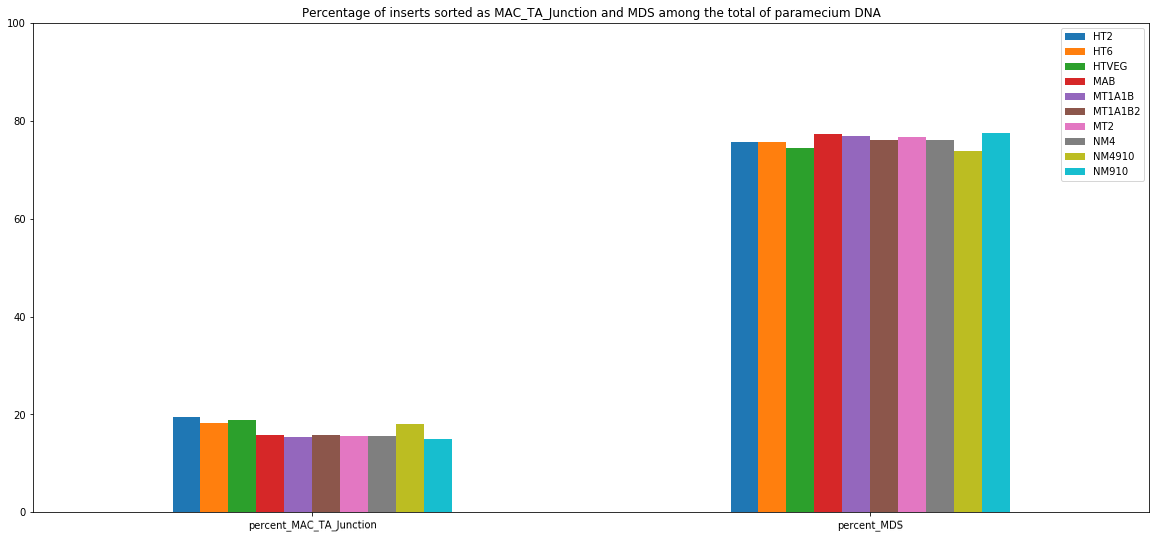
MDS and MAC_TA_Junction represent a vast majority
MIC specific and IES are as rare as expected
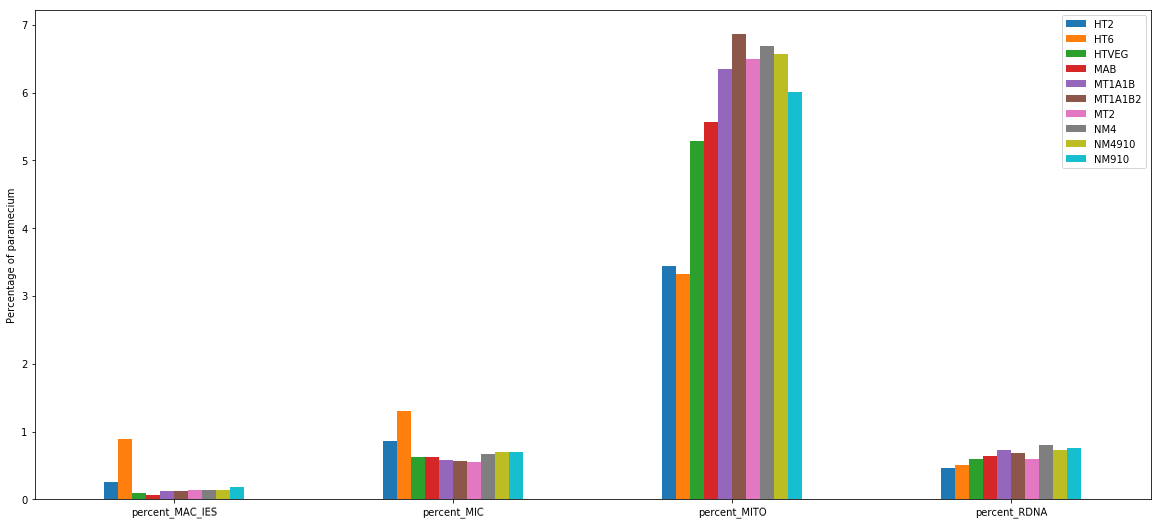
+ Applying the retention filter divides the number of "MAC_IES" approximately by 50%
mDNA and rDNA are quite abundant too
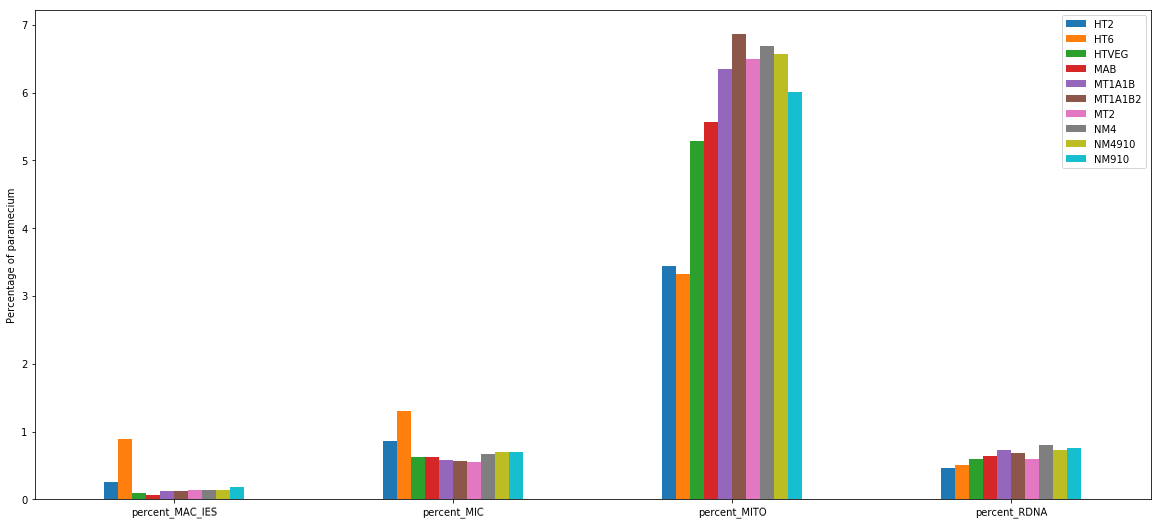
% of total Pramecium DNA
(MIC, MAC, RDNA, mito)
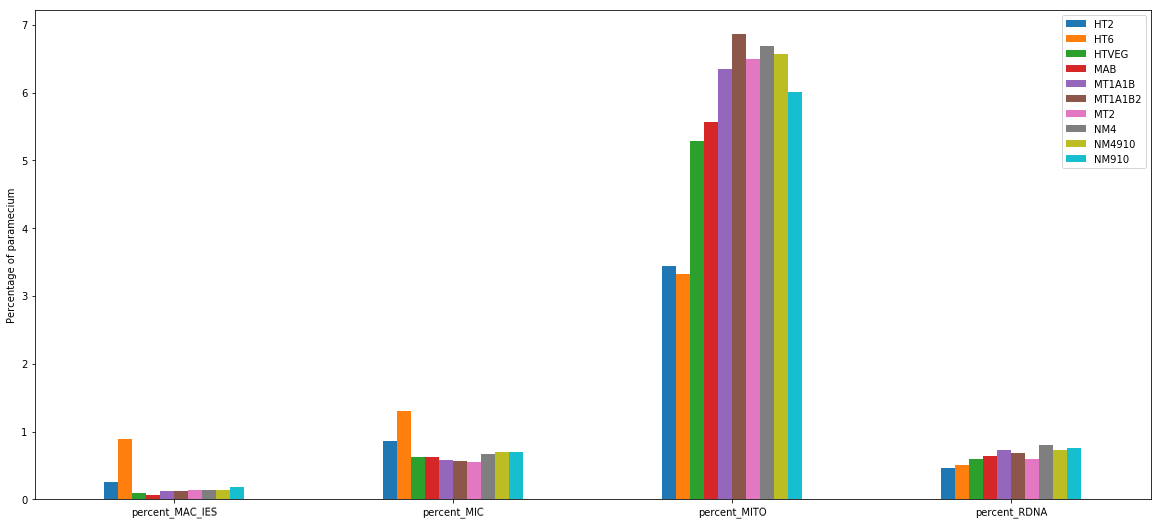
Conclusion on the sorting
- We reach the expected theoritical counts
- Statisfying implementation
- Hand checking of many IES OK
2. Analysis of methylation
Can we trust our technique ?
The Bayesian ambush

Let's admit that
We measure methylation in E. coli
We have a no-so-bad test:
99% Sensitivity = P(D | M)
99% Specificity = P(ND | NM)
Our global fraction of n6mA among all adenines is around 1%
- How much n6mA will we detect ?
- What's the positive predictive value ? (PPV) that is P(M|D)
1.98%
~50%
Half of our detections will be false positive
P(A|B) != P(B|A) unless P(A) = P(B)
The FDR varies with the real methylation fraction
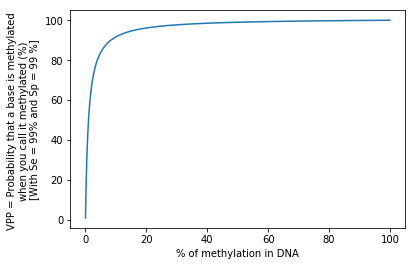
The testing dilemma
- Our test gives us the proportion of n6mA
- ...But we need the proportion of n6mA to estimate de proportion of n6mA !

To develop a medical test (ex: cancer screening), we must already know who has cancer or not !
This is a prior
e.g: From clinical knowledge, biological knowledge, biochemical knowledge, etc
Some priors for Paramecium
About Paramecium, preliminary data tend to show that:
- 0.5 to 2,5% n6mA
- > 90% in AT
- Vast majority of methylated AT = Symetrically-methylated
About PacBio SMRT, best case scenario.
- Sensitivity of in-sillico ~ 99%
- Specificity of in-sillico ~ 99%
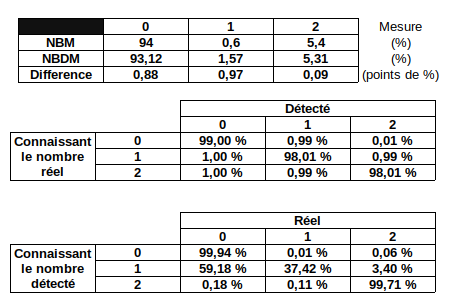
-
Global level of n6mA detected: ~2%
- (Reality: ~1%)
-
True positives inside AT: 85%
- (FDR 15%)
-
True positives outside AT: 10%
- (FDR 90%)

Approximate scenario for Paramecium
(Rough estimations,
Order of magnitude)
Assess the Se and Sp would help
- With in sillico control ? No one knows
Se, Sp : When is a n6mA modified ?
For n6mA, PacBio produces:
- A modification score --> Slowing of the polymerase
- An identification score --> Kinetic signature of a modification
They are PHRED-transformed p-values of two different statistical tests, that rely on the mean of the IPDs

PHRED scores
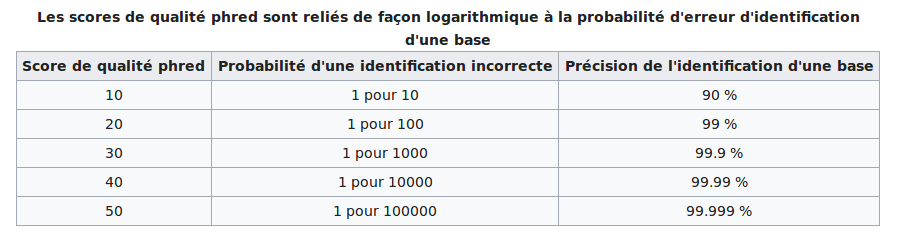
The scores are PHRED-transformed p-values
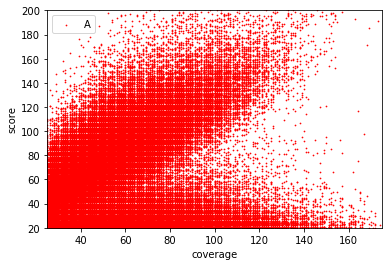
Typical covscore plot
Modification score / coverage
Using flat threshold on modification score = Hudge lack of power
Coverage-dependant threshold
We implemented two thresholds that are function of the coverage:
- A Gaussian Mixture Model (GMM) trained on MAC HTVEG
- A very simple linear equation
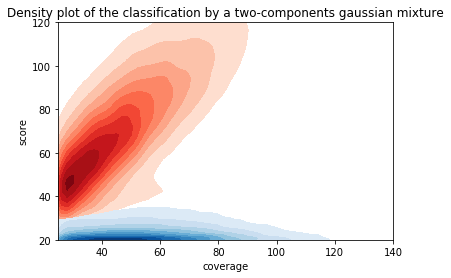
Thresholding
How to chose ?
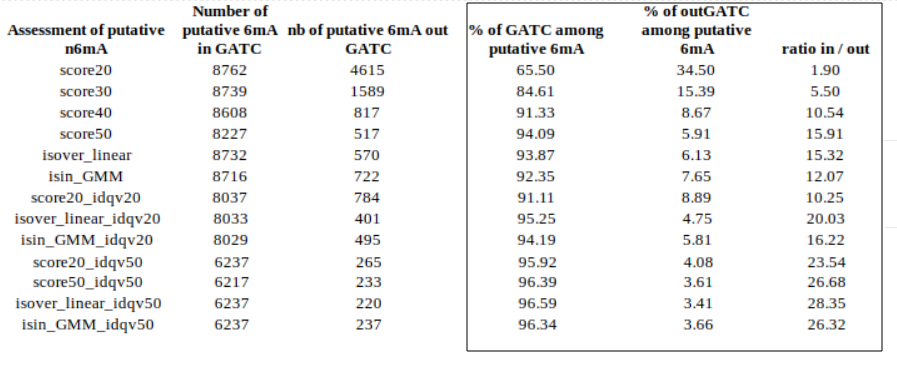
Choosing a threshold: E. coli contaminants
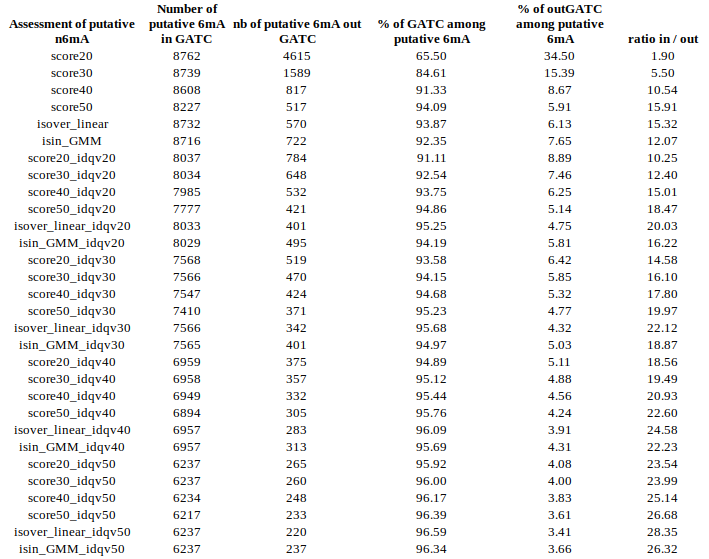
- Almost 100% of GATC sites are methylated
- Vast majority (>95%) of the methylation is located in the GATC sites
-
1.6% of adenines are located in a GATC site
- ~ 1.6% of adenines should be methylated
-
Most strains: ~20.000 GATC sites
- x% symetrically methylated (?)
-
Some methylation outside GATC
- maintained by specific motif-driven enzymes
Paramecium is fed with E. coli
GATC
CTAG
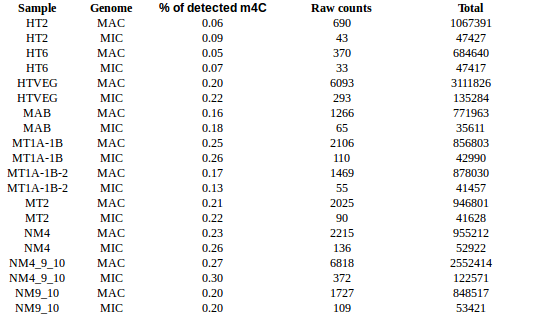
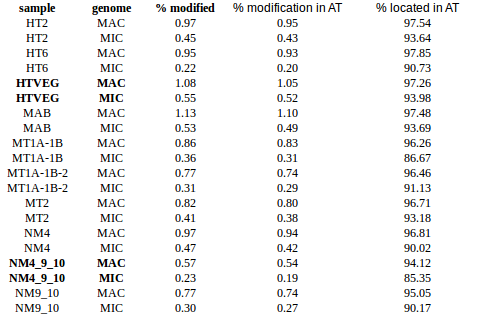
experiment HT2 1 HTVEG 926 MAB 487 MT1A1B 1131 MT1A1B2 222 MT2 166 NM4 468 NM4910 138 NM910 357
Available data for E. coli
-
HT2/6: Starved !
-
1.702% of A are in a GATC site
-
Nb GATC sites: 4672
Number of consensus which mapped with >99% accuracy on a common strain reference genome
inside GATC
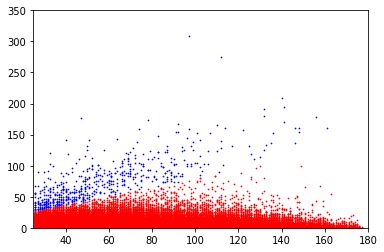
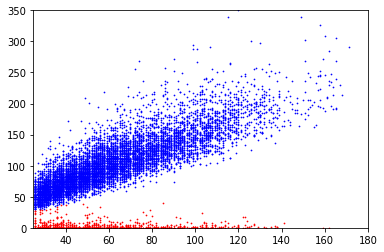
covscore plots of bases above the linear separator in E. coli
outside GATC
Only adenines with coverage>25X are considered
Coverage
Score
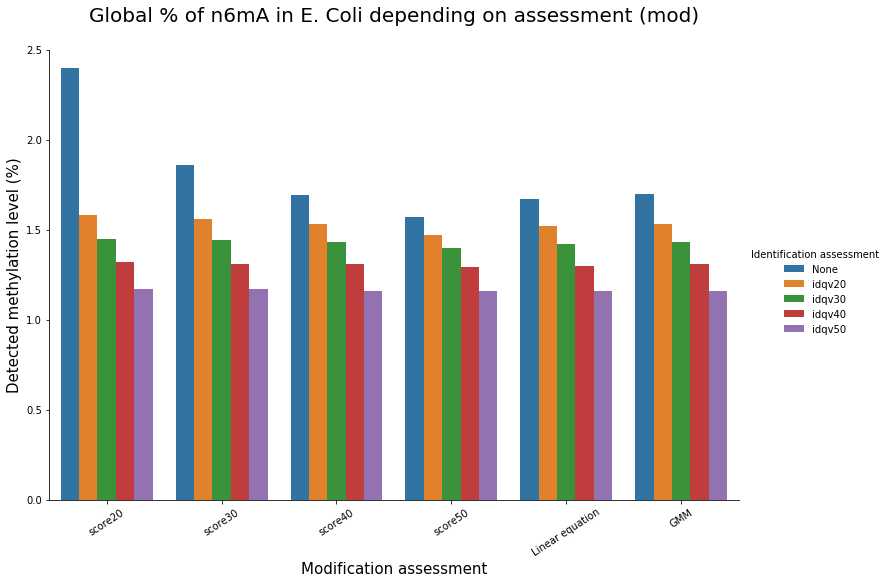
Methylation level (E. coli)
inside VS outside GATC (E. coli)
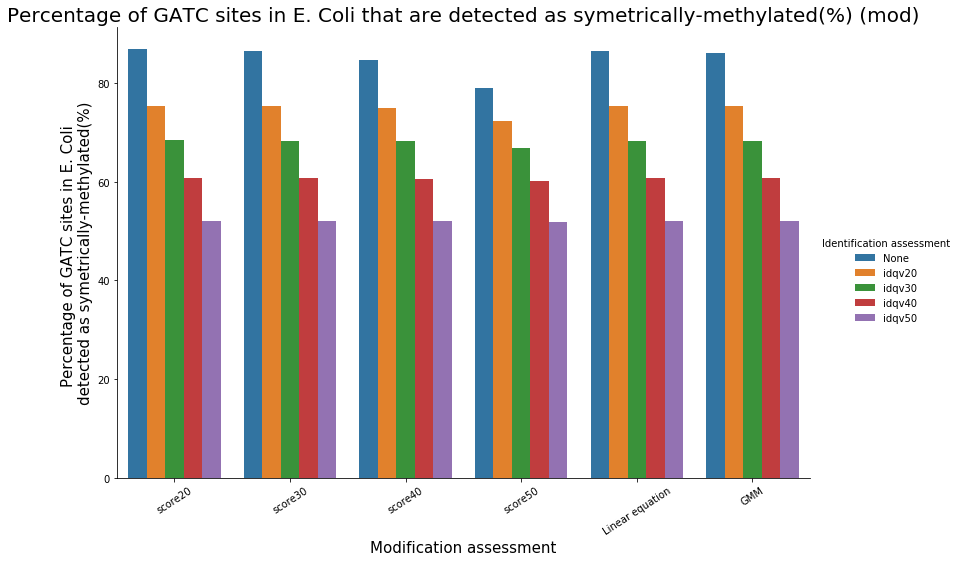
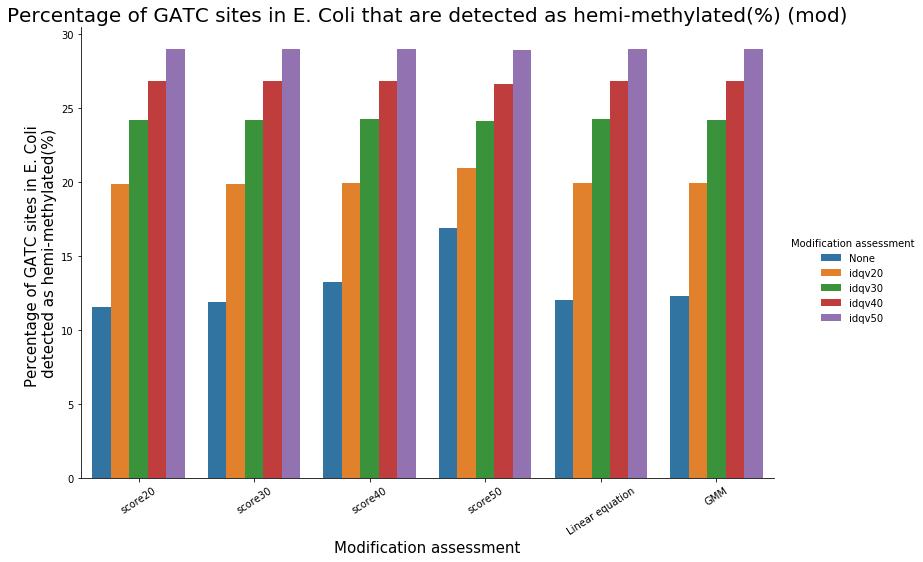
Identification assessment
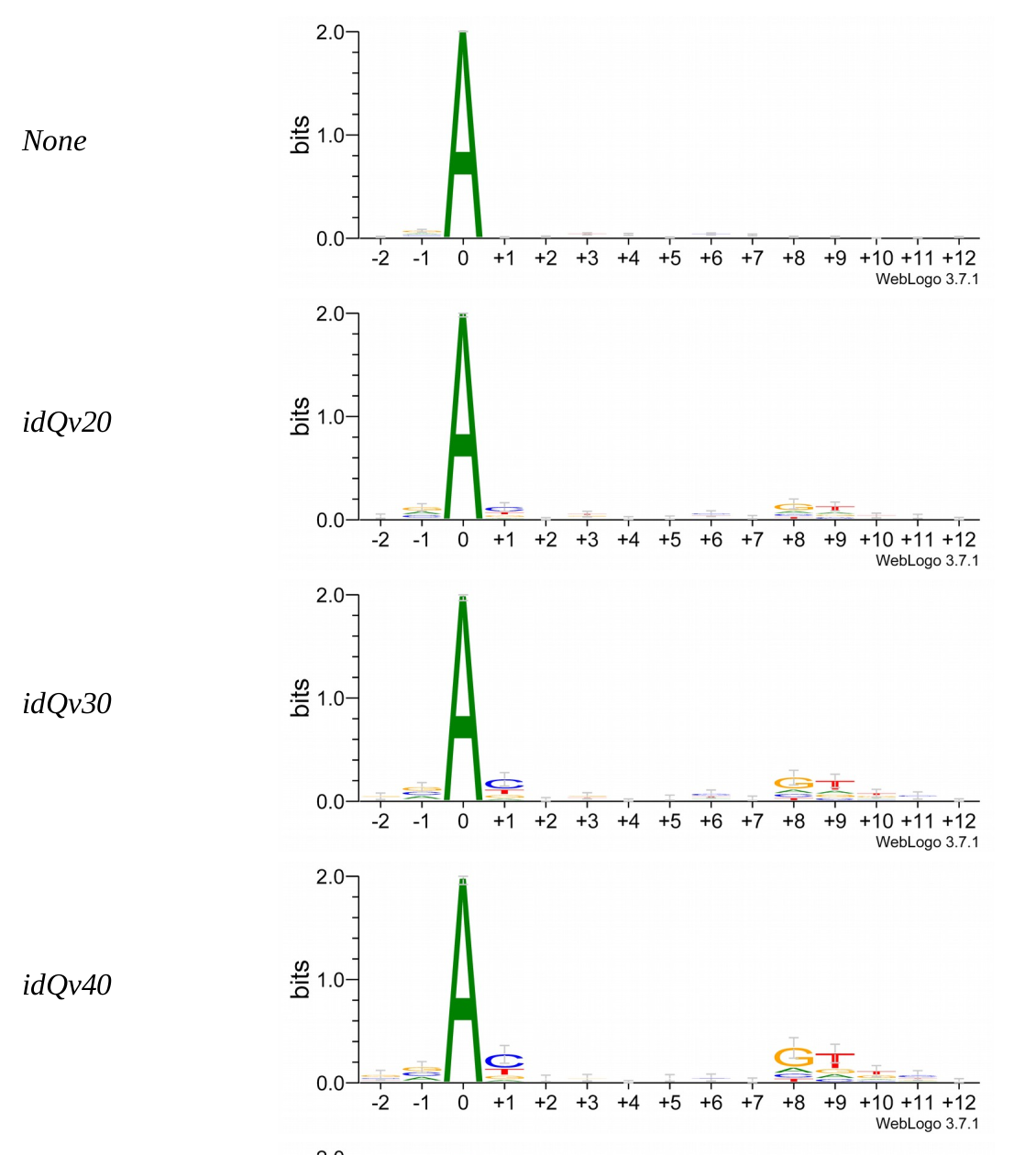
Methylation outside GATC sites
Modification assessment: Score20
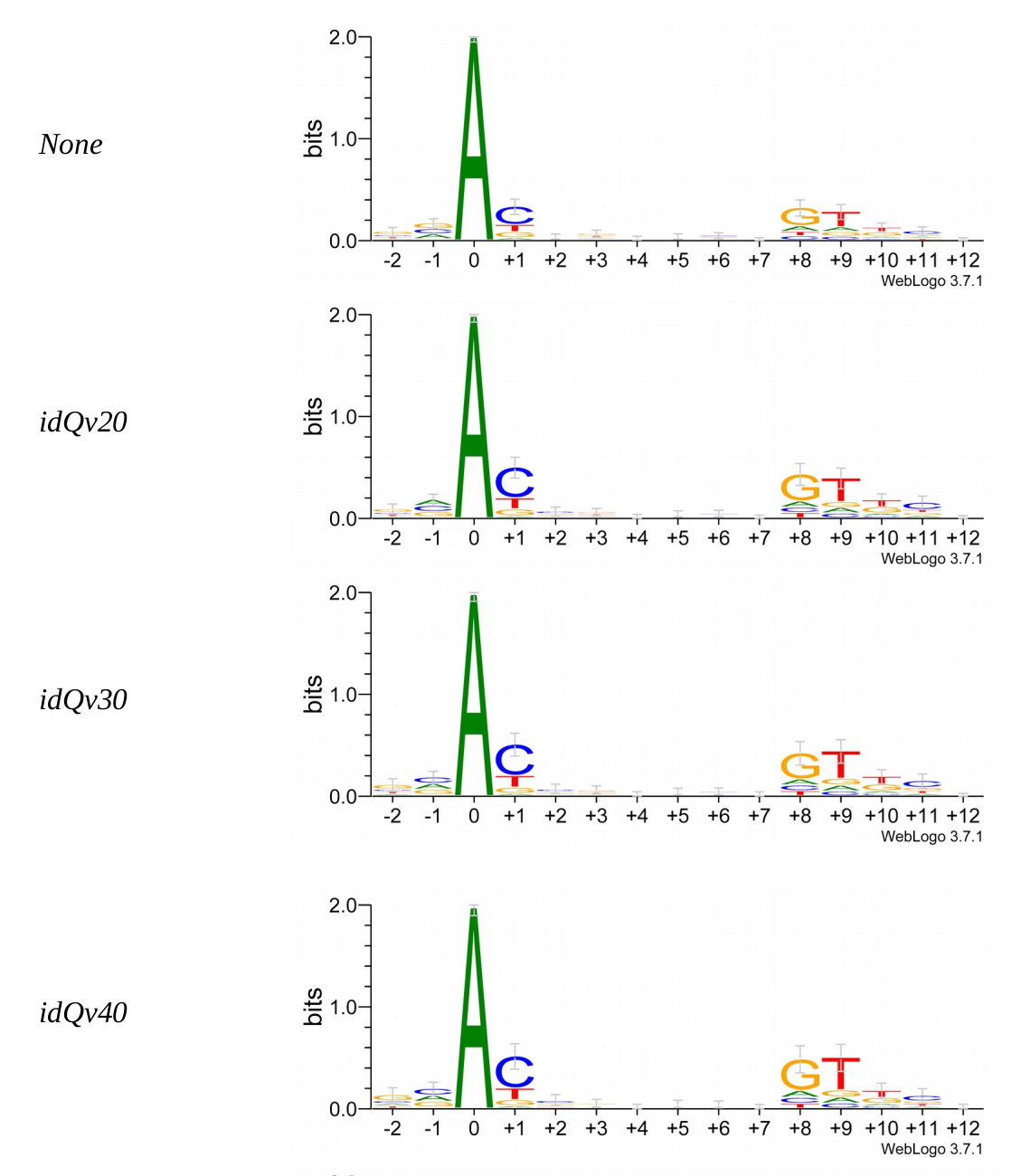
Methylation outside GATC sites
Modification assessment: Linear equation
Conclusion on E. coli
- From what we expected:
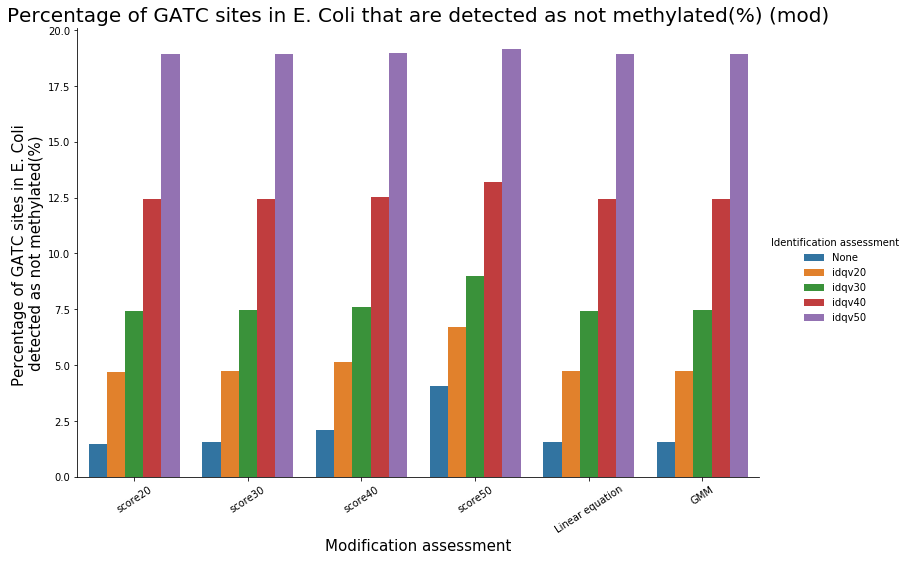
- Never 100% of GATC ! Only ~ 75% symetric
- ~ Global methylation as expected
- Motif-driven outside GATC as expected
-
Ratio in/out GATC ~ expected
- We also learnt:
- LInear equation > GMM > Flat threshold
- Seeking rare events requires higher specificity
-
Adding any idQv provide much higher specificity
Conclusion on E. coli (2)
-
We can draw only quite limited conclusions:
- Digested DNA ?
- Unconsistent litterature
- Specific methylation of this E. coli strain ?
Se, Sp remain +/- unknown
In a perfect world
In an ideal world:
p-value
SMSN n6mA testing
Prior knowledge of FDR
Assessed with Se, Sp and A priori on litterature
FDR control based on A priori knowledge
+
Likelihood ratio between different hypothesis
DNA n6mA
Analysis of Paramecium tetraurelia
Enfin !
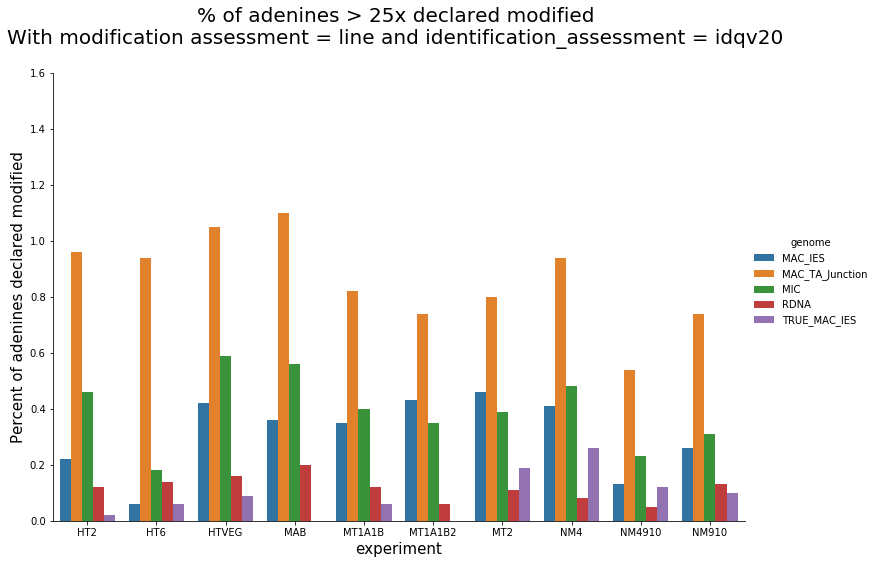
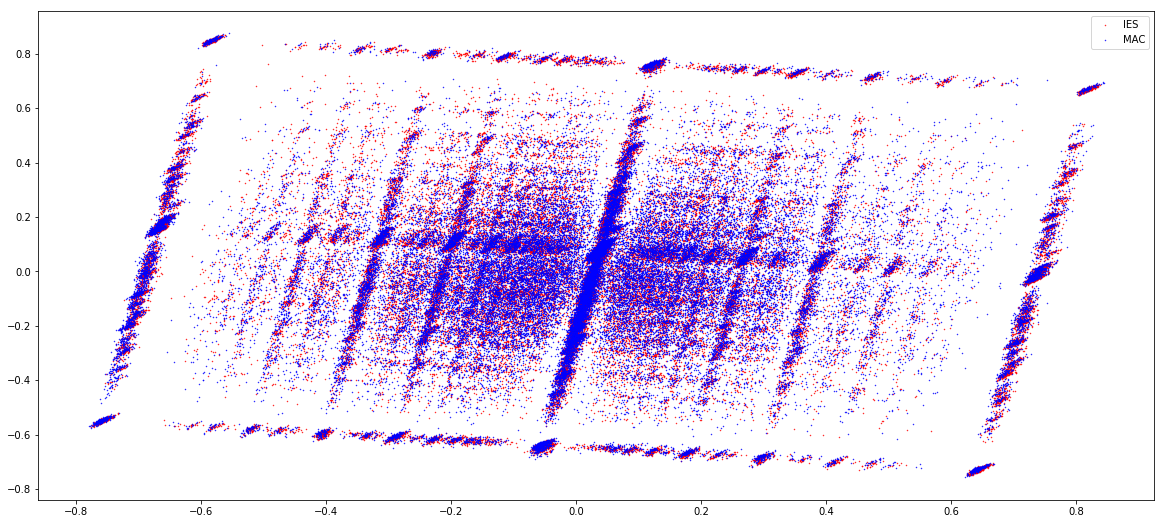
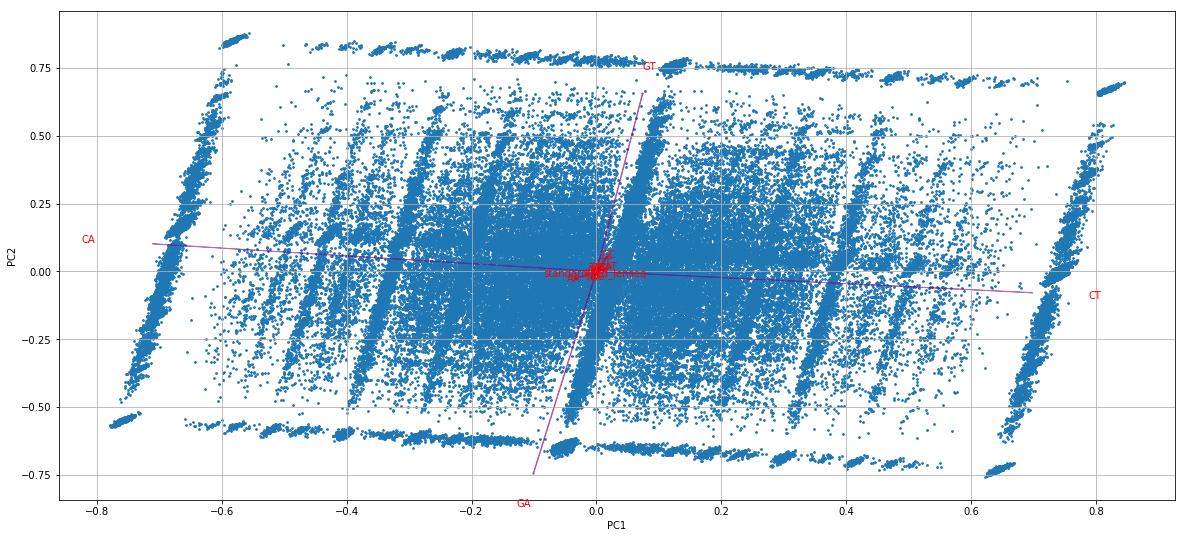
Per experiment comparaison (1)
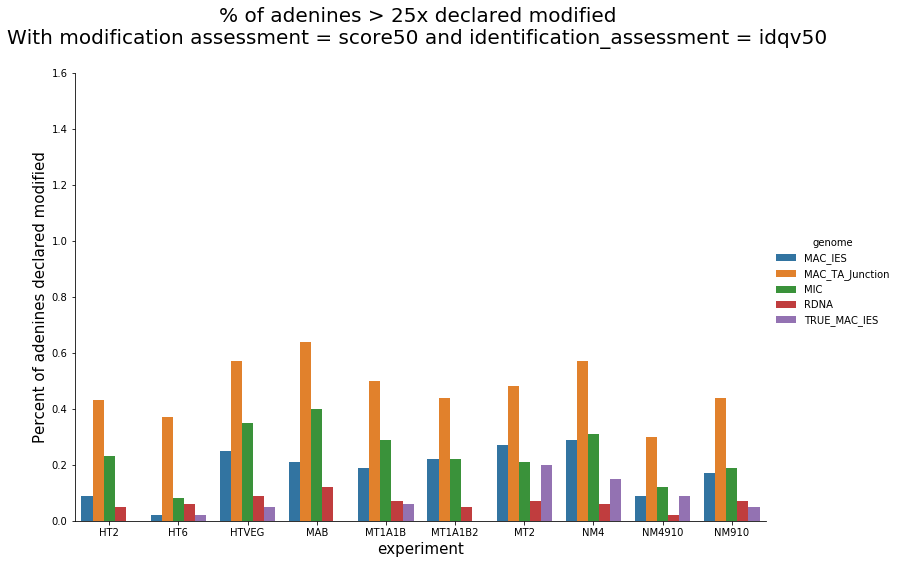
Per-experiment comparaison (2)
In the vegetative MAC
-
~95% of the methylation locates in AT dinucleotides in the MAC(*)
-
slightly lower in the MIC (5 to 5 points less)
-
True in any condition
-
-
75% of the methylation in an AT dinucleotide is actually symetrically modified, independantly from being in the MAC or the MIC(*)
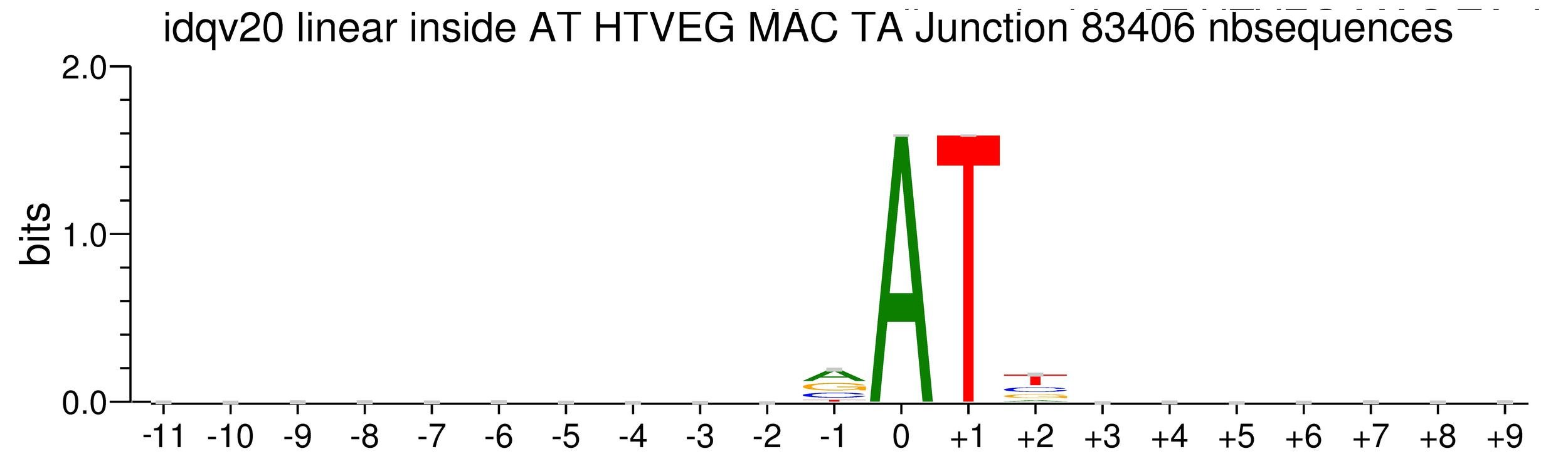
Kept in MIC and MAC (All conditions)
(*) Linear equation / idQv20
Outside AT sites
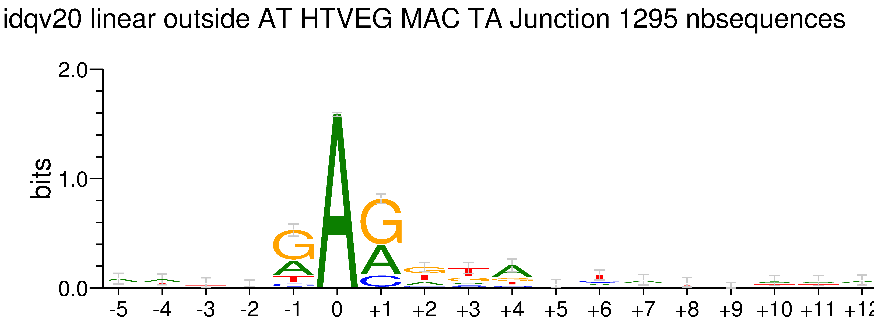
Kept in the MAC for all experimental conditions
Impossible to tell in the MIC (not enough sequences)
In the MAC
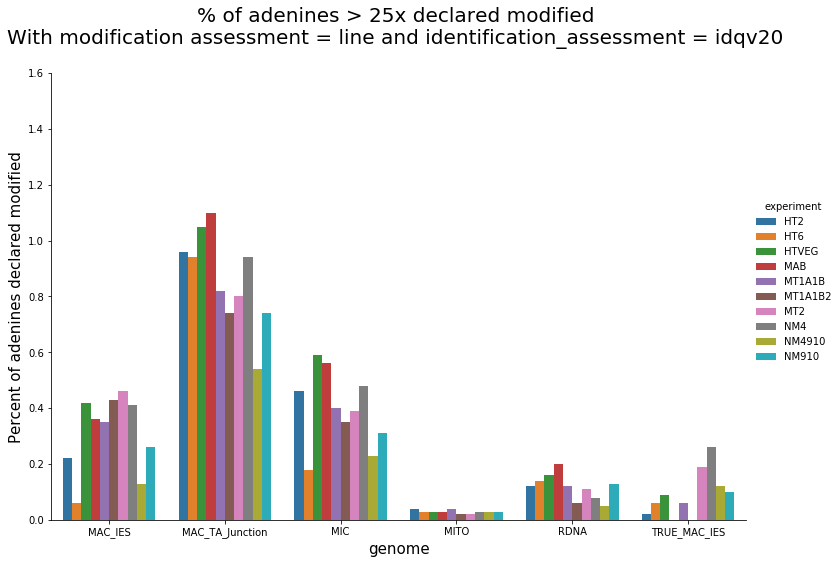
Per genome comparaison
mDNA
42% GC
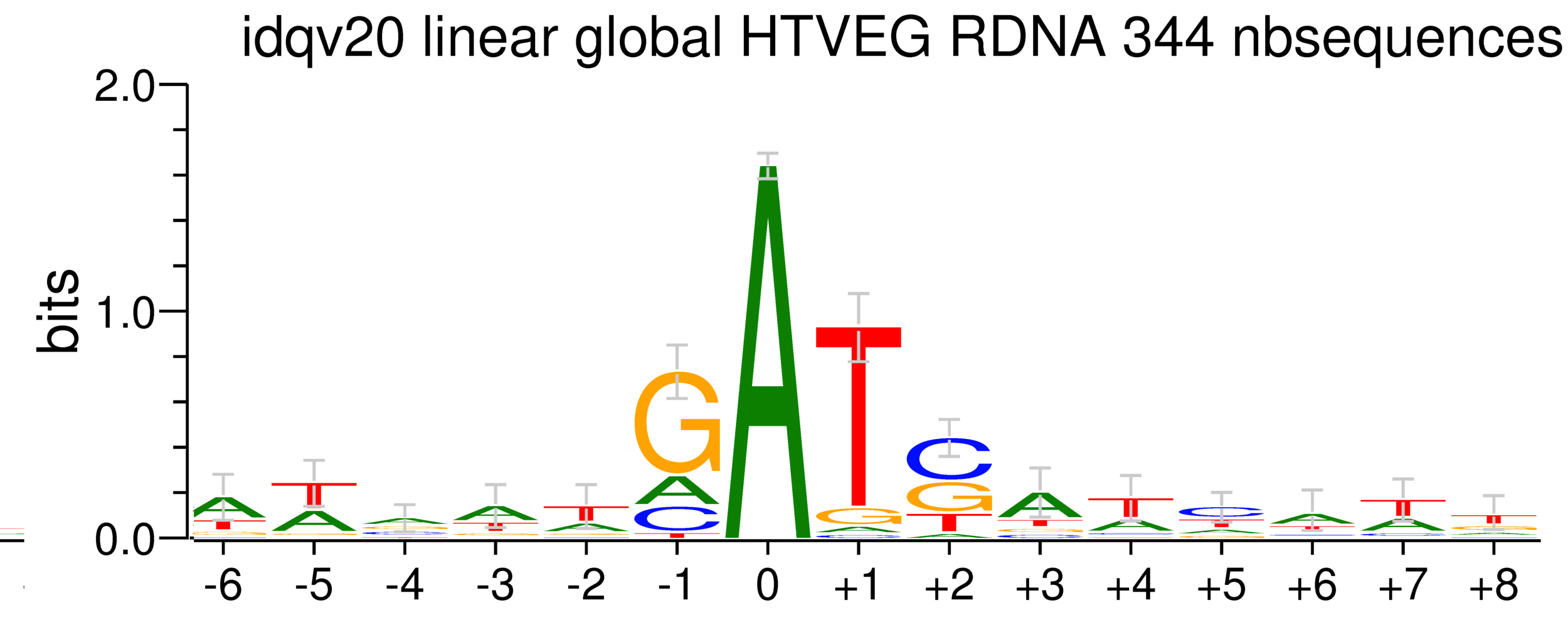
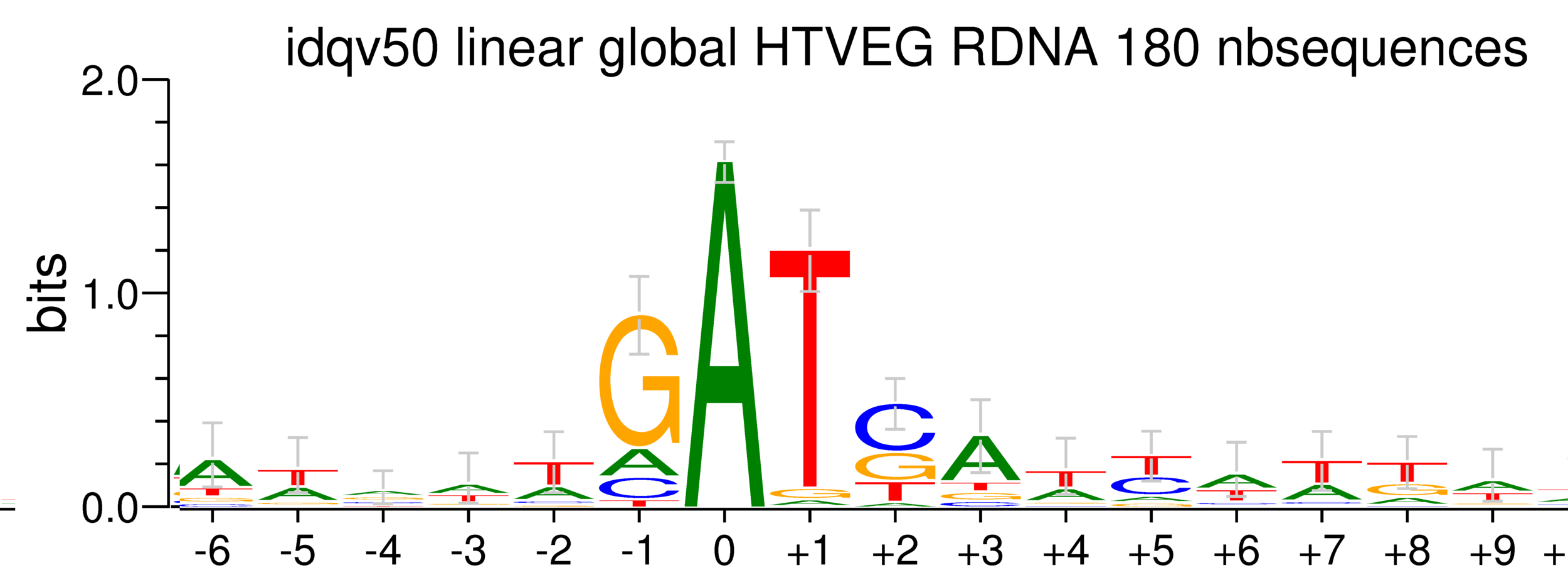
rDNA
38% GC
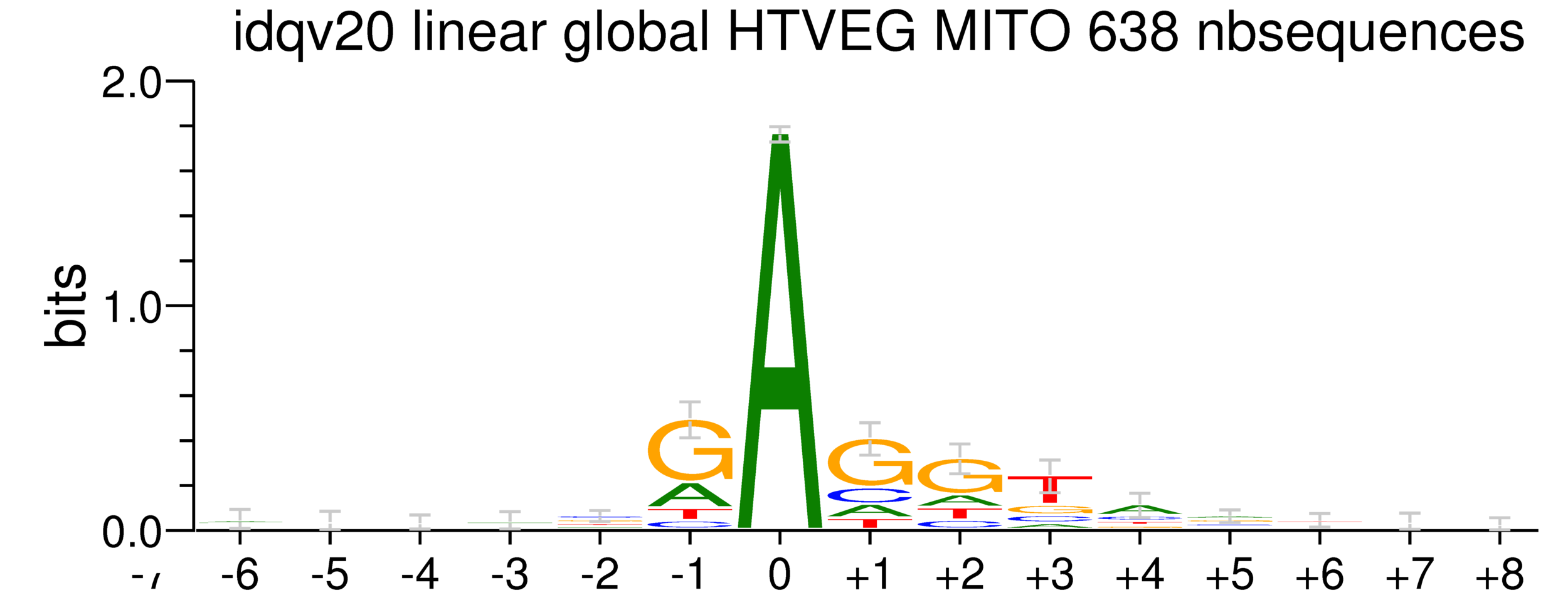
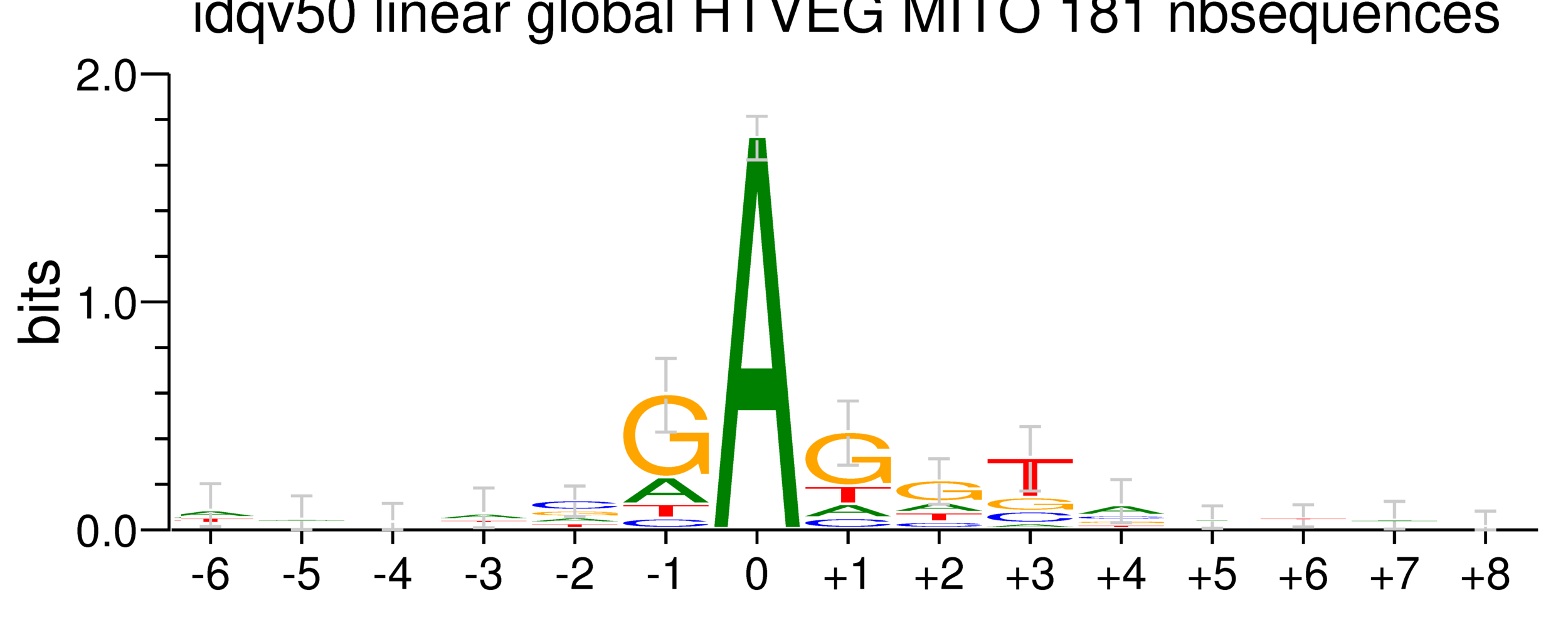
5. Investigation on m4C

Logo from HTVEG MAC
Identical everywhere
Conclusion
Many methodological advances:
- Sorting of the sequences
- SMsn in-sillico Pipeline
- Thresholding of n6mA f(coverage)
- Deeper understanding of FDR and its bayesian consequences with E. coli
On Paramecium:
- MAC methylation refinement
- First time we have an insight into IES in the MIC
- MIC methylation could only be due to MIC sequences retained in the MAC
- 4mC ?
Perspectives
Short-term
- Methylation of Scan-RNA dependant VS independant IES
- Filtering the MIC on the retention level ?
- Investigate the differences between the silencings and the vegetative state
Mean-term
- FDR procedure with a priori ?
Later: Quit PacBio SMRT
- Content of IES (already started but stopped)
- New nanopore sequencing
- mtF-like proteins sequencing en cours

Sorry for the headaches !! Thanks for your time :)
Thanks !

Additionnal

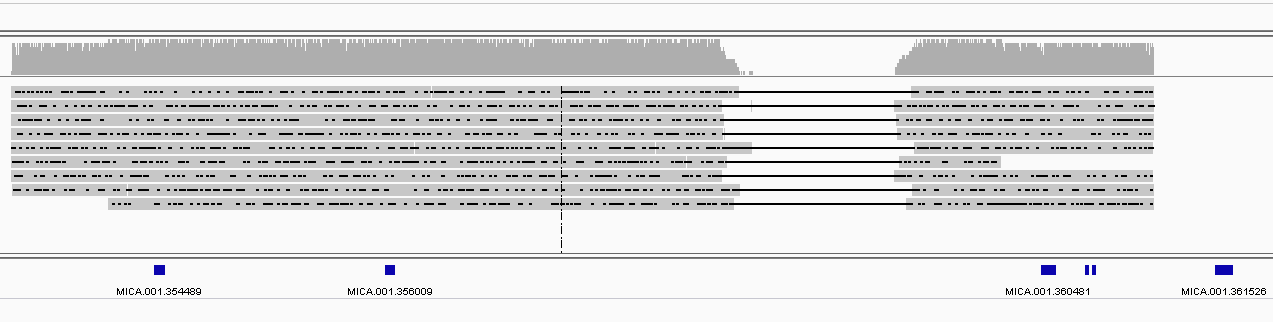
Output example

IESs (1 & 2)
MAC (1 & 2)
GMM + idQV20
- Raises the % located in AT
- Methylated fraction goes down to 0.9-1%
- NM4-9-10 goes down to 50% in the MAC
- Logos don't change significantly


Logo from HTVEG MAC
Identical everywhere
Laura landwebehr 2020
Oxytrichia trifallax
Modifications in AT/TA
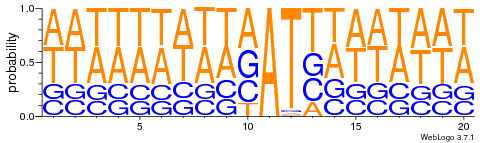
- 95% AT
- Same MIC/MAC in AT
- No difference between experiments
- ~75% methylated symetrically

Modest variations in the silencing
FIndings in cytosines


Logo from HTVEG MAC
Identical everywhere
Modifications out AT
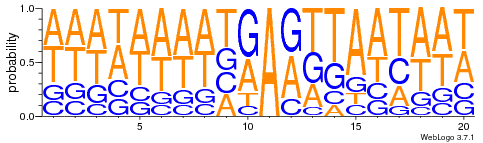
What interests us most
We didn't find no difference between experiments
Sexuated reproduction in Paramecium
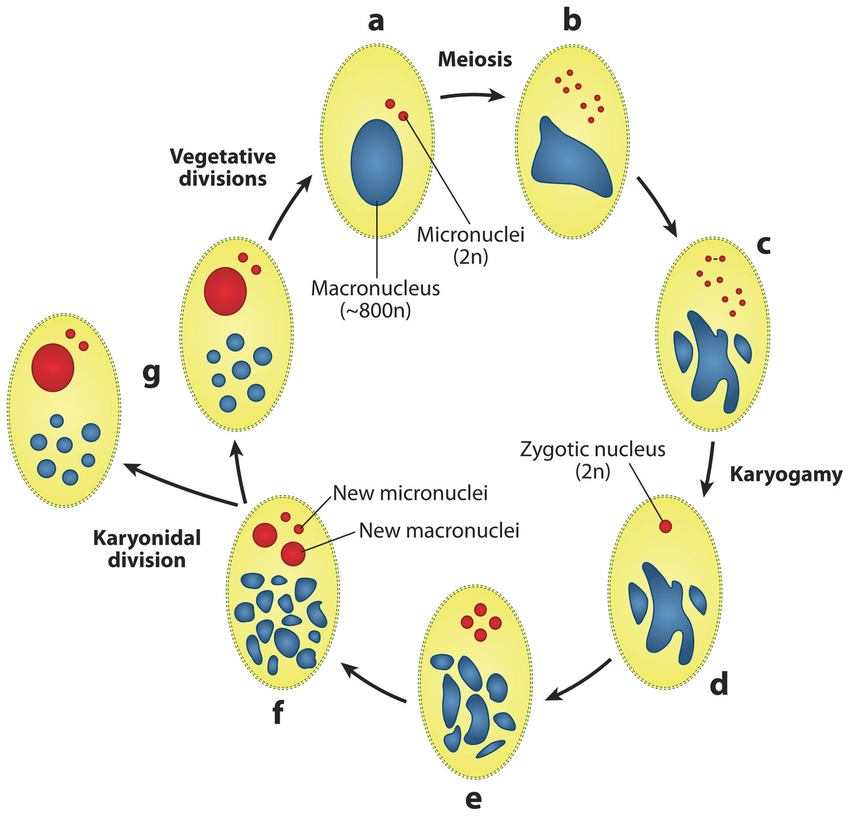
The old MAC (maternal) drives everything during the formation of the new one:
- Active transcription
- Sexual determination (RNA)
- Excision of IES
= Non-mendelian / Cytoplasmic heridity
p values (A)
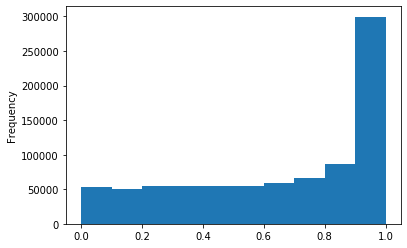
p-values (A score >20)
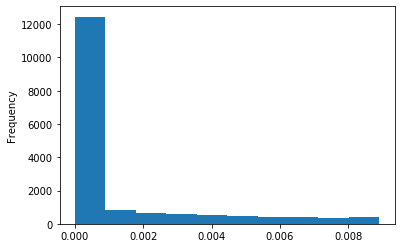
Out GATC score < 20
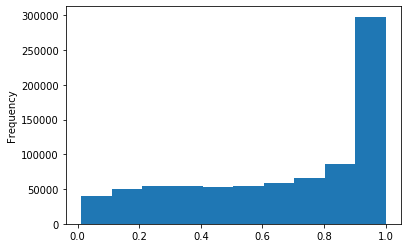
Out GATC
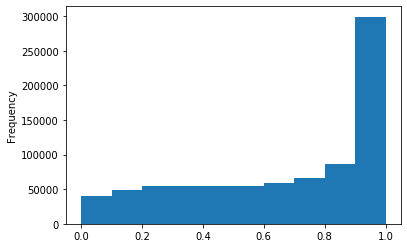
ipdRatio score 20
ipdRatio idv20/score20
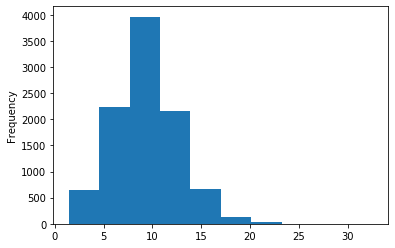


A outAT score 20 isQv20 (812 seq)
A outAT score20 idQv20 + Strong BH correction (176 seq)
ipdRatio out GATC before filtering BH vs after (qv20/idqv20)
In GATC

2.1 Retroingineering
A lazy polymerase
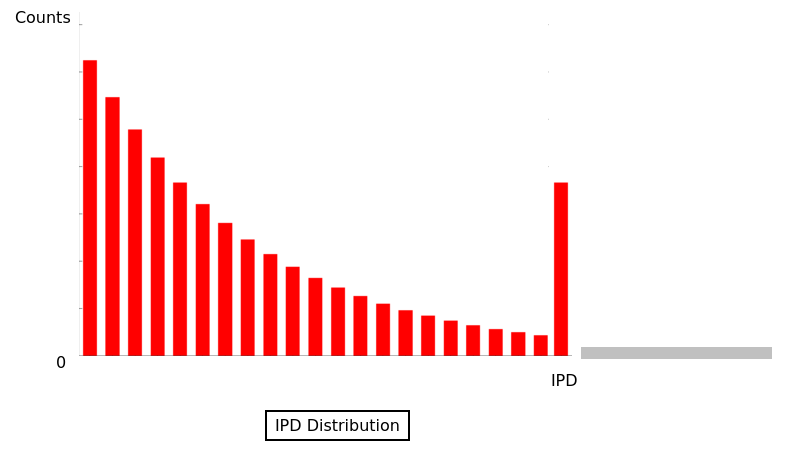
- Pauses
- Not related to DNA methylation
- Averaging is impossible with the pauses
- Outliers that must be removed
After rigorous checking, I stated that the capping as implemented was not a problem for our SMSN approach
2.1 Retroingineering
The capping of IPDs
-
modelPrediction is the predicted IPD value by the model in a given context of nucleotides at this position
-
globalIPD is the mean of all the IPD values of the read.
-
localIPD represents all IPDs that have been mapped at a given position in the genome, including those from other sequences
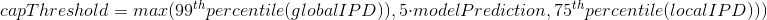
Conclusion on the capping
- Isn't coded as advertized by PacBio
- The way it's implemented for AggSN is problematic and doesn't really make sense
- Paradoxally, it should be more relevant for our approach than for the default one
- We expect no methylation to be undetected due to the capping
2.1 Retroingineering
In-sillico control: ipdtools
- In-sillico control = Prediction of the polymerase speed (IPD)
- Black box
- Impossible to use without PacBio's default software !
Recently, I have coded ipdtools. It predicts:
- Any IPD of unmethylated sequence
- With any PacBio's chemistry (RSII, Sequel I, Sequel IIv2)
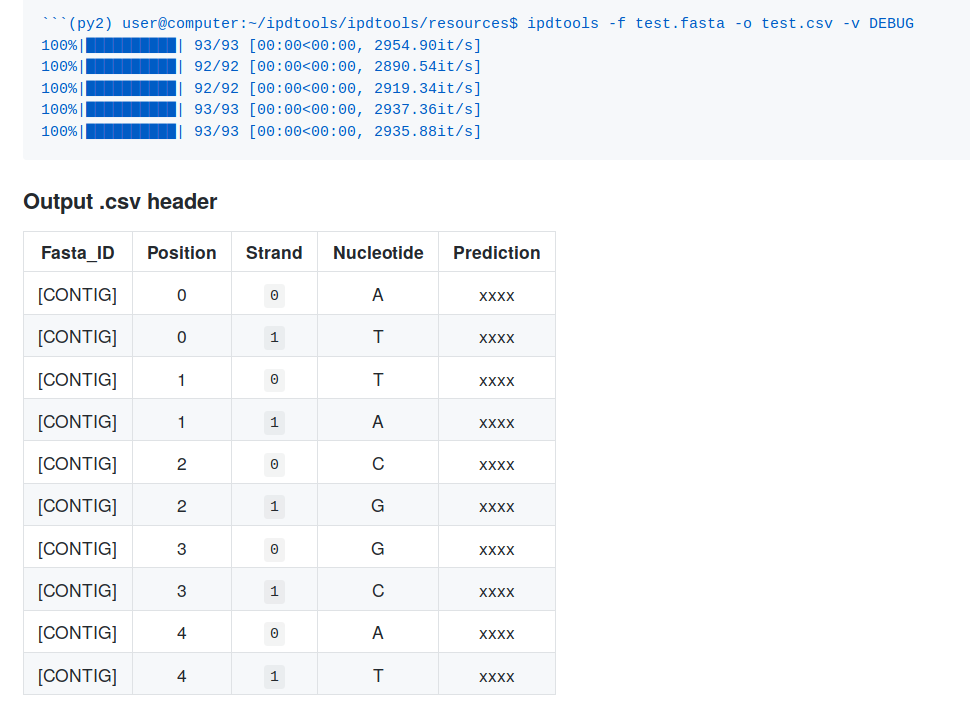


2. Understanding / Retroingineering of PacBio's softwares
Motivations
- REMINDER :
- No tool existed for our kind of analysis:
- SMSN
- In-sillico control
- .bam format PacBio Sequel I
- We had to develop our tools
- First idea = Just customize the PacBio pipeline
Main problems encountered:
- The capping of IPDs
- Use the in-sillico model
3. Developping our own pipeline
Problems that we solved:
- Launch the methylation analysis program for each molecule separately
- Produce the right inputs (headers, indexinf files, etc)
- Produce outputs even in case there is no modification found
- Parallelize everything
- Optimizations on the alignment process
Develop our own pipeline with PacBio's tools


"smrtrue"
Private Github repository
AggSN or SMSN ?
Within the total DNA:
- MAC/MIC dna ratio = 200:1 --> Random sampling
- We don't want to mix MIC and MAC information
- We must use the SMSN method !


SMSN implemented on Github by J. Beaulaurier
But:
- Old RSII data
- Doesn't support new formats
- Very concerning bugs
- Doesn't work with in-sillico control (which is not benchmarked)
Using SMSN in our case is mandatory but also new, and requires to develop our own tools
--> "true_smrt" python package
Section seminar
By biocompibens
Section seminar
lightened
- 101



