Elasticsearch

How search works

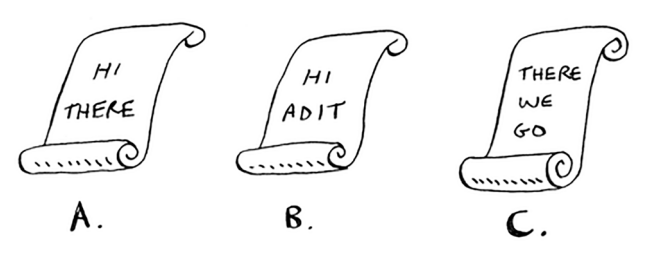
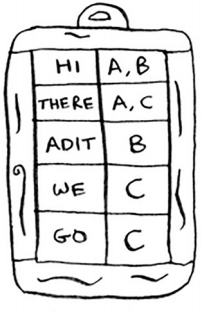
=>
Source: Grokking Algorithms - An illustrated guide for programmers and other curious people
Inverted Index
Data structure mainly used by search engines
Terminology
ES stores documents represented as a JSON document
A mapping is like a schema definition in a relational database.
A type used to represent the type of document, e.g. an email, a user, or a tweet. Types are deprecated and are in the process of being removed
Let's see :)

ES API
ES API
REST like client :)
ES API
Search API
WE FOUND THE JOKE

Elasticsearch is not for search :)
ES API

Query
Match query: match queries accept text/numerics/dates, analyzes them, and constructs a query.
Term query: The term query finds documents that contain the exact term specified in the inverted index
What is full search?
The operator dilemma @ ING
{
"query":{
"match":{
"message":{
"query":"are pere",
"operator":"or"
}
}
}
}
Query
Analizer: examines the text of fields and generates a token stream.
Tokenizer: break field data into lexical units, or tokens.
Query
Query String
{
"query" : {
"query_string": {
"query": "mer per",
"fields": [
"message"
]
}
}
}
Takeaways
Elasticsearch is for search and is not a joke :)
Working with ES means:
- define mappings toghetter with analizers and tokenizers
- store/index documents
- write a query to get documents
Personal takeaways
A lot of breaking changes in ES releases: not only APIs but also concepts
https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/6.0/breaking-changes-6.0.html
A lot of cool new thinks added :) -> SQL queries
Not a really good documentation
Deep concepts ->
https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/guide/currentQuery DSL
https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch//reference/current/query-dsl.html
ES @ING
ElasticSearch
By Bogdan Posa
ElasticSearch
- 1,026



