更多樹
講師:張秉中
目錄
- 重心樹
- 樹同構
- 換根DP
- 樹背包問題
- 淺談LCT
重心樹
上次講太少了QQ
圖
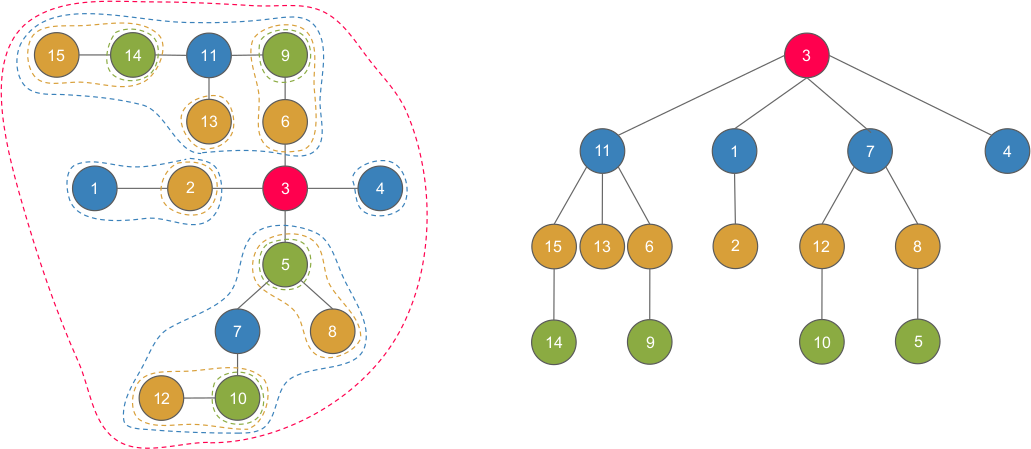
性質
- 深度log(n)
- 重心樹上兩點LCA必定在其路徑上
- 蓋重心樹,在各點記錄到紅點的最短距離,令其為\(ans[u]\)
- 修改\(v\)時沿著重心樹往上改,並且更新最短距離
- 各點距離最近的紅點變為\(min(ans[u],dist(u,v))\)
- 查詢\(v\)時沿著重心往上走,並且計算答案為
- \(shortest =min(shortest,ans[u]+dist(u,v))\)
還可以記錄其他資訊
- 像是該連通塊各點到重心的距離之類的
- 這樣只需要 \(O(NlogN)\)的記憶體
樹同構
問題(cses1700)
- 給兩個有根樹,判斷其是否可以將根結點以外的點重新編號使兩樹長一樣
Hash
ll dfs(vector<int> tree[],int now,int par){
vector<ll> tmp;
for(auto nxt:tree[now]){
if(nxt == par)continue;
tmp.push_back(dfs(tree,nxt,now));
}
sort(tmp.rbegin(),tmp.rend());
ll re = 1;
for(auto &i:tmp){
re*= p;
re += i;
re %= mod;
}
return re;
}重新編號
map<vector<int>,int> mp;
int idx = 0;
void dfs1(int now,int par){
vector<int> tmp;
for(auto nxt:tree[now]){
if(nxt == par)continue;
dfs1(nxt,now);
tmp.push_back(dp[nxt]);
}
sort(tmp.begin(),tmp.end());
if(!mp[tmp]){
dp[now] = mp[tmp] = ++idx;
}
else dp[now] = mp[tmp];
return;
}- 所有點當根試一輪?
- 有一些特殊點數量很少?
- 所有點當根試一輪?
- 有一些特殊點數量很少?
- 選重心當根!(一棵樹最多只有兩個重心)
換根DP
直接看題目
先處理單點的距離和
- 顯然樹DP
- 以要求的點為根且深度為0,答案就是各點深度和
- DP時在各點紀錄深度大小
- 複雜度O(N)
暴力作法
- 對每個點為根都樹DP一次算答案
- 複雜度 O(N^2),爛掉了
觀察
- 假如現在已經以1為跟算完答案了
- 我們以和1相鄰的點算的答案比較
- 以2為例
1
1
1
2
2
2
3
3
4
0
觀察
- 假如現在已經以1為跟算完答案了
- 我們以和1相鄰的點算的答案比較
- 以2為例

0
2
2
1
3
1
4
4
5
1
觀察
- 假如現在已經以1為跟算完答案了
- 我們以和1相鄰的點算的答案比較
- 以2為例

0
2
2
1
3
1
4
4
5
1
觀察
- 當我們把根從u變成v時,以u為根時v的子樹所有點深度會-1,其他點的深度會+1
- 令f(u)表示以u為根時的深度和
- 可以推得,f(v) = f(u)-size(v)+(n-size(v))
於是,我們得到一個算法
- 先以任意點為根(通常選1)樹DP一次,算一個點的答案以及各點子樹大小
- DFS第二次
- 第二次DFS經過點u時用u的父節點的答案計算u的答案
流程

3
1
5
1
4
1
2
1
1
10
19
流程

3
1
5
1
4
1
2
1
1
10
19
19-3+(10-3) = 23
23
流程

3
1
5
1
4
1
2
1
1
10
19
23-1+(10-1) = 31
23
31
流程

3
1
5
1
4
1
2
1
1
10
19
23-1+(10-1) = 31
23
31
31
流程

3
1
5
1
4
1
2
1
1
10
19
19-5+(10-5) = 19
23
31
31
19
流程

3
1
5
1
4
1
2
1
1
10
19
19-5+(10-5) = 19
23
31
31
19
21
27
36
27
28
做完了!
- 複雜度:O(N)
其他換根DP
樹背包問題
先看題目
一些觀察
- 會形成一棵樹,節點的父節點是直接先修課
- 把沒有直接先修課的點想成接到0號點
- 所求就是以0為根大小為m+1的樹的最大權重和
考慮樹DP
- 另DP(u,i)表示u的子樹選<=i個包含u的最大權重和
- 令u為v的父節點
- dfs的同時計算個節點的DP(u,i) for 1<=i<=m+1

考慮樹DP

0,5,5,5,5,5
考慮樹DP

0,5,5,5,5,5
0,4,4,4,4,4
0,2,7,7,7,7
考慮樹DP

0,5,5,5,5,5
0,4,4,4,4,4
0,2,7,11,11,11
code 大概長這樣
const int mxn = 303;
vector<int> tree[mxn];
int dp[mxn][mxn]
void dfs(int now,int par){
for(auto nxt:tree[now]){
if(nxt == par)continue;
dfs(nxt,now);
for(int i = mxn-1;i>=2;i--){
for(int j = 1;j<i;j++){
dp[now][i] = max(dp[now][i],dp[now][i-j]+dp[nxt][j]);
}
}
}
}
複雜度
優化
sz紀錄目前的子樹大小
const int mxn = 1010;
vector<int> tree[mxn];
int dp[mxn][mxn];
int sz[mxn];
void dfs(int now,int par){
sz[now] = 1;
for(auto nxt:tree[now]){
if(nxt == par)continue;
dfs(nxt,now);
sz[now] += sz[nxt];
for(int i = sz[now];i>=2;i--){
for(int j = max(i-sz[now]+sz[nxt],0);j<=min(i-1,sz[nxt]);j++){
dp[now][i] = max(dp[now][i],dp[now][i-j]+dp[nxt][j]);
}
}
}
}另一種寫法
sz紀錄目前的子樹大小
const int mxn = 1010;
vector<int> tree[mxn];
int dp[mxn][mxn];
int sz[mxn];
void dfs(int now,int par){
sz[now] = 1;
for(auto nxt:tree[now]){
if(nxt == par)continue;
dfs(nxt,now);
for(int i = sz[now];i>=2;i--){
for(int j = 1;j<=sz[nxt];j++){
dp[now][i+j] = max(dp[now][i+j],dp[now][i]+dp[nxt][j]);
}
}
sz[now] += sz[nxt];
}
}題目
Splay
簡介
旋轉
- 把自己深度-1
- 分為左旋、右旋
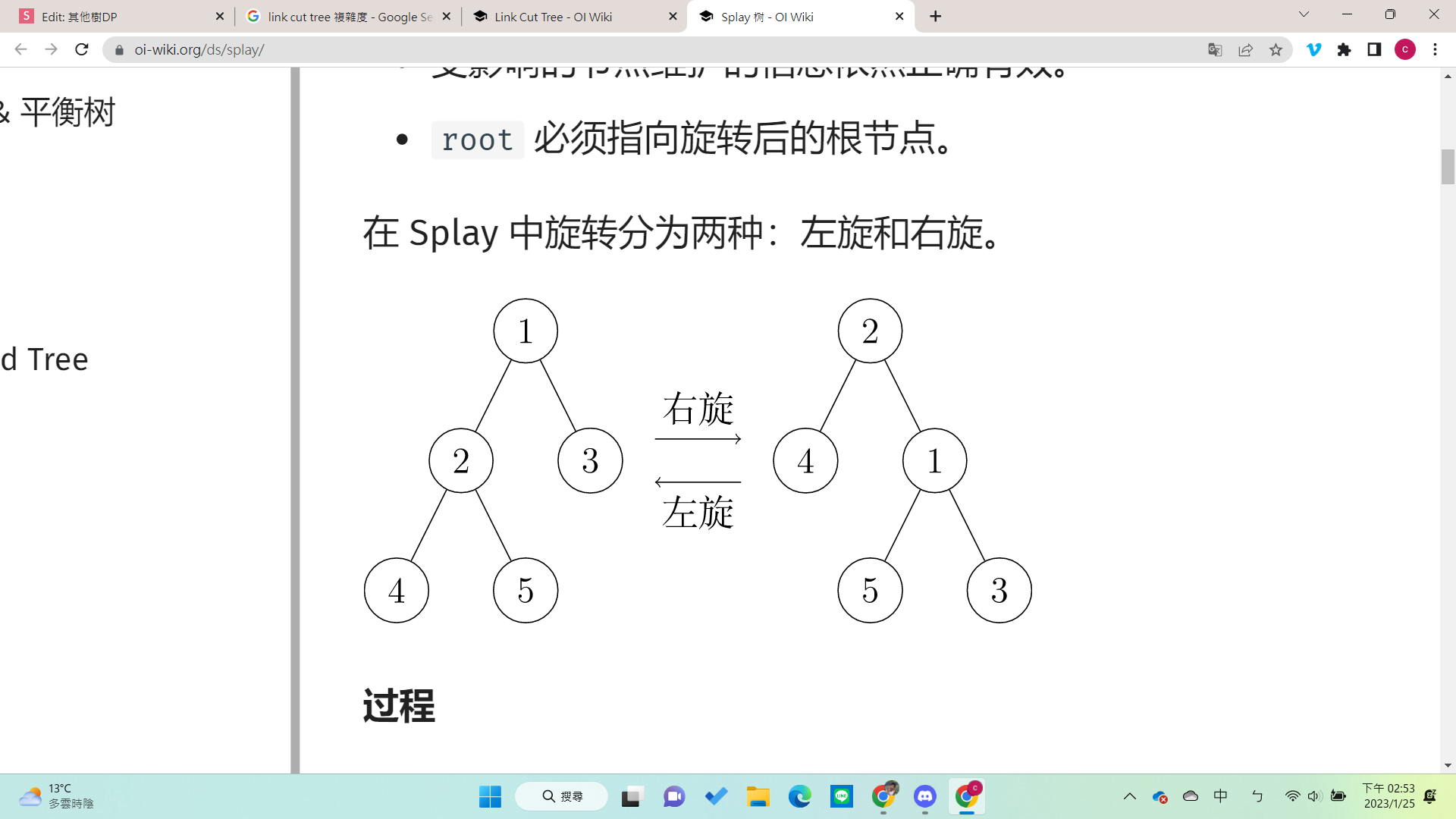
左旋
- rc不動
- f 的右邊變成lc
- p的左邊變成f
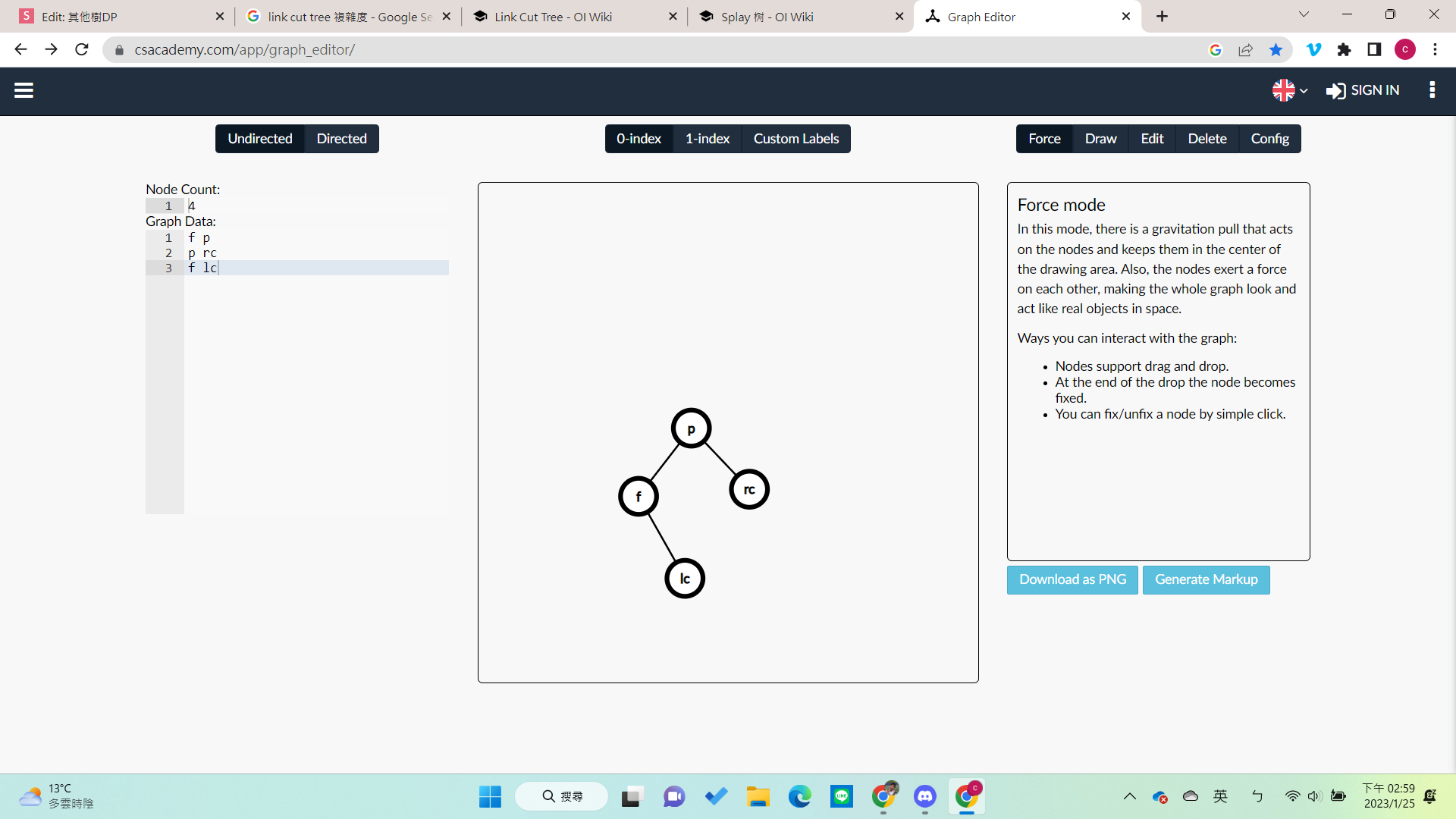
右旋
- lc不動
- f 的左邊變成rc
- p的右邊變成f
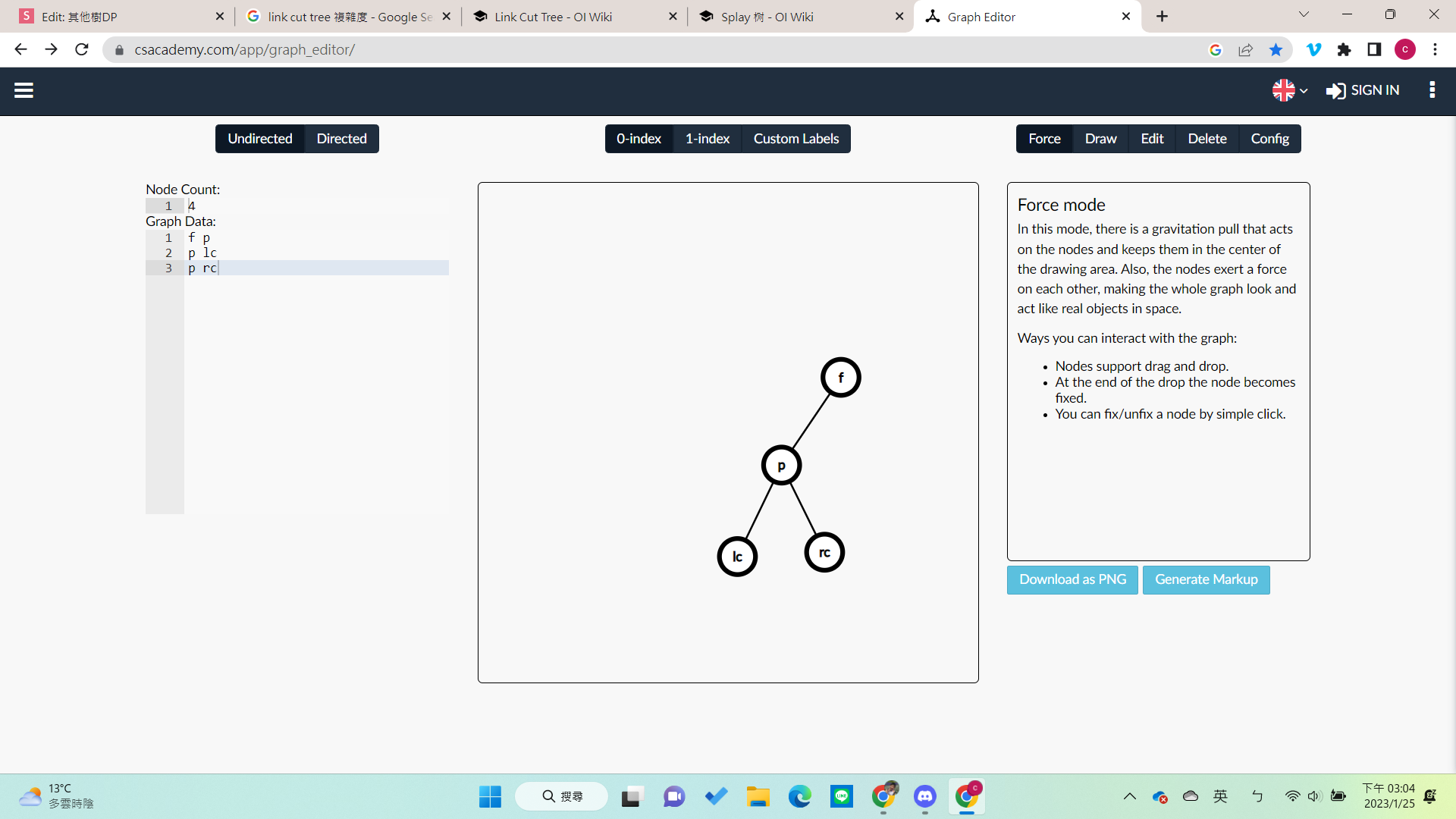
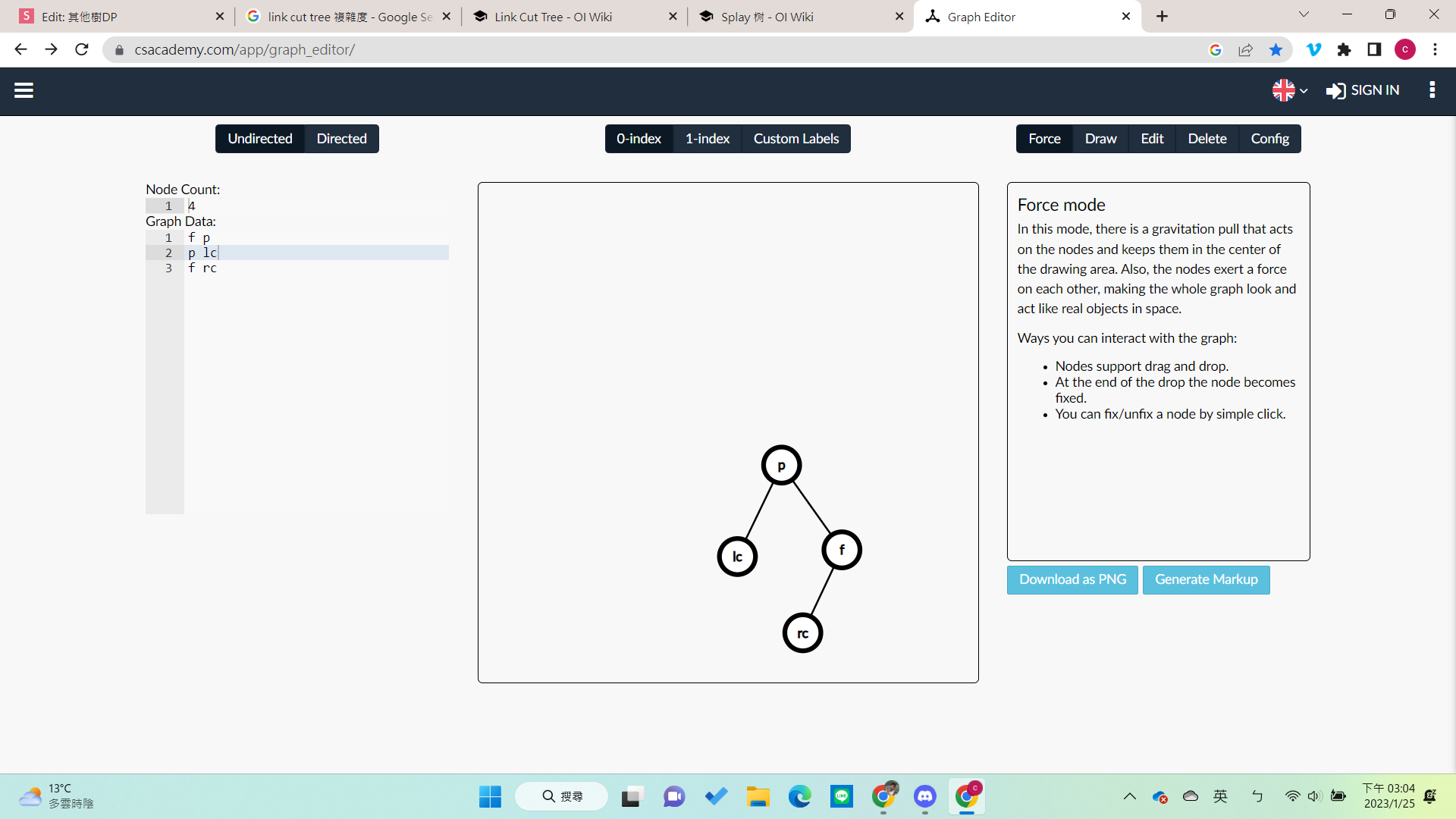
code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int mxn = 2e5+10;
int childs[mxn][2];
int par[mxn];
bool get(int id){
if(!id||!par[id])return 0;
if(childs[par[id]][0] == id)return 0;
else if(childs[par[id]][1] == id)return 1;
else{
cout<<"ERROR "<<id<<endl;
return 0;
}
}
void rotate(int id){
push(par[id]);
push(id);
int lr = get(id);
int p = par[id];
int g = par[par[id]];
childs[g][get(p)] = id;
par[id] = g;
childs[p][lr] = childs[id][lr^1];
par[childs[id][lr^1]] = p;
childs[id][lr^1] = p;
par[p] = id;//注意pull的順序
pull(p);
pull(id);
pull(g);
return;
}splay
- splay的轉動主要就是左右旋這兩種組合成的
- 主要是判自己,父親跟祖父三代的關係來轉
- 分case!
Case 1:沒有祖父
zig
- 直接左旋或右旋把自己變成根結點
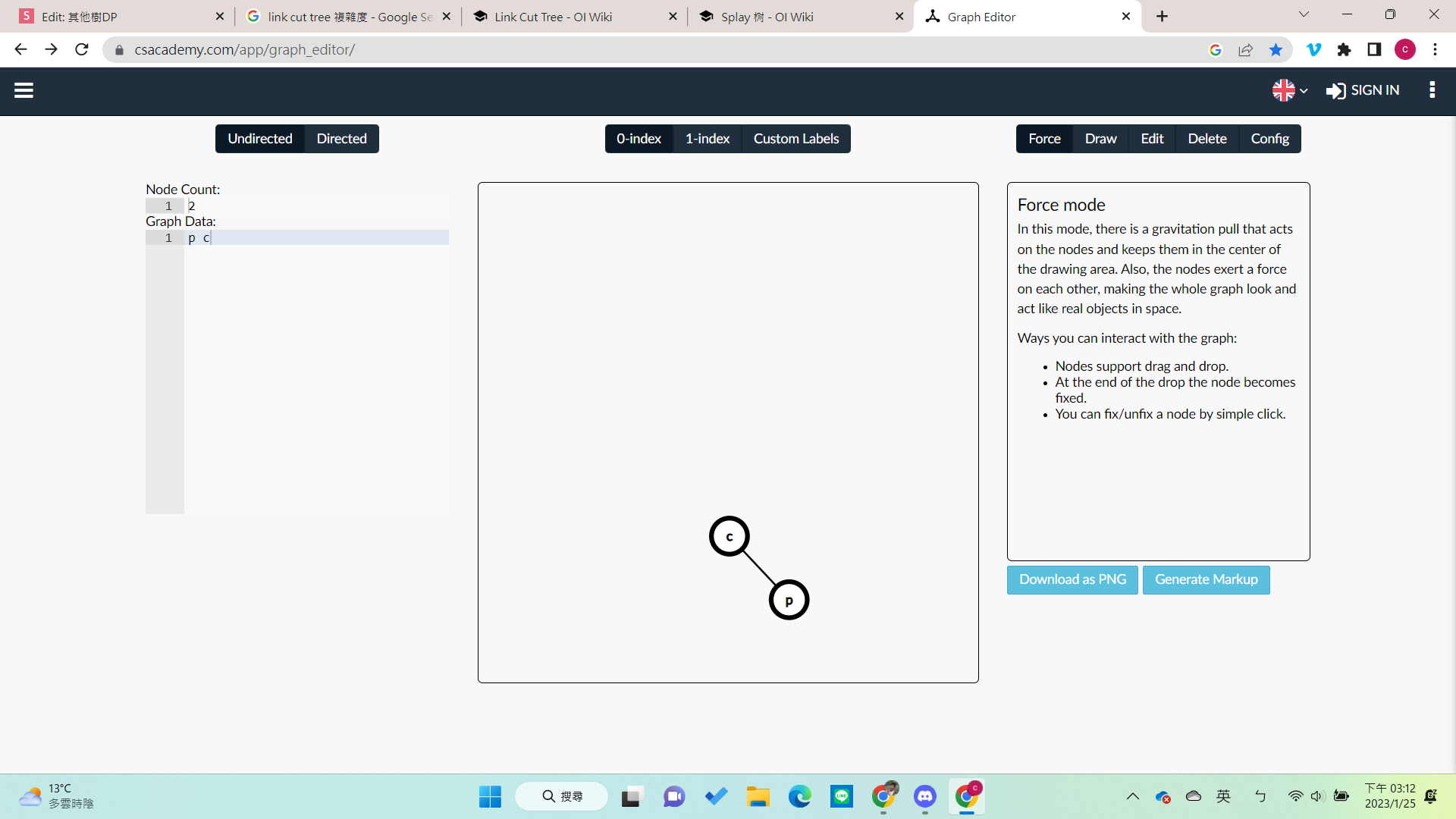
Case 2:祖父跟父親方向相同
zig-zig
- 先轉父親再轉自己
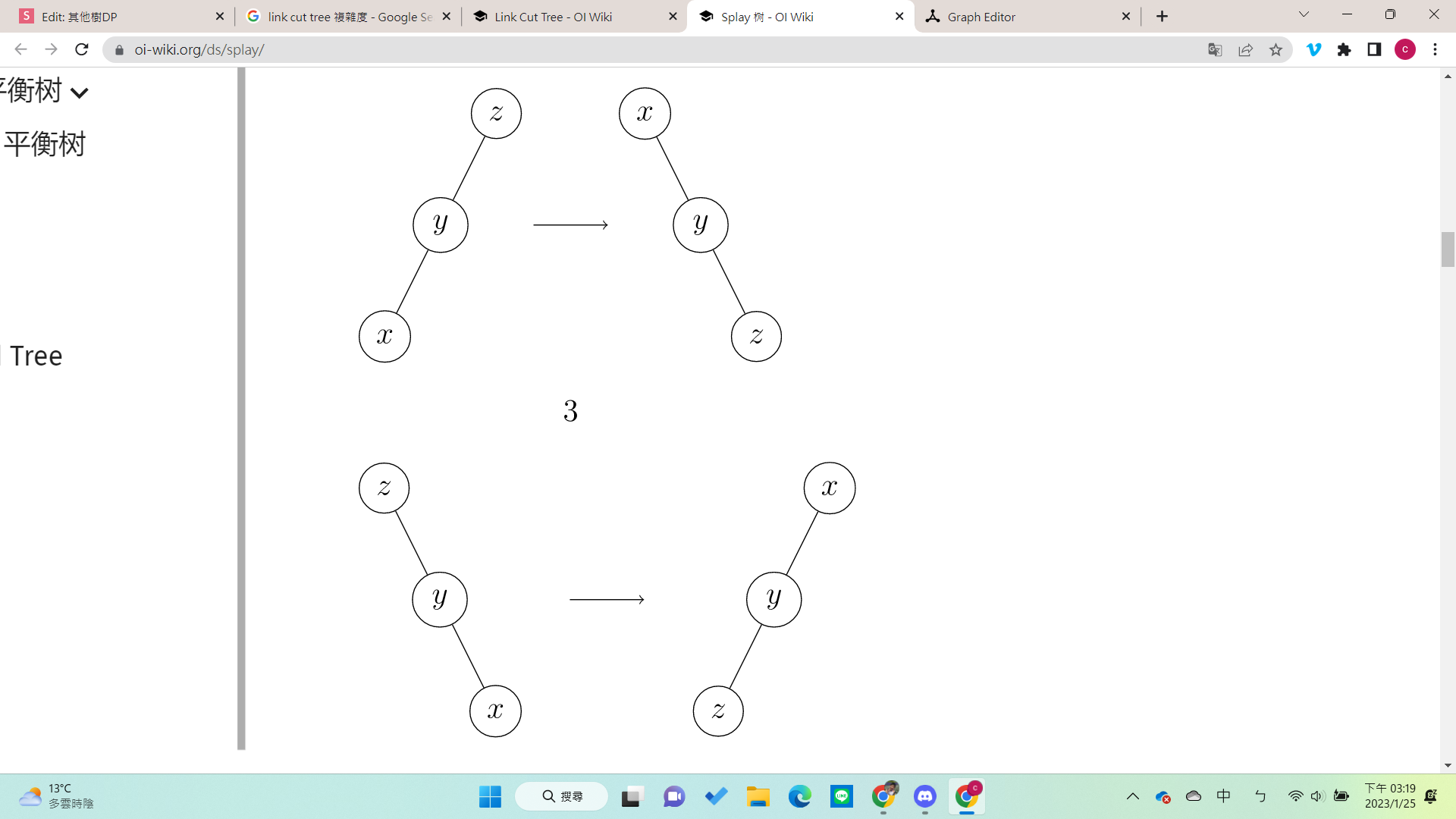
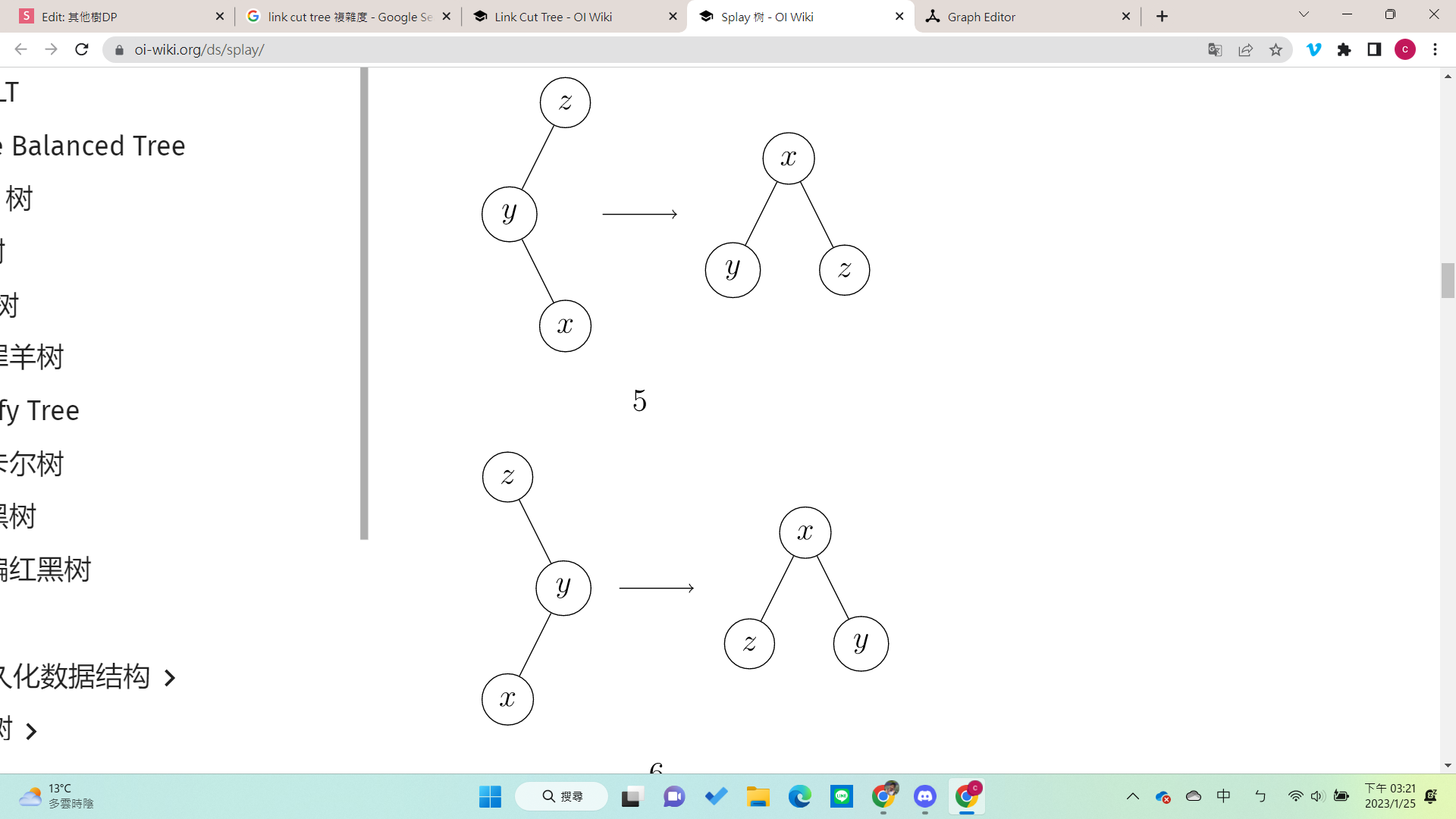
Case 3:祖父跟父親方向相反
zig-zag
- 自己轉兩次
code
void splay(int id){
if(!id)return;
while(par[id]){
if(par[par[id]])push(par[par[id]]);
push(par[id]);
push(id);
if(!par[par[id]]){
rotate(id);
return;
}
if(get(par[id]) == get(id))rotate(par[id]);
else rotate(id);
rotate(id);
}
}
然後pull跟push要記得做
其他性質
- 可以上懶標(轉動的同時push+pull)
- 可以merge,split
- 基本上treap可以做的他應該都行
- 做完所有操作要記得splay一下
複雜度證明
勢能分析
- \(x\)代表一個樹的狀態(長相)
- 令第i次操作所花費的時間為\(c_i(x)\)
- 先假設一個函數\(\Phi_i(x)\)
- 使得\(c'_i(x) = c_i(x)+\Phi_i(x)-\Phi_{i-1}(x)\)
- 則\(\sum_0^t c'_i(x) \ge \sum_0^t c_i(x)\) 的條件為 \(\Phi_{t}(x)-\Phi_0(x) \ge 0\)
複雜度證明
勢能分析
- 在這裡,我們通靈出\(\Phi(x)=\sum log|x|\)(\(|x|\)為子樹大小)
- 然後,我們開始分析三種操作的\(c(x)+\Phi(x)-\Phi'(x)\)
Case 1
zig
\(c(x) = 1\)
\(\Delta\Phi(x) = log|c'|+log|p'|-log|p|-log|c|\)
\(=log|p'|-log|c|(|p|=|c'|)\)
\( \le log|c'|-log|c|(|p'|\le|c'|)\)
\(c(x)+\Delta \Phi(x) \le 1+log|c'|-log|c| \le 3\times (log|c'|-log|c|)+1\)

Case 2:祖父跟父親方向相同
zig-zig
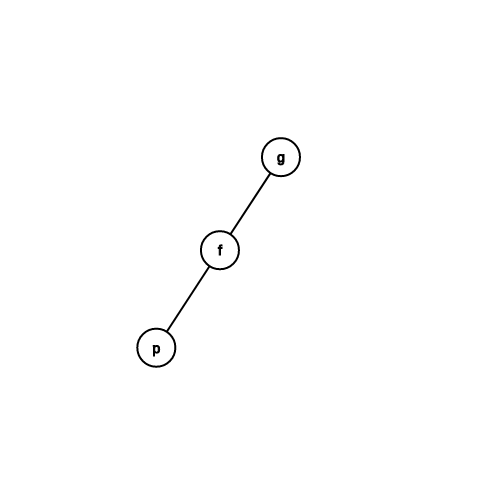
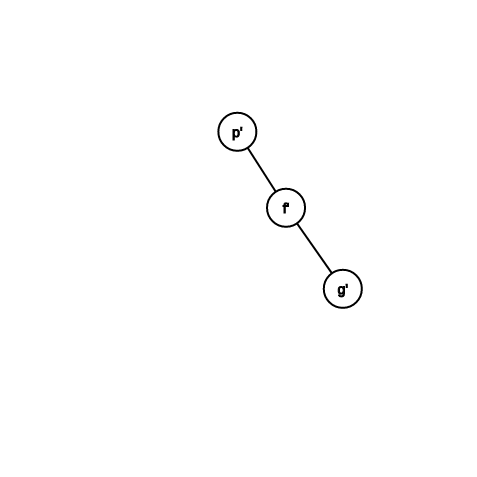
\(c(x) = 2\)
\(\Delta\Phi(x) = log|p'|+log|f'|+log|g'|-log|g|-log|f|-log|p|\)
\(=log|f'|+log|g'|-log|f|-log|p|(|g|=|p'|)\)
\(\le log|p'|+log|g'|-2\times log|p| (|p|\le |f| , |f'|\le |p'|)\)
\(又log|g'|+log|p| \le 2\times log \frac{|g'|+|p|}{2}\le 2\times (log|p'|-1)\)
\(因此log|g'| \le 2\times (log|p'|-1)-log|p|\)
\(c(x)+\Delta \Phi(x) \le 3\times (log|p'|-log|p|)\)
Case 3:祖父跟父親方向相同
zig-zag
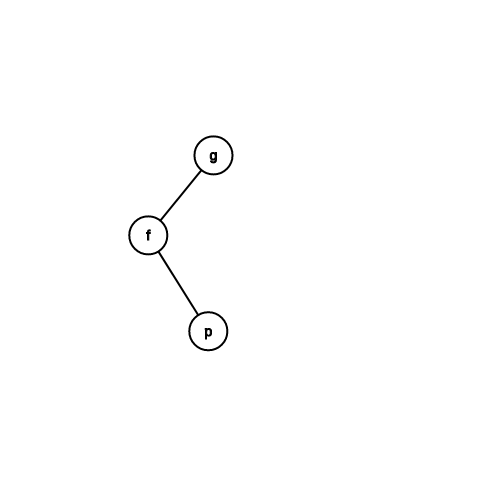
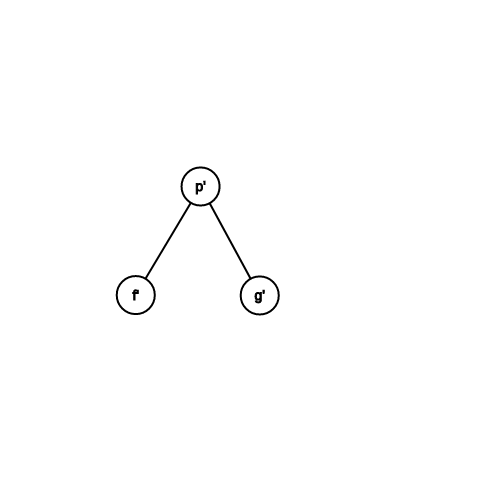
\(c(x) = 2\)
\(\Delta\Phi(x) = log|p'|+log|f'|+log|g'|-log|g|-log|f|-log|p|\)
\(=log|f'|+log|g'|-log|f|-log|p|(|g|=|p'|)\)
\(\le log|p'|+log|g'|-2\times log|p| (|p|\le |f| , |f'|\le |p'|)\)
\(\le 2\times (log|p'|-1)-2\times log|p|(因為log|f'|+log|g'| \le log \frac{|f'|+|g'|}{2} \times 2)\)
\(c(x)+\Delta \Phi(x) \le 2\times (log|p'|-log|p|) \le 3\times (log|p'|-log|p|)\)
複雜度證明
勢能分析
- 每一次splay為多次zig-zig,zig-zag+一次zig
- \(c'_i(x) = 3\times (log|p'|-log|p|)\)+[is zig]
- \(\sum c'(x) = 3\times(log|p'|-log|p_0|)+(zig count \le 1) \ge c(x)=\)實際時間
- 因此複雜度為log(n)
merge
- merge可以先把左樹的最大跟右樹的最小分別splay
- 然後直接把左樹的右節點設成右樹
- 記得懶標
void merge(int a,int b){
if(!a||!b)return;
splay(a);
splay(b);
push(a);
push(b);
while(childs[a][1]){
a = childs[a][1];
push(a);
}
while(childs[b][0]){
b = childs[b][0];
push(b);
}
splay(a);
push(a);
splay(b);
childs[a][1] = b;
par[b] = a;
pull(a);
return;
}find rank
- 直接在樹上找第k小
- 然後可能要splay
int find(int head,int k){
if(!k)return 0;
splay(head);
while(head&&k){
push(head);
int ls = childs[head][0],rs = childs[head][1];
if(sz[ls]+1 == k){
splay(head);
return head;
}
else if(sz[ls]+1<k){
k -= sz[ls]+1;
head = rs;
}
else head = ls;
}
splay(head);
return head;
}split
- 可以把第k大的點splay
- 然後切斷根與右節點
pair<int,int> split(int head,int k){
if(k == 0){
splay(head);
return make_pair(0,head);
}
head = find(head,k);
splay(head);
int tmp = childs[head][1];
childs[head][1] = par[tmp] = 0;
pull(tmp);
pull(head);
return make_pair(head,tmp);
}- 講師刻不出來QQ
練習
- tioj 1633
- 其他treap或pbds題
Link Cut Tree
回顧一下HLD
- 在HLD,我們用子樹大小來分鍊
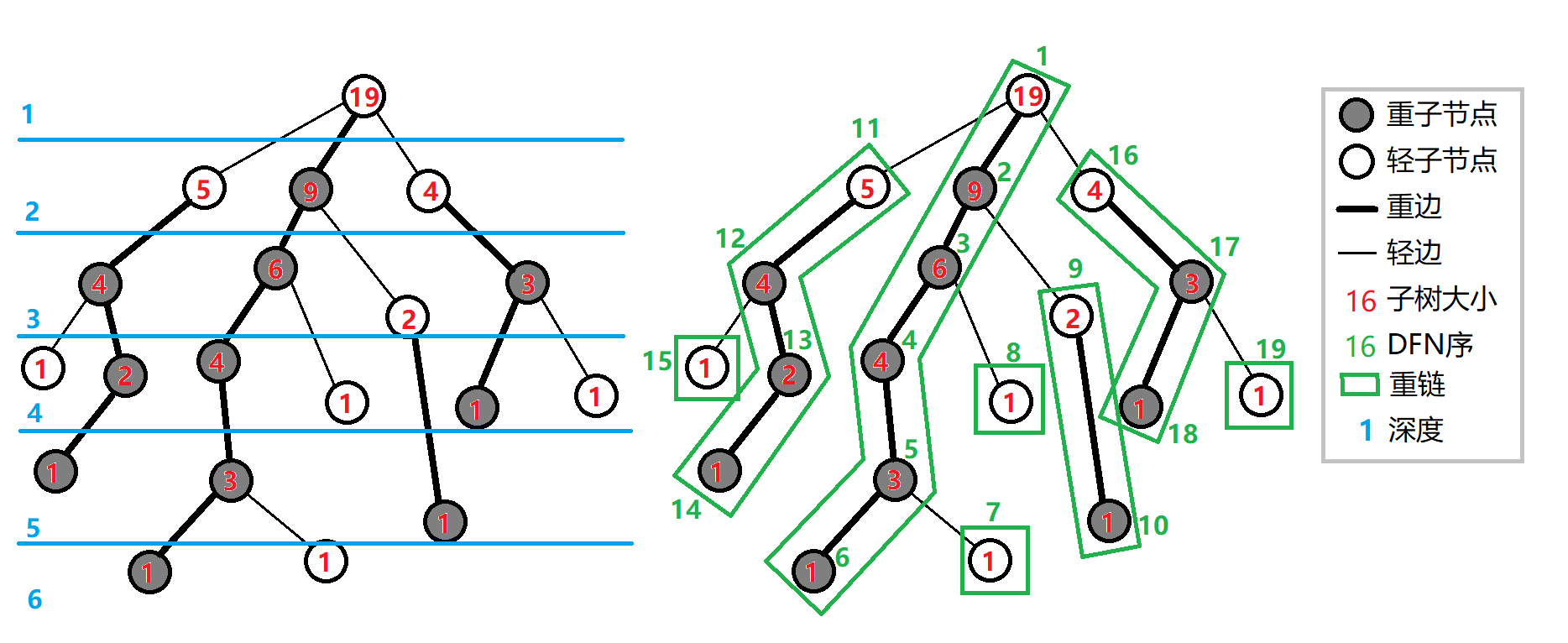
實虛鍊剖分
- 實鍊虛鍊是我們自己訂的,可以任意變動
實
虛
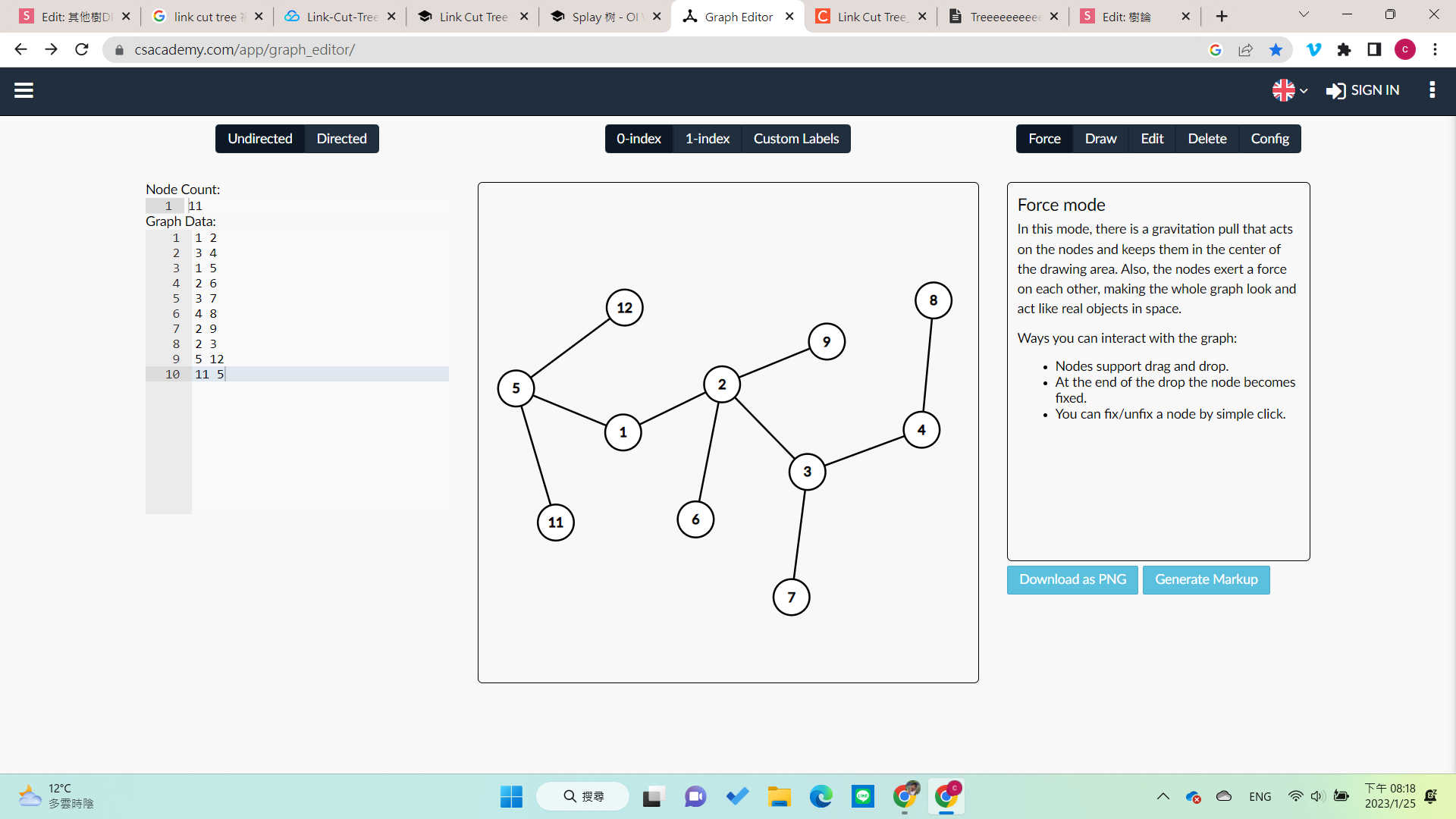
實虛鍊剖分
- 對於實鍊,我們用splay維護資訊
實
虛

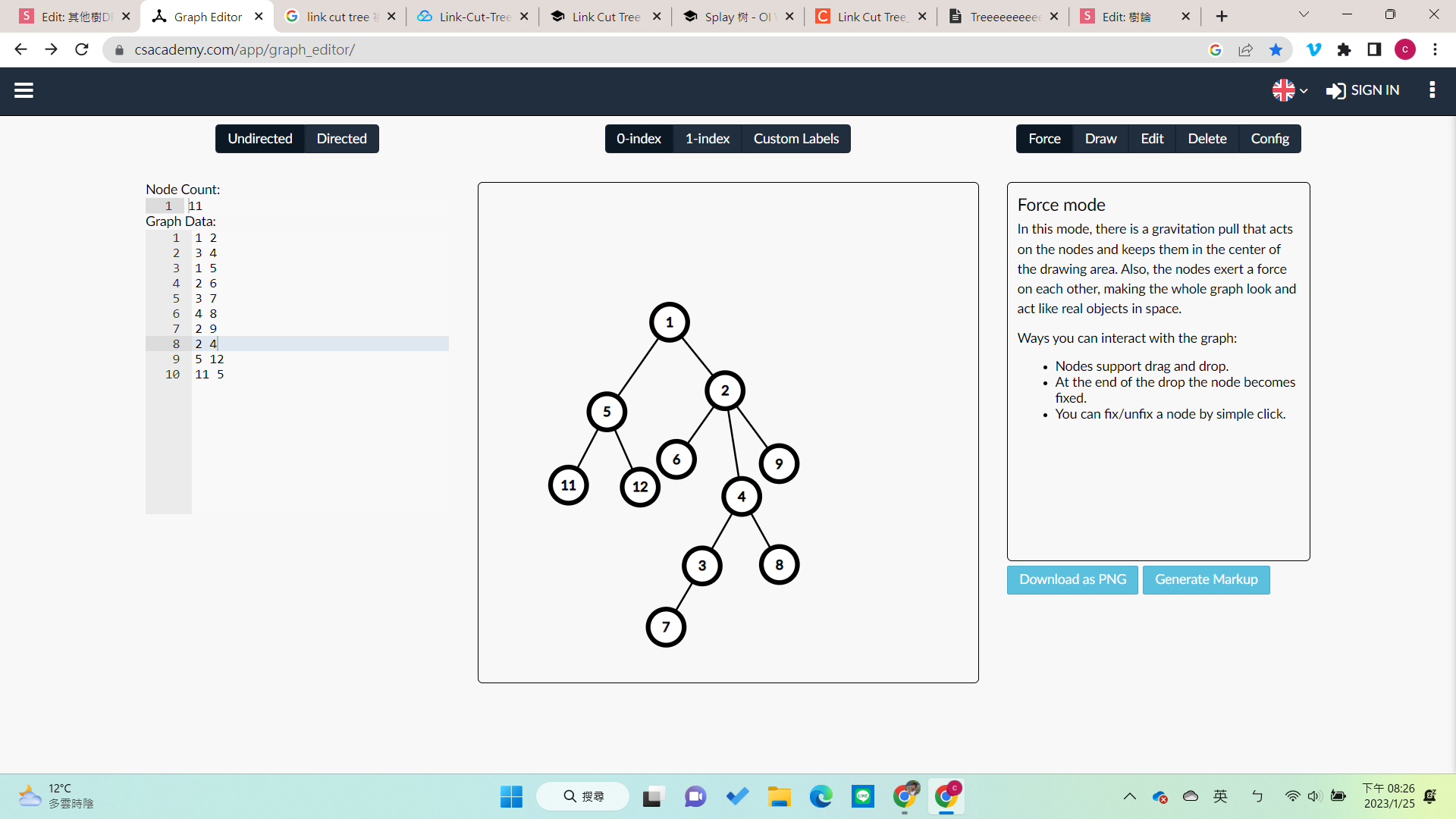
串接
- LCT最重要的功能
- 把某個點到根節點之間的邊都變成實鍊
- 偷一下圖(我畫不出來QQ)
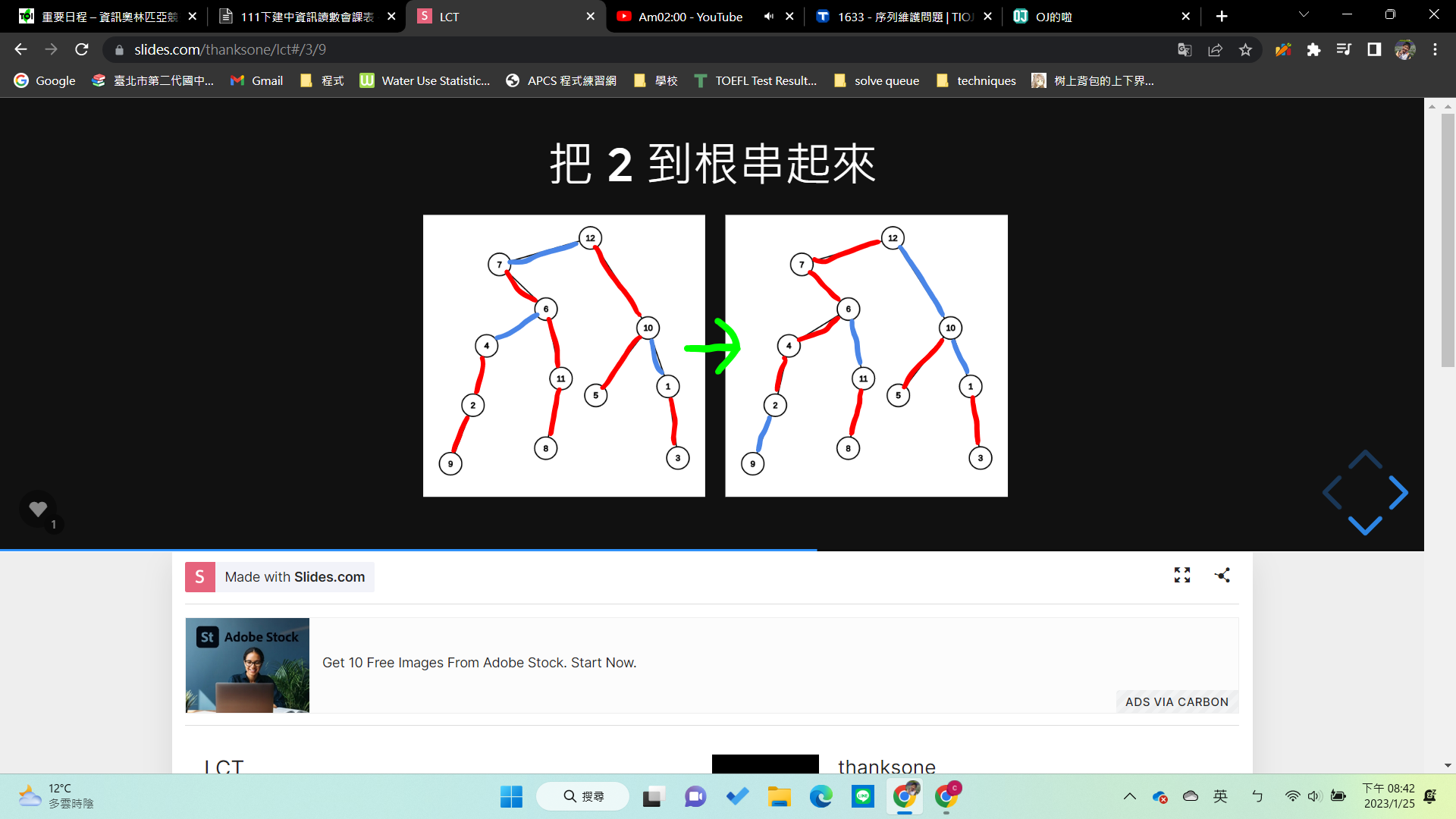
串接
- 在splay的角度看
- 再偷
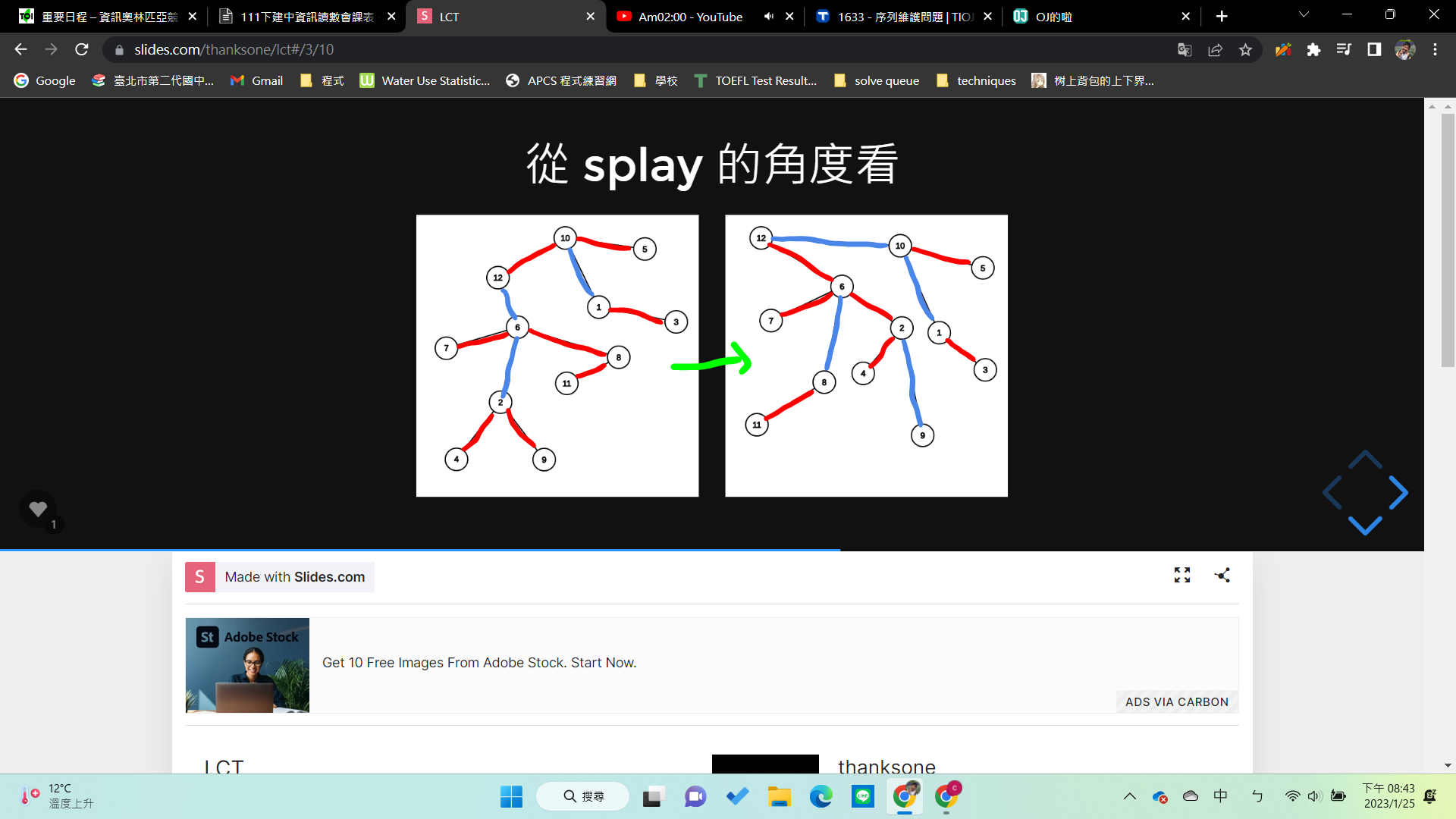
其他操作
換根
makeroot
- access之後翻轉
void makeroot(int now){
access(now);
splay(now);
rev[now] ^=1;
return;
}
找根
findroot
- access之後一直往左子節點走
- 可以用來判連通性
int findroot(int now){
access(now);
splay(now);
while(childs[now][0])now = childs[now][0];
return now;
}連接兩不連通的點
link
- 先判連通性
- 把兩點轉到根之後接起來
void link(int a,int b){
if(findroot(a) == findroot(b))return;
edges.insert({min(a,b),max(a,b)});
makeroot(a);
makeroot(b);
par[b] = a;
}斷開兩連通的點
cut
void cut(int a,int b){
if(findroot(a) != findroot(b))return;
if(a>b)swap(a,b);
if(edges.find({a,b}) == edges.end())return;
edges.erase({a,b});
makeroot(a);
access(b);
splay(b);
par[childs[b][0]] = 0;
childs[b][0] = 0;
pull(b);
return;
}複雜度
- 可以證明用splay為\(O(logN)\)
- 用其他二元樹(merge-split treap)為\(O(log^2N)\)
更多樹
- 支配樹
- 樹分塊
更多樹
By ck1100890張秉中
更多樹
- 569

