Prenatal development & infancy
Fertilization
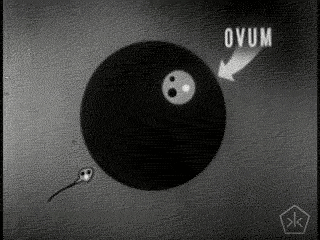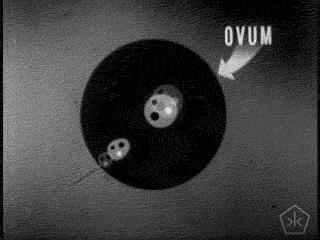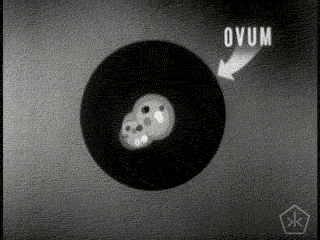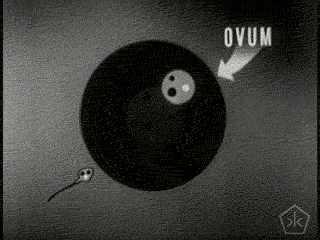
- Sperm & Ovum produced by parents, containing 50% of their DNA.
- Zygote: a fertilized ovum
- 23 unpaired chromosomes
- Dizygotic & Mono zygotic twins
- Myth of the "passive" ovum
- "Only 500 eggs" also may be false
- Gender bias in science
-
Martin, E. (1991). The egg and the sperm: How science has constructed a romance based on stereotypical male-female roles. Signs: Journal of Women in Culture and Society, 16(3), 485-501.
-
The beginnings of Ontogeny
- Everyone began life as a single fertilized cell (zygote) which contained our entire genetic code
- Each of us carries a “genetic code” from our parents
- This single cell then begins to divide…
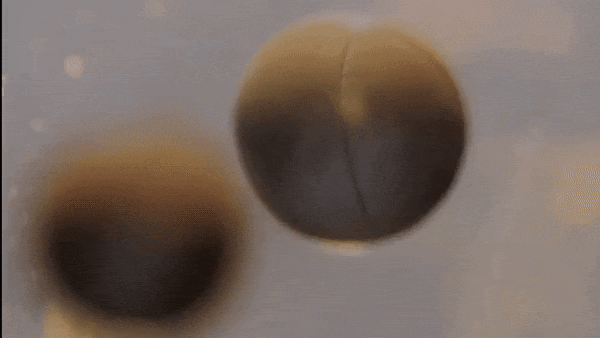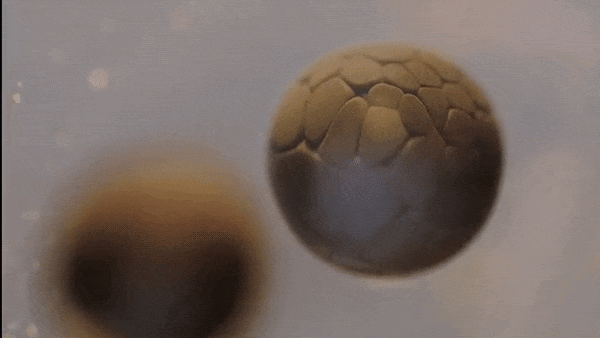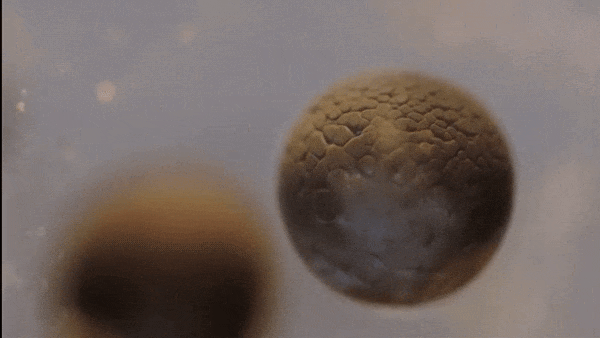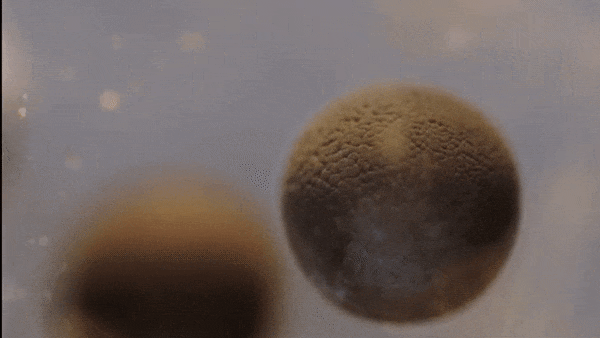
Mitosis
- All body cells (except the sperm and egg)
- 46 chromosomes in 23 pairs
- Body cells reproduce by a process called mitosis
- (except sperm & egg - meiosis)
- During mitosis, the cell’s nucleus -including the chromosomes—duplicates itself and the cell divides
- 2 new cells are formed, each containing the same chromosomes, genes, and DNA as the original cell

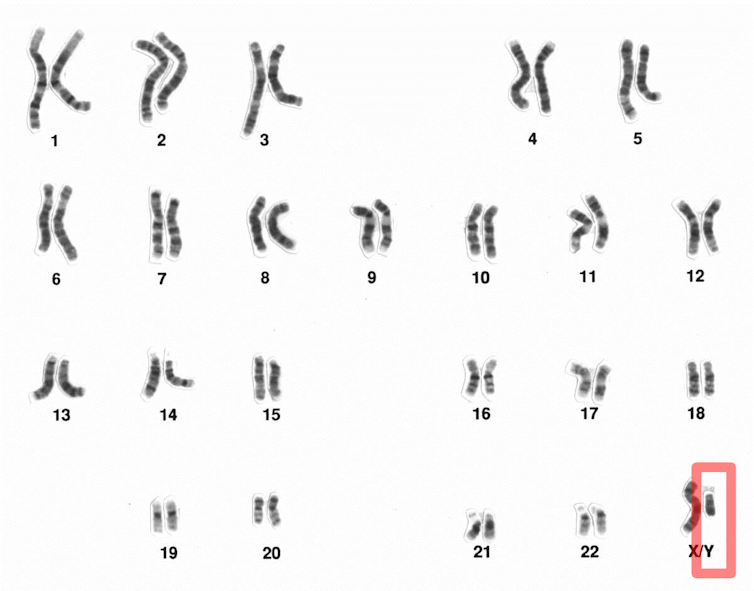
Sex and intersex
- 23rd pair known as "sex chromosomes". XX/XY
- Y chromosome has sex-determining region Y (SRY) protein
- X-linked and y-linked
- XXY: Klinefelter syndrome
- XO: Turner’s syndrome
- XXX: Triple X syndrome
- XYY: XYY syndrome
- XX SRY-positive karyotype
- XY: Androgen insensitivity

Stages of Prenatal Development
- First Trimester (wks 1-12)
- Zygote wks 1-2
- Embryo wks 3-8
- Fetus wks 9+
- Second Trimester (wks 13-28)
- Third Trimester(wks 29-40)

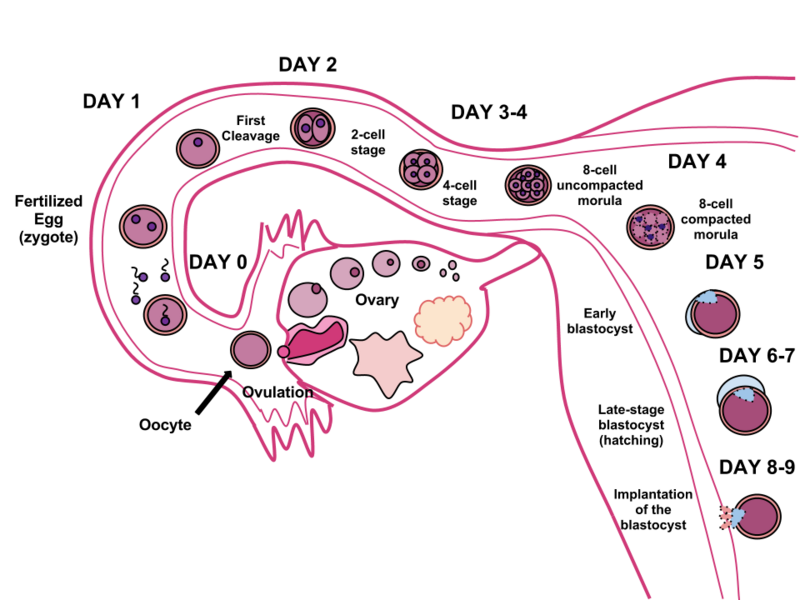
First 2 weeks
Carnegie stages 23 stages of first 56 days
Stage 1 (day 1) fertilization of zygote
Stage 2-4 (days 2-6) cleavage, single cell to embryoblast
Stage 5 (days 7-15) Implantation

The Embryo
Weeks 3-8 aka days 14-56 aka stages 5-23
First sign of pregnancy at week 6
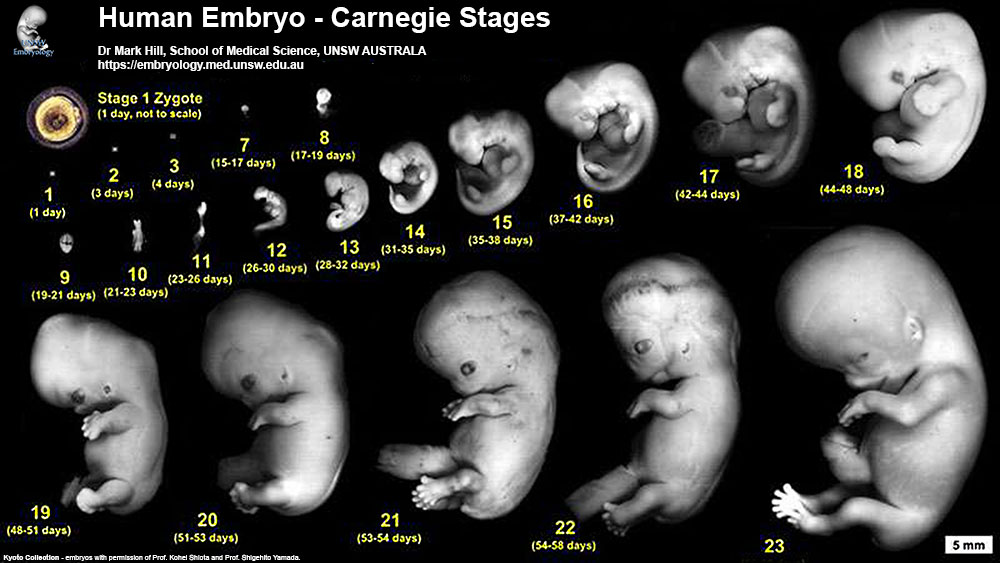
The Embryo
10-25% of pregnancies
Prenatal Experience
- Movement
- hand to mouth, thumb-sucking, kicking, hand-grasping, punching, twisting/rolling, hiccup
- Tactile Stimulation
- own activity, twin’s activity
- Smell
- odors in amniotic fluid (from mother’s food)
- Taste
- Babies taste the amniotic fluid; develop early preference for flavors in the fluid (from mother’s food)
Prenatal Experience
- Hearing
- Voices – rhythm, pitch & prosody (rise and fall)
- Music
- Heartbeat
- Stomach growling
- Vision
- Open eyes at 28 weeks
- some bright sunlight can filter through the womb
- can see dim shapes at 33 weeks
- vision is the last sense to develop
Prenatal Learning & Development
- Prenatally, children come to prefer familiar tastes and sounds
- Newborns recognize the auditory patterns of speech, rhythm and prosody of the language spoken around them
- Babies are born crying in the intonation of their culture’s language
- Study with French vs. German babies
- Newborns prefer their mother’s voice to other voices, and prefer stories read by mother while they were in the womb!
Teratogens: Harmful environmental influences
- Prescription/OTC Drugs
- Aspirin, Caffeine, Thalidomide
- Nicotine
- Alcohol & other Drugs
- Fetal Alcohol Syndrome (FAS)
- Radiation
- Pollution
- Lead
- Disease
- HIV, parasites, chicken pox

Socioeconomic factors
- 16% US children born into poverty (2017, record low)
- 10% Adults uninsured
- w/o insurance, childbirth alone coasts $10,000+
- Full pregnancy can costs up to $250,000

- Poverty threatens prenatal and postnatal development
- Poorer nutrition
- Less resources
- Increased stress
- Negative interactions
- Incarceration
Childbirth
- Human children are born “earlier” (less mature) than other animals because:
- Upright walking humans have smaller pelvises than apes
- Human children have large heads & brains


Newborn reflexes
- eye blink
- Rooting/Sucking Reflex
- Moro Reflex
- Palmar grasping Reflex
- Stepping Reflex
- Babinski Response



Prenatal development & Infancy
By cypurr
Prenatal development & Infancy
Textbook Ch 3
- 289



