HTML AND CSS


&
Hypertext Markup Language (HTML)
Is the standard markup language for creating web pages and web applications. With Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) and JavaScript it forms a triad of cornerstone technologies for the World Wide Web.[1] Web browsers receive HTML documents from a webserver or from local storage and render them into multimedia web pages. HTML describes the structure of a web page semantically and originally included cues for the appearance of the document.
WIKI
A BIT OF HISTORY


Invented @
By
STANDARDS
- November 24, 1995
- HTML 2.0 was published as IETF RFC 1866. Supplemental RFCs added capabilities:
- November 25, 1995: RFC 1867 (form-based file upload)
- May 1996: RFC 1942 (tables)
- August 1996: RFC 1980 (client-side image maps)
- January 1997: RFC 2070 (internationalization)
- January 14, 1997
- HTML 3.2 was published as a W3C Recommendation.
- December 18, 1997
- HTML 4.0 was published as a W3C Recommendation.
- April 24, 1998
- HTML 4.0 was reissued with minor edits without incrementing the version number.
- December 24, 1999
- HTML 4.01 was published as a W3C Recommendation.
- May 2000
- ISO/IEC 15445:2000 ("ISO HTML", based on HTML 4.01 Strict) was published as an ISO/IEC international standard.
- October 28, 2014
- HTML5 was published as a W3C Recommendation.
- November 1, 2016
- HTML 5.1 was published as a W3C Recommendation.
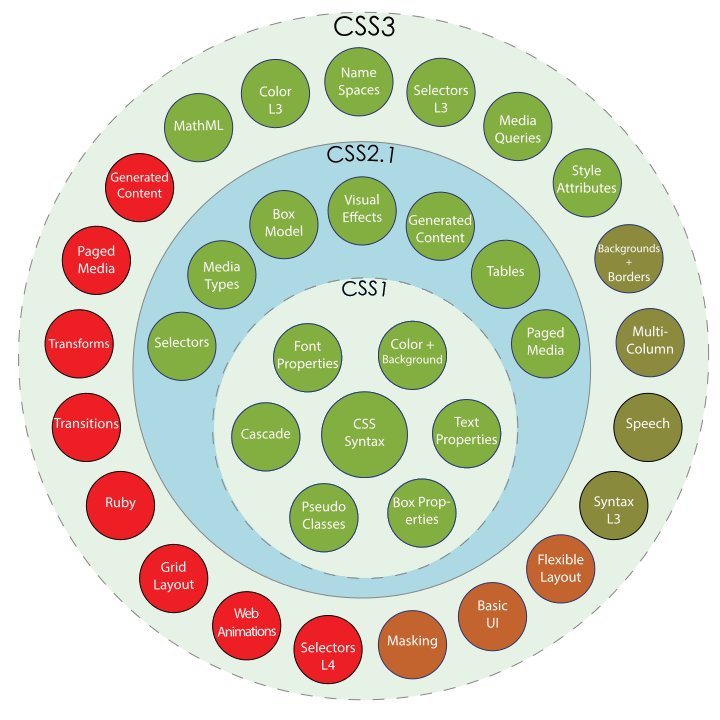
MODERN WEB


CSS

STANDARDS
SELECTORS
PatternMatchesFirst defined
in CSS level
| E | an element of type E | 1 |
| E:link | an E element is the source anchor of a hyperlink of which the target is not yet visited (:link) or already visited (:visited) | 1 |
| E:active | an E element during certain user actions | 1 |
| E::first-line | the first formatted line of an E element | 1 |
| E::first-letter | the first formatted letter of an E element | 1 |
| .c | all elements with class="c" | 1 |
| #myid | the element with id="myid" | 1 |
| E.warning | an E element whose class is "warning" (the document language specifies how class is determined) | 1 |
| E#myid | an E element with ID equal to "myid" | 1 |
| E F | an F element descendant of an E element | 1 |
| * | any element | 2 |
| E[foo] | an E element with a "foo" attribute | 2 |
| E[foo="bar"] | an E element whose "foo" attribute value is exactly equal to "bar" | 2 |
| E[foo~="bar"] | an E element whose "foo" attribute value is a list of whitespace-separated values, one of which is exactly equal to "bar" | 2 |
| E[foo|="en"] | an E element whose "foo" attribute has a hyphen-separated list of values beginning (from the left) with "en" | 2 |
| E:first-child | an E element, first child of its parent | 2 |
| E:lang(fr) | an element of type E in language "fr" (the document language specifies how language is determined) | 2 |
| E::before | generated content before an E element's content | 2 |
| E::after | generated content after an E element's content | 2 |
| E > F | an F element child of an E element | 2 |
| E + F | an F element immediately preceded by an E element | 2 |
| E[foo^="bar"] | an E element whose "foo" attribute value begins exactly with the string "bar" | 3 |
| E[foo$="bar"] | an E element whose "foo" attribute value ends exactly with the string "bar" | 3 |
| E[foo*="bar"] | an E element whose "foo" attribute value contains the substring "bar" | 3 |
| E:root | an E element, root of the document | 3 |
| E:nth-child(n) | an E element, the n-th child of its parent | 3 |
| E:nth-last-child(n) | an E element, the n-th child of its parent, counting from the last one | 3 |
| E:nth-of-type(n) | an E element, the n-th sibling of its type | 3 |
| E:nth-last-of-type(n) | an E element, the n-th sibling of its type, counting from the last one | 3 |
| E:last-child | an E element, last child of its parent | 3 |
| E:first-of-type | an E element, first sibling of its type | 3 |
| E:last-of-type | an E element, last sibling of its type | 3 |
| E:only-child | an E element, only child of its parent | 3 |
| E:only-of-type | an E element, only sibling of its type | 3 |
| E:empty | an E element that has no children (including text nodes) | 3 |
| E:target | an E element being the target of the referring URI | 3 |
| E:enabled | a user interface element E that is enabled | 3 |
| E:disabled | a user interface element E that is disabled | 3 |
| E:checked | a user interface element E that is checked (for instance a radio-button or checkbox) | 3 |
| E:not(s) | an E element that does not match simple selector s | 3 |
| E ~ F | an F element preceded by an E element | 3 |
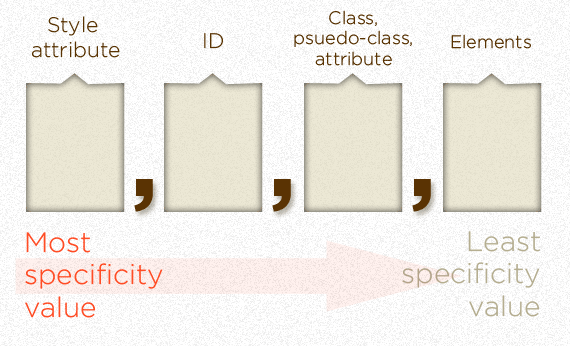
SPECIFICITY
MEDIA

OPTIMIZATION
HTML AND CSS
By diodredd
HTML AND CSS
- 542



