The 60s called
And they have some ideas for your code.
Presented by: Dave Smith
In the 60's, some people were working
to shape the future of computing.
Some people weren't.

Keep this in mind...

Lisp ... has assisted a number of our most gifted fellow humans in thinking previously impossible thoughts.
- Edsger Dijkstra, 1972
ancient Concepts You use today
- Garbage Collection
-
First Class Functions
- Closures
garbage collection
Invented in 1959 by John McCarthy to improve Lisp
Before Garbage Collection
void my_function() {char *data = malloc(1024);return; // oops! memory leak}
After Garbage Collection
function my_function() {var data = [1, 2, 3, 4, ..., 1024];return; // data will be freed later}
First class Functions
Defined by Christopher Strachey in the mid-1960's.
Example 1: Function Returning a Function
function counter() {var n = 0;return function() {n++;return n;}}c = counter();c(); // returns 1c(); // returns 2
Example 2: Function as Argument
$("button").click(function(event) {// handle the click}
Example 3: Storing Functions in Data Structures
var handlers = [function() { ... },function() { ... }];var thingsToRun = {red: function() { ... },blue: function() { ... },green : function() { ... }}
Example 4: Storing data structures on functions?
function Thing() {this.name = "Bob";this.foo = [1138, 42, 1701];}var thing = new Thing();
Closures
Peter J. Landin defined the term in 1964
Closure Definition:
- A reference to a function
- With the enclosing environment
Closure Example:
(function () {var name = "Bob, the Closure String";$("button").click(function() {alert("My closure has a name variable: " + name)});})();
IIFE's are closures!
JavaScript developers use closures more than
any other developer community I've seen.
Some examples:
Garbage Collection
+
First Class Functions
+
Closures
=
Very Productive Programming

lesser known* ancient concepts
- Referential Transparency
-
Function Composition
- Lazy Evaluation
- Immutability
* Warning: Subjective statement.
Referential Transparency
Defined by Christopher Strachey in 1967
a.k.a. The philosophy that contributes to React's speed.
Definition of Referential Transparency
The ability to replace a function with its return value.
Every mathematical expression is referentially transparent
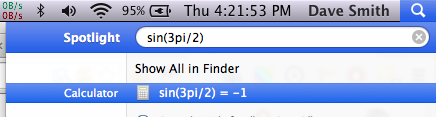
I can write:
sin(3*pi/2)
or I can write:
-1
They are equivalent.
Side note: OS X Spotlight is nifty
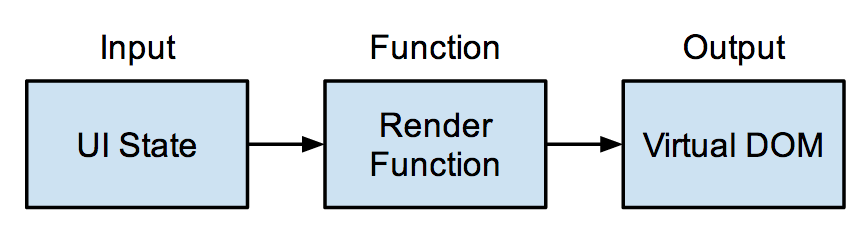
How React uses referential transparency
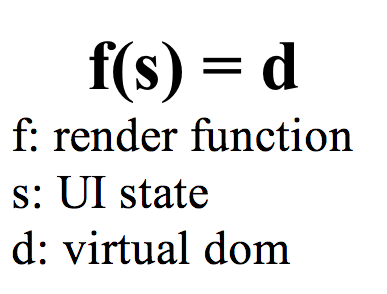
To put it more mathematically:
function composition
Applying functions to the result of functions
Maybe popularized by Haskell Curry in the 1960s?
See also: Currying
The mathy version:
f(g(x))
Without Composition
function capitalize(list) {for (var i=0; i<list.length; i++) {list[i] = list[i].toUpperCase();}}
Not composable because:
- No return value
-
Mutates the input list
With Composition
function upper(str) {return str.toUpperCase()}function capitalize(list) {return list.map(upper)}
Wins:
- Can be chained with other functions
- Referentially transparent
- Easily testable
Great reading: http://eloquentjavascript.net/chapter6.html
Promises use composition:
$.get("http://example.com").then(doSomething).then(doSomethingElse).then(andFinish)
What does then() return?
"Callbacks are imperative, promises are functional "
https://blog.jcoglan.com/2013/03/30/callbacks-are-imperative-promises-are-functional-nodes-biggest-missed-opportunity/
https://blog.jcoglan.com/2013/03/30/callbacks-are-imperative-promises-are-functional-nodes-biggest-missed-opportunity/
lazy evaluation
Invented for computer programming in 1976
Definition:
Delay the evaluation of an expression until it is needed
Why:
- Performance wins
- Construct infinite data sets
Example: Expensive CPU operation
Eager evaluation:
function findNextPrime(previousPrime) {// do lots of workreturn nextPrime;}
Lazy evaluation:
function findNextPrime(previousPrime) {return function() {// do lots of workreturn nextPrime;}}
The caller decides when (or if) to actually do the work.
JavaScript has weak built-in support for lazy evaluation
But Python's support is awesome:
translated_string = trans("Hello, world!") The variable "translated_string" will not get translated until the first time someone tries to read its value.
immutability
Don't know when this concept was invented.
But it was probably Lisp.
Everything is Lisp.
((((((((((((((((((((((((x)))))))))))))))))))))))
Definition of immutability:
Objects can be created, but not altered.
var x = {name: "Bob"};x.name = "Fred"; // Not allowed!
Benefits of immutable data:
- More easily testable
- Easier concurrency
- No side effects
- Easier flyweights

JavaScript strings are immutable
Most string methods return new strings.
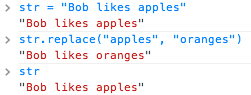
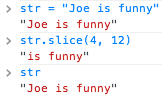
JavaScript has no enforcement for immutable objects.
Or does it...
Whoa. Object.freeze()
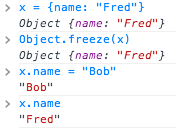

Reference:
OTher concepts from ANTIQUITY
-
Tail recursion
- Side effects
- Pure functions
The 60's gave us functional programming.
The 60's are coming back
"Boundaries" by Gary Bernhardt
The 60's in modern languages
Swift
Clojure
Scala
Visual F#
The 60's were awesome
The 60's called
By djsmith
The 60's called
- 4,766











