Classes, IDs, Display, Background Images

CSS Two

class Attribute
- The class attribute lets us add one or more CSS classes to an element
- Multiple elements may all use the same class saving you the need to write the same CSS rules multiple times
- If multiple classes that contain competing CSS declarations are applied to an element, the class lower in the sheet takes precedence
- You can give multiple classes to one element, just separate the names with a space
- To select classes in CSS, use a period before the class name
<p class="hero-text">
Content content content.
</p>
<p class="hero-text red">
More content.
</p>.hero-text {
font-size: 25px;
}
.red {
color: red;
}id Attribute
- The id attribute can also be used to apply CSS styles to elements
- ids differ from classes in that they should be used only once in a document
- ids supersede class meaning that for an element with both an id and a class, the styles assigned to the id will always beat out class styles
<button class="form-btn" id="submit">Submit</button>#submit {
background-color: green;
}
.form-btn {
background-color: white;
border: 3px solid blue;
}
button {
padding: 10px 20px;
border: none;
background-color: blue;
}CSS Specificity
When an element has conflicting styles added to it, CSS specificity determines which style is used.
It works like a point system. The highest score styling block is applied.
Selecting the element: 1 point
Selecting the class: 10 points
Selecting the id: 100 points
Inline Styling: 1000 points
<div class="example" id="test"></div>HTML
CSS
#test {
height: 100px;
width: 100px;
background-color: cyan;
}
.example {
height: 100px;
width: 100px;
background-color: blanchedalmond
}
Display Properties
Specifies the display behavior of an element
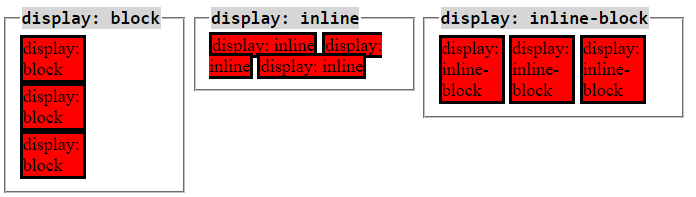
block - Stacks vertically and takes full width available, unless otherwise specified. Can change height and width.
inline - allows horizontal stacking. Size is only what it needs for its content. Can't change height or width.
inline-block - allows horizontal stacking. Can change height and width.
Background Images
- background-image adds an image to the background of the element. Note that the size of the image can make this tricky.
- background-position moves the image from its original place
- background-repeat helps control what happens if the background image is too small. The default is to repeat horizontally and vertically, but other options include no-repeat, space, and round
- background-size helps control the size of the image being used.
- background-attachment helps control how the background moves when scrolling. Options include fixed, local and scroll.
div {
width: 100vw;
height: 200px;
background-image: url(“https://image.com/cat”);
background-position: center;
background-repeat: no-repeat;
background-size: contain;
background-attachment: fixed;
}Day 3: CSS Two
By Devmountain
Day 3: CSS Two
- 1,888



