Android Data Sync
Dmytro Danylyk
Timee GmbH.

What is data synchronization?
"Data synchronization - is the process of establishing consistency among data from a source to a target data storage and vice versa and the continuous harmonization of the data over time." - Wikipedia
Download data from server
Sync
Event Bus
Table A was updated
Table B was updated
Table C was updated
Activity A reload data
Activity B reload data
Activity C reload data
GCM
User Action
(pull-to-refresh)
(data on server updated)
Database
(request data from server and save to database)
Sync
Event Bus
Table A was updated
Table B was updated
Table C was updated
Activity A reload data
Activity B reload data
Activity C reload data
GCM
User Action
(pull-to-refresh)
(data on server updated)
Database
(request data from server and save to database)
Sync
Event Bus
Table A was updated
Table B was updated
Table C was updated
Activity A reload data
Activity B reload data
Activity C reload data
User Action
(pull-to-refresh)
GCM
(data on server updated)
Database
(request data from server and save to database)
Sync
Database
Event Bus
Table A was updated
Table B was updated
Table C was updated
Activity A reload data
Activity B reload data
Activity C reload data
User Action
(pull-to-refresh)
GCM
(data on server updated)
(request data from server and save to database)
Sync
Event Bus
Table A was updated
Table B was updated
Table C was updated
Activity A reload data
Activity B reload data
Activity C reload data
User Action
(pull-to-refresh)
GCM
(data on server updated)
Database
(request data from server and save to database)
Sync
Event Bus
Table A was updated
Table B was updated
Table C was updated
Activity A reload data
Activity B reload data
Activity C reload data
User Action
(pull-to-refresh)
GCM
(data on server updated)
Database
(request data from server and save to database)
Upload data to server
Event Bus
Table A was updated
Table B was updated
Table C was updated
Activity A reload data
Activity B reload data
Activity C reload data
Sync
User Action
(updated profile)
Database
(save data to database and upload to server)
Sync
Event Bus
Table A was updated
Table B was updated
Table C was updated
Activity A reload data
Activity B reload data
Activity C reload data
User Action
(updated profile)
Database
(save data to database and upload to server)
Sync
Event Bus
Table A was updated
Table B was updated
Table C was updated
Activity A reload data
Activity B reload data
Activity C reload data
Database
(save data to database and upload to server)
User Action
(updated profile)
Sync
Event Bus
Table A was updated
Table B was updated
Table C was updated
Activity A reload data
Activity B reload data
Activity C reload data
User Action
(updated profile)
Database
(save data to database and upload to server)
Layers
User Credentials
Storage
User Interface
Sync
Communication
User Credentials Layer
Responsibilities:
- store user credentials
- retrieve user credentials
User Credentials Layer
Where to store user credentials?
External Storage
Not secure.
Where to store user credentials?
Preferences
External Storage
Can be cleared by user.
Where to store user credentials?
Preferences
External Storage
SQLite Databases
Can be cleared by user.
Where to store user credentials?
Preferences
Account Manager
External Storage
SQLite Databases
Why Account Manager?
- Gives users a central point to define their credentials via Settings - Accounts

Why Account Manager?
- Gives users a central point to define their credentials via Settings - Accounts
- User data is not cleared when user Clear Cache / Clear Data
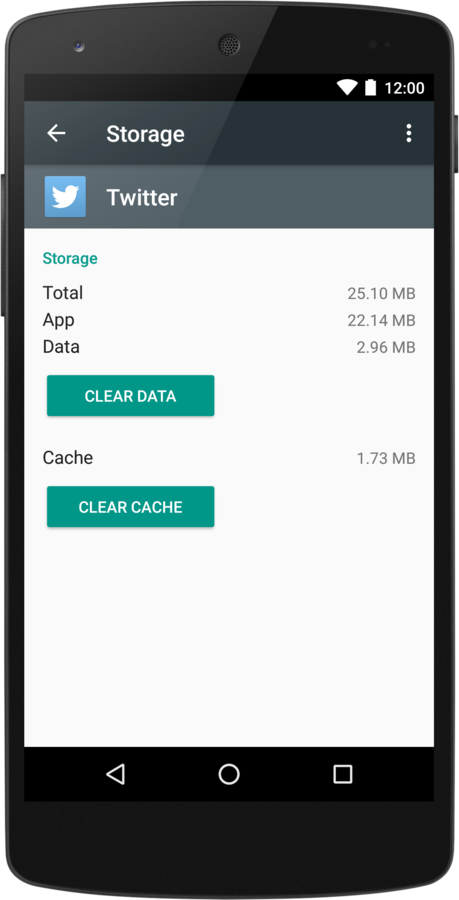
Why Account Manager?
- Gives users a central point to define their credentials via Settings - Accounts
- User data is not cleared when user Clear Cache / Clear Data
- Provide possibility to turn on Auto-sync data

Why Account Manager?
- Gives users a central point to define their credentials via Settings - Accounts
- User data is not cleared when user Clear Cache / Clear Data
- Provide possibility to turn on Auto-sync data
- Provide settings screen where user can trigger, turn on/off sync

Account Manager usage
AccountManager accountManager = AccountManager.get(getApplicationContext());
// create new account
Account account = new Account(username, accountType)
// add account and auth token
accountManager.addAccountExplicitly(account, password, userData);
accountManager.setAuthToken(account, authTokenType, accessToken);How to add new account ?
Account Manager usage
// to get account manager
AccountManager accountManager = AccountManager.get(getApplicationContext());
// to get account
Account[] accounts = accountManager.getAccountsByType(getAccountType(context));
Account account != null && accounts.length != 0 ? accounts[0] : null;
// to get auth token
String authToken = accountManager.peekAuthToken(account, authTokenType);How to get account ?
Want to know more?
developers.google.com
/android/guides/http-auth
Sync Layer
Sync Layer
Responsibilities:
- perform requests to server
- use storage layer to cache data to storage
- send global app events via communication layer
How to make data sync?
Thread
Runs only when application is launched.
How to make data sync?
Thread
Service
Requires writing extra logic to handle automated execution, network checking, etc.
How to make data sync?
Thread
Service
Sync Adapter
Requires ContentProvider (or StubProvider if you are not using ContentProvider).
How to make data sync?
Thread
GCM Network Manager
Service
Sync Adapter
Not possible to execute immediate Task.
How to make data sync?
GCM Network Manager
Sync Adapter
- Schedule one-off vs. periodic tasks.
- Awareness of network activity.
- Awareness of device charging state.
- Automatic back-off and failure retry.
- Persistence of tasks across boot.
When to sync?
At regular intervals
Run a sync adapter after the expiration of an interval you choose, or run it at a certain time every day.
When to sync?
At regular intervals
When the system sends out a network message
Run a sync adapter when the Android system sends out a network message that keeps the TCP/IP connection open; this message is a basic part of the networking framework.
When to sync?
At regular intervals
When the system sends out a network message
When device data changes
Run a sync adapter when data changes on the device. This option allows you to send modified data from the device to a server, and is especially useful if you need to ensure that the server always has the latest device data.
When to sync?
At regular intervals
When the system sends out a network message
When device data changes
When server data changes
Run the sync in response to a GCM message from a server, indicating that server-based data has changed. This option allows you to refresh data from the server to the device without degrading performance or wasting battery life by polling the server.
Regular intervals sync
/*
* Specifies that a sync should be requested with the specified the account,
* authority, and extras at the given frequency.
*/
long intervalSeconds = TimeUnit.MINUTES.toSeconds(60);
ContentResolver.addPeriodicSync(account, authority, bundle, intervalSeconds);Sync Adapter usage
When the system sends out a network message
/*
* Set whether or not the provider is synced when it receives a network tickle.
*/
ContentResolver.setSyncAutomatically(account, authority, true);Sync Adapter usage
When device data changes
/*
* Start an asynchronous sync operation
*/
ContentResolver.requestSync(mAccount, AUTHORITY, settingsBundle);Sync Adapter usage
When server data changes
public class MyGcmListenerService extends GcmListenerService {
@Override
public void onMessageReceived(String from, Bundle data) {
String type = data.getString("type");
switch (SyncType.fromString(type)) {
case SyncType.FEED:
SyncAdapter.syncFeed();
break;
case SyncType.PROFILE:
SyncAdapter.syncProfile();
break;
}
}
}Sync Adapter usage
Want to know more?
developer.android.com
/training/sync-adapters
Storage Layer
Storage Layer
Responsibilities:
- save data to persistent storage
- retireve data from persistent storage
Where to store data?
Preferences
Can be used for small amount of data.
Where to store data?
Preferences
SQLiteDatabase
- Require a lot of extra code, unless you use ORM
- Doesn't support lazy loading
Where to store data?
Preferences
SQLiteDatabase
Realm
- Easy to implement
- Fast
What is realm?
"Realm is a mobile database: a replacement for SQLite & ORMs." - realm.io
Realm usage
public class User extends RealmObject {
@PrimaryKey
private String name;
private int age;
// Standard getters & setters
}Model
Realm usage
// Query to look for all users
RealmResults<User> result1 = realm.where(User.class).findAll();
// Query with conditions
RealmResults<User> result2 = realm.where(User.class)
.equalTo("name", "John")
.or()
.equalTo("name", "Peter")
.findAll();Read
Realm usage
User user = new User("John");
user.setEmail("john@corporation.com");
// Copy the object to Realm. Any further changes must happen on realmUser
realm.beginTransaction();
realm.copyToRealm(user);
realm.commitTransaction();Write
Realm usage
private void reloadData() {
// new thread
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
// switch to ui thread
List<User> userList = UserDAO.newInstance().getAll();
runOnUiThread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
mAdapter.setData(userList);
}
});
}
}).start();
}SQLite data loading flow
Realm usage
private void loadData() {
// ui thread, because query of 5000 objects takes around 4 ms
mAdapter.setData(UserDAO.newInstance().getAll());
}
private void reloadData() {
// no need to reload data, since realm result
// represent all changes made in table
mAdapter.notifyDataSetChanged();
}Realm data loading flow
Want to know more?
realm.io/docs/java/latest
Communication Layer
Communication Layer
Responsibilities:
- deliver global app events
How to deliver global app events?
Local Broadcast
Require extra code to store / retrieve data from intent
How to deliver global app events?
Local Broadcast
Event Bus
Simplifies the communication between components
What is event bus?
"EventBus - allows publish-subscribe-style communication between components without requiring the components to explicitly register with one another (and thus be aware of each other)"
Greenrobot usage
public class SyncEvent {
private Type mType;
private Status mStatus;
// Additional fields if needed
}Define event
Greenrobot usage
public class MyActivity extends Activity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
EventBus.getInstance().register(this);
}
}Subscribe to event
Greenrobot usage
public class MyActivity extends Activity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
EventBus.getInstance().register(this);
}
@Override
protected void onDestroy() {
EventBus.getInstance().unregister(this);
super.onDestroy();
}
}Subscribe to event
Greenrobot usage
public class MyActivity extends Activity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
EventBus.getInstance().register(this);
}
@Override
protected void onDestroy() {
EventBus.getInstance().unregister(this);
super.onDestroy();
}
public void onEvent(SyncEvent event) {
if(event.mType == Type.PROFILE) {
if(event.mStatus == Status.COMPLETED) {
// reload UI
}
}
}
}Subscribe to event
Greenrobot usage
public class Sync {
protected void doProfileSync() {
EventBus.getInstance().post(new SyncEvent(Type.Profile, Status.IN_PROGRESS));
// sync logic
EventBus.getInstance().post(new SyncEvent(Type.Profile, Status.COMPLETED));
}
}Fire event
Want to know more?
github.com
/greenrobot/EventBus
User Interface Layer
User Interface Layer
Responsibilities:
- display data
- use storage layer to retrieve data from storage
- listen to global app events from communication layer
Upload data to server
void onSaveClicked(User user) {
UserProfileDAO.update(user);
SyncAdapter.syncProfile();
}void update(User user) {
realm.beginTransaction();
realm.copyToRealmOrUpdate(user);
realm.commitTransaction();
}User Interface
Storage
void syncProfile() {
sendProfileEvent(Status.IN_PROGRESS);
doGet();
doPost(UserProfileDAO.getModified());
sendProfileEvent(Status.COMPLETED);
}void onSaveClicked(User user) {
UserProfileDAO.update(user);
SyncAdapter.syncProfile();
}void update() {
realm.beginTransaction();
realm.copyToRealmOrUpdate(user);
realm.commitTransaction();
}User Interface
Storage
Sync
RealmResults<User> getModified() {
return
realm.where(User.class)
.equalTo("isModified", true)
.findAll();
}Storage
void syncProfile() {
sendProfileEvent(Status.IN_PROGRESS);
doGet();
doPost(UserProfileDAO.getModified());
sendProfileEvent(Status.COMPLETED);
}void onSaveClicked(User user) {
UserProfileDAO.update(user);
SyncAdapter.syncProfile();
}void update() {
realm.beginTransaction();
realm.copyToRealmOrUpdate(user);
realm.commitTransaction();
}User Interface
Storage
Sync
RealmResults<User> getModified() {
return
realm.where(User.class)
.equalTo("isModified", true)
.findAll();
}Storage
public void onEvent(SyncEvent e) {
if(e.type == Type.PROFILE
&& e.status == Status.COMPLETED) {
// reload UI
}
}
}User Interface
Communication
void sendProfileEvent(Status s) {
EventBus.getInstance.send(
new SyncEvent(Type.Profile, s);
);
}Download data from server
void onPullToRefresh() {
SyncAdapter.syncProfile();
}User Interface
void syncProfile() {
sendProfileEvent(Status.IN_PROGRESS);
doGet();
doPost(UserProfileDAO.getModified());
sendProfileEvent(Status.COMPLETED);
}void onPullToRefresh() {
SyncAdapter.syncProfile();
}User Interface
Sync
RealmResults<User> getModified() {
return
realm.where(User.class)
.equalTo("isModified", true)
.findAll();
}Storage
void syncProfile() {
sendProfileEvent(Status.IN_PROGRESS);
doGet();
doPost(UserProfileDAO.getModified());
sendProfileEvent(Status.COMPLETED);
}void onPullToRefresh() {
SyncAdapter.syncProfile();
}User Interface
Sync
RealmResults<User> getModified() {
return
realm.where(User.class)
.equalTo("isModified", true)
.findAll();
}Storage
public void onEvent(SyncEvent e) {
if(e.type == Type.PROFILE
&& e.status == Status.COMPLETED) {
// reload UI
}
}
}User Interface
Communication
void sendProfileEvent(Status s) {
EventBus.getInstance.send(
new SyncEvent(Type.Profile, s);
);
}F.A.Q.
"No, requests like sign in, sign up, search (if result is not cached) are performed directly in activity."
Are all application requests performed via sync?
"If user data is always considered as most recent you should do POST, then GET.
If server data is always considered as most recent you should do GET, then POST."
What to do first during sync, GET or POST?
"Add to all your data objects isModified field. When user update object in database set isModified field to true. During sync, upload all objects where isModified equals true."
Which data to upload during POST?
"Track if activity is visible in onPause / onResume methods and render screen only if data was updated and activity is visible."
Having several activities in stack which listen to the same event, cause inefficient view render.
@dmytrodanylyk
dmytrodanylyk.com
slides.com/dmytrodanylyk
S
Android Data Sync
By Dmytro Danylyk
Android Data Sync
- 17,040



