CE6190 Project
Du Mingzhe
Liu Fengming
Li Yanzhou
Sun Dianxiang
Group 22
G2204045F
G2104574F
G2201488K
G2201037D
Zero-shot semantic segmentation
-
Traditional semantic segmentation: train the model on the seen classes and test the model on the seen classes
-
Zero-shot semantic segmentation: train the model on the seen classes and test the model on the unseen classes

Attempt 1
Inserting Text Projection Layer to ZegFormer
What is ZegFormer?
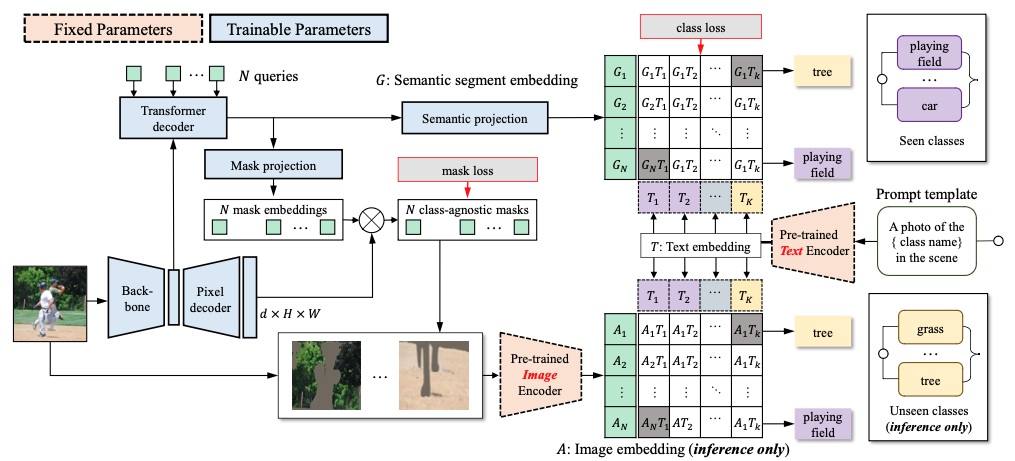
MaskFormer:
Generate class-agnostic segments
CLIP:
zero-shot classification on the segments
-
Dataset: COCO-Stuff
-
156 seen classes + 15 unseen classes
-
-
Metric
-
Mean IoU between the prediction and the ground truth
-
Seen, Unseen, Harmonic
-
Experiment
-
Add a text projection layer to further transform the text feature given by the CLIP text encoder
-
Implemented as a MLP (512 → 384 → 512)
-
Alleviates the overfitting to the seen classes
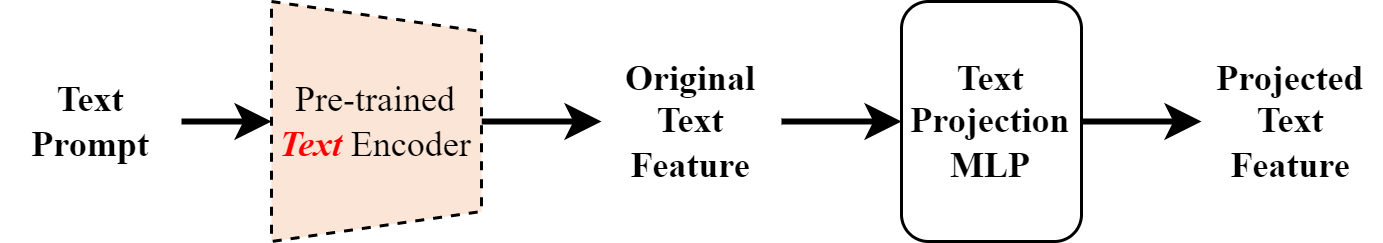
Modification
Result
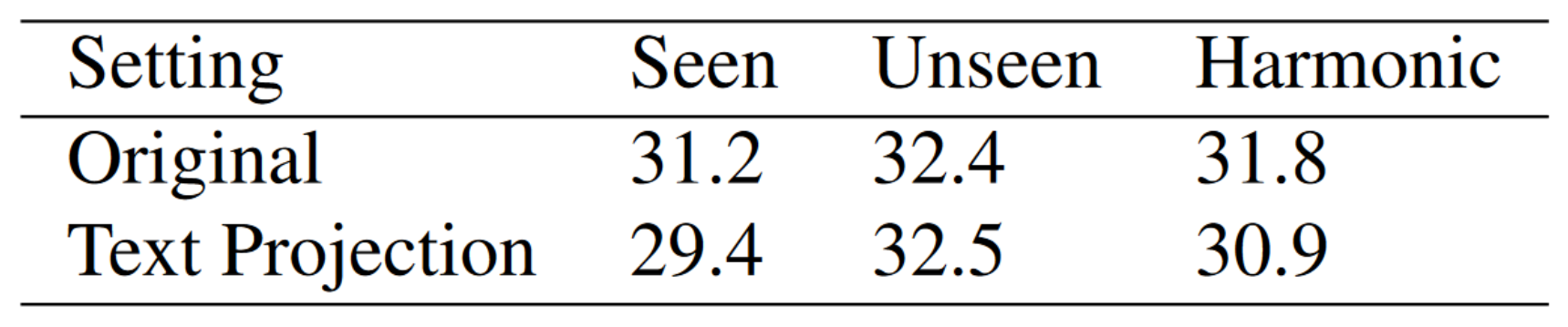
- mIoU:
- Decreases for seen classses
- Increases for unseen clasess
- Overfitting for seen classes is slightly improved
Attempt 2
Adapting CRIS to Zero-shot Semantic Segmentation
What is CRIS?
-
CRIS: CLIP-Driven Referring Image Segmentation
-
Referring Image Segmentation
- Segment out the object referred by the sentence
- Can be converted to zero-shot semantic segmentation
-
Prompt Engineering
-
e,g, "This is a photo of <class name>"
-
Performing referring image segmentation on the prompt = Performing zero-shot semantic segmentaion on the class name
-

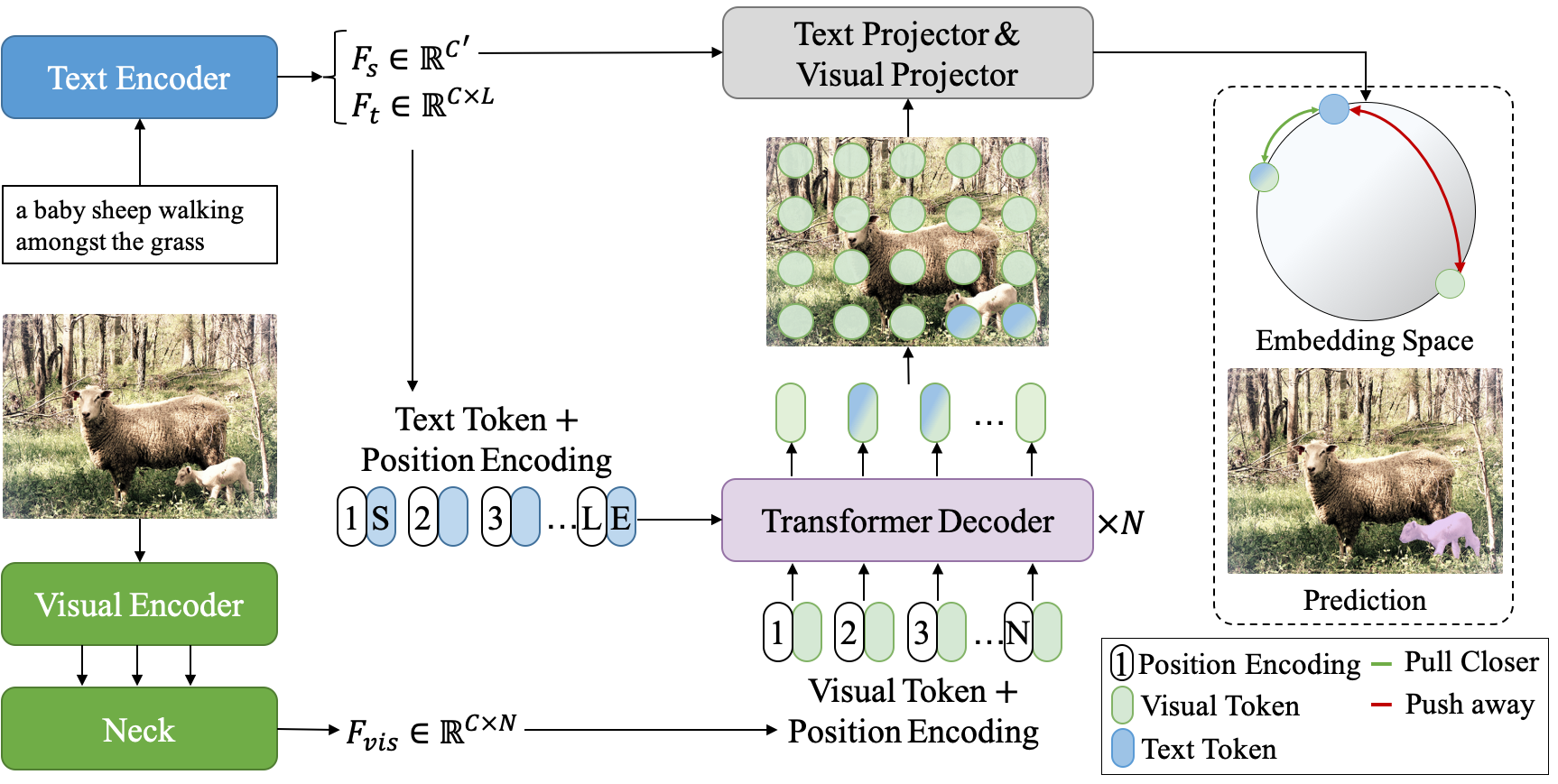
What is CRIS?
- Text-to-pixel matching
- The loss function helps to pull semantically similar pixels together and push dissimilar pixels away
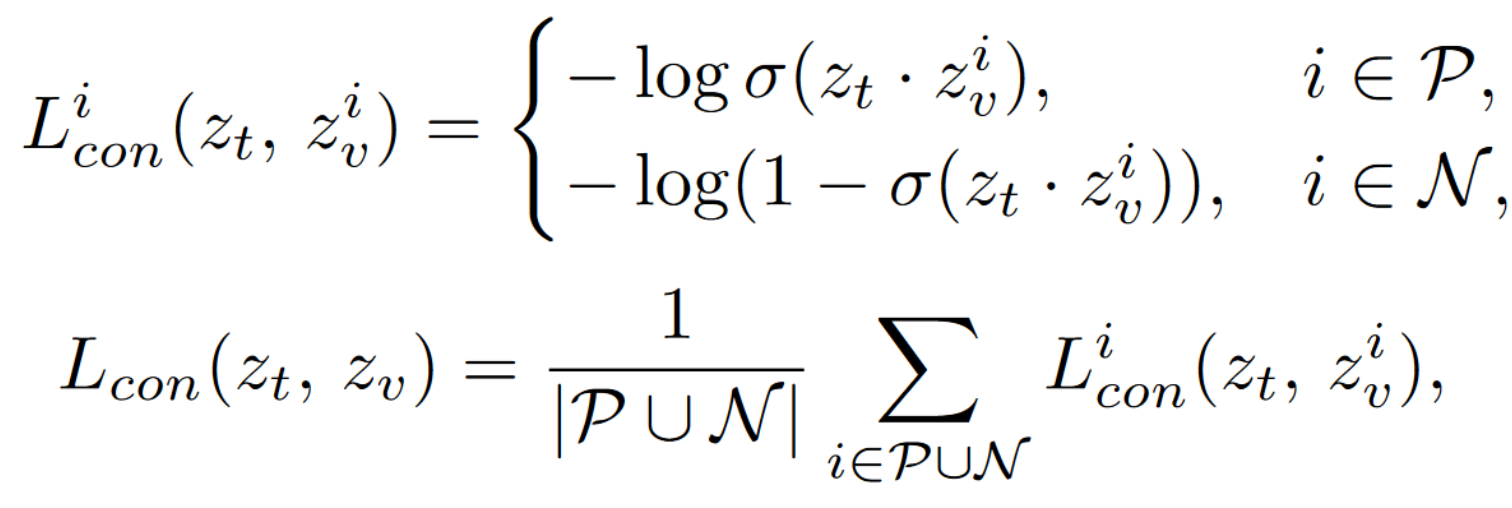
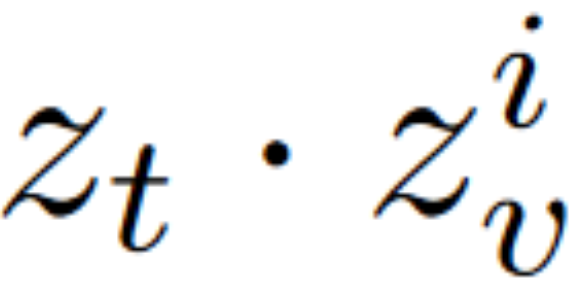
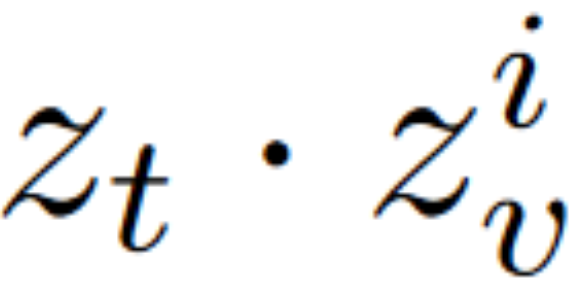
Modification 1
Modification 2
Modifications
- Improve the segmentation performance on small objects
- Modification 1: image level
- Modification 2: pixel level
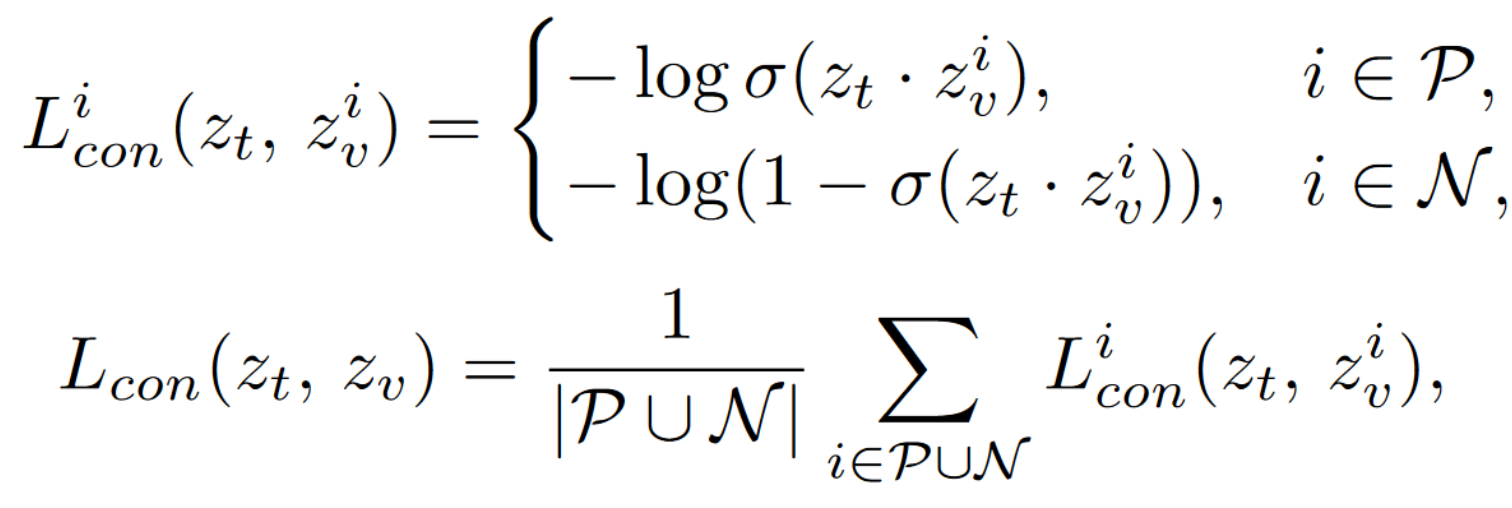
Modification 1: Image-level
-
In the vanilla setting, a large object segment has the same weight as a small object segment.
-
The total loss is less sensitive to the mismatching of smaller objects.
-
Therefore, we multiply the loss with a coefficient beta that is inversely proportional to the segment size.
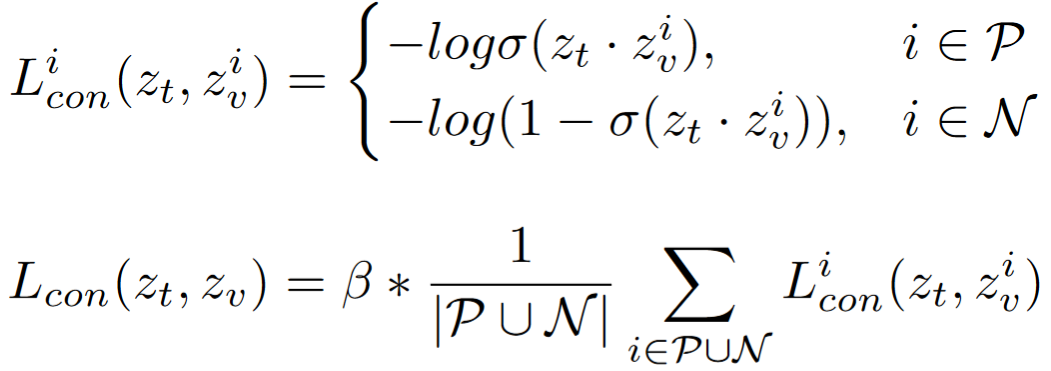
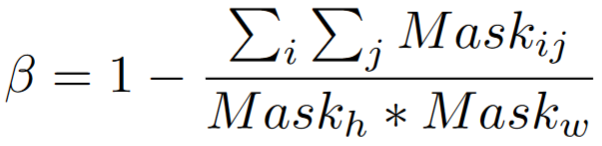
Modification 2: Pixel-level
- A smaller object occupies a smaller area.
- The pixels in the positive set P are much less than in the negative set N.
- Missing a matching in P is not that significant.
- Therefore, we multiply the loss on the positive side with an alpha > 1, so as to make the positive matching to be more oustanding.
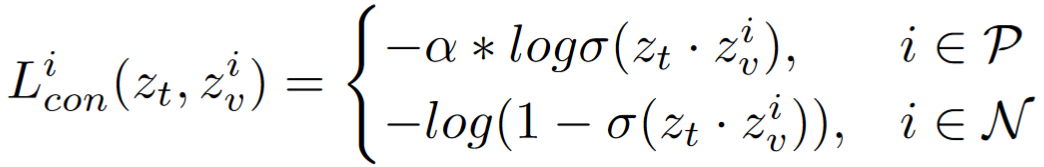
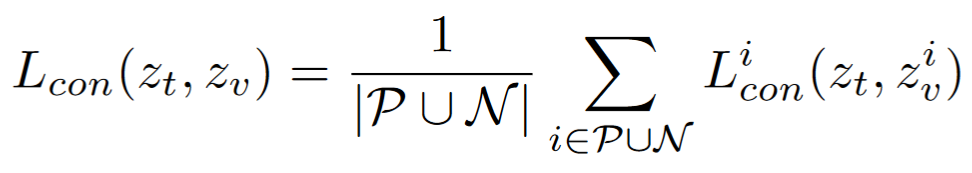
-
Dataset: COCO-Stuff
-
156 seen classes + 15 unseen classes
-
-
Metric
-
Mean IoU between the prediction and the ground truth
-
Seen, Unseen, Harmonic
-
-
Prompt Engineering
-
e,g, "This is a photo of <class name>"
-
Performing zero-shot semantic segmentation guided by the class name
-
Experiment
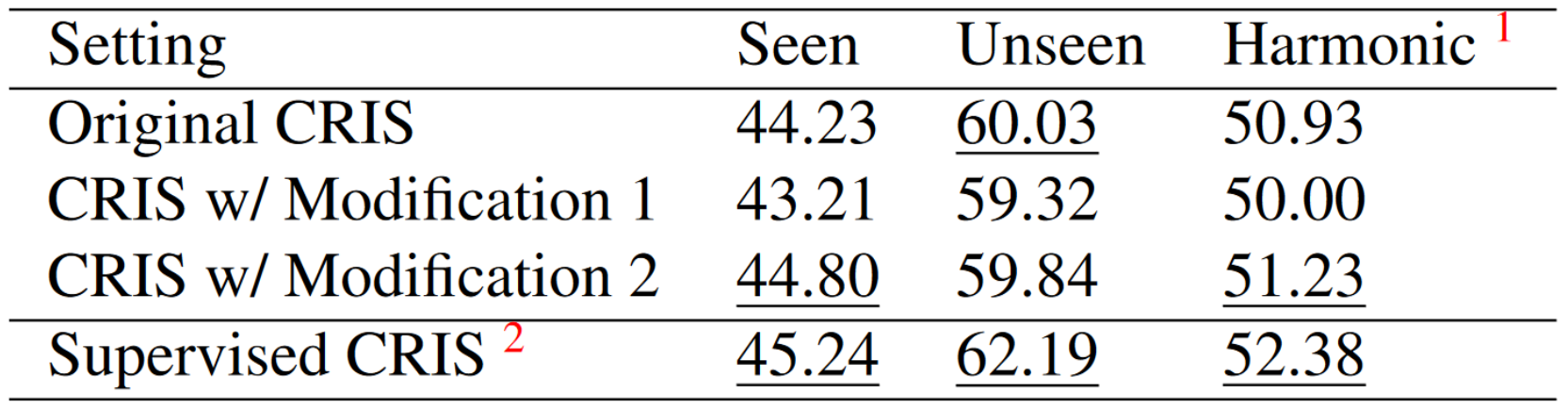
Result
Result Analysis
Examples

Reflection
- Construct Consistent Evaluation Metrics.
- Modify the MaskFormer part in ZegFormer to improve the class-agnostic segmentation performance.
- Polish the CRIS model to segment all objects in an image simultaneously.
- Produce a comprehensive survey among ZegFormer, CRIS-like and traditional models.
Conclusion
- We have tried to modify two models, ZegFormer and CRIS, to do the zero-shot semantic segmentation tasks.
- Insert a text project module to ZegFormer so that it is less overfit to the seen classes.
- Construct two novel loss functions in the CRIS model
- Achieve an impressive performance.
Thank you
Milestones
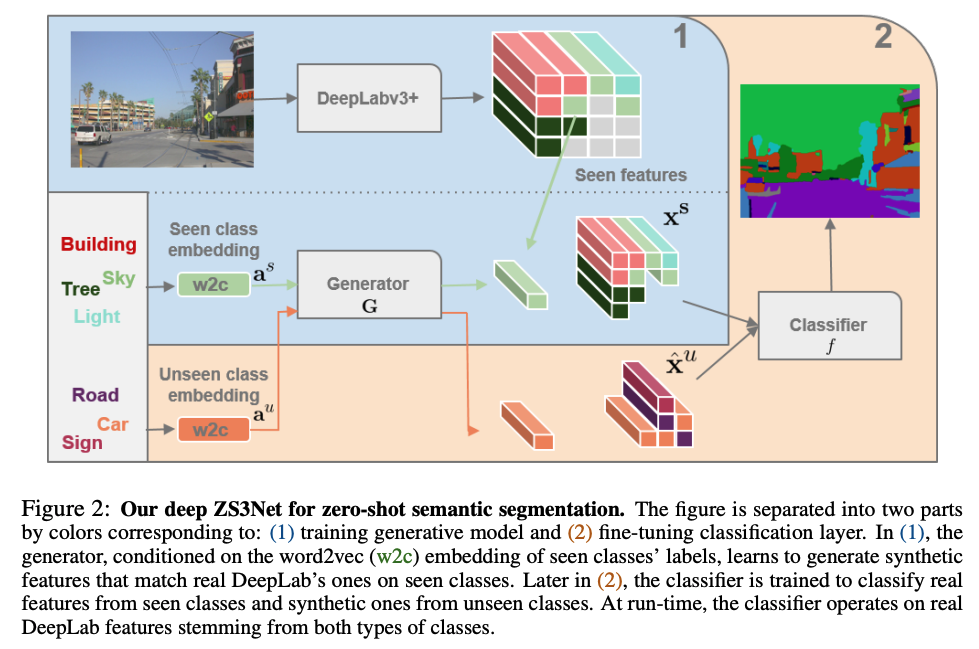
ZS3Net
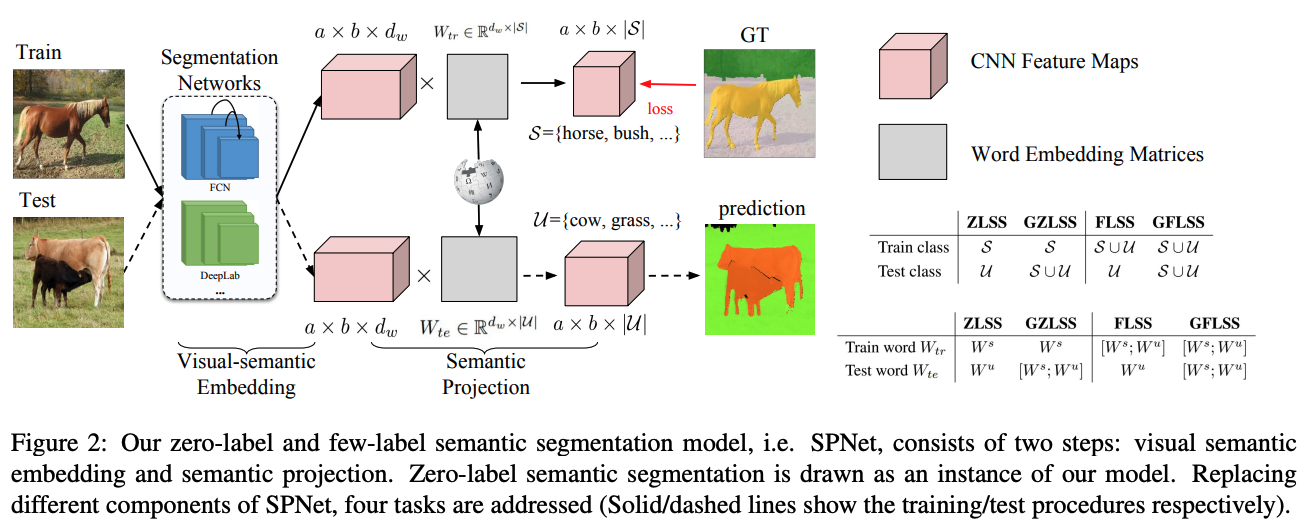
SPNet
CE6190
By elfsong
CE6190
- 20



