
RxJS
"lodash for async"- Ben Lesh

Front-end async data
DOM Events (0 - N)
Mouse events
Keyboard events
Object events
Drag events
Clipboard events
Media events

Front-end async data
DOM Events (0 - N)
Alternative user Inputs ( 0 - N)



Front-end async data
DOM Events (0 - N)
Alternative user Inputs (0 - N)
AJAX Calls ( single )



Front-end async data
DOM Events (0 - N)
Alternative user Inputs (0 - N)
AJAX Calls ( single )
Web Sockets ( 0 - N )


Front-end async data
DOM Events (0 - N)
Alternative user Inputs (0 - N)
AJAX Calls ( single )
Web Sockets (0 - N)
Animations (cancellable)


JavaScript async approaches







Plant
Cultivate
HeatUp







Callbacks
function doPopCorn() {
plant("🌰", (crop) => {
farm(crop, (brote) => {
recolect(sprout, (corn) => {
heatUp(corn, (popCorn) => {
eatPopCorn(popCorn);
})
})
})
});
}
Callbacks
so...
the peeling?
the transportation?
function hacerPalomitasMaiz() {
plant("🌰", function (crop) {
farm(crop, function (sprout) {
recolect(sprout, function (corn) {
peel(corn, function (grain) {
heatUp(grain, function (popoCorn) {
andOtherThing(popoCorn, function (x) {
andOtherThing2(x, function (y) {
andOtherThing3(y, function (z) {
eatPoporCorn(z);
})
})
})
})
})
})
})
});
}the ...?

function hacerPalomitasMaiz() {
sembrar("unaSemillita", function (cultivo) {
cultivar(cultivo, function (brote) {
recolectar(brote, function () {
calentar(mazorca, function (palomitasMaiz) {
servirPalomitasMaiz(palomitasMaiz);
})
})
})
});
}
Promises
function doPopCorn() {
plant("🌰").then(farm)
.then(recolect)
.then(heatUp)
.then(eatPopoCorn);
}



Promises

¿and if... I want to stop the process?
¿and ... the other seeds?

Promises
Promises are:
- Garanteed Future
- Promises can't be cancelled
- Inmutable
- Single Value
DOM Events (0 - N)
Alternative user Inputs (0 - N)
AJAX Calls ( single )
Web Sockets (0 - N)
Animations (cancellable)

We need a JavaScript type to handle multiple values

Iterable
- iterable.iterator() to get an iterator
- iterator.next() to get a result
- result.value : the value yeilded
- result.done : wheter or not it's complete
- errors are trhown during iterator.next() call

Iterable
const iterator = seeds.iterator();
while (true) {
try {
var result = iterator.next(); // do it async
} catch (err) {
handleError(err);
break;
}
if (result.done) {
break;
}
var seed = result.value;
doPopCorn(seed);
}
iterables alone aren't great for async

Iterable -> Observable
(iterable turned inside out)
let result = iterator.next();
let value = result.value;observer.next = (value) => doStuff(value)try{
let result = iterator.next();
} catch(err) {
handleError(value)
}observer.error = (error) => handleError(value)let result = iterator.next();
if (result.done){
handleCompletion(value)
break;
}observer.complete= (error) => handleCompletion(value)let iterator = iterable.iterator();observable.observer(observer);
Iterable -> Observable
let observer = {
next(value) { /*handle next value */},
error(err) { /*handle error */},
complete() { /*handle completion */}
};
let observable = new Observable(observer => {
const token = doAsyncStuff((err, value) => {
if (err) {
observer.error(err);
} else {
observer.next(value);
observer.complete();
}
});
return () => {
cancelAsyncThing(token);
}
});
observable.observer(observer);
Observable


Observable creation
helpers
- Observable.of(value,value,value)
- Observable.from(promise/iterable)
- Observable.fromEvent(item,eventName)
- Observable.interval(milliseconds)
- Observable.timer(milliseconds)
- Observable.ajax(url)

Observable subscription ( then)
x.then(handlerFn,errorFn)
Promises
x.subscribe(handlerFn,errorFn, completeFn)
observables

Error handling (catch)
Promises
observables
x.catch(error => {
if (error instanceof Array) {
return Promise.resolve('okay');
} else {
throw error;
}
});x.catch(error => {
if (error instanceof Array) {
return Observable.of('okay');
} else {
throw error;
}
});
Observables can be retried
myObservable.retry(3);
myObservable.retryWhen(errors =>
errors.delay(3000));
Finally
Promises
observables
x.finally(()=> {
//done
});x.finally(()=> {
//done
});
Operators
observable
.filter(x => x > 10)
.map(x => x * 2)
.subscribe(x => console.log(x));
Sets have operators
iterable
.filter(x => x > 10)
.map(x => x * 2)
.forEach(x => console.log(x));Observables have operators too!
Operators for observables differ from the operators for the iterables. They apply the operation for each item not the whole collection.

Operators
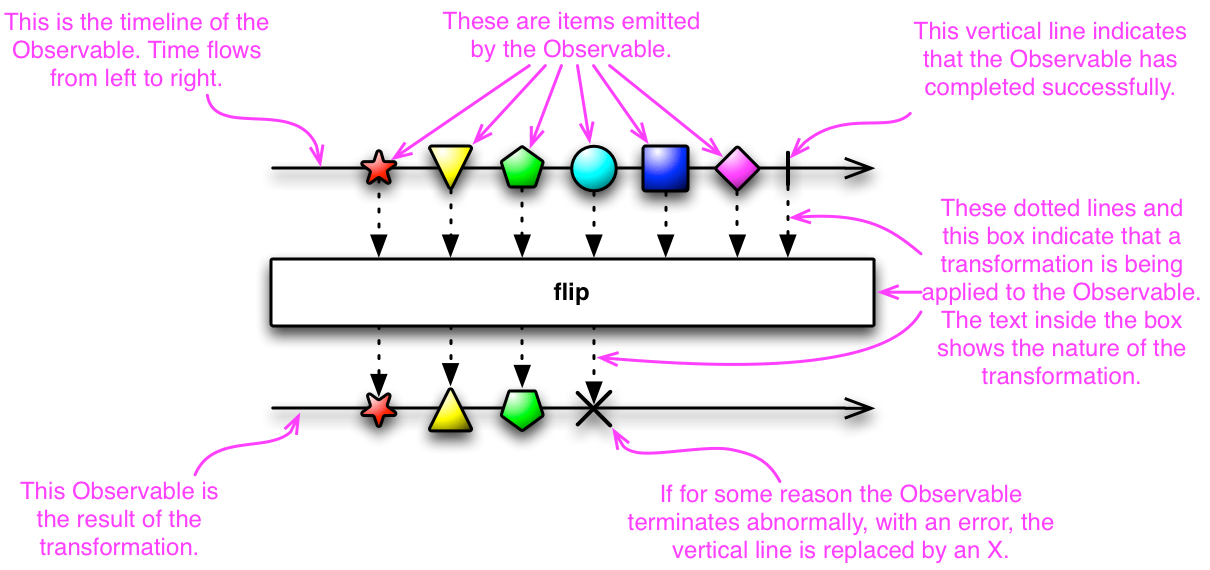

Simple operators
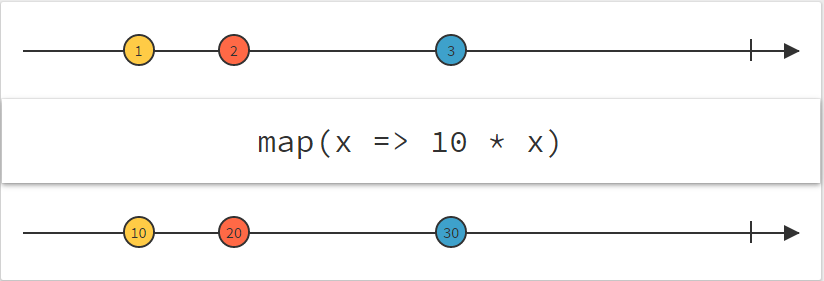

Simple operators
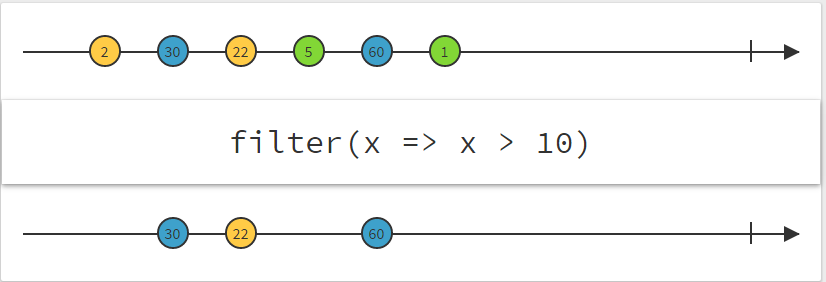

Simple operators
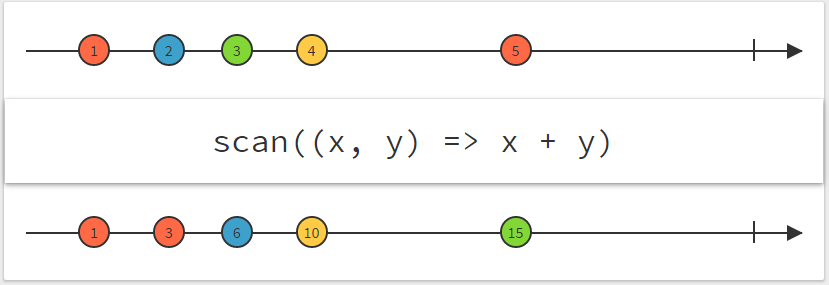

Simple operators
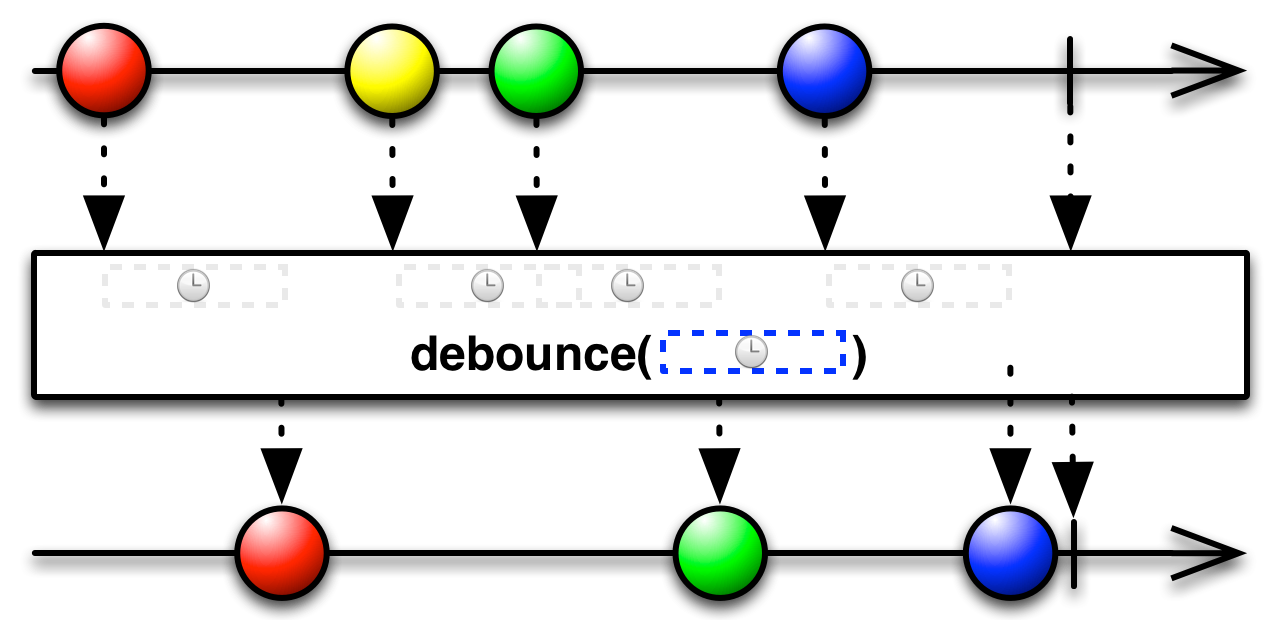

Simple operators
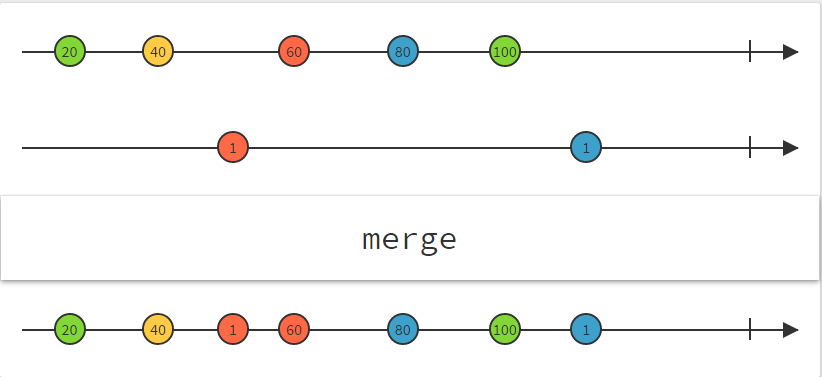

Simple operators
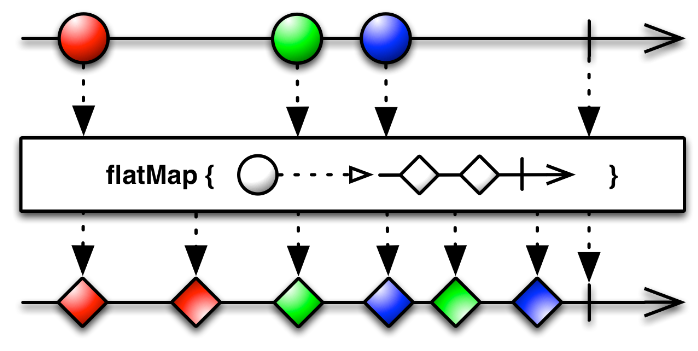

Simple operators
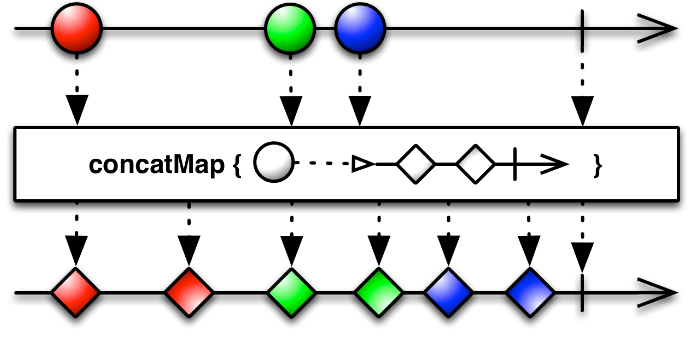

Simple operators
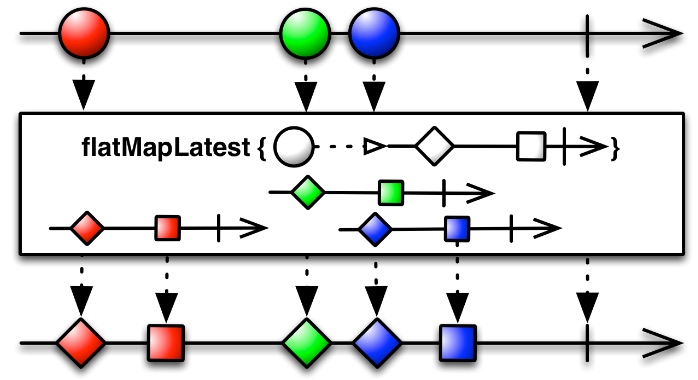

Simple operators
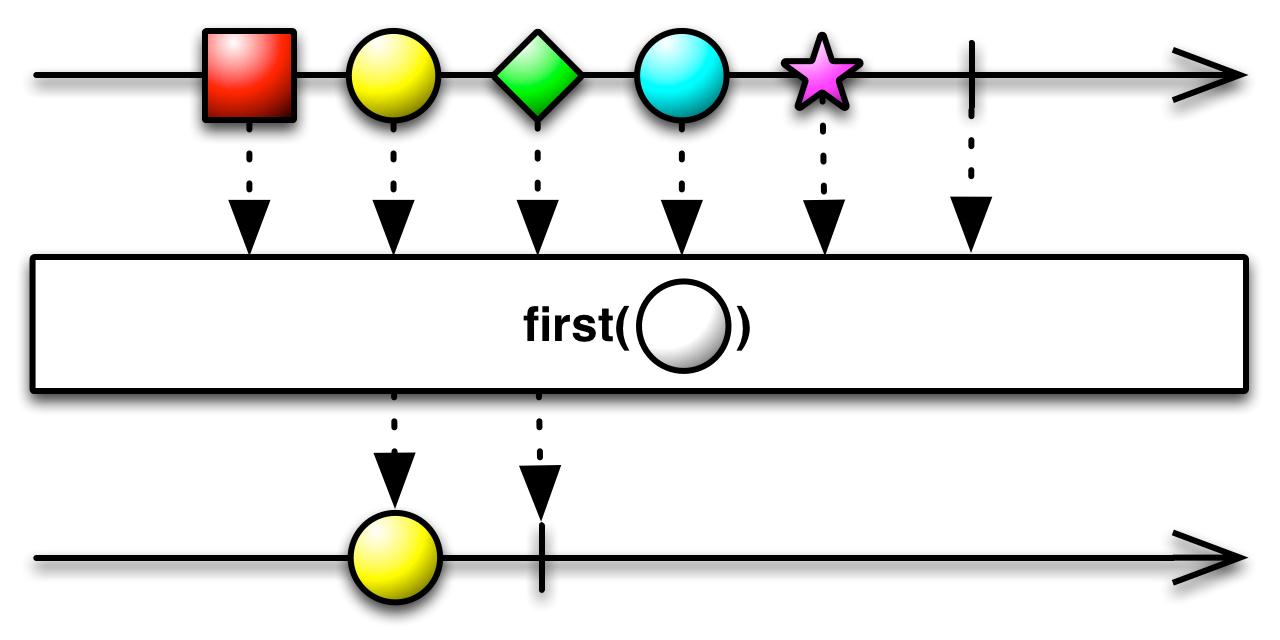

Simple operators
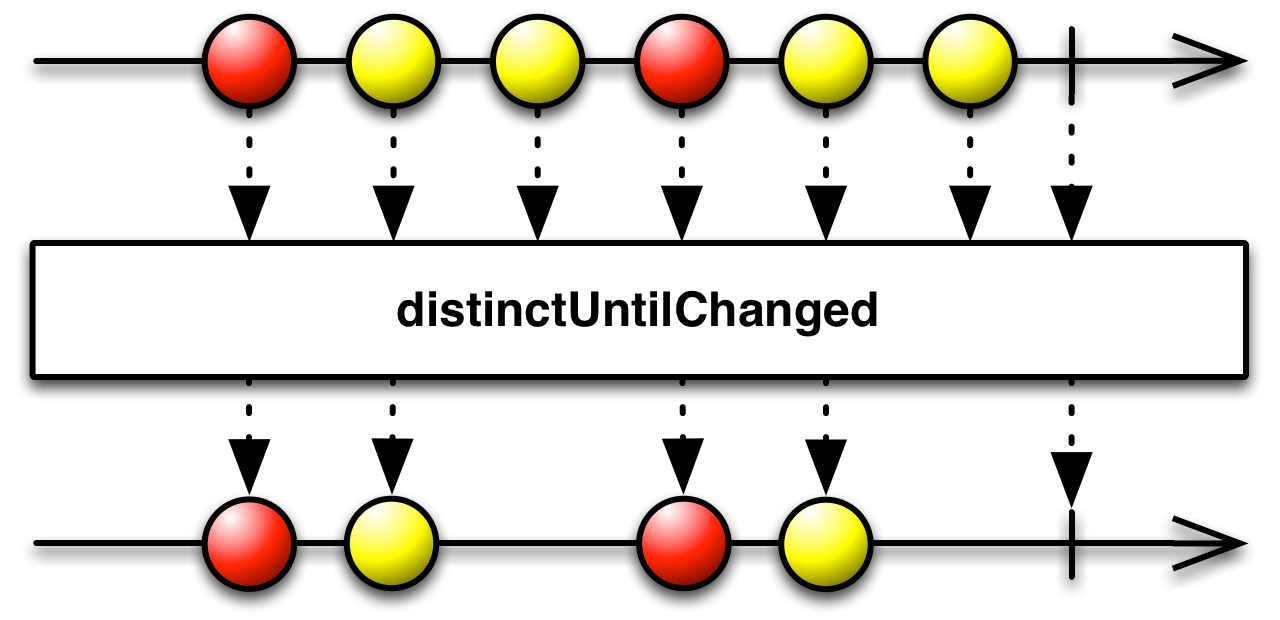

How Operators Works
- Subscribe is the last operator we can have.
- The result of the operator subscribe is a subscription.
- We can call the method unsubscribe on the subscription to cancel the stream.
To remember:

Observable
let observable = Rx.Observable.of("🌰", "🌰", "🌰");
observable.mergeMap(plant)
.mergeMap(farm)
.mergeMap(recolect)
.mergeMap(heatUp)
.subscribe(poporCorn => eat(poporCorn));
So...What's RxJS
Reactive programming
Treating events as collections
Manipulate sets of events with "operators
Lazy. Observables will not generate values until they are subscribed to
Future can be ignored (unsubscribe)

Typeahead
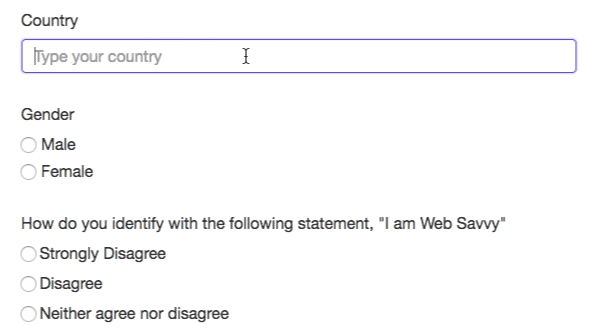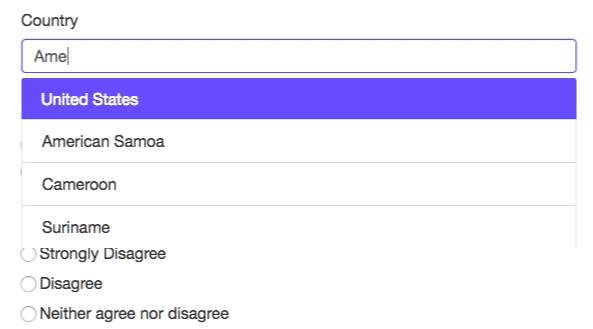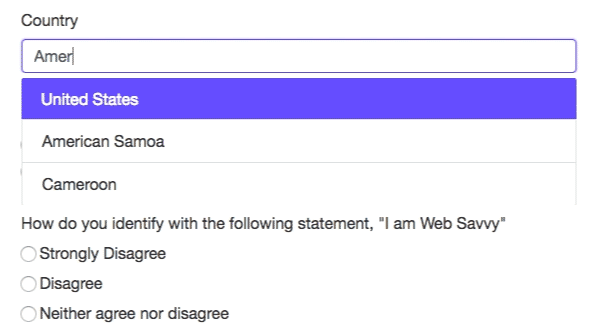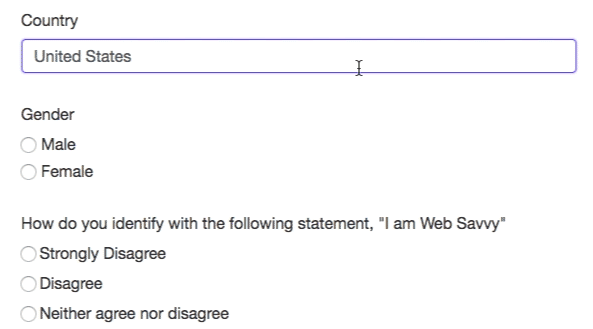

Typeahead
RxJS-English
By Felipe Jaramillo Gómez
RxJS-English
- 402



