$scope
Scope events propagation
Types
- Broadcasted
- Emitted
Broadcasted
$scope.$broadcast('MyEvent',args...)
$scope.$on('MyEvent', function(event,args...) {
//do something
});Events to the scope children
Emitted
$scope.$emit('MyEvent',args...)
$scope.$on('MyEvent', function(event,args...) {
//do something
});Events to the scope parents
$scope.watch
$scope.watch depths
- by reference
- collection contents
- by value
By reference
Detects a change when the whole value returned by the watch expression switches to a new value. If the value is an array or an object, changes inside it are not detected. This is the most efficient strategy.
scope.name = 'misko';
scope.$watch('name', function(newValue, oldValue) {
scope.counter = scope.counter + 1;
});Watch collection
Detects changes that occur inside an array or an object: When items are added, removed, or reordered. The detection is shallow - it does not reach into nested collections. Watching collection contents is more expensive than watching by reference
$scope.names = ['igor', 'matias', 'misko', 'james'];
$scope.$watchCollection('names', function(newNames, oldNames) {
});
By value
Detects any change in an arbitrarily nested data structure. It is the most powerful change detection strategy, but also the most expensive.
scope.name = 'misko';
scope.$watch('name', function(newValue, oldValue) {
scope.counter = scope.counter + 1;
}, true);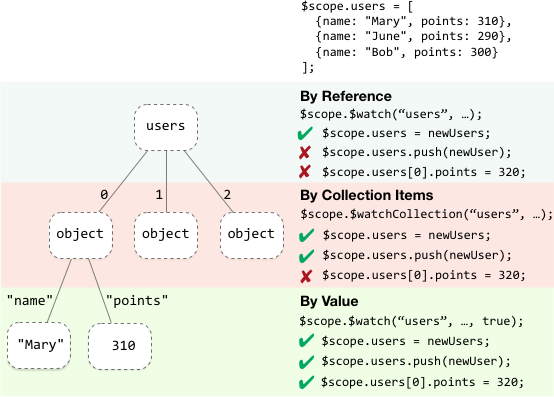
$scope
By Felipe Jaramillo Gómez
$scope
- 178



