MEMOIR:
Memory Measurement Model
Implementation Ressource
Jan Göttmann, M.Sc.


MEMOIR
What is MEMOIR ?
- Flexible toolbox of experiments tailored for the Memory Measurement Model (M3)
- Features Verbal, Visual and Numerical domain
- Customizable for different research enviroments (behavioral and electrophysiological)
- Customizable for different samples (e.g. general population vs. student sample)


MEMOIR
Aim of the Talk
- Present the latest results from behavioral pilot studies.
- Discuss possible shortcomings and problems based on these results, such as error rates, difficulty, and timing.
- Provide feedback for further development, including which features are desirable and which tasks could be important to implement.

The Memory Measurement Model (M3)

Memory Measurement Model (M3)
Measurement models for simple, complex, and updating working memory tasks.

Main Idea:
Colour
Position
1
2
3
4

Memoranda
Memoranda
Memoranda
Read out loud
Read out loud
Read out loud
First Position has to be recalled
Time
F
V
L
C
H
M
M
H
F
L
H
O
D
T
V
C
Z
B
K
P
J
R
Other Item
Distractor in other Position
Not Presented Lure (NPL)
Correct Item
Distractor in Position

Memory Measurement Model
V
F
L
M
C
H
Memoranda
Memoranda
Memoranda
Read out loud
Read out loud
Read out loud
Second Position has to be recalled
Time
C
F
M
K
B
L
P
H
Z
V
H
O
D
T
R
J
Other Item
Distractor in other Position
Not Presented Lure (NPL)
Correct Item
Distractor in Position

Memory Measurement Model
F
V
L
M
C
H
Memoranda
Memoranda
Memoranda
Read out loud
Read out loud
Read out loud
First Position has to be recalled
Time
Correct Item
Distractor in Position
Distractor in other Position
Other Item
Not Presented Lure (NPL)

Memory Measurement Model
- Group Level Parameters show acceptable recovery
- Group-level parameters can map aging effects in memory decline
- No systematic parameter trade-offs
- No data for the recovery of subject-level parameters
- Which experimental features are important to achieve a good parameter recovery?

Emprical results
Current Research
Memory Measurement Model
We ran simulations to investigate the shortcomings of the current research !
MEMOIR: Experimental Designs
Conlusions from Simulations
- Subject Parameters can be recoverd with acceptable to very good fit for the complex span model !
Important experimental features
- Sufficient Number of NPLs ! Minimum of 8 NPLs should scale the response set!
- At least two freetime conditions
- 250 retrievals minimum, but 500 even better (but time consuming)
- Accuracy has to midranged to maximize the precision - avoid floor and ceiling effects!


Experiments

Experiments: Cued Complex Span Tasks
?
Relevant Stimuli
Distractor
Secondary Task: Evaluate Hue of Colour (Blue vs. Red)

Experiments: Cued Complex Span Tasks
2. Position
M3: Empirical Application
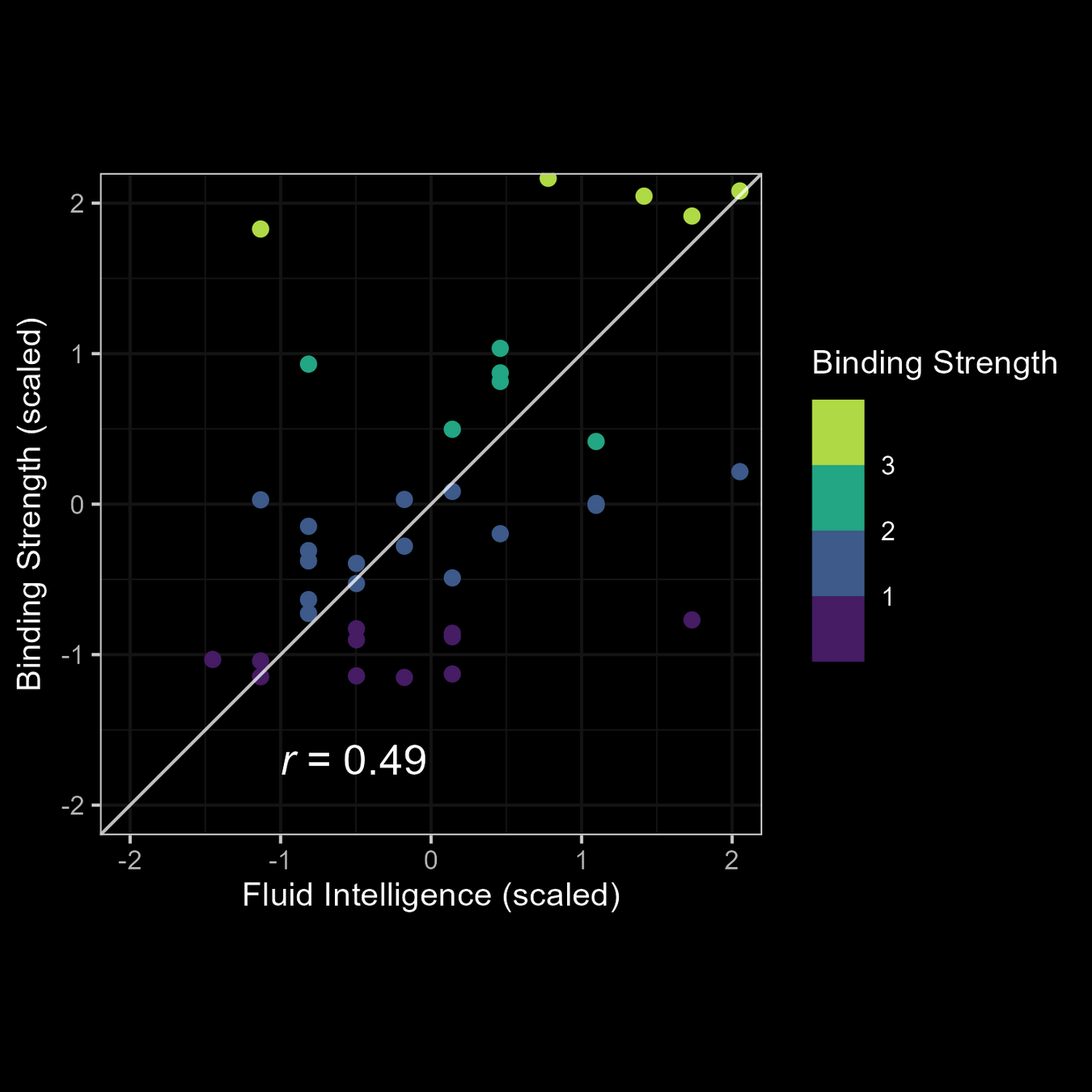
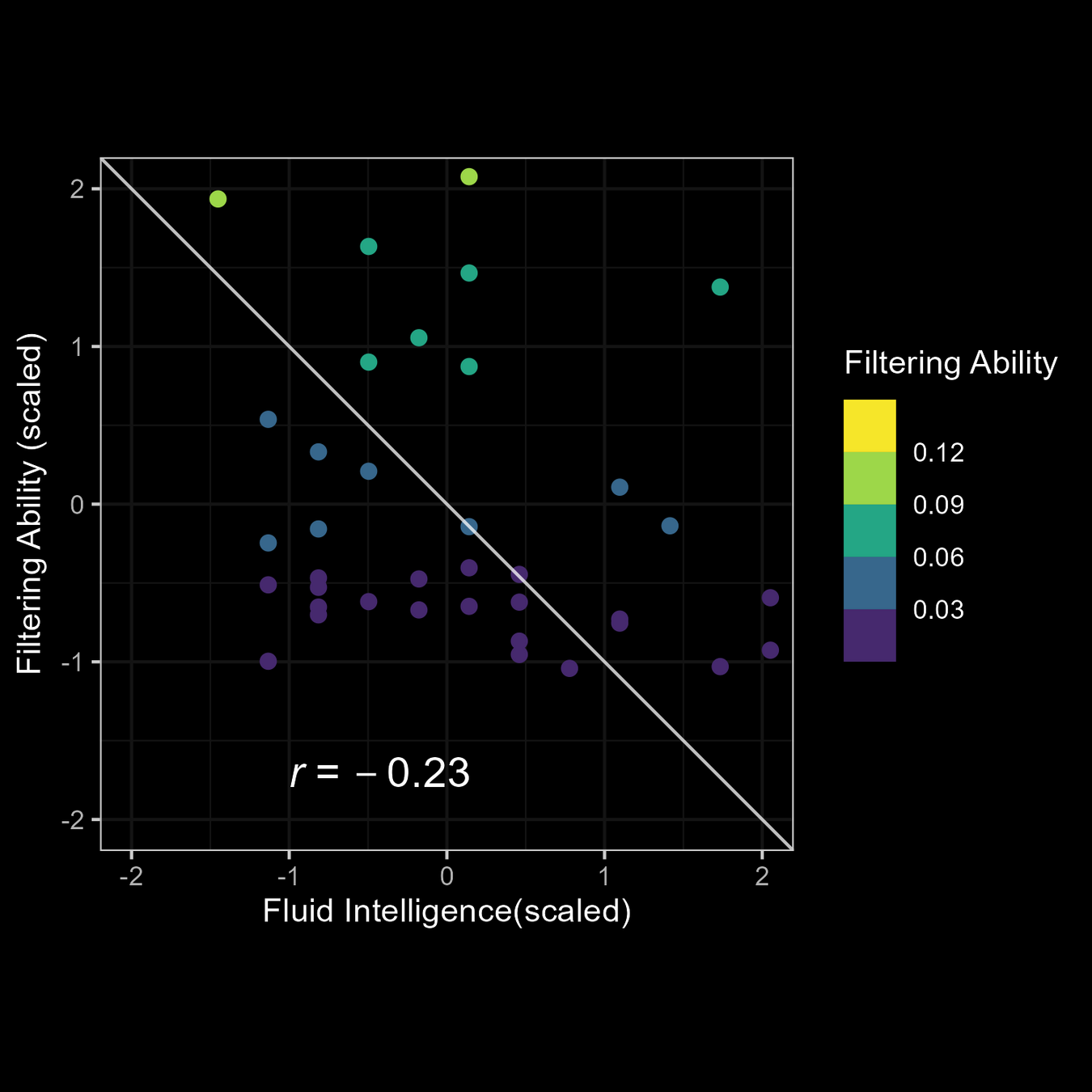
Relationship of M3 Parameters with fluid intelligence
Which Experimental features express the models assumptions most consistently ?

- Random vs. Sequential Recall ?
- Timing Effects on model parameters ?
- Difficulty has to be mid-ranged!
Experiments: Cued Complex Span Tasks


Random vs. Sequential Recall ?

- Set Size 5 in both tasks
- ACC to high for verbal domain, to low for visual domain
- Secondary Task Accuracy was in genral > .75
- Recall Sequence has no effect (no significant difference, only marginal)
Experiments: Cued Complex Span Tasks

Set Size Effect for different domains
- Set Size 4 for Visual Task
- \(\mu_{ACC} \sim .56\)
- Set Size 6 for Verbal Task
- \(\mu_{ACC} \sim .64\)
- Increased Encoding Time to 1000 ms (from 600ms)

Experiments: Cued Complex Span Tasks

Discussion
Experiments: Cued Complex Span Tasks
- What are your suggestions for features to be integrated?
- Is it worth testing the validity of the model parameters in regard to experimental manipulations (e.g. timing)?
- Which tasks could be interesting to implement for the M3 Model?

Thank you for Your Attention!

@JanGoettmann
github.com/jgman86

jan.goettmann@uni-mainz.de

MEMOIR Talk
By Jan Göttmann
MEMOIR Talk
- 46



