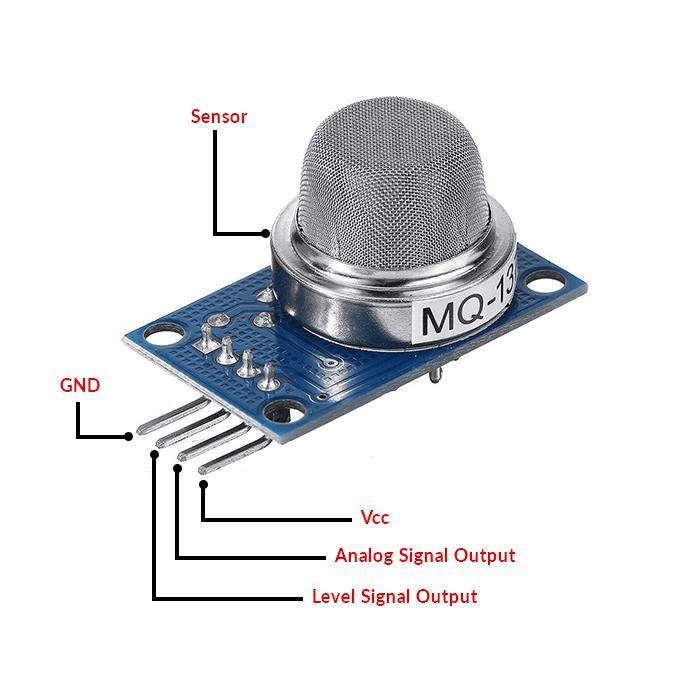
Gas sensor detector
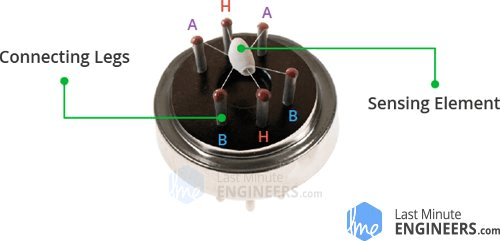
Tin Dioxide (SnO2) which is an n-type semiconductor that has free electrons
- Gas sensors, also known as gas detectors, are essential electronic devices that identify and detect various gases.
- They are particularly used to detect toxic or explosive gases and measure gas concentration. Selection encompasses a wide range of gas sensors, including the MQ series, Carbon Monoxide, Methane Gas, Hydrogen Gas, Alcohol Detectors, LPG detectors, Ozone Gas detectors, Air Quality sensors, and more,
-
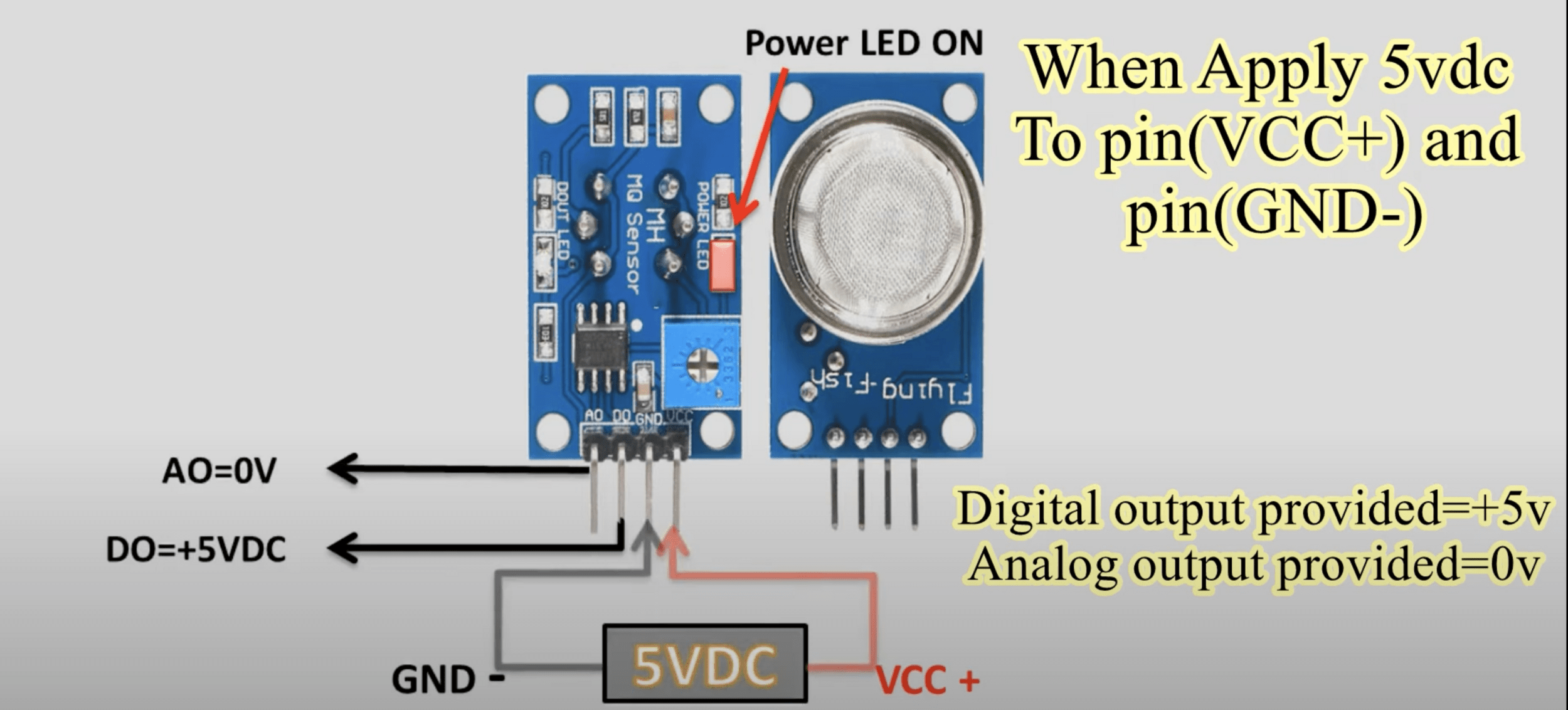
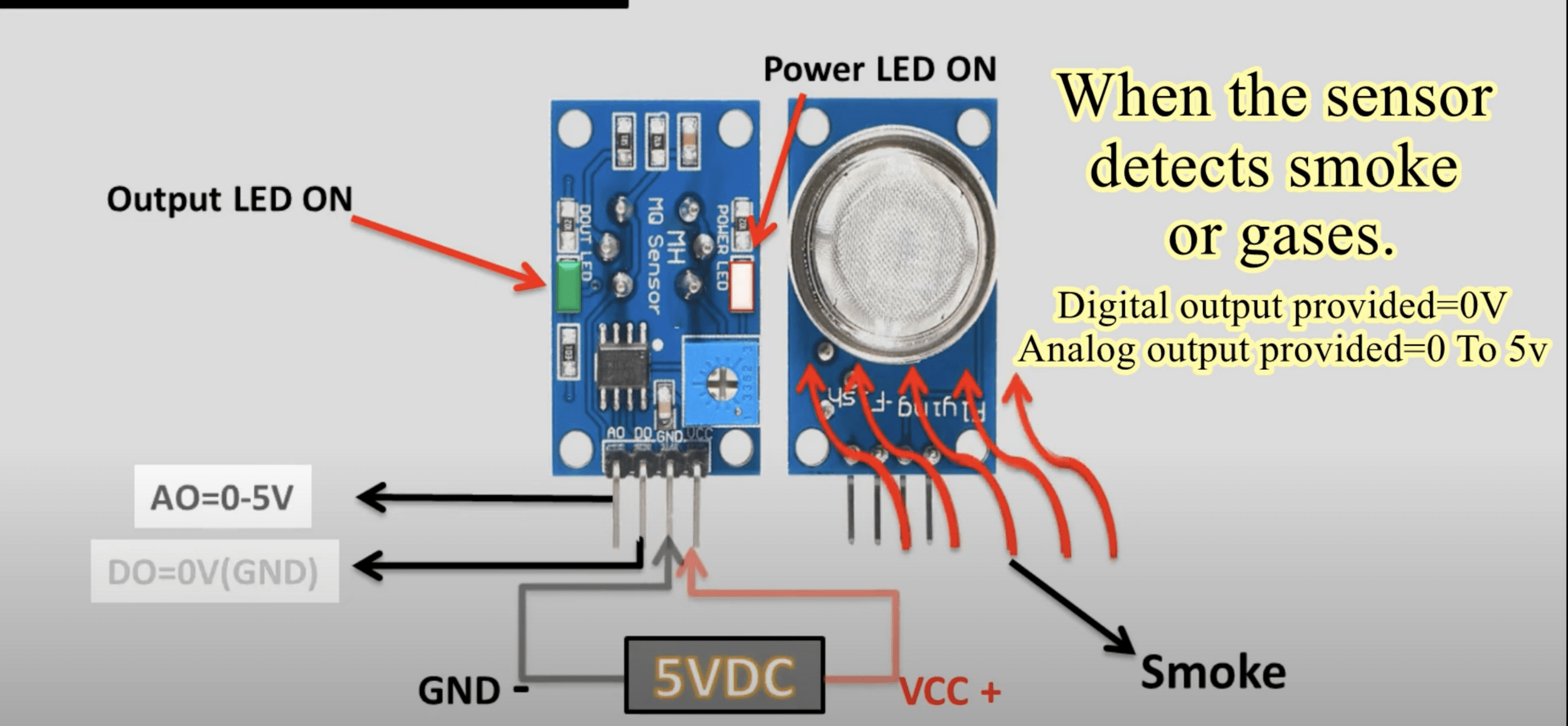
Sensor: The detector has a sensor that can detect the presence of certain gases in the atmosphere. The type of sensor depends on the type of gas you are trying to detect. For example, a semiconductor sensor is often used to detect combustible gases, while an electrochemical sensor might be used to detect carbon monoxide.
-
Signal Processing: When the sensor detects gas, it changes its electrical resistance. This change is measured and processed by the detector's electronics. The processed signal is then compared to a pre-set level or threshold.
-
Alarm: If the processed signal exceeds the threshold, the detector triggers an alarm. This could be a visual alarm (like a flashing light), an audible alarm (like a siren), or both. Some detectors can also send a signal to a control panel or a connected device, triggering further actions like shutting off a gas valve or alerting emergency services.
-
Reset: Once the gas concentration drops below the threshold, the detector resets and is ready to detect gas again.
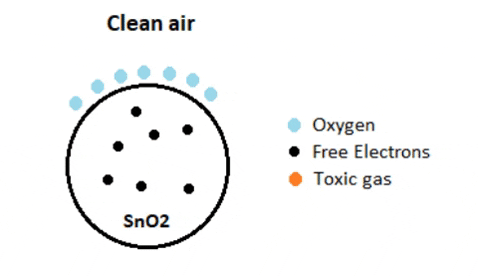
Normally the atmosphere will contain more oxygen than combustible gases. The oxygen particles attract the free electrons present in SnO2 which pushes them to the surface of the SnO2. As there are no free electrons available output current will be zero.
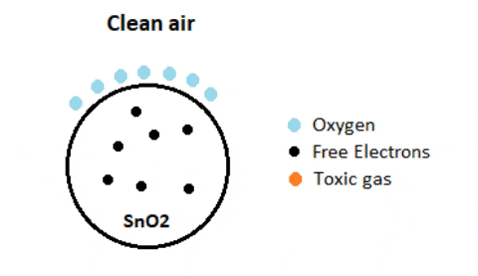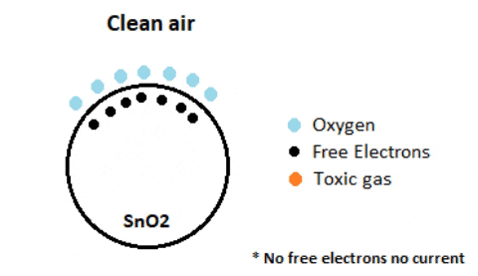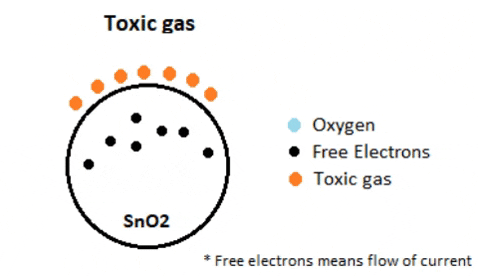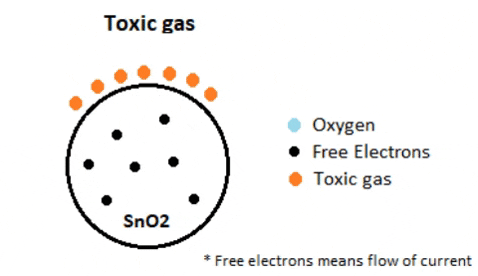
When the sensor is placed in the toxic or combustible gases environment, this reducing gas (orange color) reacts with the adsorbed oxygen particles and breaks the chemical bond between oxygen and free electrons thus releasing the free electrons. As the free electrons are back to its initial position they can now conduct current, this conduction will be proportional the amount of free electrons available in SnO2, if the gas is highly toxic more free electrons will be available.
deck
By Gulshan Nadaph
deck
- 352



