Deep Learning: Brief Intro
CS6700
Presented by: Harshavardhan
Objectives
- Motivate DL
- What is DL?
- How to do DL?
Acknowledgements
The Supervised Learning Problem
x
y

Car
Not Car

The Supervised Learning Problem
f(x,\theta) \approx y
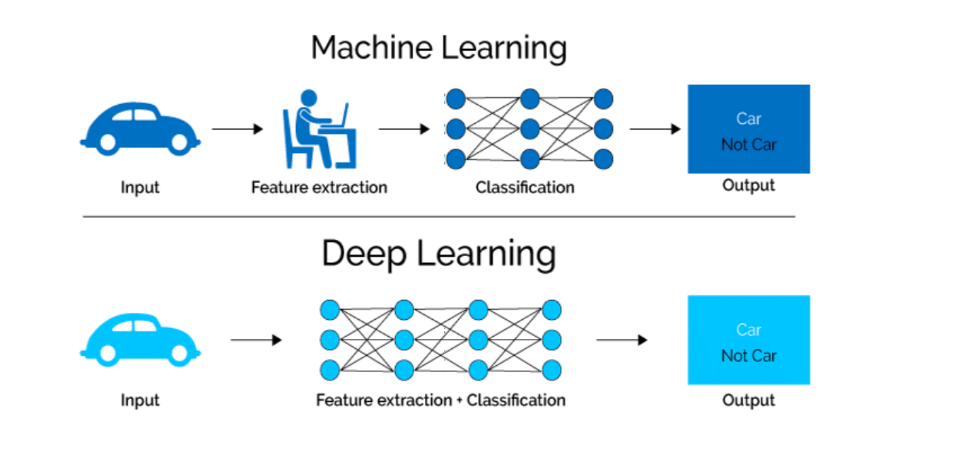
ML Learner
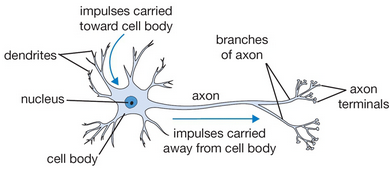
Neuron
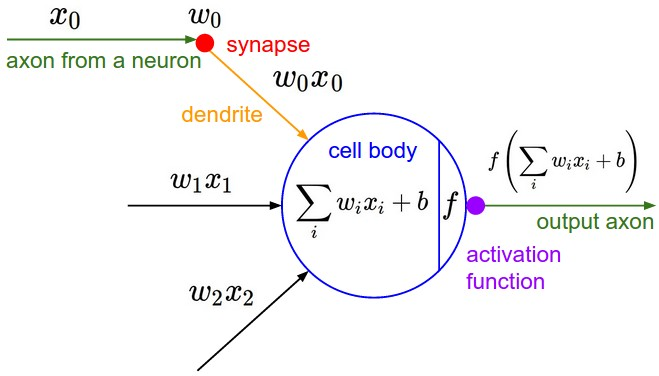
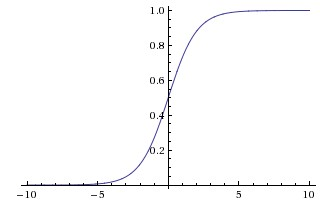
Activation Functions
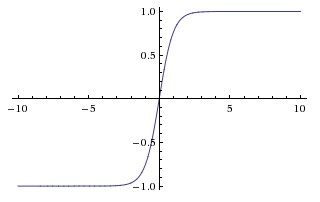
tanh(x)
\frac{1}{1+e^{-x}}
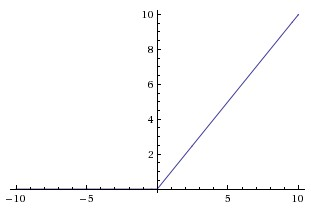
ReLU(x)
Feed-forward Neural Nets
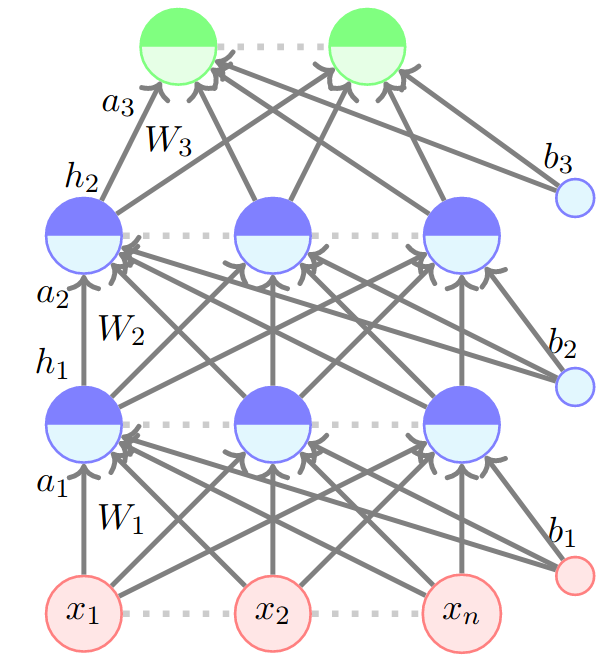
h_3 = \hat{y}
Output
= O(W_3f(W_2f(W_1x + b_1)+b_2)+b_3)
Parameters
\theta = [W_i, W_2, W_3, b_1, b_2, b_3]
Objective
Minimize Loss Function
\mathcal{L}(\theta;x,y)
- Mean squared Error
- Cross Entropy
\frac{1}{N}\sum_{i=1}^N (\hat{y_i}-y_i)^2
-\frac{1}{N}\sum_{i=1}^N \sum_{j=1}^C y_{i,c}\log(\hat{y}_{i,c})
Gradient Descent
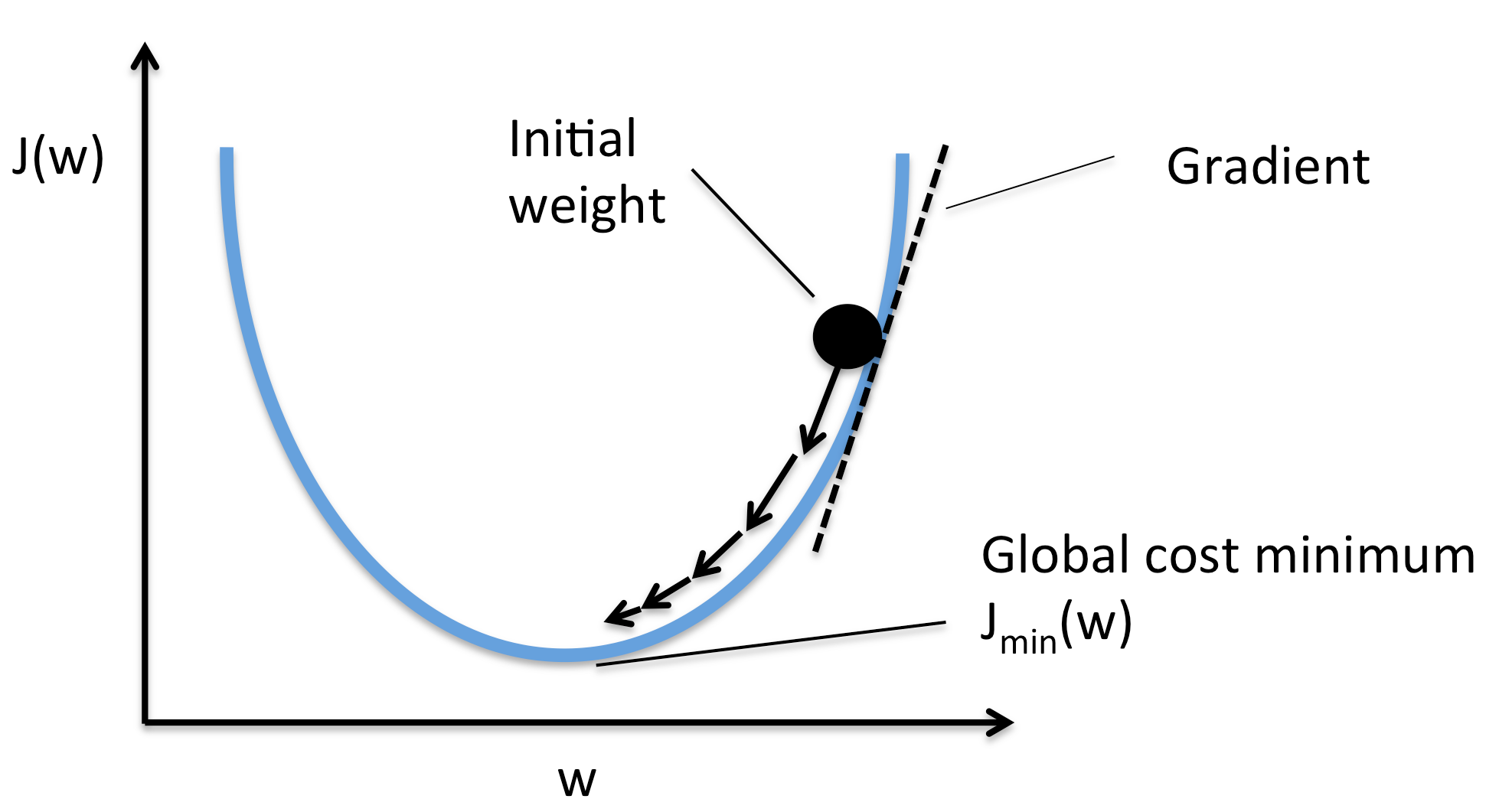
w \leftarrow w - \eta\frac{dJ}{dw}
Gradient Descent
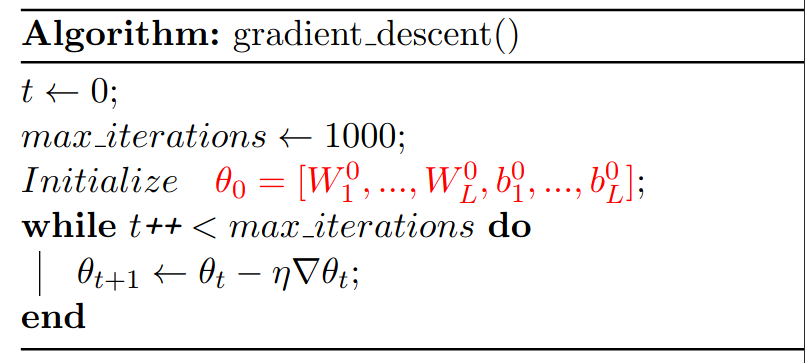
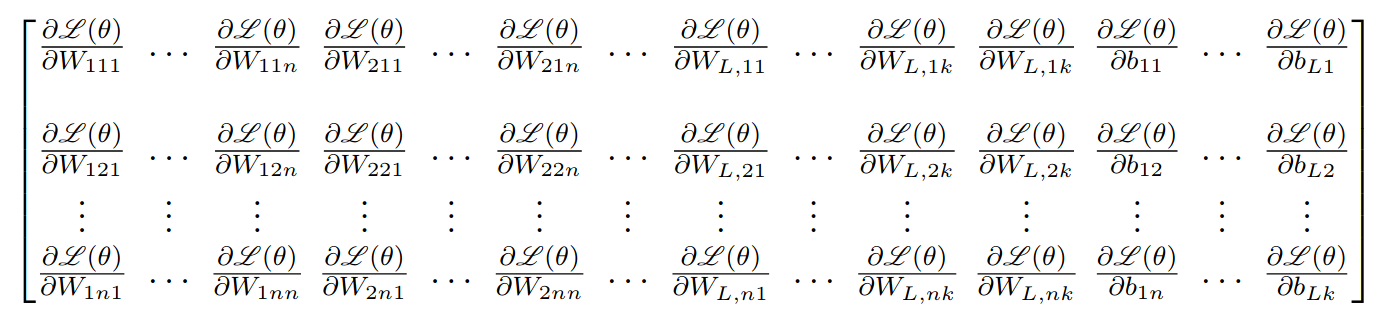
\nabla\theta=
Backpropogation Chain rule
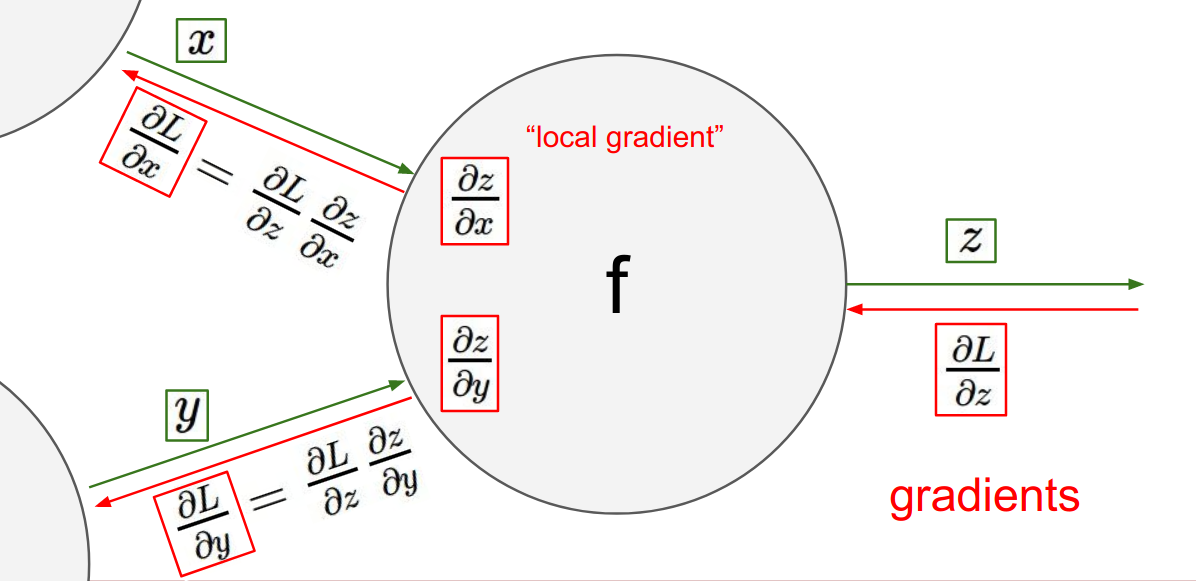
=
Backpropagation
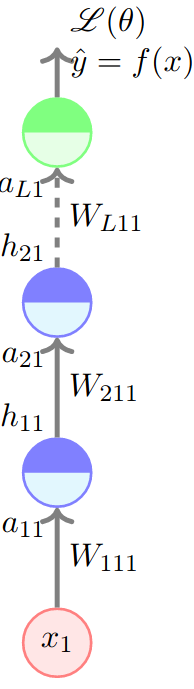

Backpropagation
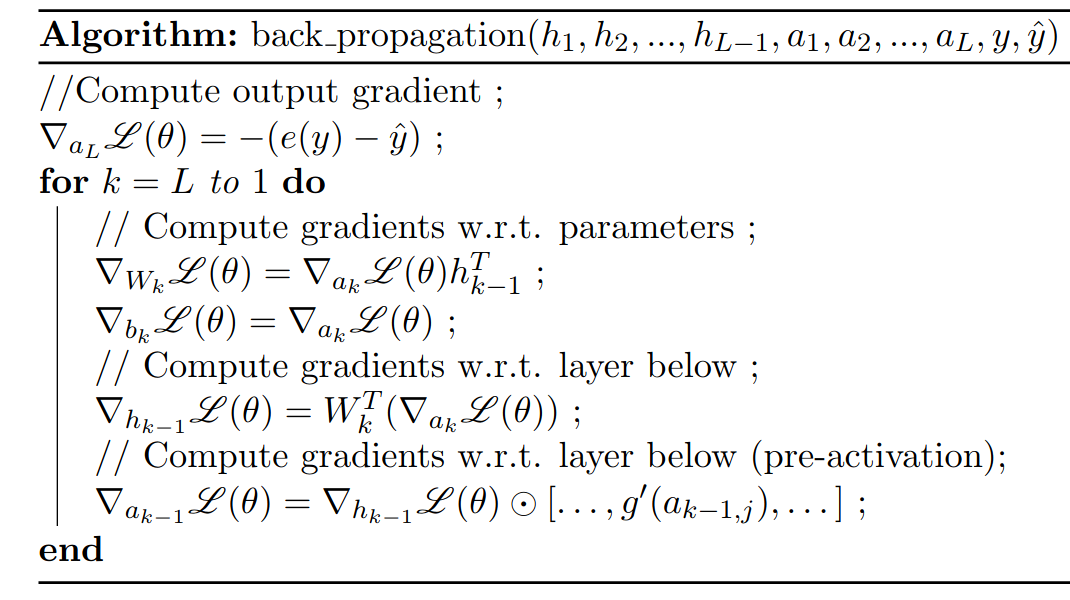

Regularization
Neural Networks are very good function approximators
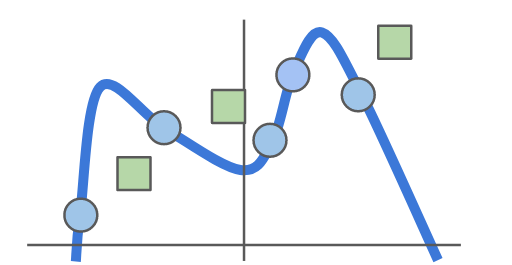
Regularization
\mathcal{L}_{total}(\theta) = \mathcal{L}(\theta;x,y) + \lambda R(\theta)
Make NN simpler
Regularization
\sum_{i,j,k}W_{i,j,k}^2
\sum_{i,j,k}|W_{i,j,k}|
L2
L1
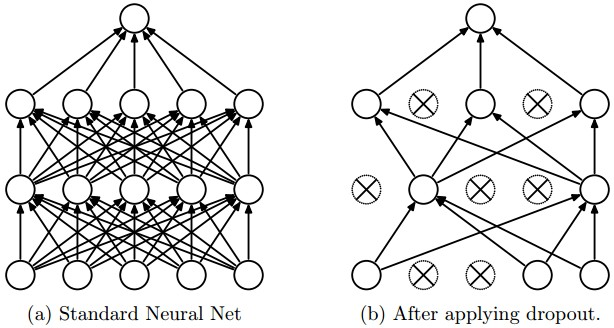
Deep Learning Frameworks

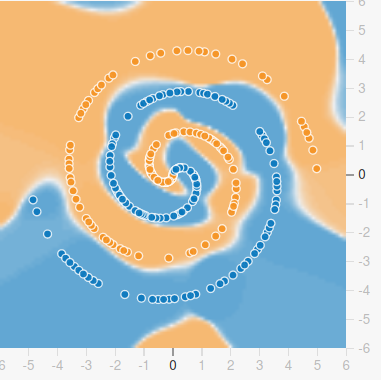
Why DL? : great function approximators
Why DL?: Representation matters
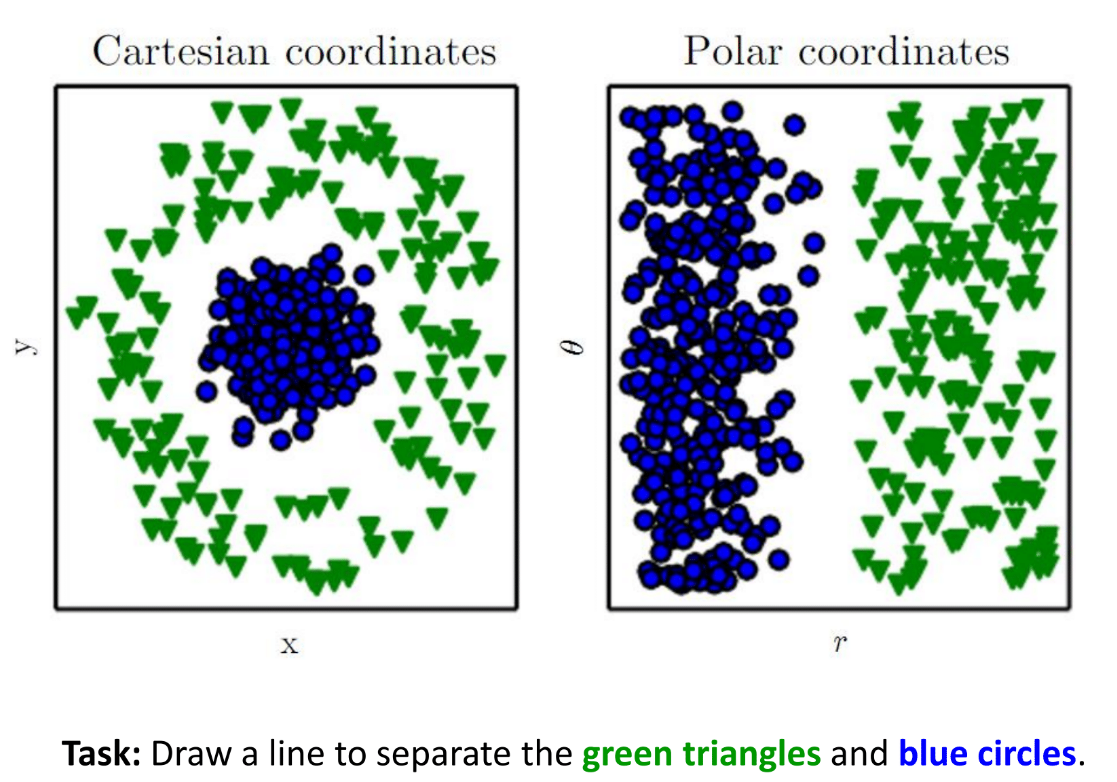
Why DL?: Representation matters

Thank You!
Deep Learning: Brief Intro
By Harshavardhan Kamarthi
Deep Learning: Brief Intro
- 243



