Learning Bayes-optimal
dendritic opinion pooling
Jakob Jordan
Department of Physiology, University of Bern, Switzerland
25.08.2022, Giessbach meeting, Giessbach, Switzerland

Jordan, J., Sacramento, J., Wybo, W. A., Petrovici, M. A., & Senn, W. (2021).
Learning Bayes-optimal dendritic opinion pooling. arXiv preprint arXiv:2104.13238.

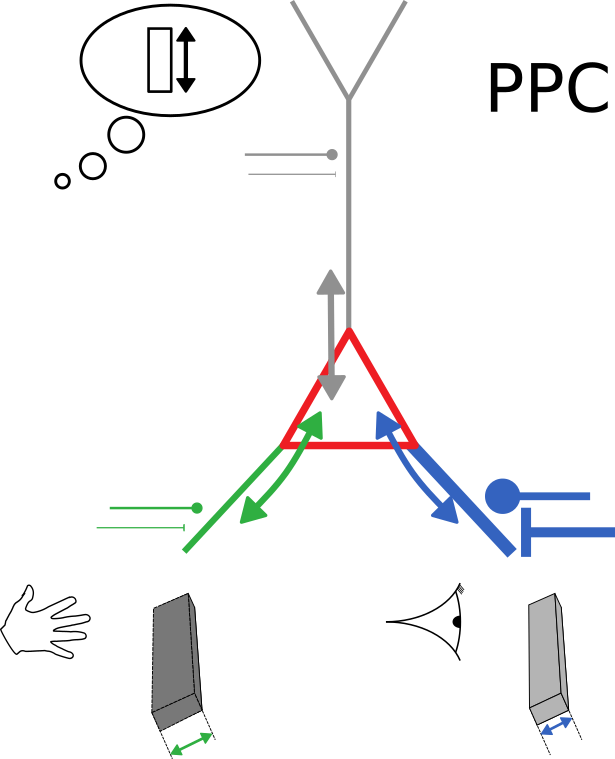
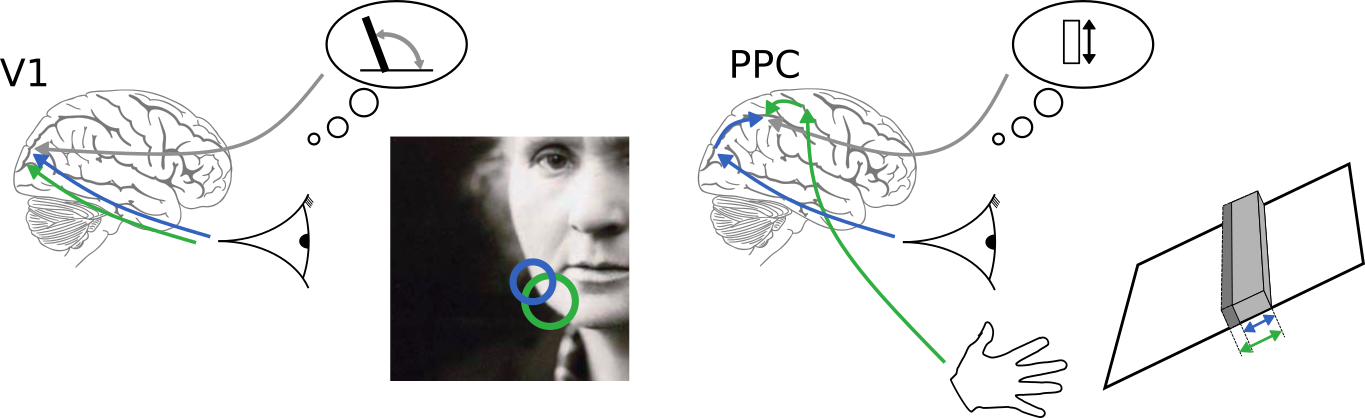
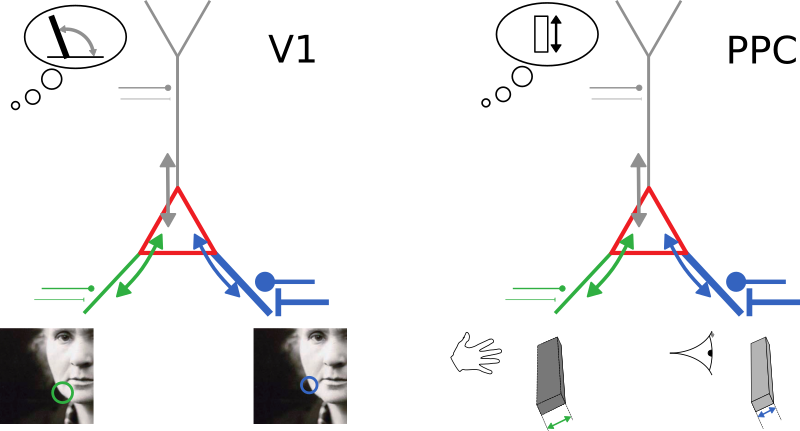
(High-level) neuronal representations reflect contributions from multiple modalities
How to combine information from uncertain sources?




visual
auditory
olfactory
"uncertainty"
How to estimate the uncertainty of each source?
Can single cortical neurons learn to optimally integrate information from uncertain sources?
Can single model neurons with plausible dynamics learn to optimally integrate information from uncertain sources?
An observation
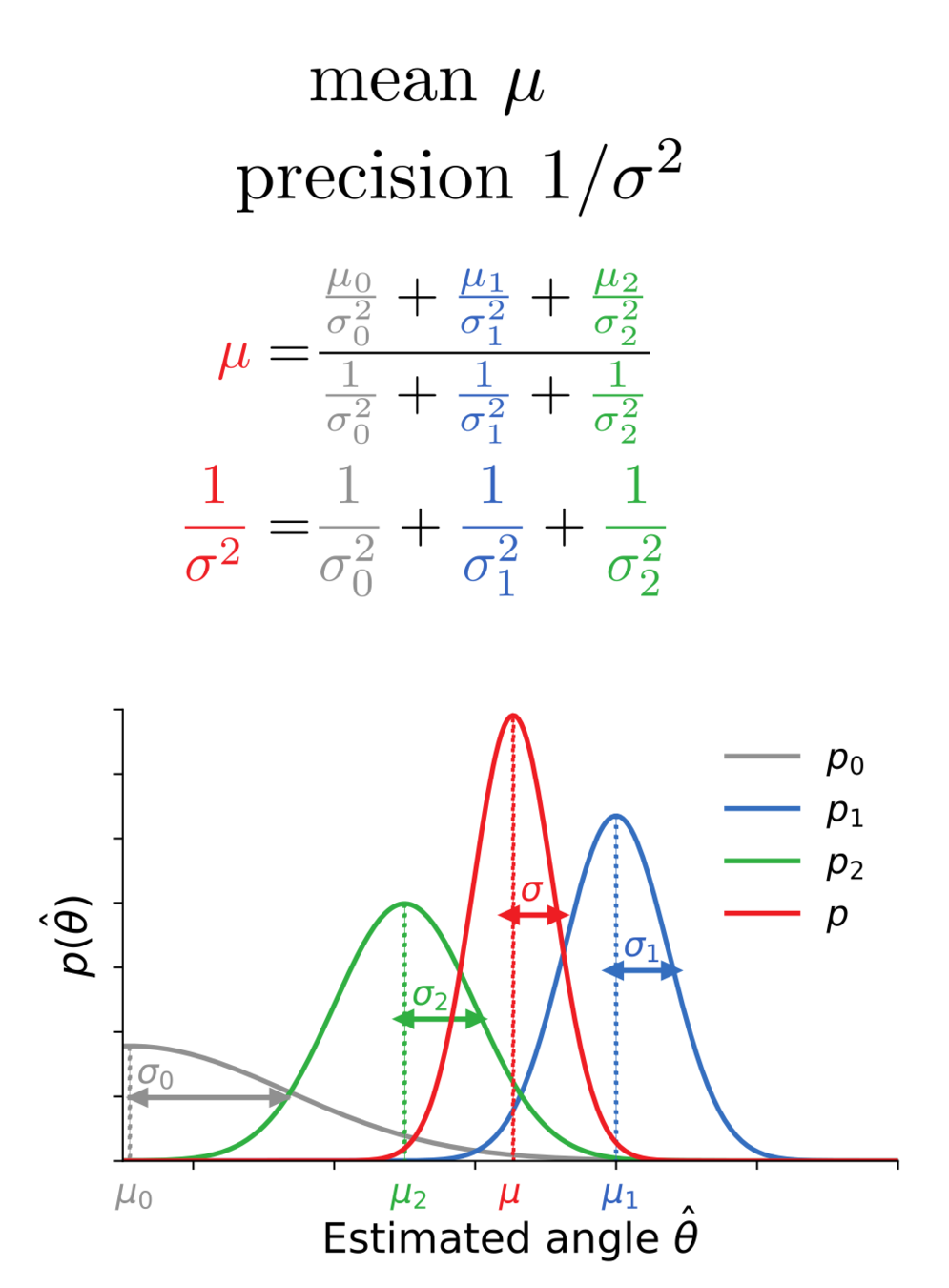
Bayes-optimal inference
"Slow" membrane potentials
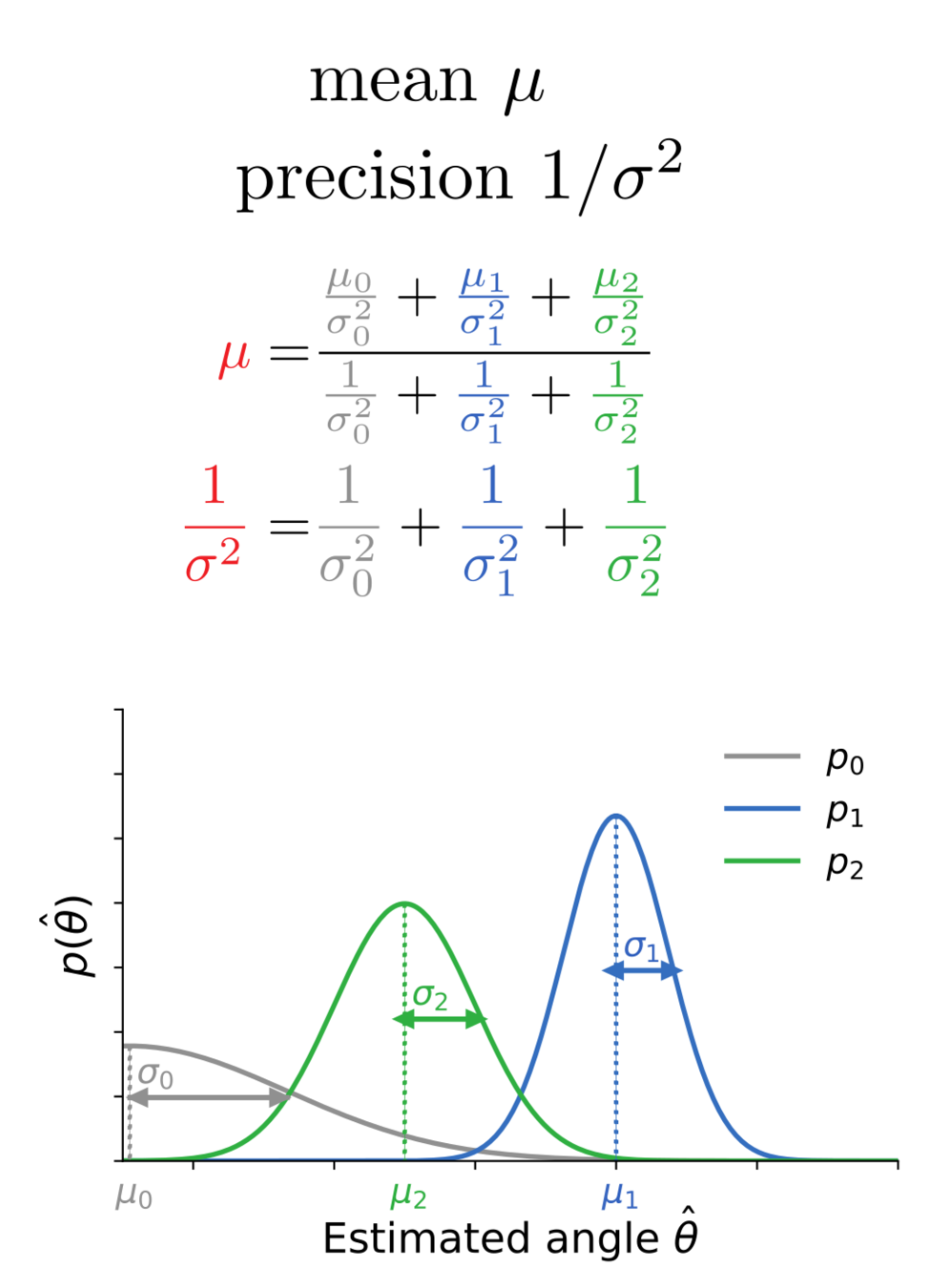
mean
precision
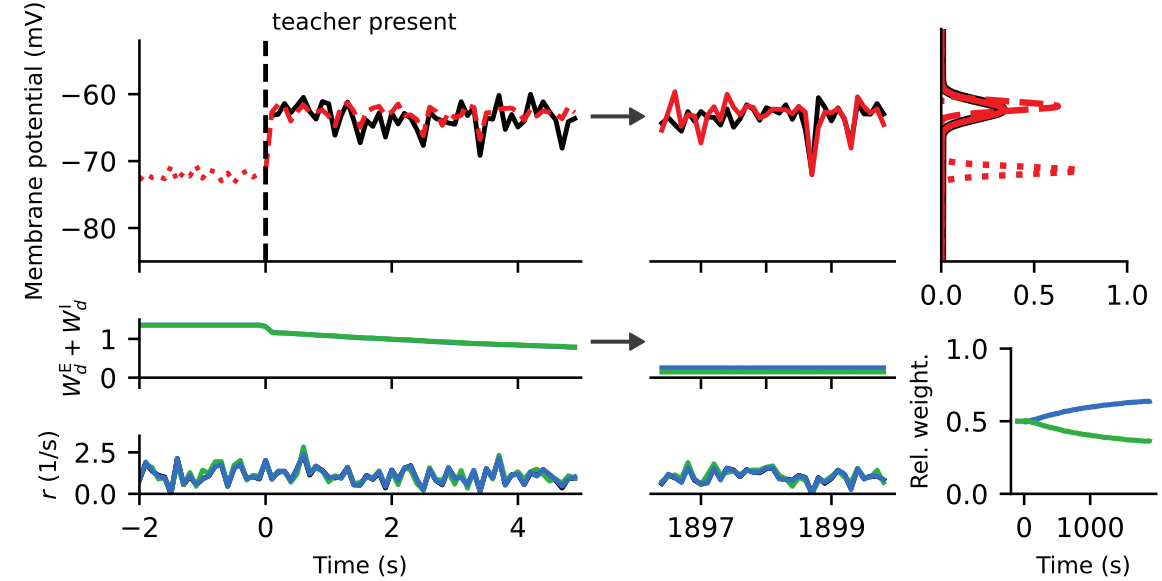
Membrane potential dynamics from noisy gradient ascent
Membrane potential mean
= mean of the posterior
Membrane potential variance
= inverse precision of the posterior
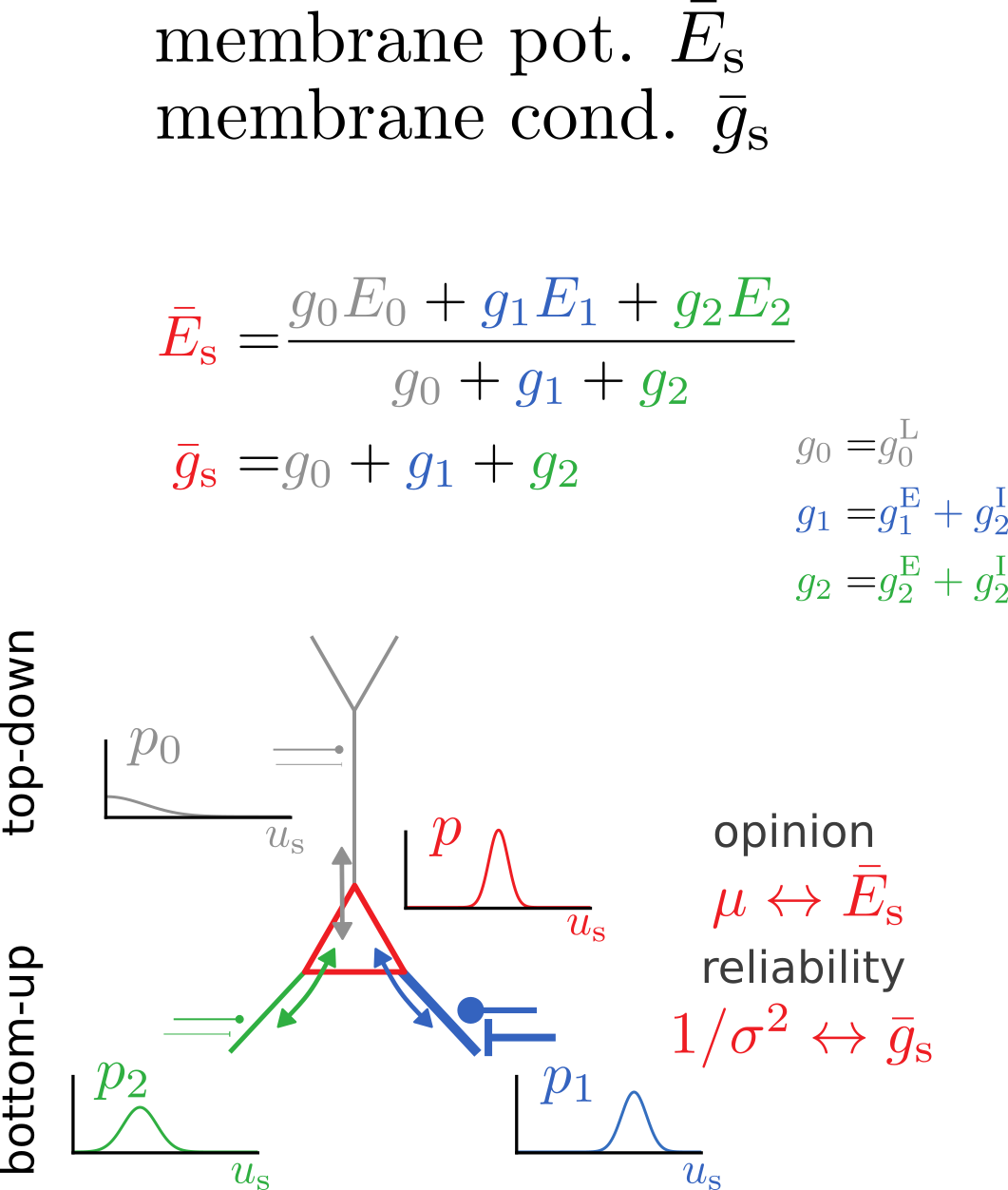
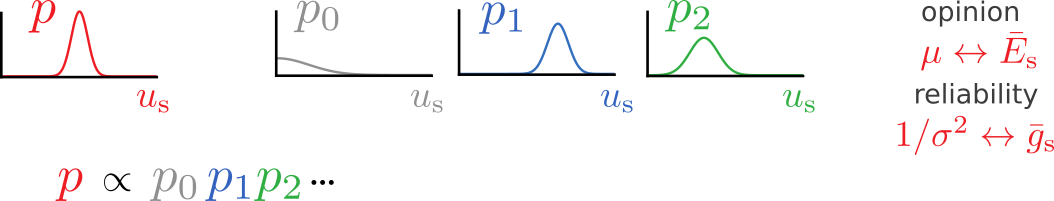
Somatic membrane potential distribution
Somatic membrane potential dynamics
Synaptic plasticity from matching target distributions
Prediction for experiments:
Synaptic plasticity modifies excitatory/inhibitory synapses
- in approx. opposite directions to match the mean
- in identical directions to match the variance
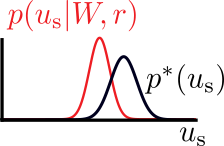
target
actual
Learning Bayes-optimal inference of orientations from multimodal stimuli
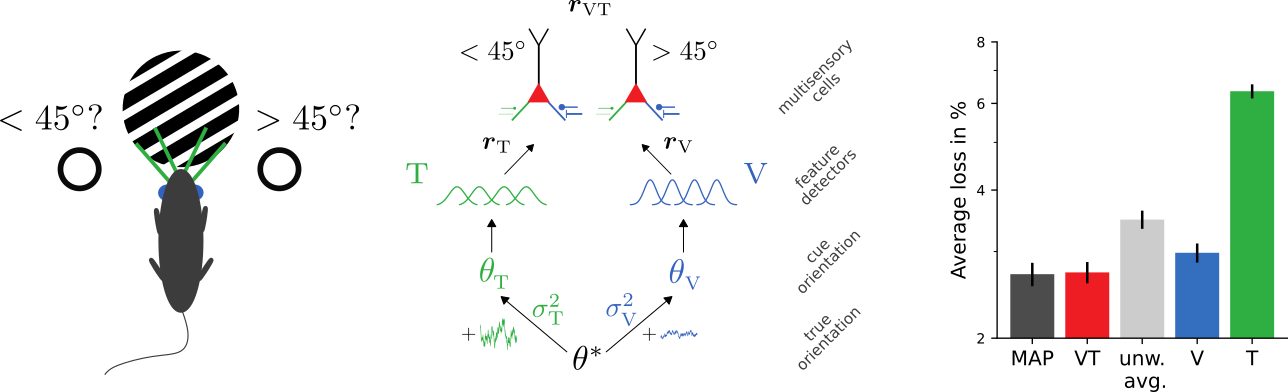
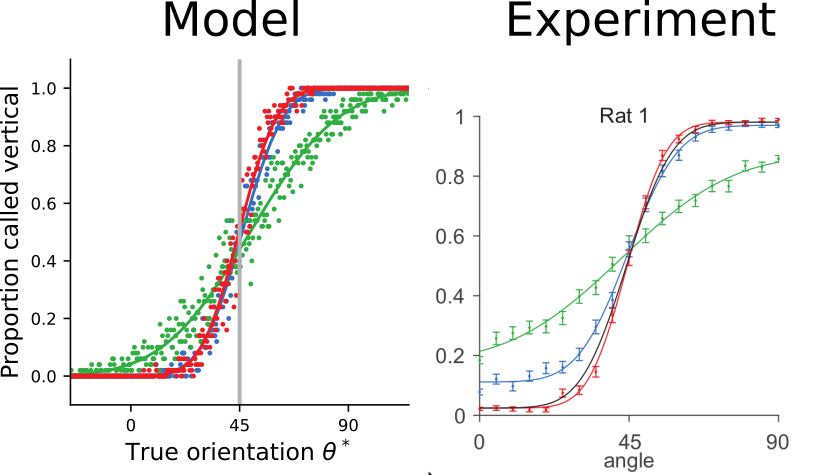
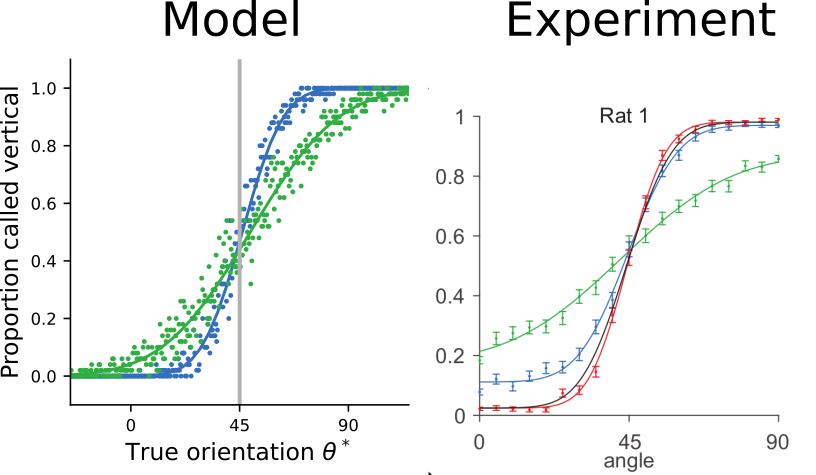
The trained model approximates ideal observers
and reproduces psychophysical signatures of experimental data
[Nikbakht et al., 2018]
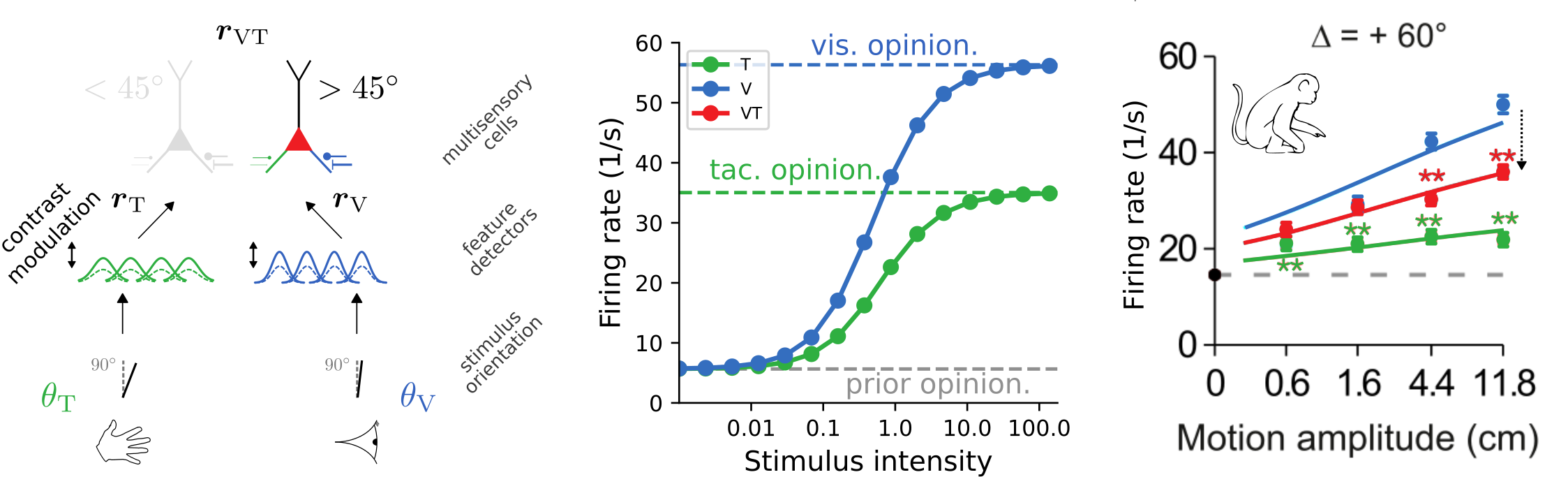
Cross-modal suppression as
reliability-weighted opinion pooling
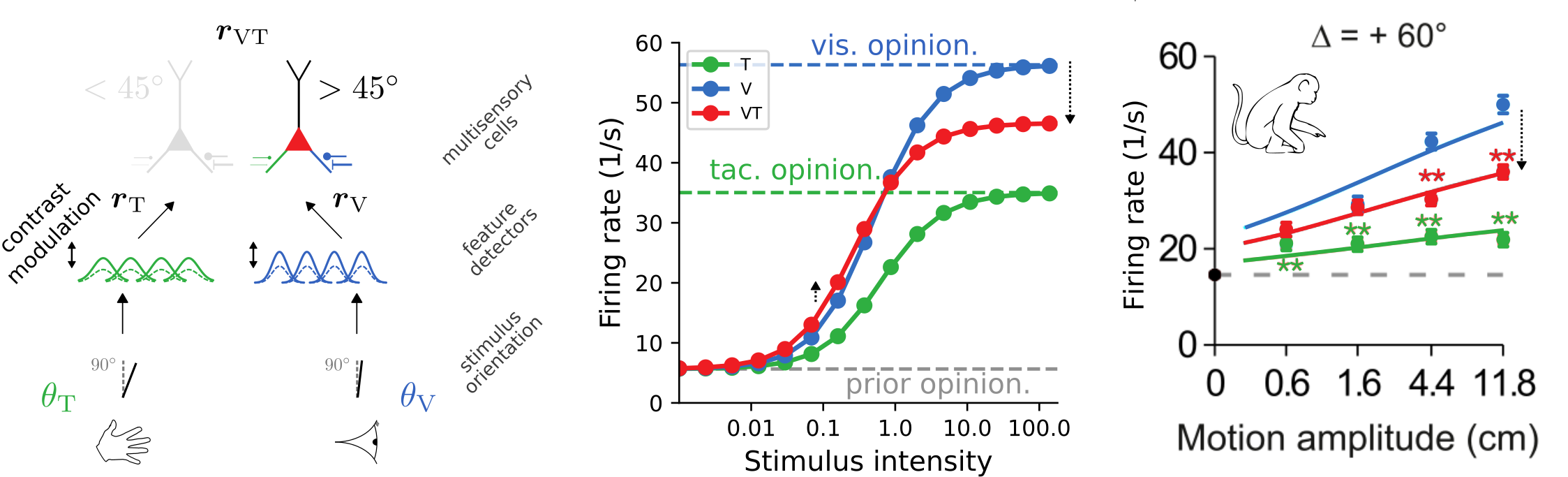
- low stimulus intensities: firing rate is enhanced
- high stimulus intensities: firing rate is suppressed
- prediction for experiments: strength of suppression depends on relative reliabilities of the two modalities
[Ohshiro et al., 2017]
Summary
Single neurons with conductance-based synapses can learn to be optimal cue integrators.
Jordan, J., Sacramento, J., Wybo, W. A., Petrovici, M. A., & Senn, W. (2021).
Learning Bayes-optimal dendritic opinion pooling. arXiv preprint arXiv:2104.13238.


- Membrane-potential dynamics compute maximum-a-posteriori estimates.
- Membrane conductances represent reliabilities of these estimates.
- Synaptic plasticity allows neurons to match target membrane potential distributions.
Neurons with conductance-based synapses
naturally implement probabilistic cue integration
Membrane potential dynamics from noisy gradient ascent

Time-averaged membrane potentials
= mean of the posterior
Membrane potential variance
= inverse precision of the posterior
Synaptic plasticity from stochastic gradient ascent
Prediction for experiments:
Synaptic plasticity modifies excitatory/inhibitory synapses
- in approx. opposite directions to match the mean
- in identical directions to match the variance
\(u_\text{s}^*\): sample from target distribution \(p^*(u_\text{s})\)
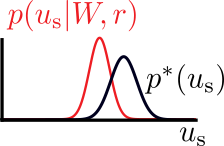
target
actual
Synaptic plasticity performs
error-correction and reliability matching
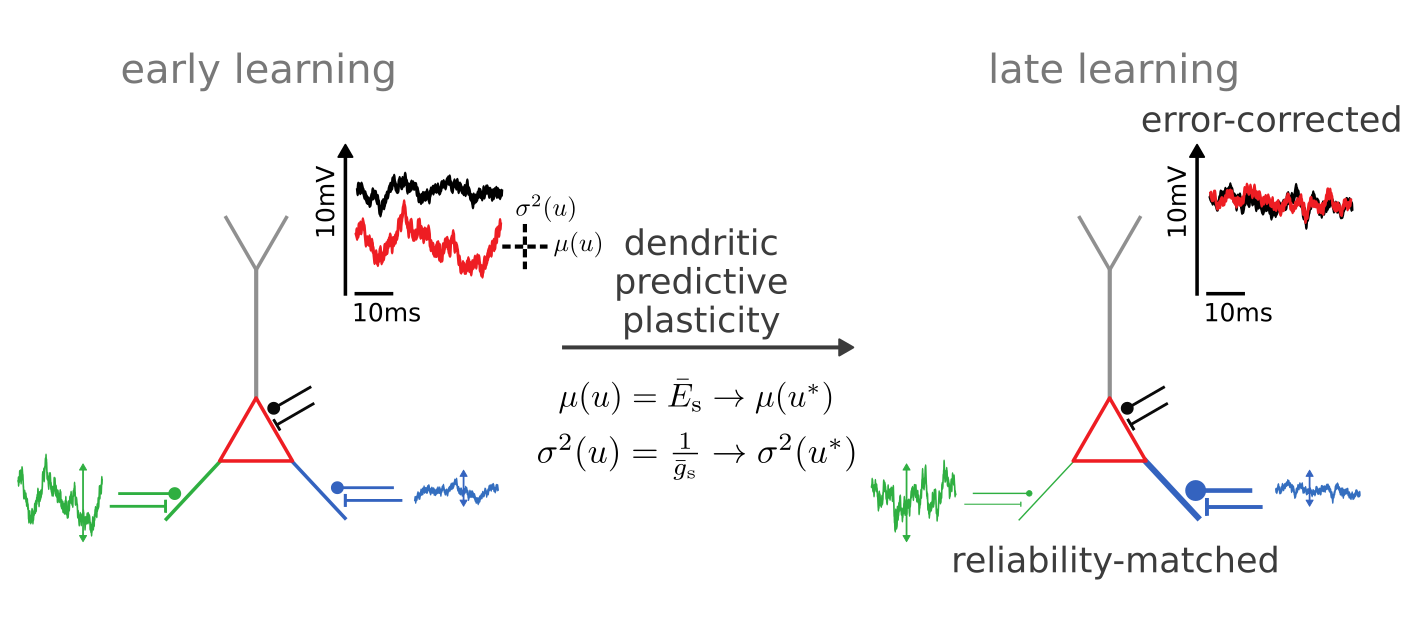
Learning Bayes-optimal dendritic opinion pooling
By jakobj
Learning Bayes-optimal dendritic opinion pooling
- 201



