Machine Learning
James L. Weaver
Developer Advocate
Email: jweaver@pivotal.io
http://JavaFXpert.com

@JavaFXpert


About the Presenter
Java Champion, JavaOne Rockstar, plays well with others, etc :-)
Developer Advocate & International Speaker for Pivotal


@JavaFXpert
Author of several Java/JavaFX/RaspPi books

From introductory video in Machine Learning course (Stanford University & Coursera) taught by Andrew Ng.


@JavaFXpert

@JavaFXpert

Self-driving cars
Generating image descriptions


@JavaFXpert

@JavaFXpert
Supervised Learning

Supervised learning regression problem

@JavaFXpert


@JavaFXpert
Unsupervised Learning

Unsupervised learning finds structure in unlabeled data

@JavaFXpert

(e.g. market segment discovery, and social network analysis)

@JavaFXpert
Reinforcement Learning

AlphaGo is a recent reinforcement learning success story

@JavaFXpert


@JavaFXpert
Supervised Learning

(Let's dive in now)
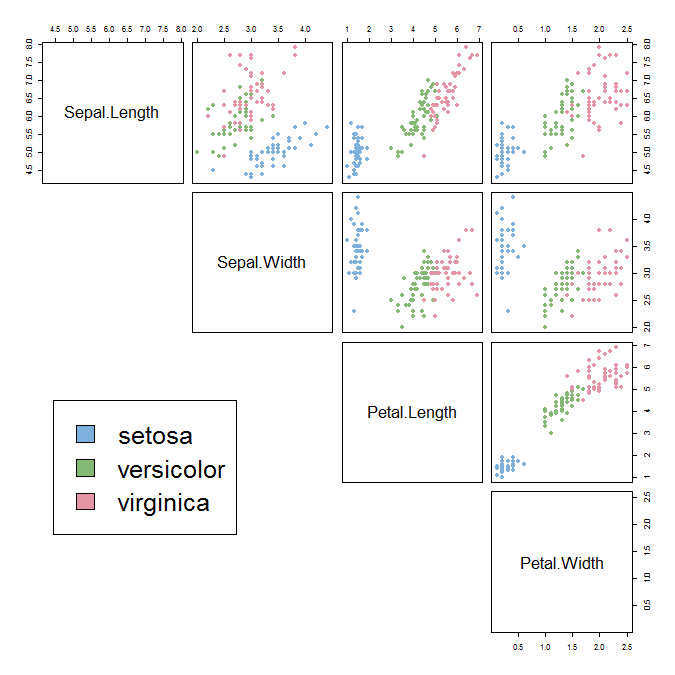
Supervised learning classification problem

@JavaFXpert
(using the Iris flower data set)



@JavaFXpert

Modeling the brain works well with machine learning
(ya think?)

@JavaFXpert

(inputs)
(output)

Anatomy of an Artificial Neural Network

@JavaFXpert
(aka Deep Belief Network when multiple hidden layers)

Neural net visualization app (uses Spring and DL4J)

@JavaFXpert

Entering feature values for prediction (classification)

@JavaFXpert

Visual Neural Network application architecture

@JavaFXpert

Spring makes REST services and WebSockets easy as π

@JavaFXpert
The app leverages machine learning libraries found at deeplearning4j.org


@JavaFXpert
To quickly create a Spring project, visit start.spring.io

Simple neural network trained for XOR logic

@JavaFXpert

forward propagation
Feedforward calculations with XOR example

@JavaFXpert
For each layer:

Multiply inputs by weights:
(1 x 8.54) + (0 x 8.55) = 8.54
Add bias:
8.54 + (-3.99) = 4.55
Use sigmoid activation function:
1 / (1 + e
-4.55
) = 0.99
Simple neural network trained for XOR logic

@JavaFXpert

back propagation (minimize cost function)
Back propagation

@JavaFXpert
(Uses gradient descent to iteratively minimize the cost function)

Output from training Iris dataset

@JavaFXpert
In iterationDone(), iteration: 0, score: 1.0726
In iterationDone(), iteration: 300, score: 0.2017
In iterationDone(), iteration: 600, score: 0.0482
In iterationDone(), iteration: 900, score: 0.0266
Examples labeled as 0 classified by model as 0: 9 times
Examples labeled as 1 classified by model as 1: 14 times
Examples labeled as 1 classified by model as 2: 3 times
Examples labeled as 2 classified by model as 2: 27 times
==========================Scores========================
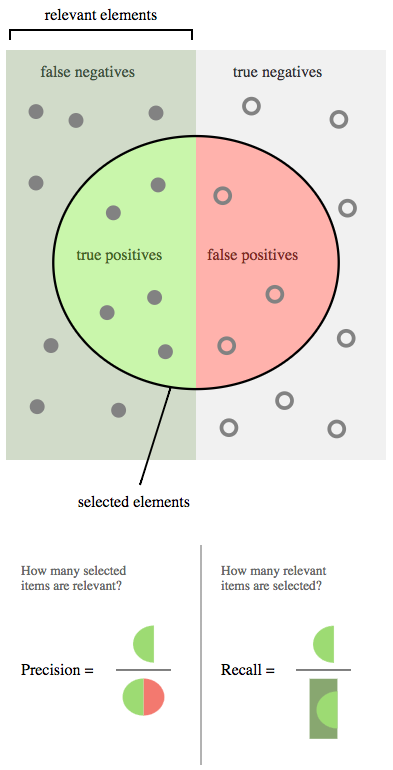
Accuracy: 0.9434
Precision: 0.9667
Recall: 0.9412
F1 Score: 0.9538
Great website for data science / machine learning enthusiasts

@JavaFXpert

Let’s use a dataset from kaggle.com to train a neural net on speed dating

@JavaFXpert

Identify features and label we’ll use in the model

@JavaFXpert
Let’s use 65% of the 8378 rows for training and 35% for testing

Code that configures our speed dating neural net

@JavaFXpert


Trying our new speed dating neural net example

@JavaFXpert

In this example, all features are continuous, and output is a one-hot vector
Making predictions with our speed dating neural net

@JavaFXpert
Note that input layer neuron values are normalized

Regression Sum example

@JavaFXpert
Features are continuous values, output is continuous value

Training a neural network to play Tic-Tac-Toe

@JavaFXpert

Tic-Tac-Toe neural network architecture

@JavaFXpert


Input layer: 9 one-hot vectors (27 nodes)
- 1,0,0 (empty cell)
- 0,1,0 (X in cell)
- 0,0,1 (O in cell)
Hidden layer: 54 sigmoid neurons
Output layer: One-hot vector (9 nodes)
Client developed in JavaFX with Gluon mobile
0
0
0
0
0
1
1
1
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
0
/player?gameBoard=XXOOXIIOI
&strategy=neuralNetwork
"gameBoard": "XXOOXXIOI",
{
}
...
Java/Spring REST microservice
Tic-Tac-Toe training dataset

@JavaFXpert
0, 1,0,0, 1,0,0, 1,0,0, 1,0,0, 1,0,0, 1,0,0, 1,0,0, 1,0,0, 1,0,0
3, 0,1,0, 0,0,1, 1,0,0, 1,0,0, 1,0,0, 1,0,0, 1,0,0, 1,0,0, 1,0,0
3, 0,1,0, 1,0,0, 0,0,1, 1,0,0, 1,0,0, 1,0,0, 1,0,0, 1,0,0, 1,0,0
1, 0,1,0, 1,0,0, 1,0,0, 0,0,1, 1,0,0, 1,0,0, 1,0,0, 1,0,0, 1,0,0
1, 0,1,0, 1,0,0, 1,0,0, 1,0,0, 0,0,1, 1,0,0, 1,0,0, 1,0,0, 1,0,0
2, 0,1,0, 1,0,0, 1,0,0, 1,0,0, 1,0,0, 0,0,1, 1,0,0, 1,0,0, 1,0,0
1, 0,1,0, 1,0,0, 1,0,0, 1,0,0, 1,0,0, 1,0,0, 0,0,1, 1,0,0, 1,0,0
2, 0,1,0, 1,0,0, 1,0,0, 1,0,0, 1,0,0, 1,0,0, 1,0,0, 0,0,1, 1,0,0
2, 0,1,0, 1,0,0, 1,0,0, 1,0,0, 1,0,0, 1,0,0, 1,0,0, 1,0,0, 0,0,1
4, 0,1,0, 0,0,1, 1,0,0, 0,1,0, 1,0,0, 1,0,0, 0,0,1, 1,0,0, 1,0,0
...
Play cell
Game board cell states before play
Leveraging the neural network as a function approximator
Tic-Tac-Toe training dataset

@JavaFXpert
Generated using game theory minimax algorithm
https://github.com/JavaFXpert/tic-tac-toe-minimax written in Java by @RoyVanRijn using guidance from the excellent Tic Tac Toe: Understanding The Minimax Algorithm article by @jasonrobertfox
Taking Tic-Tac-Toe for a spin

@JavaFXpert

Is Optimizing your Neural Network a Dark Art ?

@JavaFXpert
Excellent article by Preetham V V on neural networks and choosing hyperparameters

@JavaFXpert
Reinforcement Learning

(Let's dive in now)
Using BURLAP for Reinforcement Learning

@JavaFXpert

Learning to Navigate a Grid World with Q-Learning

@JavaFXpert

Rules of this Grid World

@JavaFXpert

- Agent may move left, right, up, or down (actions)
- Reward is 0 for each move
- Reward is 5 for reaching top right corner (terminal state)
- Agent can't move into a wall or off-grid
- Agent doesn't have a model of the grid world. It must discover as it interacts.
Challenge: Given that there is only one state that gives a reward, how can the agent work out what actions will get it to the reward?
(AKA the credit assignment problem)
Goal of an episode is to maximize total reward
Visualizing training episodes

@JavaFXpert

From BasicBehavior example in https://github.com/jmacglashan/burlap_examples
This Grid World's MDP (Markov Decision Process)

@JavaFXpert

In this example, all actions are deterministic
Agent learns optimal policy from interactions with the environment (s, a, r, s')

@JavaFXpert

Q-Learning approach to reinforcement learning

@JavaFXpert
| Left | Right | Up | Down | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ... | ||||
| 2, 7 | 2.65 | 4.05 | 0.00 | 3.20 |
| 2, 8 | 3.65 | 4.50 | 4.50 | 3.65 |
| 2, 9 | 4.05 | 5.00 | 5.00 | 4.05 |
| 2, 10 | 4.50 | 4.50 | 5.00 | 3.65 |
| ... |
Q-Learning table of expected values (cumulative discounted rewards) as a result of taking an action from a state and following an optimal policy. Here's an explanation of how calculations in a Q-Learning table are performed.
Actions
States
Expected future discounted rewards, and polices

@JavaFXpert

This example used discount factor 0.9

@JavaFXpert

Low discount factors cause agent to prefer immediate rewards

@JavaFXpert

How often should the agent try new paths vs. greedily taking known paths?
Tic-Tac-Toe with Reinforcement Learning

@JavaFXpert
Learning to win from experience rather than by being trained

Inspired by the Tic-Tac-Toe Example section...

@JavaFXpert
Tic-Tac-Toe Learning Agent and Environment

@JavaFXpert

X
O
Our learning agent is the "X" player, receiving +5 for winning, -5 for losing, and -1 for each turn
The "O" player is part of the Environment. State and reward updates that it gives the Agent consider the "O" play.
Tic-Tac-Toe state is the game board and status

@JavaFXpert
| States | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| O I X I O X X I O, O won | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| I I I I I I O I X, in prog | 1.24 | 1.54 | 2.13 | 3.14 | 2.23 | 3.32 | N/A | 1.45 | N/A |
| I I O I I X O I X, in prog | 2.34 | 1.23 | N/A | 0.12 | 2.45 | N/A | N/A | 2.64 | N/A |
| I I O O X X O I X, in prog | +4.0 | -6.0 | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | -6.0 | N/A |
| X I O I I X O I X, X won | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| ... |
Q-Learning table of expected values (cumulative discounted rewards) as a result of taking an action from a state and following an optimal policy
Actions (Possible cells to play)
Unoccupied cell represented with an I in the States column
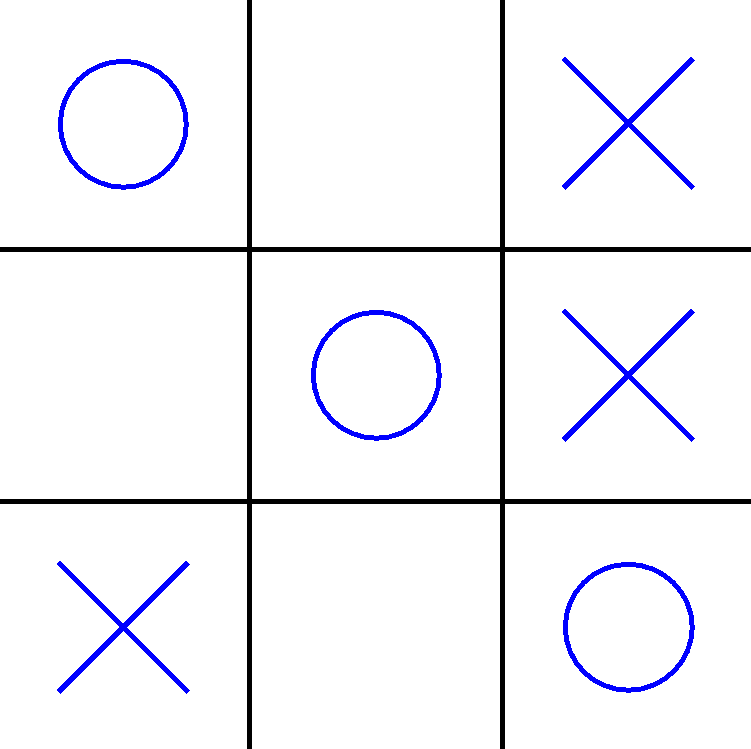
Tic-Tac-Toe with Reinforcement Learning

@JavaFXpert

Summary of neural network links (1/2)

@JavaFXpert
Andrew Ng video:
https://www.coursera.org/learn/machine-learning/lecture/zcAuT/welcome-to-machine-learning
Iris flower dataset:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Iris_flower_data_set
Visual neural net server:
http://github.com/JavaFXpert/visual-neural-net-server
Visual neural net client:
http://github.com/JavaFXpert/ng2-spring-websocket-client
Deep Learning for Java: http://deeplearning4j.org
Spring initializr: http://start.spring.io
Kaggle datasets: http://kaggle.com
Summary of neural network links (2/2)

@JavaFXpert
Tic-tac-toe client: https://github.com/JavaFXpert/tic-tac-toe-client
Gluon Mobile: http://gluonhq.com/products/mobile/
Tic-tac-toe REST service: https://github.com/JavaFXpert/tictactoe-player
Java app that generates tic-tac-toe training dataset:
https://github.com/JavaFXpert/tic-tac-toe-minimax
Understanding The Minimax Algorithm article:
http://neverstopbuilding.com/minimax
Optimizing neural networks article:
https://medium.com/autonomous-agents/is-optimizing-your-ann-a-dark-art-79dda77d103
Summary of reinforcement learning links

@JavaFXpert
BURLAP library: http://burlap.cs.brown.edu
BURLAP examples including BasicBehavior:
https://github.com/jmacglashan/burlap_examples
Markov Decision Process:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Markov_decision_process
Q-Learning table calculations: http://artint.info/html/ArtInt_265.html
Exploitation vs. exploration:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Multi-armed_bandit
Reinforcement Learning: An Introduction:
https://webdocs.cs.ualberta.ca/~sutton/book/bookdraft2016sep.pdf
Tic-tac-toe reinforcement learning app:
https://github.com/JavaFXpert/tic-tac-toe-rl

@JavaFXpert
Through the Eyes of a Self-Driving Tesla
Machine Learning
James L. Weaver
Developer Advocate
Email: jweaver@pivotal.io
http://JavaFXpert.com

@JavaFXpert


Machine Learning Exposed!
By javafxpert
Machine Learning Exposed!
Shedding light on machine learning
- 35,349