Beyond Scores:
Proximal Diffusion Models
Jeremias Sulam

Statistics and Data Science Workshop
Dec 2025









[Katsukokoiso & SORA]
[Hoogeboom et al, 2022]
[Corso et al, 2023]
Diffusion: from noise to data
Data:
\(X\sim p_0\) over \(\mathbb R^d\)

Diffusion: from noise to data
Data:
\(X\sim p_0\) over \(\mathbb R^d\)
\(t \in [0,T]\)

degradation
Diffusion: from noise to data

\(t \in [0,T]\)
\(t \in [T,0]\)
Score function
[Song et al, 2019][Ho et al, 2020]degradation
generation/sampling
Diffusion: from noise to data
How do we discretize it?
How do we obtain the score \(\nabla \ln p_t(X_t)\)?
Diffusion: from noise to data
How do we discretize it?
How do we obtain the score \(\nabla \ln p_t(X_t)\)?
[Euler-Maruyama]Diffusion: from noise to data
How do we discretize it?
How do we obtain the score \(\nabla \ln p_t(X_t)\)?
Say \(X_t \sim \mathcal N(X_0,\sigma^2 I) \).
Then, \(\nabla \ln p_t(X_t) = \frac{1}{\sigma^2}\left(\mathbb E[X_0|X_t] - X_t\right)\)
Denoisers: \(f_\theta(X_t) \approx \underset{f}{\arg\min} ~ \mathbb E \left[ \|f(X_t) - X_0\|^2_2\right]\)
[Tweedie's]
How about other discretization?
Motivation: Gradient Flow \(dX_t = -\nabla f(X) dt\)
\(X_{k+1} = X_k - \gamma \nabla f(X_k)\)
\(X_{k+1} = X_k - \gamma \nabla f(X_{k+1})\)
Forward discretization
Backward discretization
\(0=X_{k+1} - X_k + \gamma \nabla f(X_{k+1})\)
\( X_{k+1} = \underset{X}{\arg\min} \frac12 \|X-X_{k}\|^2_2 + \gamma f(X) \)
\( X_{k+1} = \text{prox}_{\gamma f}(X_k)\)
(GD)
(PPM)
\( \text{prox}_{\gamma f}(Y) \triangleq \underset{X}{\arg\min} \frac12 \|X-Y\|^2_2 + \gamma f(X) \)
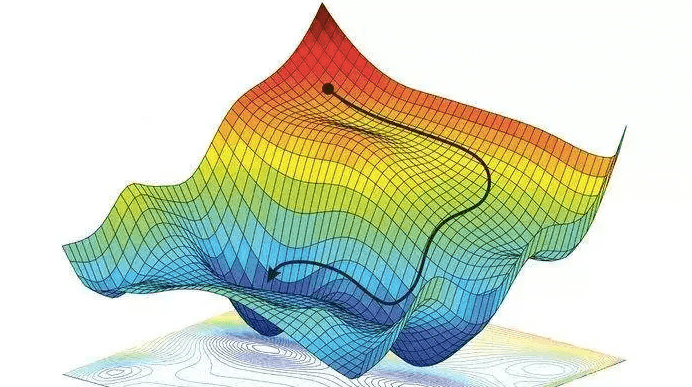
Converges for \(\gamma < \frac2{L_f}\)
Converges for any \(\gamma>0\),
\(f\):non-smooth
How about other discretization?
Converges for \(\gamma < \frac2{L_f}\)
Converges for any \(\gamma>0\),
\(f\):non-smooth
Motivation: Gradient Flow \(dX_t = -\nabla f(X) dt\)

\(X_{k+1} = X_k - \gamma \nabla f(X_k)\)
\(X_{k+1} = X_k - \gamma \nabla f(X_{k+1})\)
Forward discretization
Backward discretization
\(0=X_{k+1} - X_k + \gamma \nabla f(X_{k+1})\)
\( X_{k+1} = \underset{X}{\arg\min} \frac12 \|X-X_{k}\|^2_2 + \gamma f(X) \)
\( X_{k+1} = \text{prox}_{\gamma f}(X_k)\)
(GD)
(PPM)
Q1: Can backward discretization aid diffusion models?
Results
Q2: How do we implement proximal diffusion models?
Q1: Can backward discretization aid diffusion models?
Backward discretization:
Forward discretization:
(DDPM)
[Ho et al, 2020]Score-based Sampling:
Proximal Diffusion Algorithm:
(ProxDM)
(DDPM)
Hybrid Diffusion Algorithm:
Score-based Sampling:
Proximal Diffusion Algorithm:
(DDPM)
Hybrid Diffusion Algorithm:
(ProxDM hybrid)
(ProxDM)
Score-based Sampling:
Proximal Diffusion Algorithm:
(DDPM)
Hybrid Diffusion Algorithm:
(ProxDM hybrid)
(ProxDM)



Convergence Analysis
- Bounded moments: \(\mathbb E \|X\|^2 \lesssim d\), \(\mathbb E \|\nabla \ln p_t (X)\|^2 \lesssim dL^2\)
- Smoothness: \(\ln p_t\) has \(L\)-Lipschitz gradient and \(H\)-Lipschitz Hessian
- Step-size: \( \gamma \lesssim 1/L \)
- Regularity conditions: technical but common
Theorem [Fang, Díaz, Buchanan, S.]
(informal)
ProxDM requires \(N\gtrsim {d/\sqrt{\epsilon}}\)
To acchieve \(\text{KL}(\text{target}||\text{sample})\leq \epsilon\)
ProxHybrid requires \(N\gtrsim {d/\epsilon}\)
DDPM requires \(N\) is \(\mathcal O( d/\epsilon)\) (vanilla) or \(\mathcal O(d^{3/4}/\sqrt{\epsilon})\) if accelerated
[Chen et al, 2022][Wu et al, 2024]
Intermezzo: Related Works
Sampling acceleration
Probability Flows and ODEs (e.g. DDIM) [Song et al 2020, Chen et al, 2023, ...]
DPM-solver [Lu et al 2022]
Higher-order solvers [Wu et al, 2024, ... ]
Accelerations of different kinds [Song et al, 2023, Chen et al, 2025, ... ]
Benefits of backward discretization of ODEs/SDEs
Optimization [Rockafellar, 1976], [Beck and Teboulle, 2015] ...
Langevin Dynamics: PLA [Bernton 2018, Pereyra 2016, Wibisono 2019, Durmus et al 2018]
Forward-backward in space of measures [Chen et al 2018, Wibisono, 2025]
Q1: Can backward discretization aid diffusion models?
Results
Q2: How do we implement proximal diffusion models?
Q2: How do we implement proximal diffusion models?
Score-based Sampling:
Proximal Diffusion Algorithm:
(DDPM)
(ProxDM)

data-dependent
(MMSE) denoiser

Proximal Diffusion Algorithm:
(PDA)
Q2: How do we implement proximal diffusion models?
- When will a (data-driven) function \(f_\theta\) compute a prox?
- How do we train so that \(f_\theta \approx \text{prox}_{-\ln p}\) ?
\(\approx f_\theta\)

Q2: How do we implement proximal diffusion models?
- When will a (data-driven) function \(f_\theta\) compute a prox?
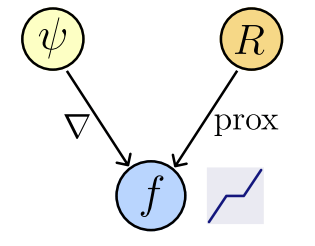
Theorem [Fang, Buchanan, S.]
Let \(f_\theta : \mathbb R^d\to\mathbb R^d\) be a network : \(f_\theta (x) = \nabla \psi_\theta (x)\),
where \(\psi_\theta : \mathbb R^d \to \mathbb R,\) convex and differentiable (ICNN).
Then,
1. Existence of regularizer
\(\exists ~R_\theta : \mathbb R^d \to \mathbb R\) not necessarily convex : \(f_\theta(x) \in \text{prox}_{R_\theta}(x),\)
2. Computability
We can compute \(R_{\theta}(x)\) by solving a convex problem

Proximal Matching Loss:Q2: How do we implement proximal diffusion models?
- How do we train so that \(f_\theta \approx \text{prox}_{-\ln p}\) ?
Theorem [Fang, Buchanan, S.]
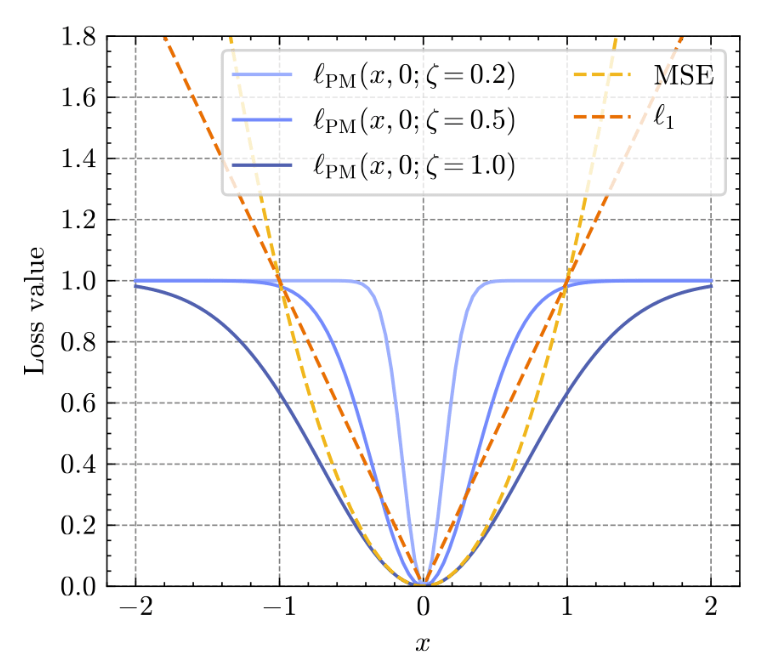
(PDA)
Q2: How do we implement proximal diffusion models?
Other parametrization & implementation details...
- Need to train a collection of proximals parametrized by \((\gamma_k,t_k)\)
- Learn the residual of the prox (à la score matching)
- Careful balance between \((\gamma_k,t_k)\) for different \(k\)
- We release the prox constraint and simply \(f_\theta \approx \text{prox}_{-\alpha_k \ln p_{k-1}}\)

Learned Proximal Networks
\(f_\theta\)
Does this all work?

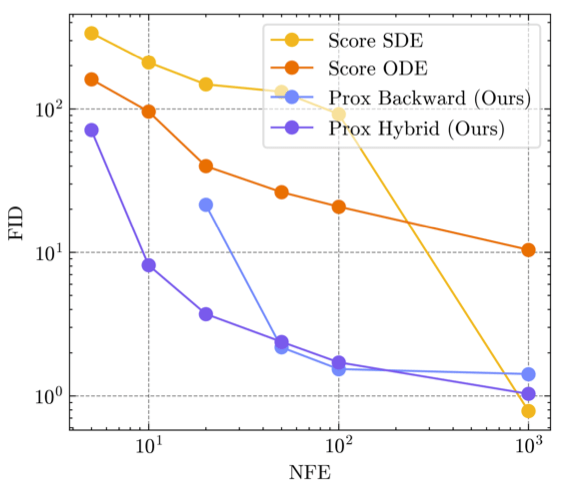

Does this all work?

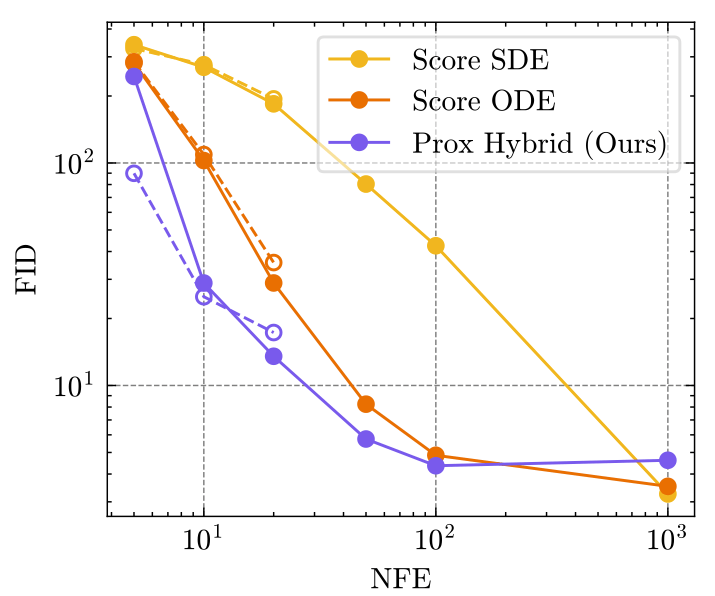

Does this all work?

Diffusion in latent spaces
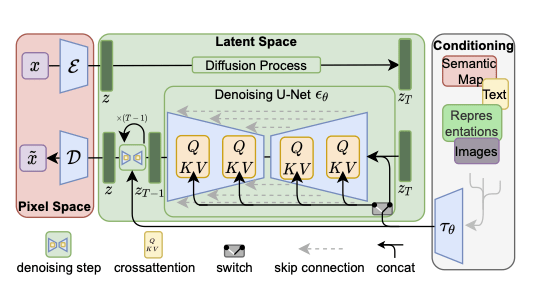
[Rombach et al, 2022]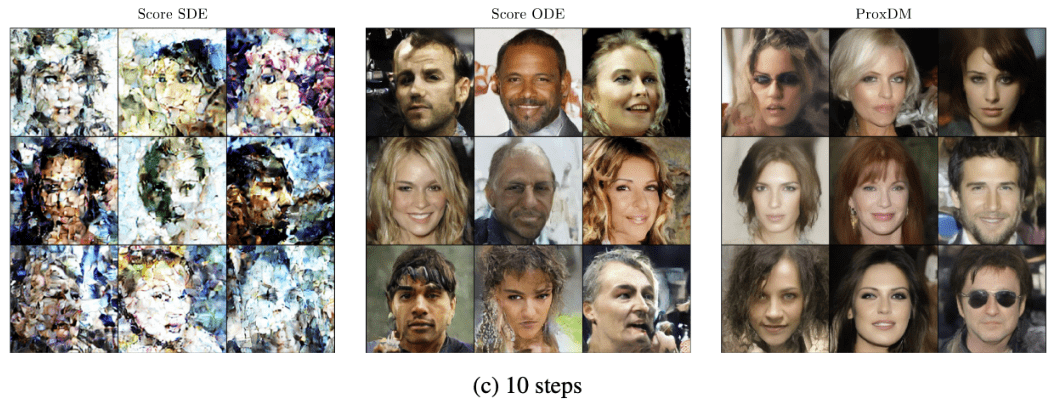

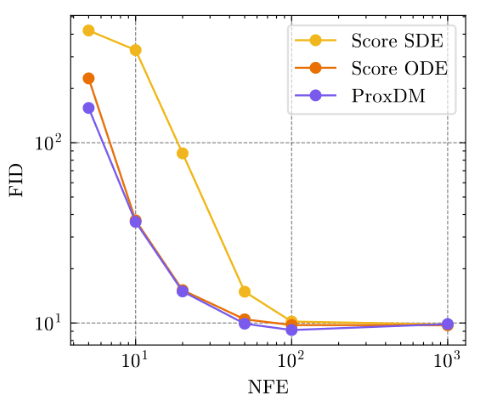
Diffusion in latent spaces
Diffusion in latent spaces
with prompt conditioning
"A woman with long blonde hair and a black top stands against a neutral background. She wears a delicate necklace. The image is a portrait-style photograph with soft lighting."
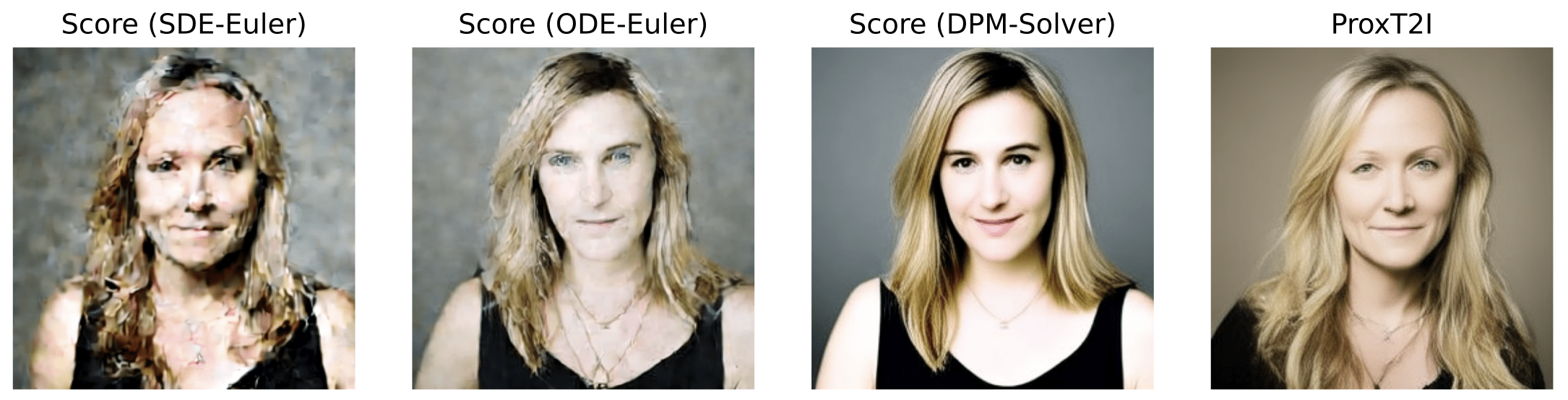
(10 steps)
"A man with curly hair and a beard, wearing a dark jacket, stands indoors. The background is blurred, showing a blue sign and warm lighting. The image style is a realistic photograph."(10 steps)

Diffusion in latent spaces
with prompt conditioning

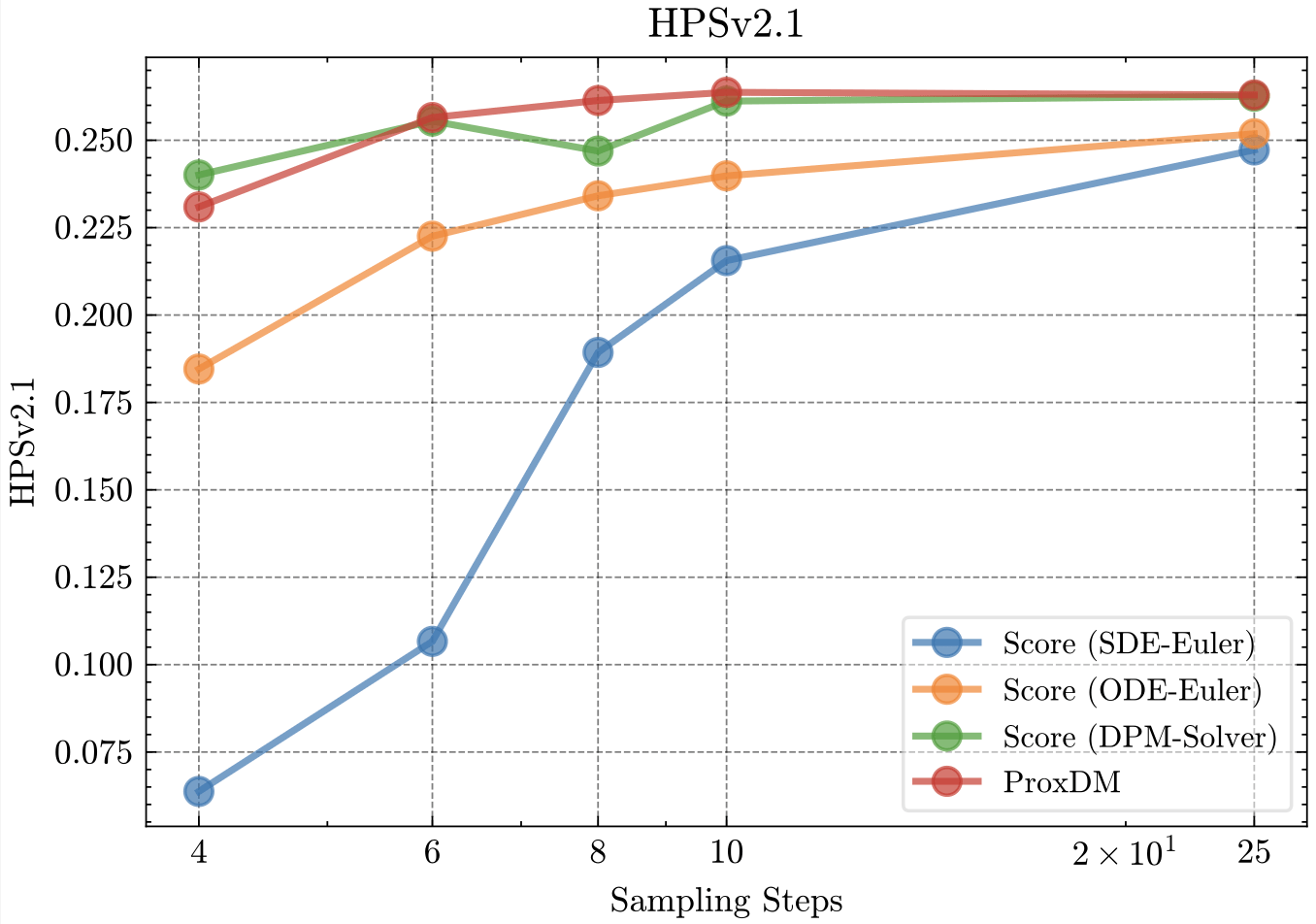
Q1: Can backward discretization aid diffusion models?
Results
Q2: How do we implement proximal diffusion models?
Q1: Can backward discretization aid diffusion models?
Results
Q2: How do we implement proximal diffusion models?
Take-home Messages
- Backward discretizations allow for a new kind of diffusion models
- Improvements are general
- Most advantages of ProxDM remain to be explored
Zhenghan Fang

Sam Buchanan
Mateo Díaz

-
Fang et al, Beyond Scores: Proximal Diffusion Models, Neurips 2025.
-
Fang et al, Learned Proximal Networks for Inverse Problems, ICLR 2024.
-
Fang et al, ProxT2I: Efficient Reward-Guided Text-to-Image Generation via Proximal Diffusion, arXiv 2025.
Appendix
Q2: How do we implement proximal diffusion models?
- How do we train so that \(f_\theta \approx \text{prox}_{-\ln p}\) ?
\( \text{prox}_{-\ln p}(Y) = \underset{X}{\arg\min} \frac12 \|X-Y\|^2_2 - \ln p(X) \)
\( = {\arg\max}~ p(X|Y) ~~~~ \text{(MAP)}\)
examples
Denoiser:
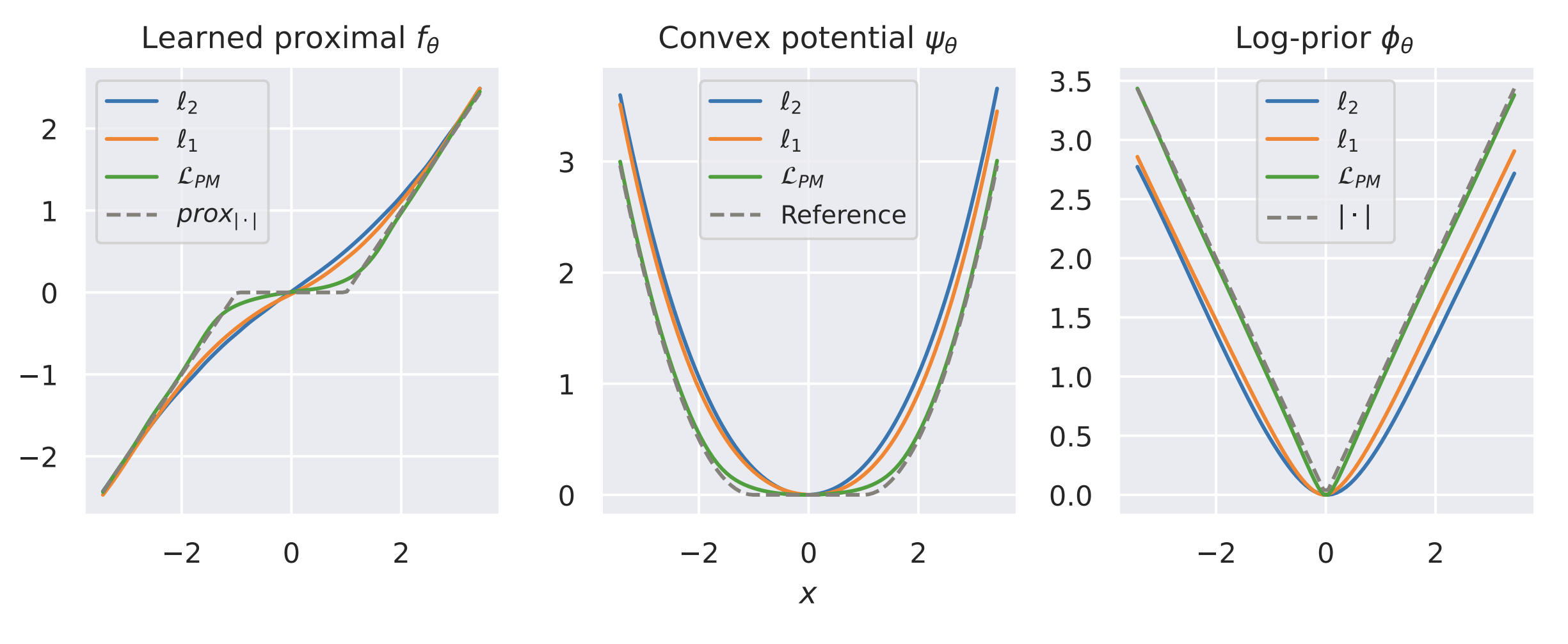
Example: recovering a prior

Q2: How do we implement proximal diffusion models?
Learned Proximal Networks
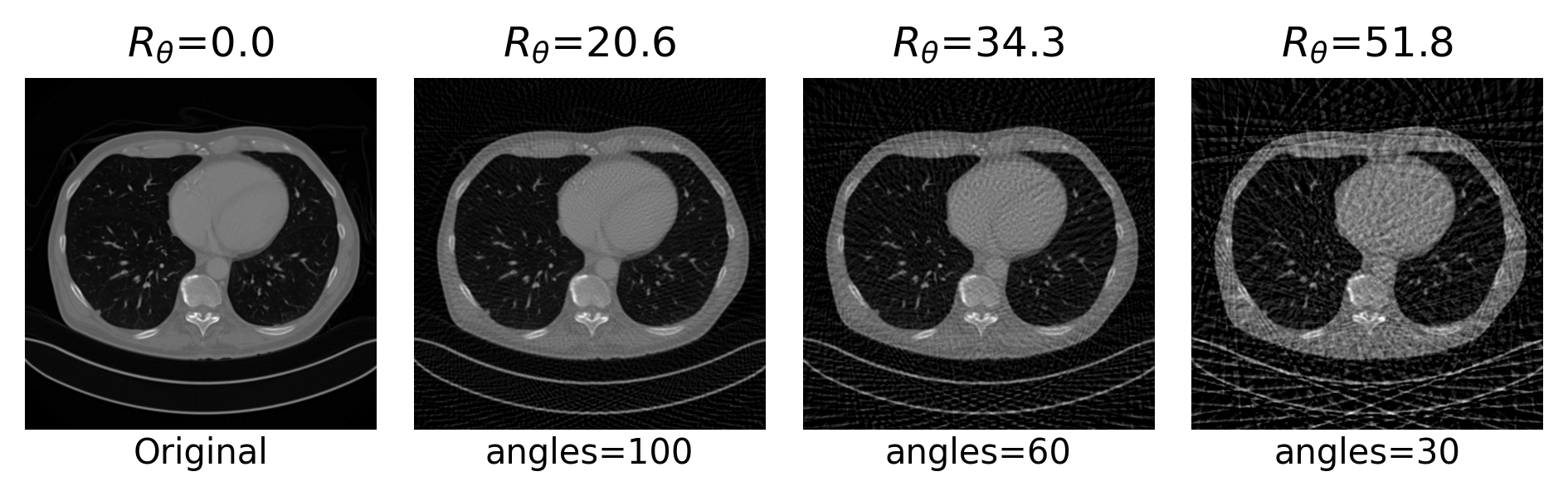
Example 2: a prior for CT
Learned Proximal Networks

Example 2: a prior for CT
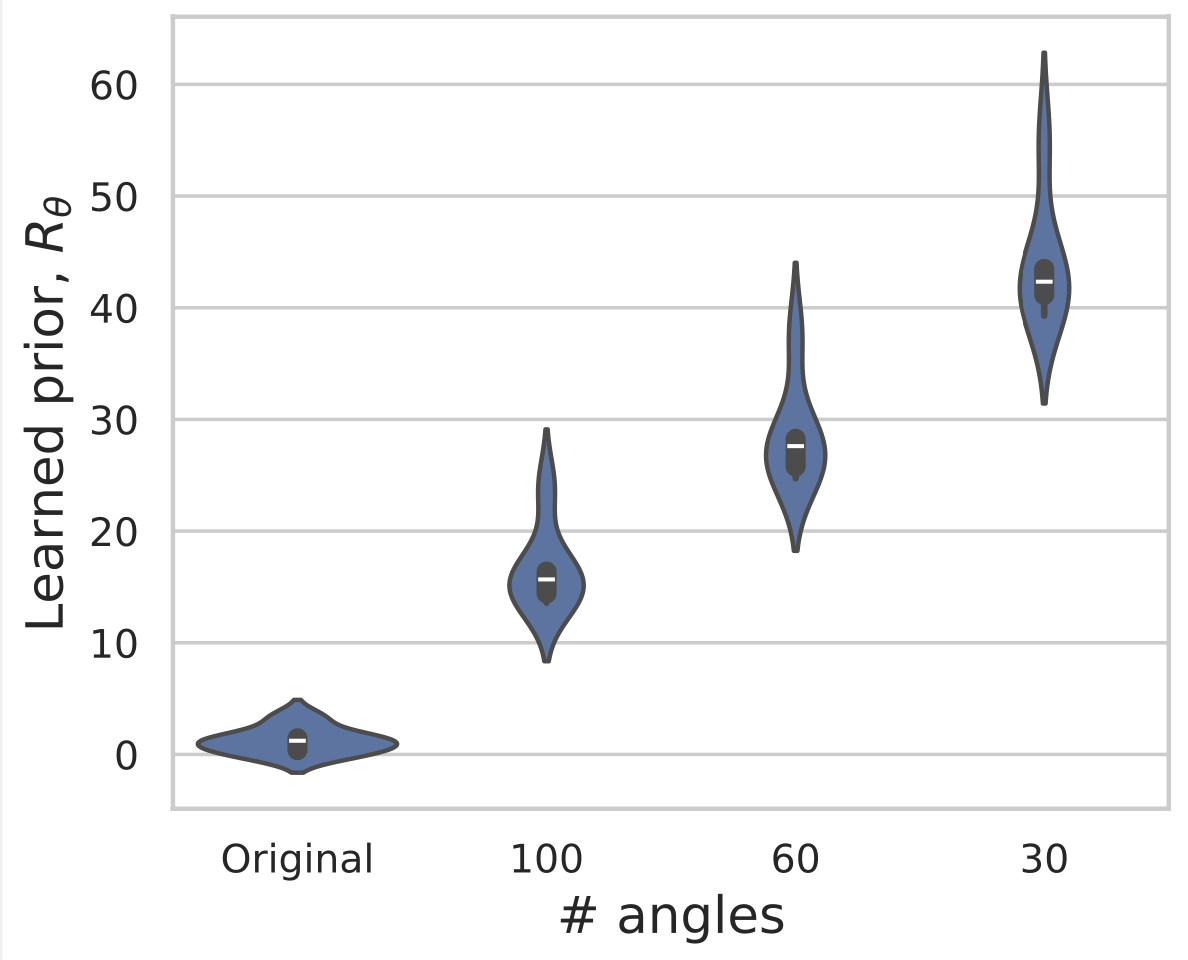
Learned Proximal Networks

Example 2: a prior for CT


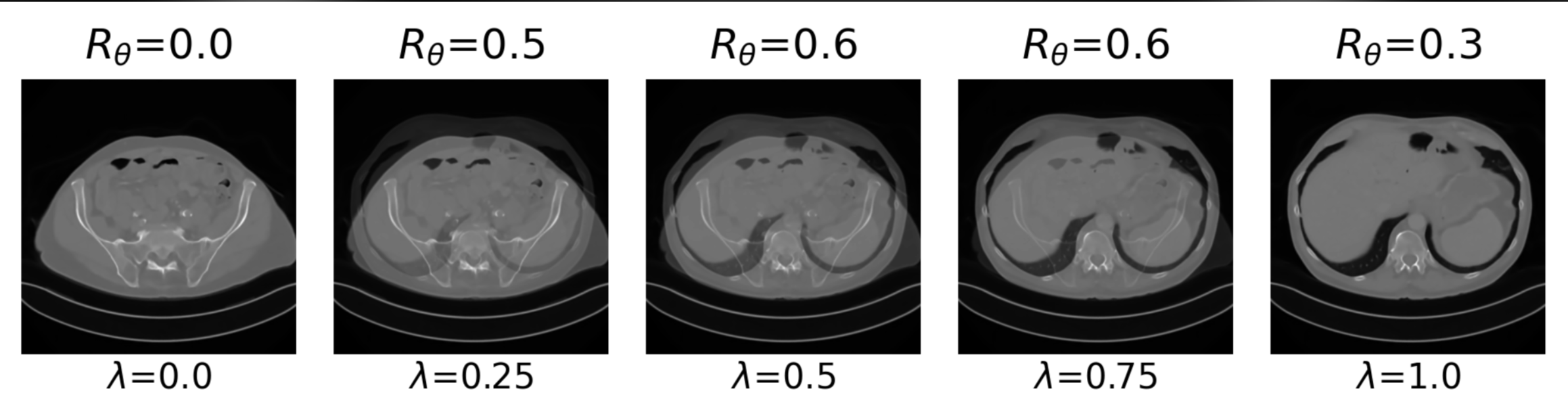
Learned Proximal Networks
Example 2: a prior for CT
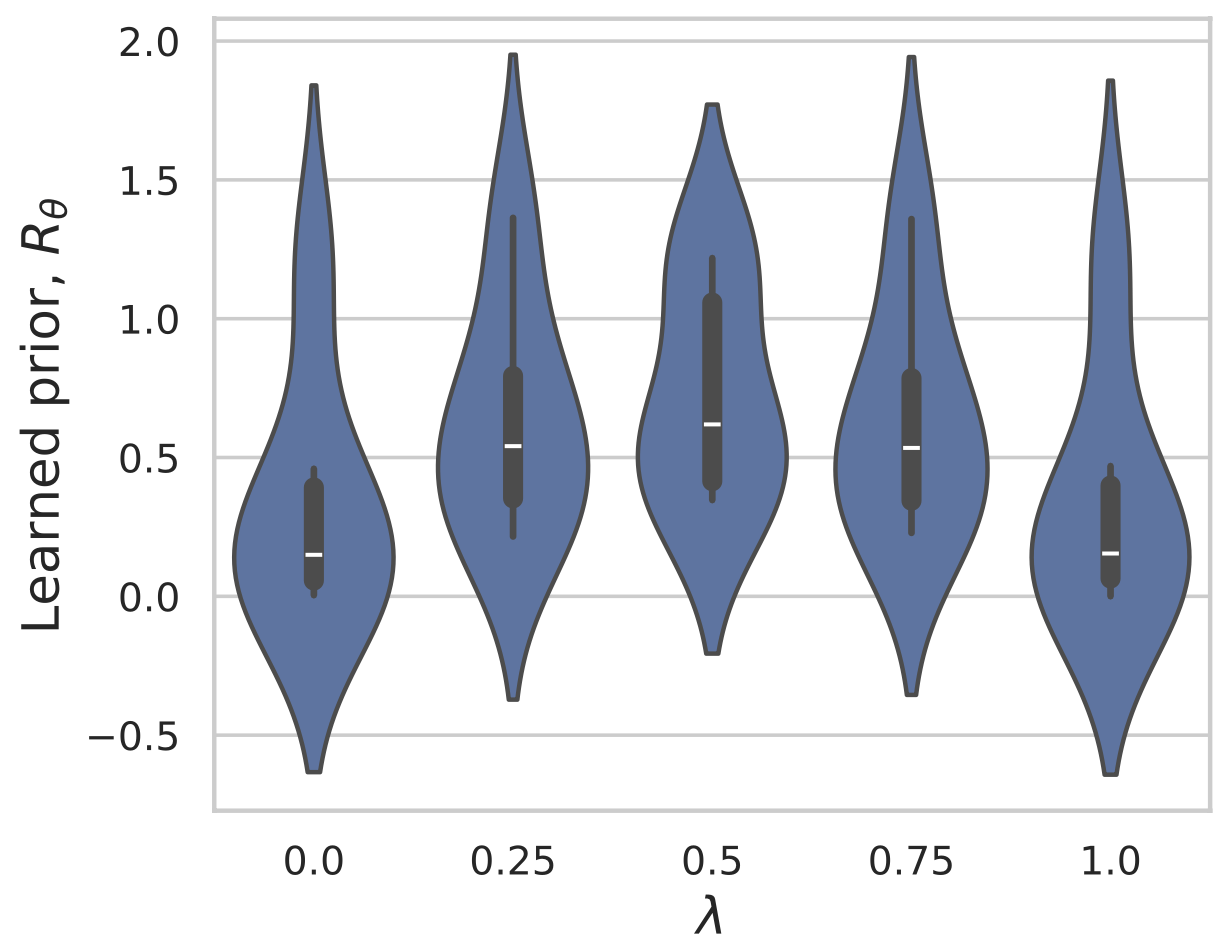




Learned Proximal Networks
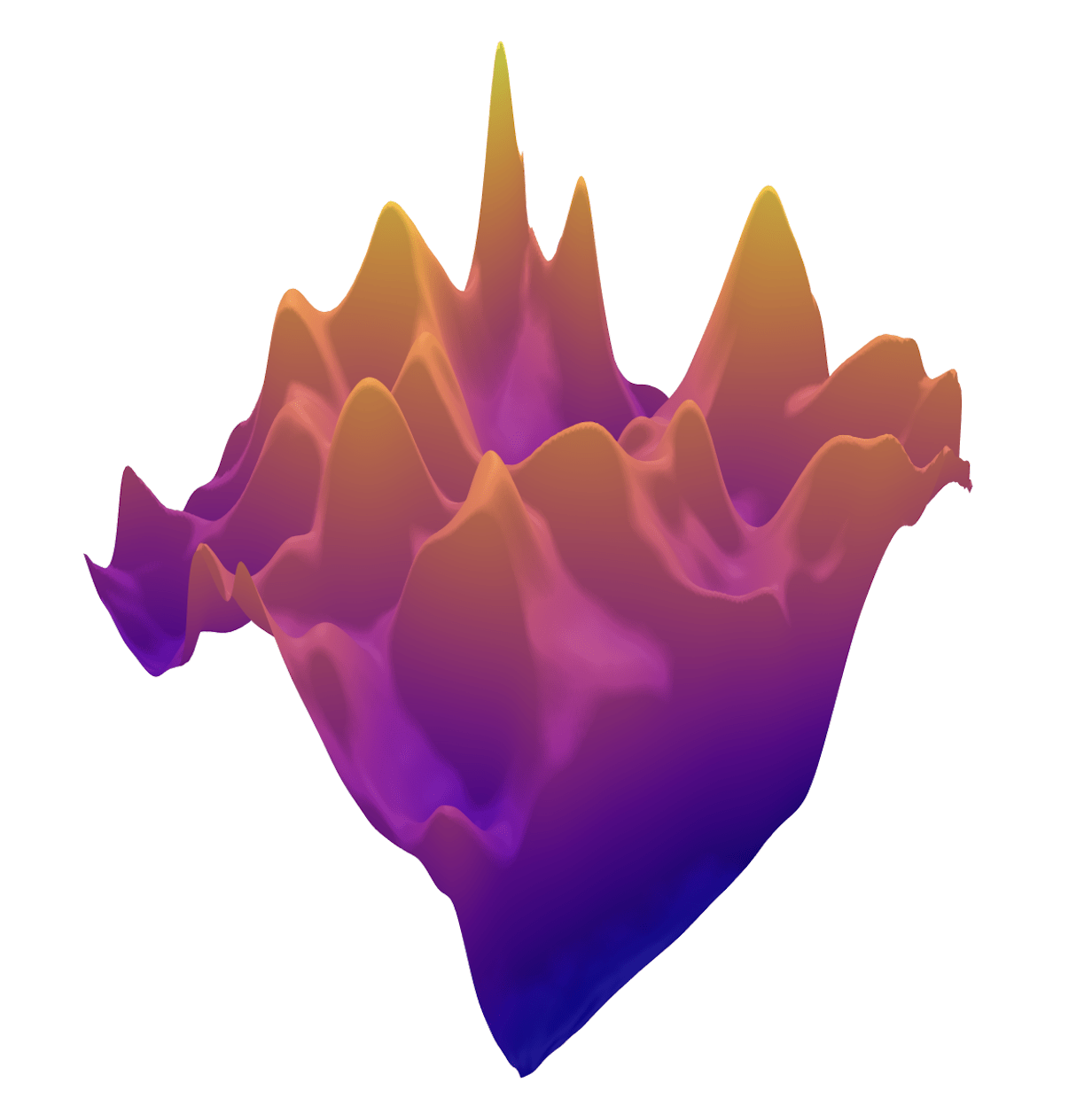
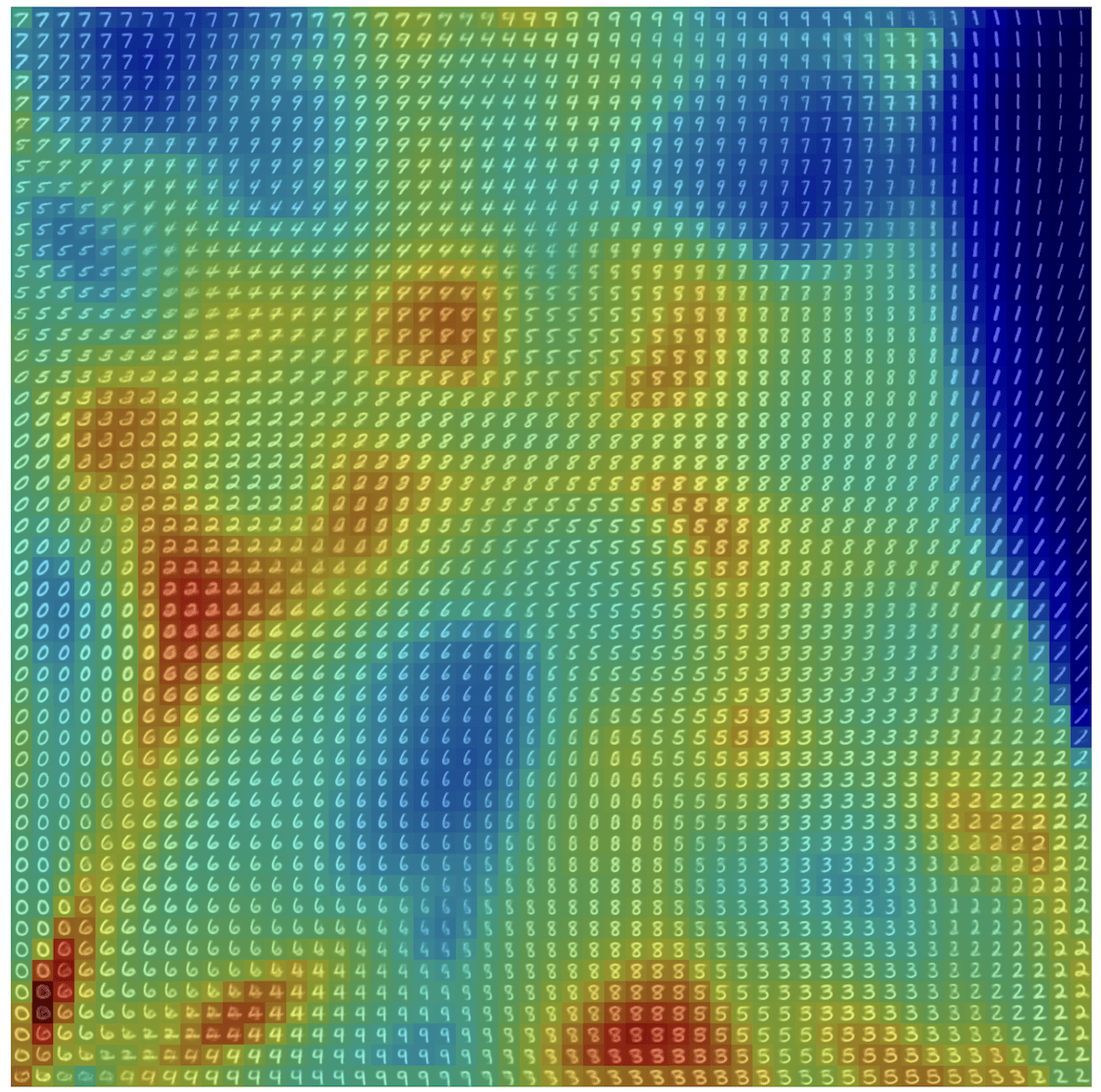
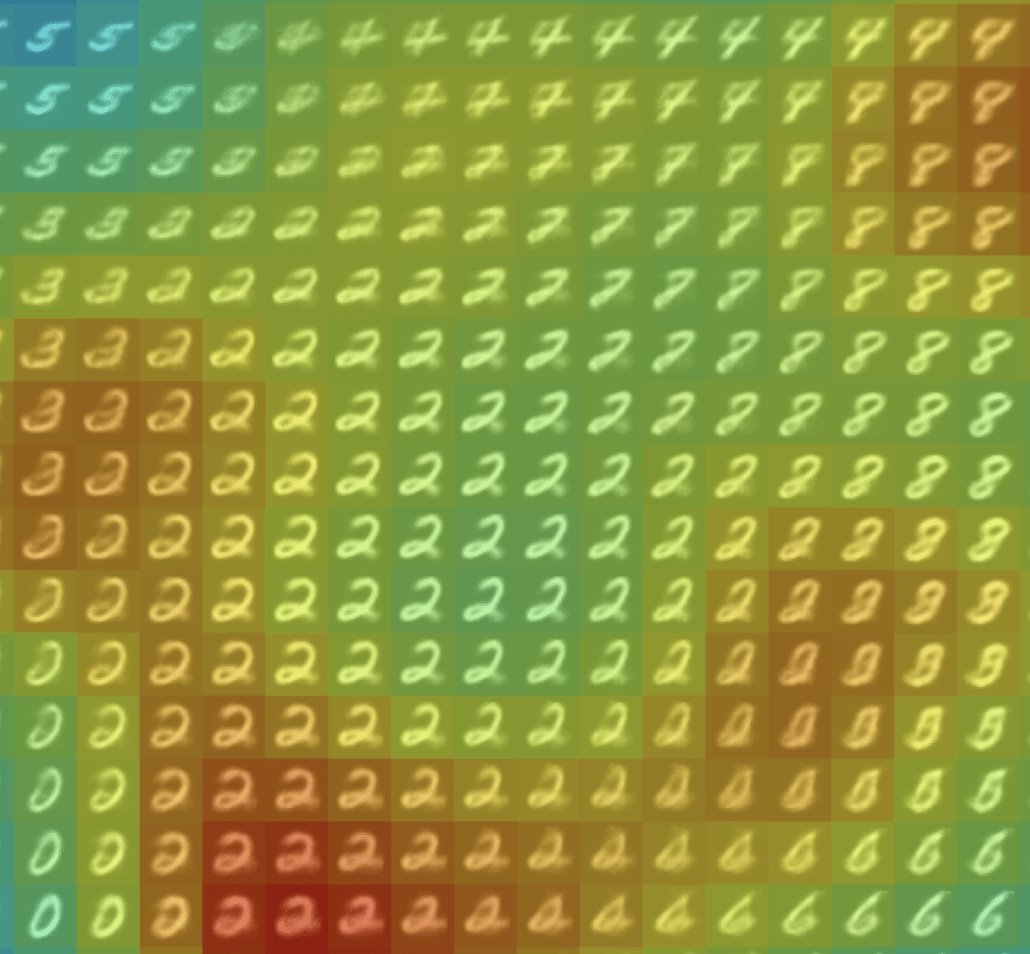
\(R(\tilde{x})\)
Example 2: priors for images
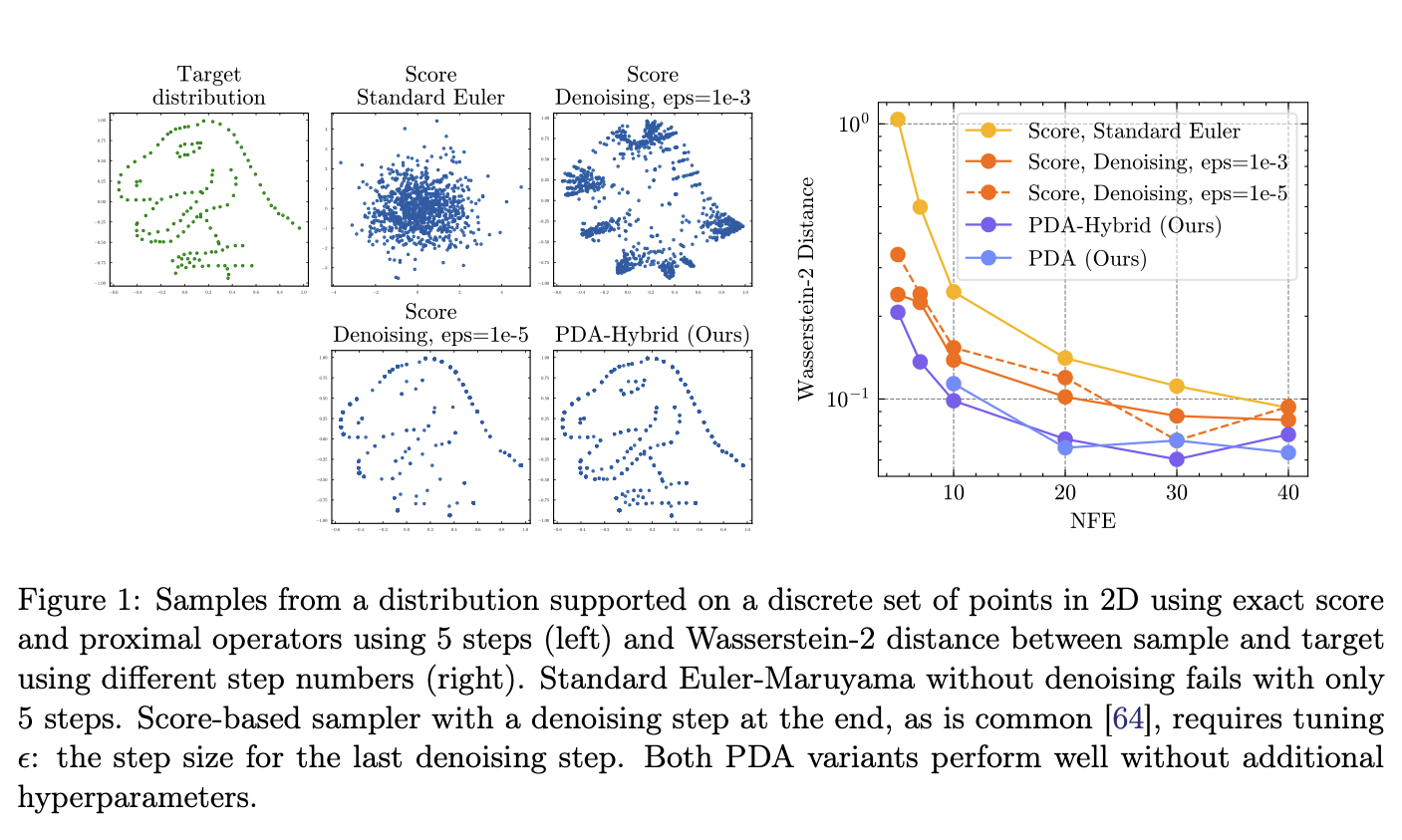
ProxDM Synthetic
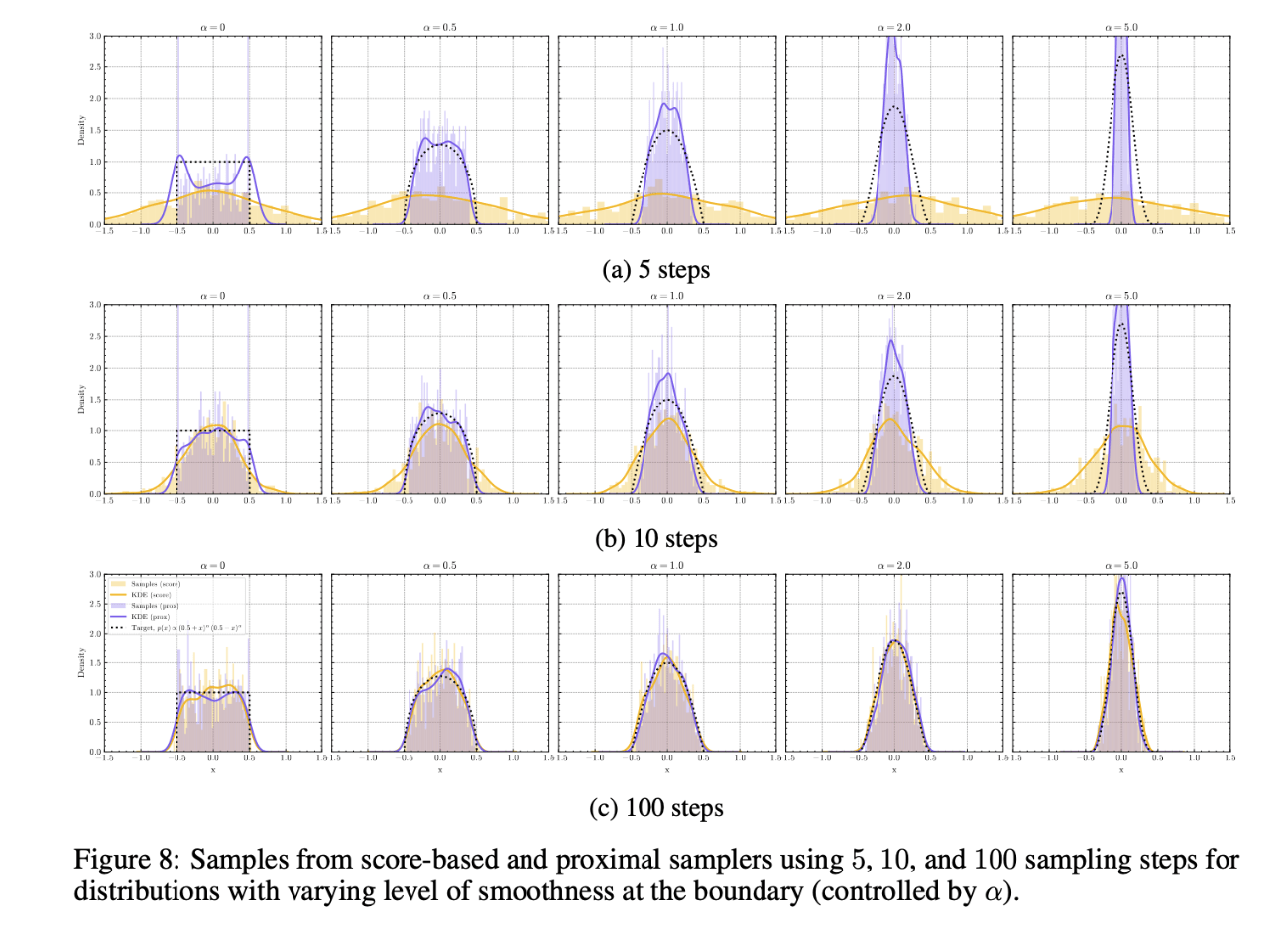
ProxDM Synthetic 2
Beyond Scores - Bogota
By Jeremias Sulam
Beyond Scores - Bogota
- 58



