Microbiology 2
By: Jillian Sperico
Biotechnology
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Morbi nec metus justo. Aliquam erat volutpat.

the exploitation of biological processes for industrial and other purposes
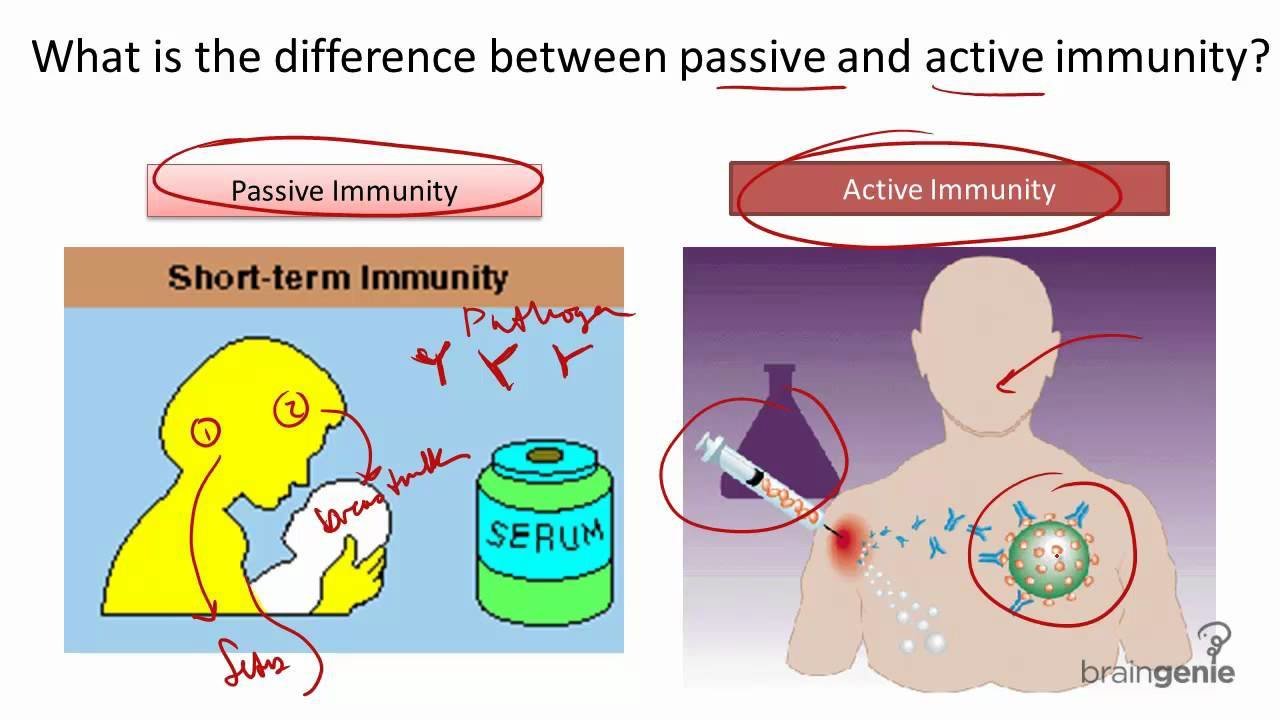
Active Immunity
the immunity that results from the production of antibodies by the immune system in response to the presence of an antigen.
Antimicrobial
an agent that kills microorganisms or stop their growth.
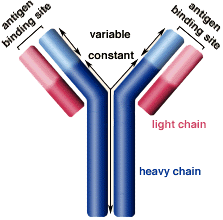
Antibody
a large, Y-shaped protein produced mainly by plasma cells that is used by the immune system to neutralize pathogens such as bacteria and viruses
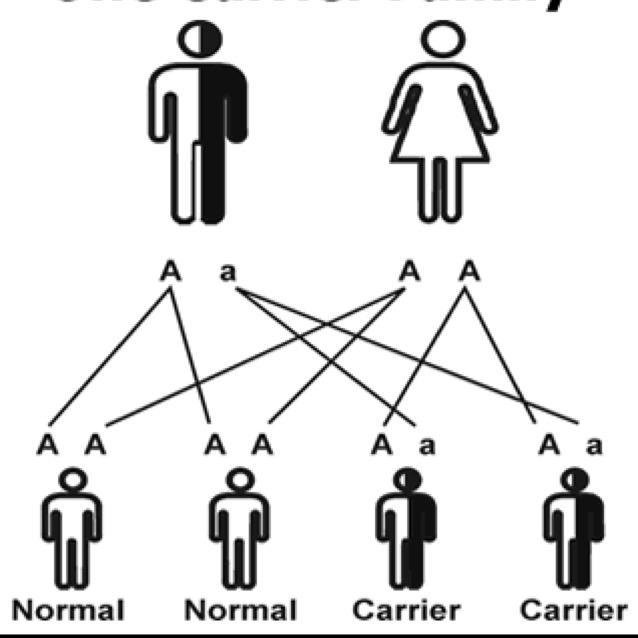
Carrier
is a person or other organism that has inherited a recessive allele for a genetic trait or mutation but does not display that trait or show symptoms of the disease.
Contagion
The transmission of an infectious disease resulting from direct or indirect contact between individuals or animals

Concentration
The measure of the amount of a sub-component (especially solute) in a solution.
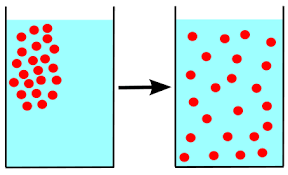
Dose
a quantity of a medicine or drug taken or recommended to be taken at a particular time.

Exposure
the state of being exposed to contact with something

Medicine
the science or practice of the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of disease (in technical use often taken to exclude surgery).
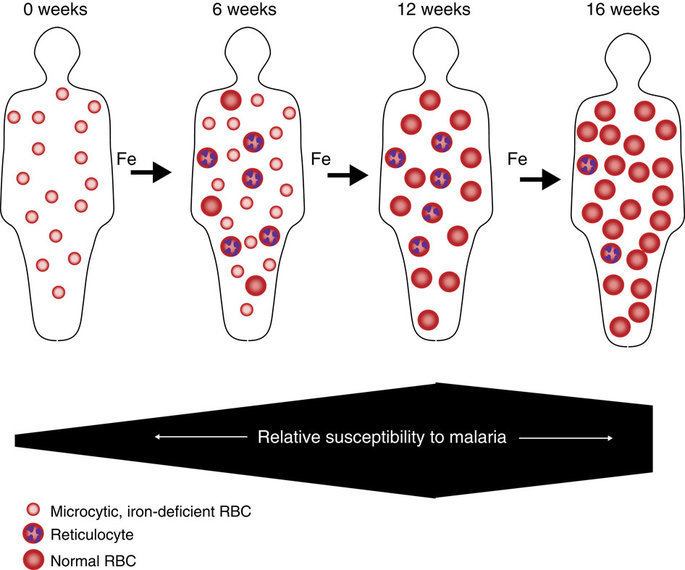
Individual Susceptibility
In epidemiology a susceptible individual (sometimes known simply as a susceptible) is a member of a population who is at risk of becoming infected by a disease.
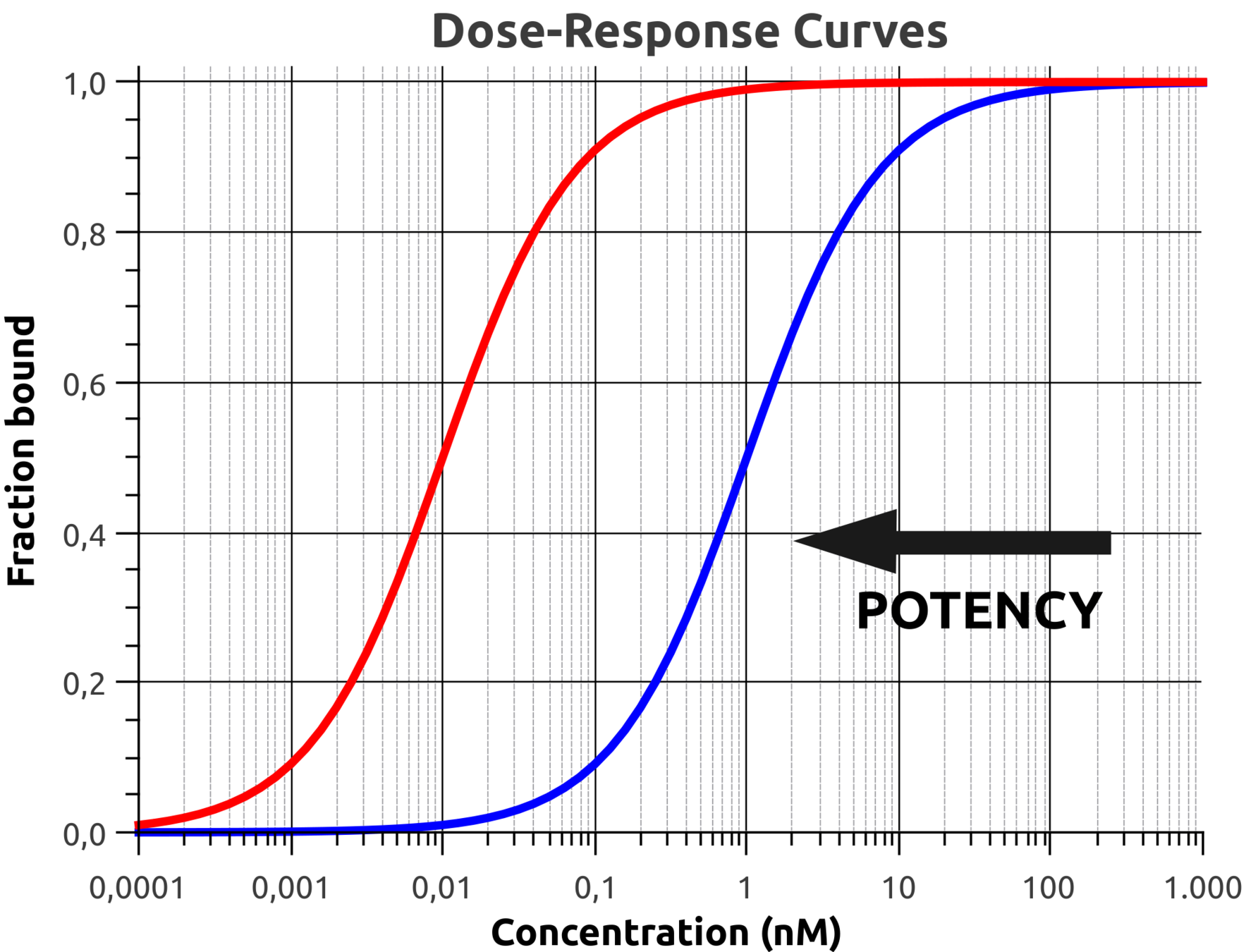
Potency
the power of something to influence or make an impression.
Antibiotic
a medicine (such as penicillin or its derivatives) that inhibits the growth of or destroys microorganisms.

Disease
a disorder of structure or function in a human, animal, or plant, especially one that produces specific signs or symptoms or that affects a specific location and is not simply a direct result of physical injury.

Epidemic
a widespread occurrence of an infectious disease in a community at a particular time.
Pandemic
an epidemic of infectious disease that has spread through human populations across a large region

Vaccine
a biological preparation that provides active acquired immunity to a particular disease
Infectious Disease
disorders caused by organisms — such as bacteria, viruses, fungi or parasites.
Non-Infectious disease
is a medical condition or disease that is not caused by infectious agents

Microbiology 2
By Jillian Sperico
Microbiology 2
- 370



