More Machine Learning
But first, a detour
Procedural Generation
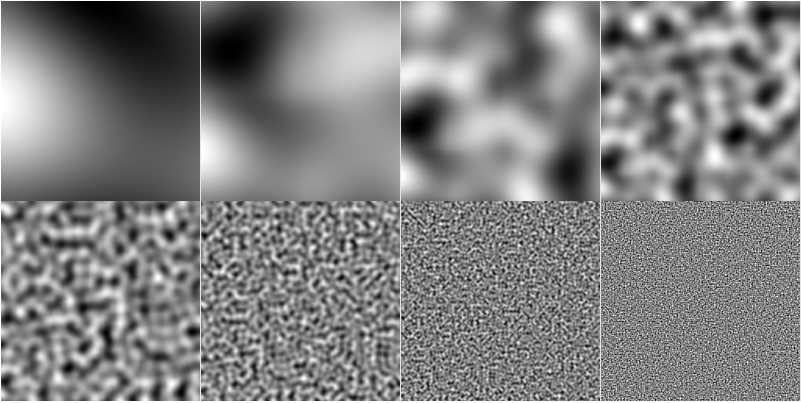
Algorithmically making "content"





Similar in distribution of "features"
Generate Similar Output Based on a Single Input
https://github.com/mxgmn/WaveFunctionCollapse
Wave Function Collapse
https://github.com/mxgmn/WaveFunctionCollapse
Wave Function Collapse
Input:
- A set of \(t\) "tiles"
- Their probability w.r.t the entire
- Adjacency rules
- (optional) Additional symmetry
- Output size \(w\) and \(h\)
Algorithm:
- Initialize states (a grid of \(w\times h \times t\) booleans)
- Choose minimum entropy cell, and "collapse" to a valid state (if no such cell, finish)
- Propogate constraints
- Goto 2
https://github.com/mxgmn/WaveFunctionCollapse
"Overlapping Model"

Catalog the frequency of appearance, and the compatibility with neighbours of each tile
https://github.com/mxgmn/WaveFunctionCollapse
Wave Function Collapse

https://github.com/mxgmn/WaveFunctionCollapse
Return to PyTorch
Last week we talked about tensors, operations on tensors and autograd
Let's talk about some higher level functionality now
Modules
A Module is the "Base class for all neural network modules"
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
class Model(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Model, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 20, 5)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(20, 20, 5)
def forward(self, x):
x = F.relu(self.conv1(x))
return F.relu(self.conv2(x))They provide a bit of "magic" behind the scenes (registration of parameters)
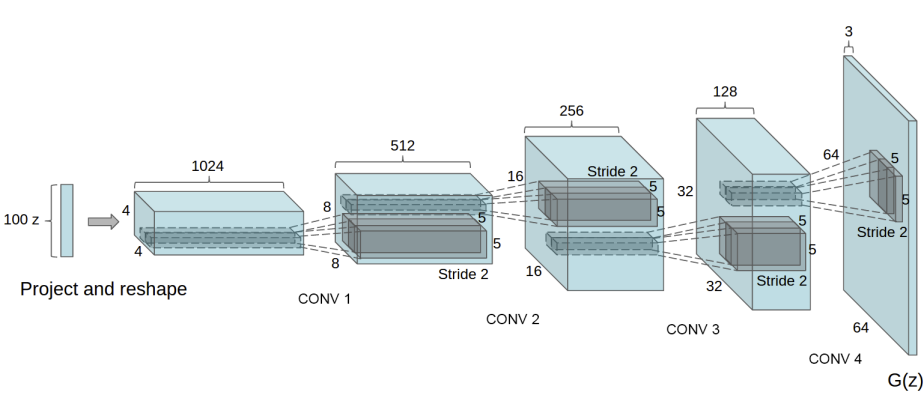
An Example Network
Generator from DC-GAN (Deep Convolutional GAN)
Loss Functions
Loss functions model the problem you're trying to solve
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
model = Model(...)
predicted = model(inputs)
loss = LossFunc(predicted, expected)
loss.backwards()Network contains computed gradient after \(backwards\) call.
Optimizers
Optimizers optimize....
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD({model_parameters}, {optim_parameters})
... code to compute loss ...
loss.backwards()
optimizer.step()These handle all the heavy lifting for optimization, you setup the gradient, the optimizer adjusts the parameters
A More Complete Example
Can we reproduce WFC quality results with a generative network?
Generator
Convolutional: 128 -> (64, 64, 95)

95 Unique tiles
Flowers
Discriminator
Convolutional: 128 -> (64, 64, 3)
Reverse of Generator
Reverse of Generator
Dense
Dense
Generated 10,000 examples in both formats.
DC-GAN
# Initialize generator and discriminator
generator = Generator()
discriminator = Discriminator()
generator.cuda()
discriminator.cuda()
lr = .0001
b1 = 0.5
b2 = .999
# Optimizers
optimizer_G = torch.optim.Adam(generator.parameters(), lr=lr, betas=(b1, b2))
optimizer_D = torch.optim.Adam(discriminator.parameters(), lr=lr, betas=(b1, b2))
# Loss function
loss_fn = nn.BCELoss()
An Example Network
Generator from DC-GAN (Deep Convolutional GAN)

An Example Network
Discriminator from DC-GAN (Deep Convolutional GAN)
Training Loop
for epoch in range(epochs):
for i, data in enumerate(dataloader, 0):
real_imgs = data[0].float().to(0)
# Train generator
optimizer_G.zero_grad()
# Sample noise as generator input
z = Variable(Tensor(np.random.normal(0, 1, (real_imgs.shape[0], latent_dim))))
real_labels = torch.ones((real_imgs.shape[0],), requires_grad=False).to(0)
fake_labels = torch.zeros((real_imgs.shape[0],), requires_grad=False).to(0)
# Generate a batch of images
gen_imgs = generator(z)
# Loss measures generator's ability to fool the discriminator
g_loss = loss_fn(discriminator(gen_imgs).view(-1), real_labels)
g_loss.backward()
optimizer_G.step()
# ...Training Loop
for epoch in range(epochs):
for i, data in enumerate(dataloader, 0):
# ... previous slide, train generator
# Train Discriminator
optimizer_D.zero_grad()
# Measure discriminator's ability to classify real from generated samples
real_loss = loss_fn(discriminator(real_imgs).view(-1), real_labels)
fake_loss = loss_fn(discriminator(gen_imgs.detach()).view(-1), fake_labels)
d_loss = (real_loss + fake_loss) / 2
d_loss.backward()
optimizer_D.step()
Wave Function Collapse (RGB)
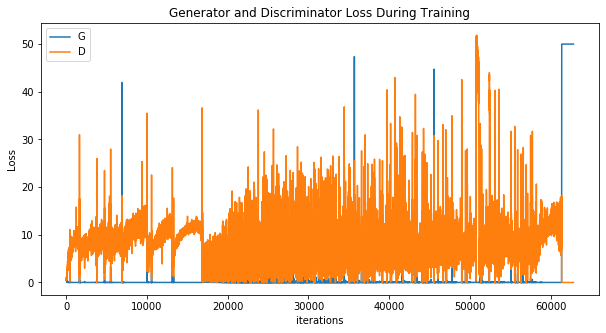
Wave Function Collapse (RGB)
Wave Function Collapse (1-hot state)
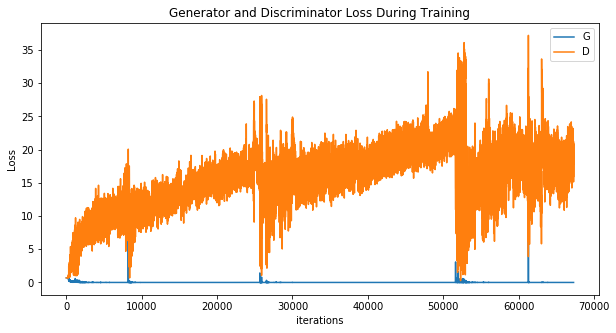
Wave Function Collapse (1-hot state)
Definitely worse...
Wave Function Collapse (Dense WGAN)
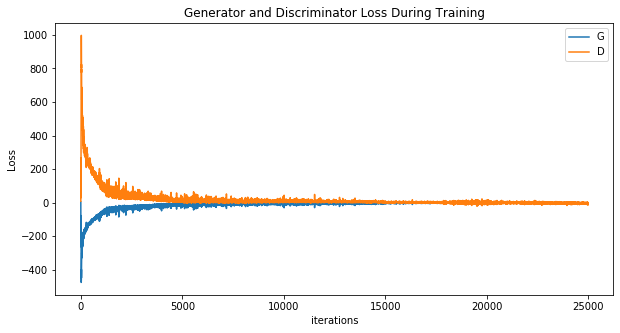
Wave Function Collapse (Dense WGAN)
Wave-function Collapse
By Joshua Horacsek
Wave-function Collapse
- 1,196



