VIRTUALIZATION
Advance Topics in Distributed Systems
Kian Paimani
September 2017

The big debate
- Goal of Operating Systems for a wide range of use-cases
- Provide the illusion that each process* has the machine to itself, yet it is allowed to have shared objects (ports, file descriptors etc.)
- Operating Systems: Embrace Isolation -- or -- Sharing?
- Important factors:
- Performance (HPC)
- Administration (VPS)
- Security (Cloud Services)
* we will temporarily use the terms Process, Application and VM interchangeably
The big debate cont.
- One can argue that none is of that much use without the other one
- True story!
- Imagine:
- Fully isolated process with NO communication and sharing protocol
- Multiple VMs/processes sharing a same host/HW with root privileges
The big debate cont.
- Context Switch:
- virtualization refers to the act of creating a virtual (rather than actual) version of something, including virtual computer hardware platforms, storage devices, and computer network resources
- We are specifically interested in creating Virtual Machines
The big debate cont.
- Two main approaches
-
Hypervisor based virtualization
- Older approach
- Used/Tested in the industry for centuries
- aka. Full Virtualization
-
Container based virtualization
- Modern, state-of-the-art approach
- Currently out of its development shell and used widely
- aka. Operating System Level Virtualization
-
Hypervisor based virtualization
agenda
virtualization techniques
demystified
- Elaborate two mentioned approaches
- Review some of the literature comparing them
- Have a closer look at a superior container-based approach:

hypervisor vs. container
- Hypervisors:
- Virtualize at the hardware level
- Either directly (Full Virtualization) or indirectly through an OS (Paravirtualization)
HW
HYPERVISOR
HYPERVISOR
HW
HOST OS
GUEST OS
APPLICATION
hypervisor vs. container CONT.
- Containers:
- Virtualize at the Operating System level
DOCKER
HW
HOST OS
DEPENDENCY
APPLICATION
Keep in mind that
- Dependencies are also an important factor (Dependencies can be a new OS!)
- They were delivered by the guest os in hypervisors
*Docker is just a representative of operating system level virtualization
hypervisor vs. container CONT.
Some remarks:
- One single kernel - Multiple kernels fighting over HW
- Overhead of each OS up and running (HPC)
- Containers are cheap - VMs are simply not
- rebooting frequently (XaaS ~ Firebase ~ Auth0)
- Docker can respond to container requests on-demand - Hypervisors (usually) allocate fix quota of resources
- Optimized resource utilization (hosting organization)
- Bottom line: Containers seem to be fast and efficient
about ISOLATION measures
- Efficiency is measurable
- Isolation on the other hand, not so easy
- Fault isolation
- One could argue that hypervisors are slightly easier to prove safe
- Resource isolation
- Is everyone receiving its fair share?
- Security isolation
- How does each Application know about its virtualized environment (configuration independence) + can it change anything? (safety)
- Fault isolation
about ISOLATION measures CONT.
- Hypervisors are easier to be proven safe (easier to verify).
- [1] provides a full argument about why this trade-off between isolation and speed is worth it and most modern approaches prefer more speed.
- Note that this is different than "Hypervisors are safer".
- In fact, [4] has a dedicated section about security of Docker and concludes that the most important vulnerability is Docker-Hub.
- Over 30% of Official Images in Docker Hub Contain High Priority Security Vulnerabilities
- Old discussion between those who believe in open-source and don't.
about ISOLATION measures CONT.
EFFICINECY
ISOLATION
Operating Systems
VServer
VMWare
Docker (LXC)
about PErFORMANCE measures
- An important use-case: High Performance Computing
- Multiple aspects are important:
- Network (NAT / Bridge / Host-Only )
- File System performance
- crucial for Big Data Processing
- Single Node performance
- native: How is the virtualized env. doing?
- SMP
- Cluster Performance
about PErFORMANCE measures
- [2] examined all of these aspects in depth
- Used Virtualization systems:
- VMWare Server (FV) / Xen (PV) / OpenVZ (OSV)
- Standard benchmarks
- Netperf for network
- IOZone filesystem
- NPB (NAS Parallel Benchmark) for performance
- Let's have a quick look at some of the results:
about PErFORMANCE measures
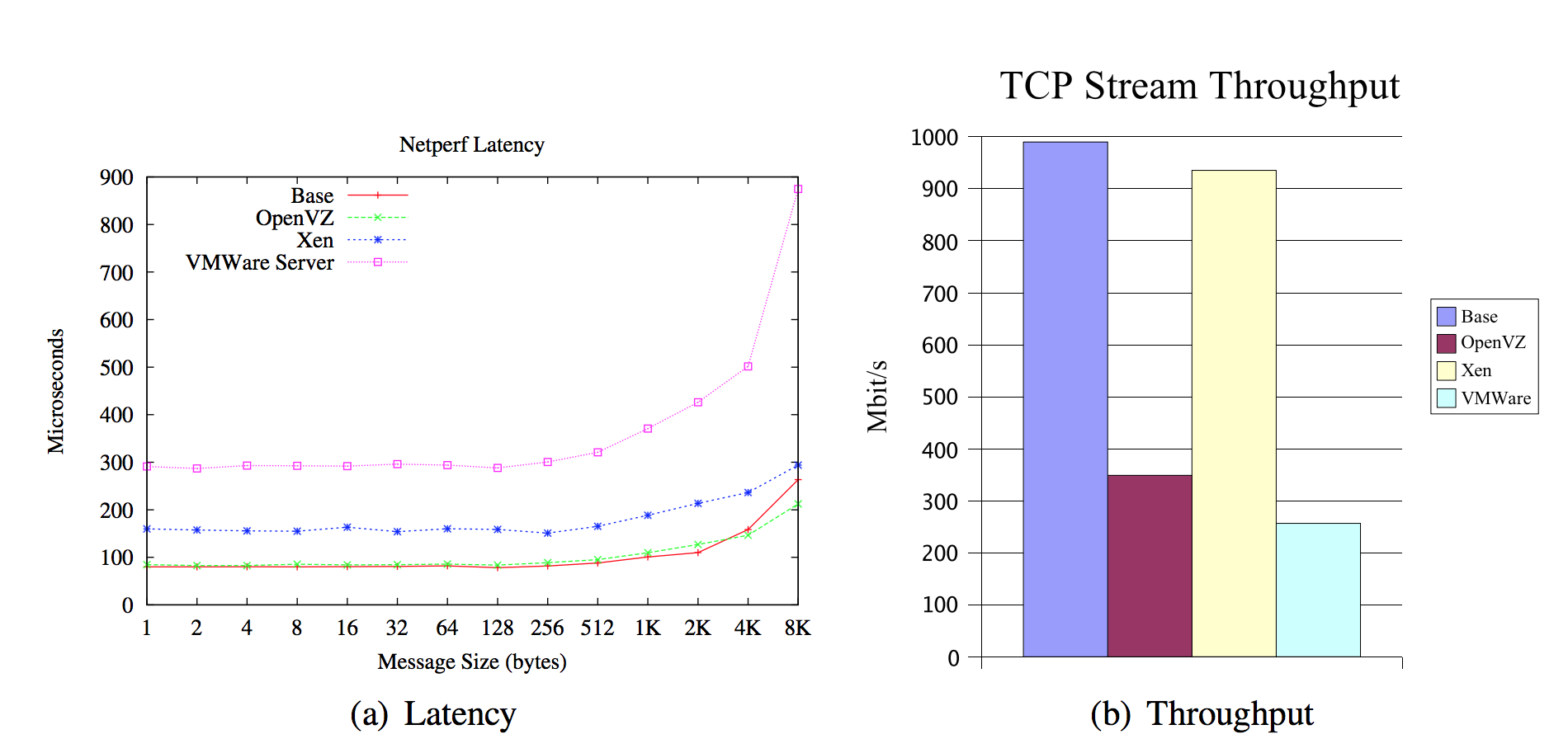
about PErFORMANCE measures
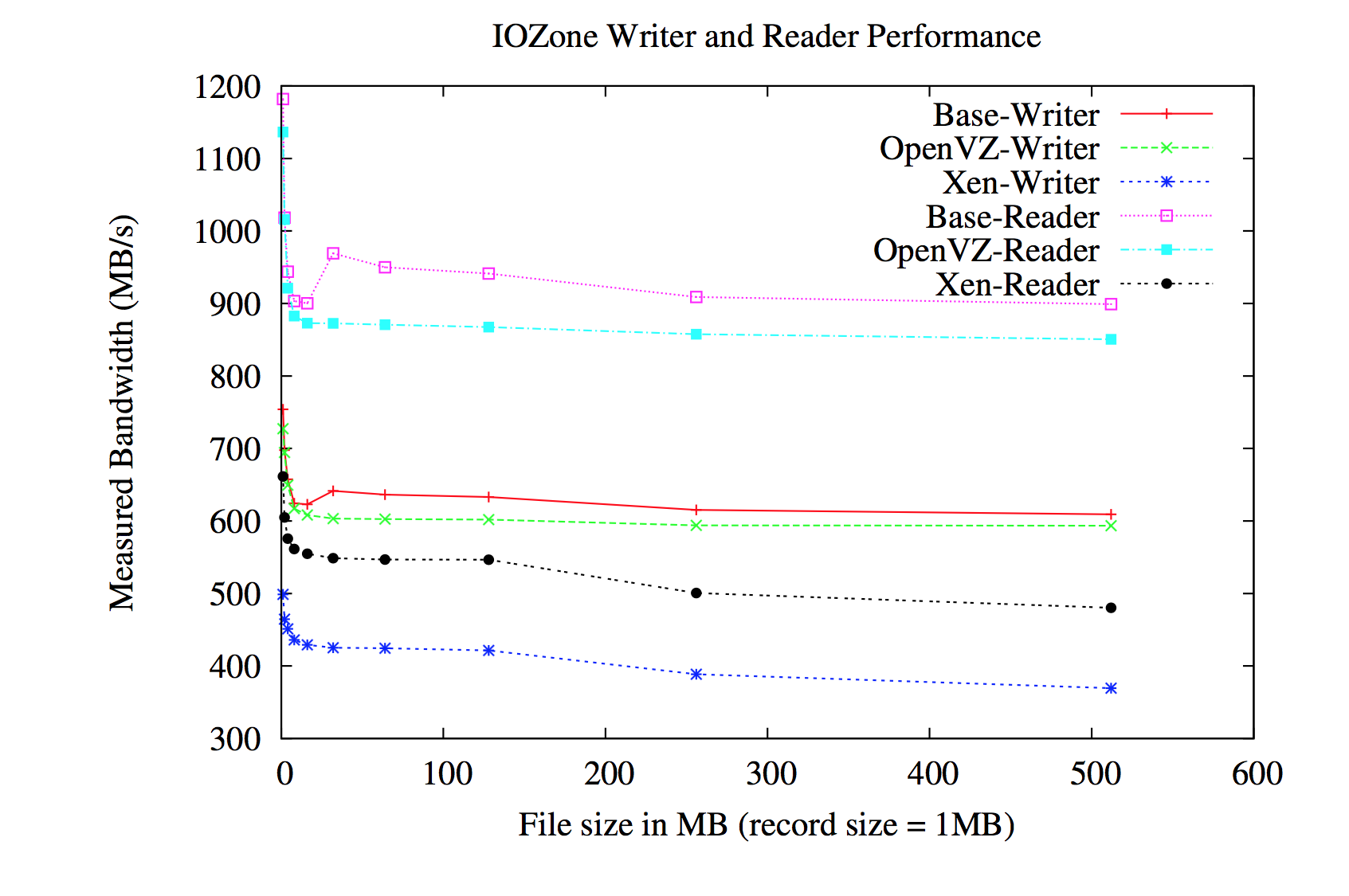
about PErFORMANCE measures
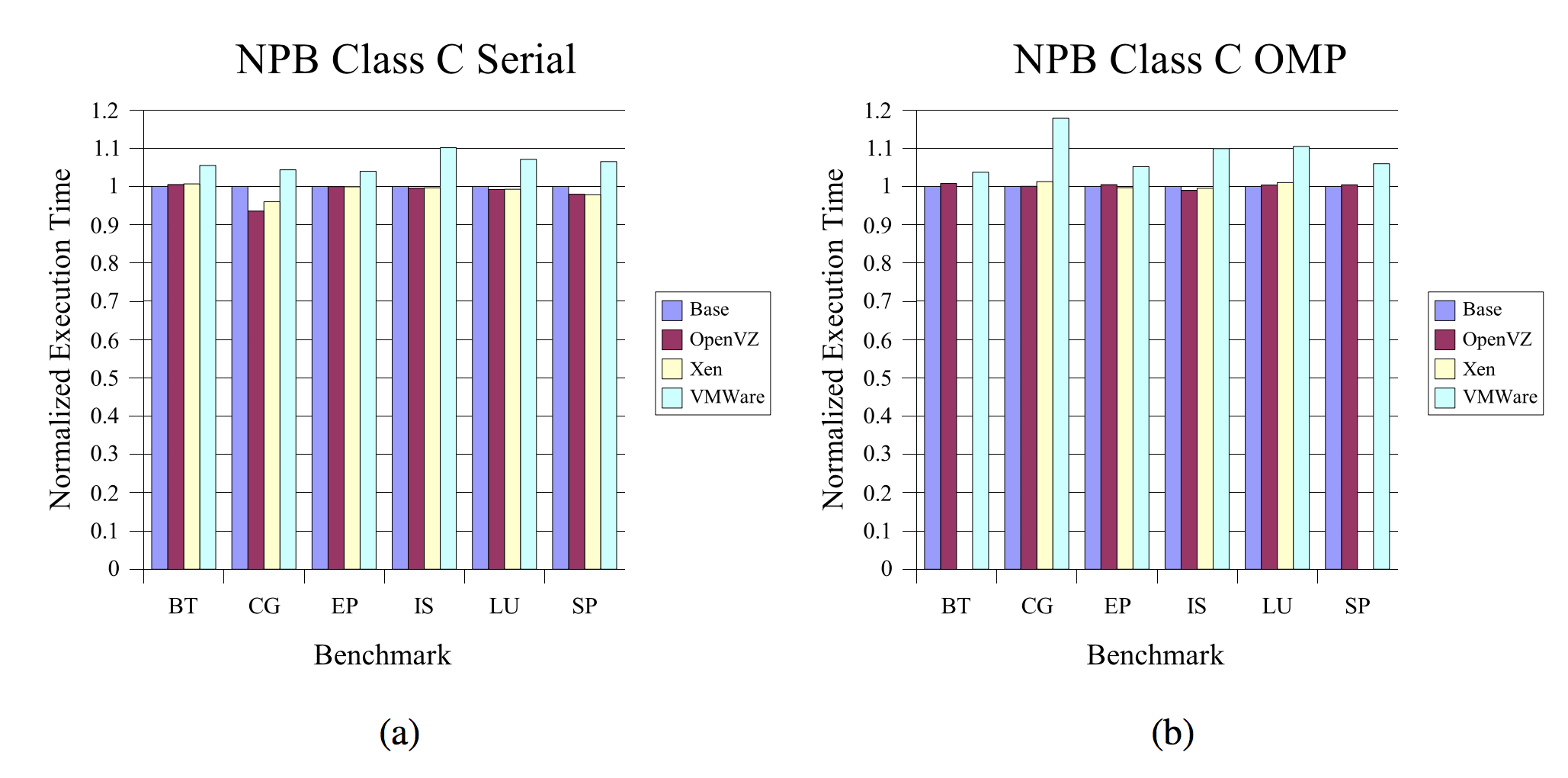
about PErFORMANCE measures

about PErFORMANCE measures
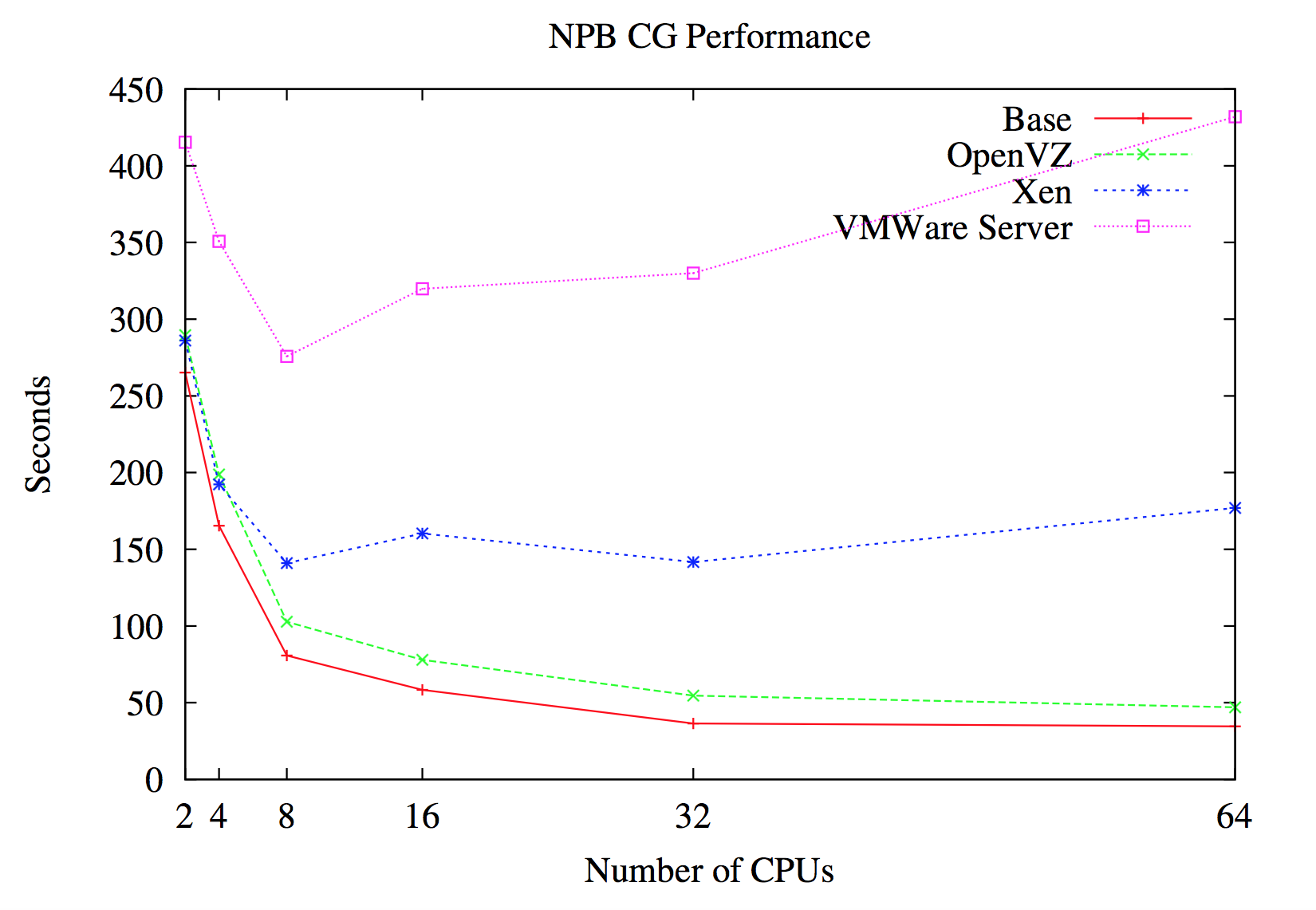
Performance and isolation
- Keeping the following points in mind:
- Type of each Virtualization software
- Importance of network latency and filesystem management
- Type of computation benchmarks
- One can conclude that:
- Container based virtualization provides significant performance improvements, while being only slightly weaker than hypervisors in isolation measures.
about docker

- Modern container based virtualization
- Based on Linux LXC and cgropus
- Open-source project at dotCloud
- Written in GO
- Actively maintained and updated (perhaps a bit too much)
about docker - technical
- Comparing to OpenVZ
- Use more recent linux functionalities
- User-friendly
- Docker's core is built on top of [4]:
-
LinuX Containers: Create isolation namespaces
- Kernel / User / Process / Network
-
Control Groups
- resource accounting and limiting
- Advanced Multi- Layered Unification Filesystem
- Aggregation of Images (Dependencies!)
-
LinuX Containers: Create isolation namespaces
about docker - motivational
- While we did talk about important use-cases such as HPC, Docker was initially designed to solve a simpler, yet a ubiquitous problem: Dependency Hell
- Docker makes applications portable and isolated by packaging them into small, fast and cheap containers
- Some aspects of dependency hell
- Conflicting dependencies
- Missing dependencies
- Platform differences
let's talk
QUESTION?
references / links
- A Comparison of Virtualization Technologies for HPC
-
Container-based Operating System Virtualization:
A Scalable, High-performance Alternative to Hypervisors -
Docker: Lightweight Linux Containers for Consistent Development and Deployment
-
Hypervisor- vs. Container-based Virtualization
-
NPB Benchmark
-
Netpref Benchmark
-
IOZone benchmark
VIRTUALIZATION
By Kian Peymani
VIRTUALIZATION
- 725



