Functors and Monads, briefly
What's a Functor?
a type of mapping between categories arising in category theory.
Functors can be thought of as homomorphisms between categories
What's a Functor?
- In Scala, this means things that can be mapped over
- Much more plainly stated: allows you to apply a mapping function to a context
val opt: Option[Int] = Some(3)
val intToString: Int => String = (i: Int) => i.toString
// apply map from type A (Int) to type B (String)
val res: Option[String] = opt.map(i => intToString(i))
> Some("3")What's a Functor?
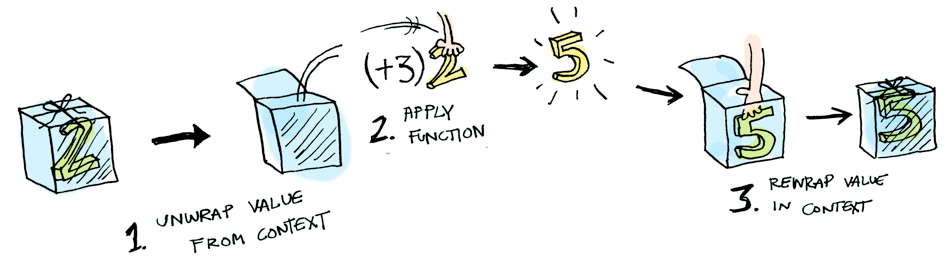
Examples of Functors
- Option[T]
- List[T]
- org.apache.spark.sql.Dataset[T] (kind of)
What's a Monad?
an endofunctor (a functor mapping a category to itself), together with two natural transformations.
- Simply stated: structures that allow you to sequence computations consisting of inputs, outputs, and their context
- Formalizing sequential programs with context
What's a Monad?
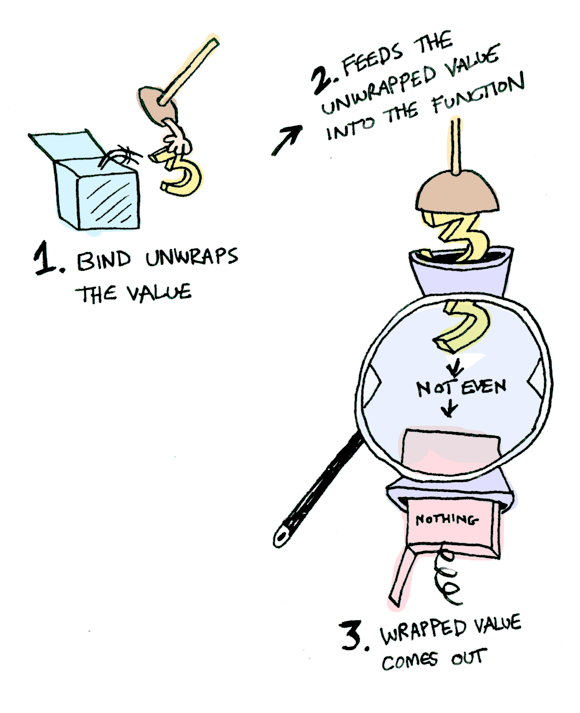
Why Monads?
- Write your functions without having to handle context every time
- Chain together functions sequentially (monadically) while automatically handling context with flatMap
- function: A => F[B]
def apiCall(url: String): Task[WebResponse] = { ... }
def saveToDatabase(resp: WebResponse): Task[DatabaseResponse] = { ... }
val dbResp: Task[DatabaseResponse] =
apiCall("http://google.com").flatMap { webResponse =>
saveToDatabase(webResponse)
}Examples of Monads
- Option[T] (optionality)
- Try[T] (error/exception handling)
- Future[T]/Task[T] (asynchrony)
- Either[A, B] (usable for error handling)
Why any of this?
- Higher-order abstractions in every day code can be captured in the type system, rooted in category theory
- Must follow higher-order logic as well - laws
- Code reuse
- Higher-order ways to structure your code
- Free monads
- Final tagless
Functor Laws
// Identity law
Some(3).map(identity) == Some(3)
// Composition
val plusOne: Int => Int = (x: Int) => x + 1
val timesThree: Int => Int = (y: Int) => y * 3
Some(3).map(plusOne).map(timesThree) == Some(3).map(plusOne compose timesThree)Monad Laws
- Left identity
- Right identity
- Associativity
- See: https://devth.com/2015/monad-laws-in-scala
Additional reading
Functors and Monads
By longcao
Functors and Monads
- 2,125



