ML for Biological Applications
Luisa Cutillo
Lecturer at the University Parthenope of Naples, IT
Visiting academic at the Dep. of Computer Science, Sheffield, UK
Twitter: @luisa_cutillo78

Why is Biology a growing application area of Machine Learning?
- Biology is an evidence driven discipline
- Large quantities of highly heterogeneous data
- Data kinds: numerical, text, image, sound, and video

Machine Learning and Bioinformatics
Bioinformatics applies mathematics, computer science, and statistics techniques to understand and organises the information associated with the biological data
Main Limitation:
Bioinformatics is sometimes driven by the need to make most of small sample size!
Why ML in Bioinformatics?
size and number of available biological datasets have skyrocketed: Bioinformatics screams out for ML!

Applications to big biological data
- Genomics
- Proteomics
- Microarray and RNA-Sequencing data
- System Biology
- Text Mining

ML in Genomics
Aim:
study the complete DNA of an organism
ML:
- Automatic Gene Prediction: determine the location of protein-encoding genes within a given DNA sequence >Extrinsic and intrinsic searches based on HMM
- Multiple Sequences Alignment: NP hard optimization problems, Consensus and iterative methods, HMM, genetic algorithms and simulated annealing. summary paper link.
- Detect and visualize genome rearrangements. Nature 2015.

ML in Proteomics
Protein folds into a 3-dim structure
Aim:
Protein secondary structure prediction
ML:
amino acids of a protein sequence are classified in helix, sheet, or coil (structural classes) using DeepCNF (deep convolutional neural fields): it relies on artificial neural networks to achieve high accuracy (~ 84%) [paper link]

ML in Microarray and RNA-Seq data analysis
Aim:
monitoring the expression of genes within a genome (microarray)
reveal the presence and quantity of RNA in a biological sample (RNA-seq)
ML:
radial basis function networks, deep learning, Bayesian classification, decision trees, and random forest

ML in Microarray and RNA-Seq data analysis
Microarrays VS RNA-SEQ
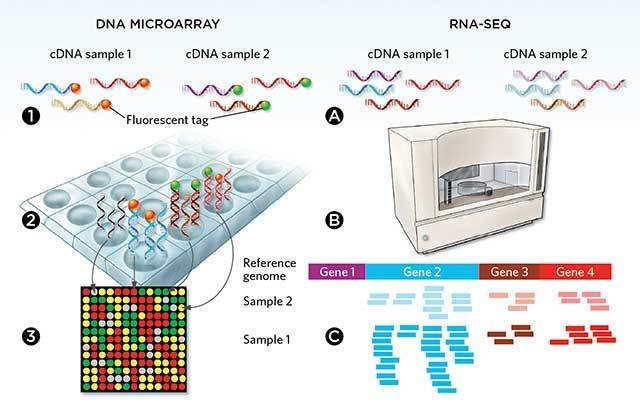

ML in Microarray and RNA-Seq data analysis
Bulk VS Single Cell RNA-SEQ


Single Cell RNA-seq
Bulk RNA-seq

ML in System Biology
Aim: study of complex interactions in biological systems of simple biological components (e.g. DNA, RNA, proteins, and metabolites) in a system.
ML: aid in the modelling of these complex interactions in domains such as genetic networks, signal transduction networks, and metabolic pathways. Methods: Probabilistic graphical models, transcription factor binding sites using Markov chain optimization, Genetic algorithms

ML in Text Mining
Aim: knowledge extraction -> searching through and compiling all the relevant available information on a given topic across all sources.
ML: knowledge extraction task using techniques such as natural language processing and Text Nailing
Examples of applications: automatic annotation of the function of genes and proteins, determination of the subcellular localization of a protein, analysis of DNA-expression arrays, large-scale protein interaction analysis, and molecule interaction analysis.

ML in Bioinformatics

Luisa Cutillo and Research Software Engineer (RSE) team, University of Sheffield

Discussion
- What is your field of interest?
- Can you share your experience?
- Questions or doubts?
WIML Biological Applications Round Table
By Luisa Cutillo
WIML Biological Applications Round Table
Overview of Machine Learning for Biological Application
- 1,381



