Epidemics

Epidemic
noun
-
a widespread occurrence of an infectious disease in a community at a particular time.
"a flu epidemic"
adjective
-
(of a disease) prevalent over a whole country or the world.
Pandemic
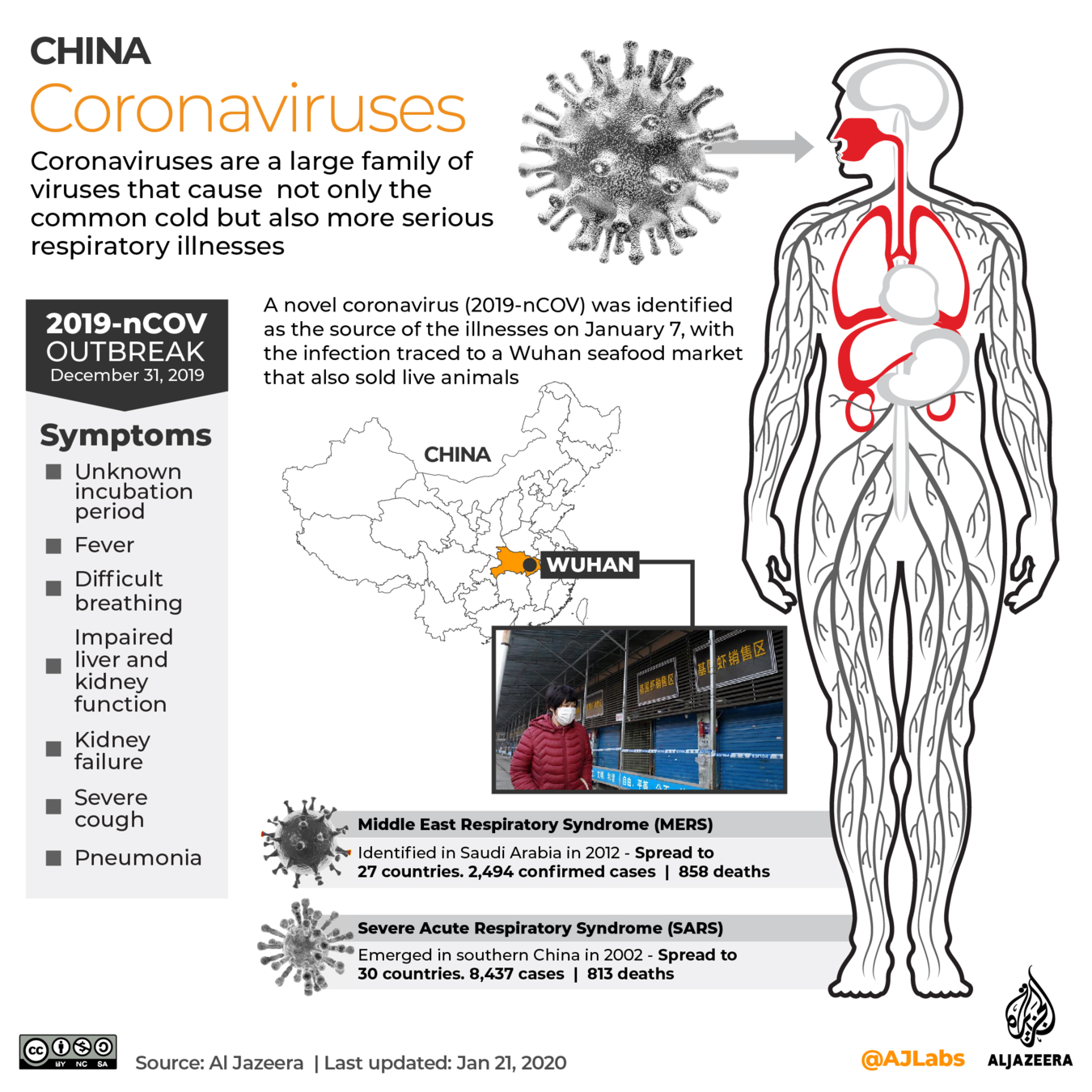
What actually is a virus?
- microscopic parasites
- much smaller than bacteria
- lack the capacity to thrive and reproduce outside of a host body.
Coronavirus - Covid-19
Get their name from spiky projections on their outer surfaces
Corona in Latin means crown
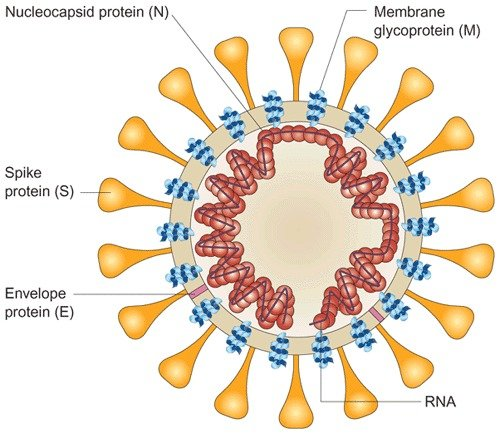
Coronavirus - Covid-19
- spike proteins extend from within the core
- the virus latches on to the vulnerable cells
- Virus hijacks cell
- Cell becomes factory to create reproduce viruses
Where do viruses come from?
HIV
SARS
Ebola





Where do viruses come from?
- Sells live animals including bats. (to eat 🤢 )
- linked to illegally traded wildlife at Wuhan's seafood market
However, the exact source of the outbreak has not been identified.

How do you get infected?
- respiratory droplets
- coughing or sneezing
- droplets of saliva or discharge from the nose.
Why China?
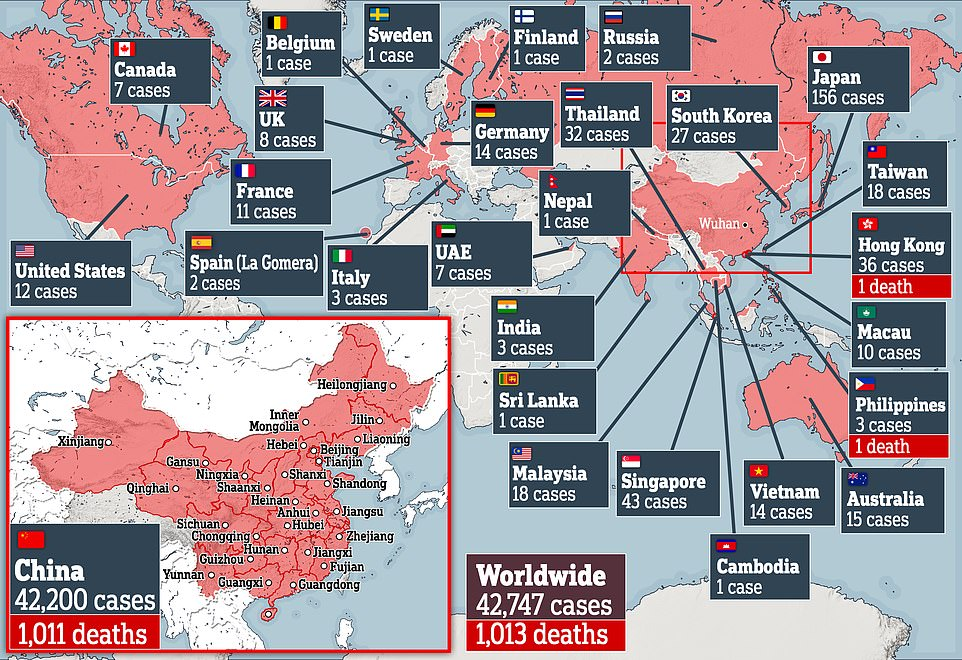
Text
Text
Animal Contact
Dense Urban Populations
"Super Spreaders"
"Super spreaders" are a big contributor to an epidemic
Transmit more than the usual
Come into contact with far more people (Job, location etc)

Why Do Some People Spread More?
- Kids
- "Super Shedders"
- Hospitals

What happens when you catch it?

Governments - Preventing Spread

- Quarantine
- Thermal Scanners
- Can't detect people who are infected but haven't got a fever yet
Stages of an epidemic
WHO keeps track of all identified viruses, animal or human, through a set of phases or stages.
Phase 1: Animals Only
Phase 2: Human Infected from Animals

Stages of an epidemic
Phase 3: Small clusters of human beings have contracted the virus in one community.
Phase 4: Human-to-human and animal-to-human virus transmission are causing outbreaks in many communities
Stages of an epidemic
Phase 5: Infection in two countries - Governments must be ready to implement their pandemic mitigation plans.
Phase 6: Global Pandemic. Illness is widespread and every governments top priority is curtailing the spread of the disease.
Stages of an epidemic
Post-Pandemic: After the increase in activity, the disease-spreading activity will begin to wane. The key at this point is to be prepared to try to prevent a second wave.
Should I be worried?
- Elderly, Pre-existing medical conditions
- The death rate in total is around 2%
- People could recover
- The numbers are starting to stabilise, especially outside of China

When to worry
- The source is not found. This makes vaccines difficult.
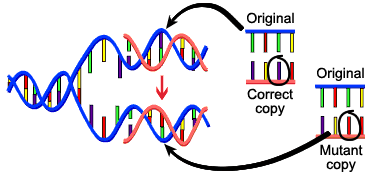
- The virus becomes unstable and starts to mutate.
Thanks
Epidemics
By Martin McKeaveney
Epidemics
- 735



