Data Mining

What is data mining?
Why is it used?
What are techniques used in data mining?
What is the history behind data mining?
Well...


Data mining starts with the process of extracting data, and searching it for patterns/ relationships to variables. Anaysts then compare these results to new chunks of data.
Basically, data mining in a computer science sense, is converting data into information that can be understood, often through the use of data mining software


Data mining is INCREDIBLY useful in multiple areas
-Video games with lots of statistics can be data mined to determine exactly how elements of a game work mathematically.
-Sales withing a store can be data mined so that trends can be discovered based on who is buying what and for how much.
-Phone companies can use data mining to measure the statistics of their provided phone calls and services. In this way, they can improve in areas that consumers use their services less, and find the reasons for this.
And the list goes on...
Essentially data mining is most useful when there is an over abundance of data that needs to be analyzed. Software can be developed to organize this data and present it to analysts.


There are also many techniques in data mining...
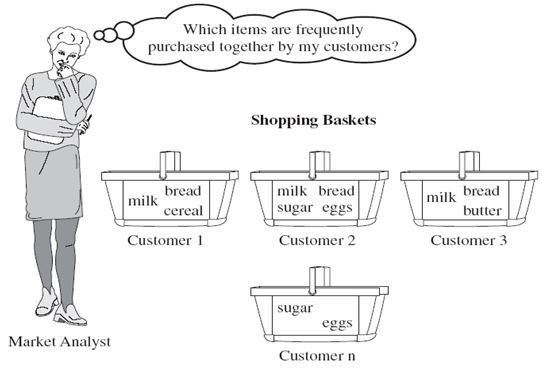
Association Rule
-this method is used when searching for data that is similar to other sets of data
-For example, if we find data that falls into a certain group, how much of that group is composed of the data we found?
-What other sets of data fall into this group?
-Once we find all the data in this group, we know to associate them.
An example could be products sold by a company. If data shows that the large majority of consumers buy product x and y at the same time and both of those products relate to product z, the company can try and market product z and it's counterparts together for greater profits.
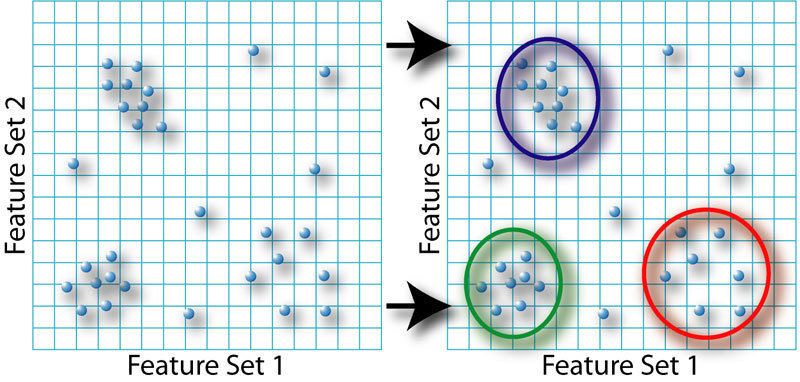
Clustering
-Clustering is a technique used in data mining in which by analyzing data you can create common groups to store the data being examined.
-This method is described as being a "bottom-up" approach.
-The reason for this is due to the fact that the user isn't looking for specific sets of data, but rather sorting the data they happen to find as they go.
An example of clustering could be a program that sorts images. If the program is able to read the primary color palettes of pictures, than you can have the program sort the pictures based on that color data. The result will be pictures grouped together that have similar color schemes.
Decision Trees
-This technique is similar to clustering, but unlike clustering's "bottom-up" approach, decision trees are more "top-down".
- By creating a decision tree, the user can measure data by passing it through the tree until it falls on to a "leaf".
Is this data an Integer?
Yes
No
Is this data a string?
Yes
No
Discard data
As you can see, this decision tree can measure data based on if it is an integer, a string, or other. This can help users determine what kinds of data they're dealing with, if they have a piece of software than can use a decision tree type system to filter the data mined.
how did data mining come about?
1974
Peter Naur publishes a book known as "Concise Survey of Computer Methods". The book talks about methods of data processing, and defines data as: "a representation of facts or ideas in a formalized manner capable of being communicated or manipulated by some process."
The book also has a definition for the term "data science"/"datalogy":
“The science of dealing with data, once they have been established, while the relation of the data to what they represent is delegated to other fields and sciences.”
1977
The International Association for Statistical Computing is founded. They claim that their mission is to link traditional statistic studies with computer sciences. In this way, they can efficiently "convert data into information and knowledge."

1989
Gregory Piatetsky-Shapiro organizes and leads the first Knowledge Discovery in Databases workshop.

1995
Gergory Piatetsky-Shapiro's workshop becomes the annual ACM SIGKDD Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining.

1996
In Tokyo, Japan, members of the IFCS (International Federation of Classification Societies) include "Data Science" in the title of the conference. This shows Data Science become commonly accepted as a field of study, in fact, members of the conference referred to data science by many names:
-data analysis
-datalogy
-and... data mining.

1997
A journal is released known as Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. Around this time, businesses start feeling a need for computational tools and data mining methods, as many companies start acquiring these assets.


2001
William S. Cleveland for Bell Labs, announces a plan to "enlarge the major areas of technical work of the field of statistics. Because the plan is ambitious and implies substantial change, the altered field will be called ‘data science.'" This plan is put into motion so that statisticians and computer scientists can work together to take full advantage of the potential data mining has.

2002
The Data Science Journal is published by the Committee on Data for Science and Technology. It talks about data systems, techniques, applications, and even potential and real legal issues.

2005
The National Science Board publishes a report on data science. Part of it reads that the NSF should work to "develop and mature the career path for data scientists and to ensure that the research enterprise includes a sufficient number of high-quality data scientists."

2008
The JISC publish a report on data scientists themselves. It claims that data scientists are, "people who work where the research is carried out – or, in the case of data centre personnel, in close collaboration with the creators of the data – and may be involved in creative enquiry and analysis, enabling others to work with digital data, and developments in data base technology.".
We can see in this year the data scientist getting a lot more attention as a valued career.

2010
Several journalists including Kenneth Cukier, Mike Loukides, Hilary Mason and Chris Wiggins, and Drew Conway, all write about data scientists extremely positively. All of them point out their skills in computing, mathematics, forecasting, statistics etc.
From this point on, it was quite clear that data scientists and data mining in general was a respected and valuable field.
Data mining is a field created by the fusion of mathematics, computer science, and statistical studies. It is incredibly useful in multiple fields of work and is a very sought after skill by employers. With multiple methods of working with data, and different pieces of hardware and software to do it with, this is a field that has plenty of room for research and expansion.
thanks for reading!
Works Cited
http://www.statsoft.com/textbook/data-mining-techniques
http://www.unc.edu/~xluan/258/datamining.html
http://whatsthebigdata.com/2012/04/26/a-very-short-history-of-data-science/
Data Mining
By matthewgervasi
Data Mining
My presentation on data mining.
- 1,010



