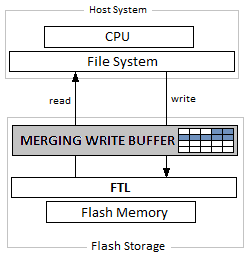
MERGING WRITE BUFFER
MANAGEMENT ALGORITHM
REDUCING ERASE-WRITE CYCLE IN FLASH STORAGE
objective
reduce the erase-write cycles in the flash memory by holding the data inside the RAM buffer
flash storage

flash storage 101
FLASH STorage 101
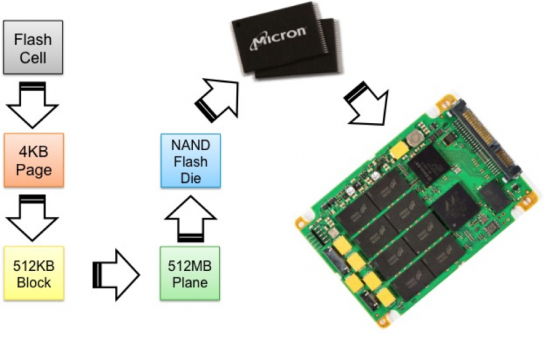
- flash cells > pages > blocks
- flash reads fast and writes slow
FLASH STorage 101
- flash writes by block and no overwrite
- single value in a cell can be changed from “1” to “0” but not the other way around
-
erase-write cycles
- writing requires the reading of an entire block from flash and into the memory of the controller
- updating it requires erasing the existing block and writing the data back to the flash device
- multi-stage process called write amplification
Source: http://www.computerweekly.com/news/2240234587/Flash-storage-101-How-solid-state-storage-works
the problem
write performance & longevity
write amplication
NAND chips are degraded slightly with every write operation and so devices have a finite number of erase-write cycles.
- SLC has a erase-write cycle count of around 100,000 per block of data.
- MLC can be as low as 5,000 per block of data.
- TLC can be as low as 1,000 per block of data.
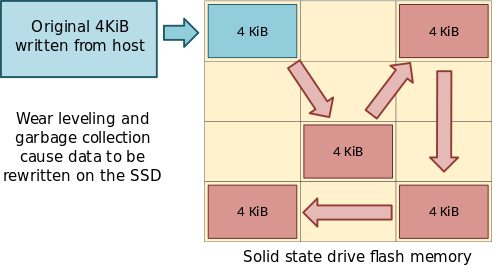
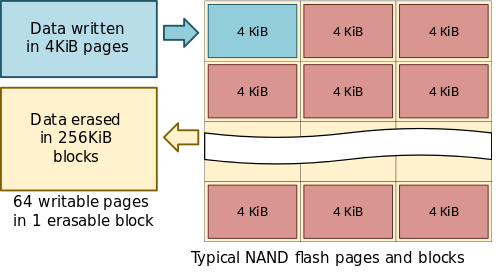
lower write amplification by minimizing the number of write cycle
related works & researches
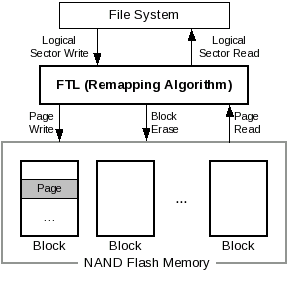
ftl (FLASH TRANSLATION LAYER)
remapping the logical blocks exported by a storage interface to physical locations within individual pages
cfLRU (cLEAN FIRST LRU)
exploit the read-write asymmetric performance of flash. Its core idea is dividing LRU linked list into two parts: working area and replacement area.
BPLRU (BLOCK PADDING LRU)
employs a page padding scheme where the log block is padded with some clean pages from the data block to reduce the number of writes.
write merging buffer
proposed scheme
write buffer
used to absorbed repeated write requests
MERGING write buffer
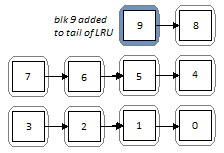
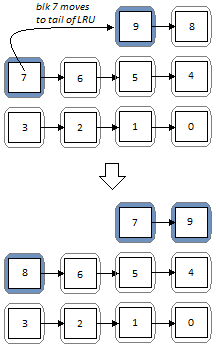
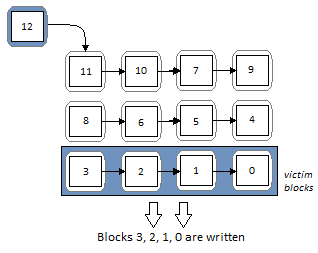
MERGING write buffer ALGORITHM
analysis & evaluation
comparison of with and without mWb
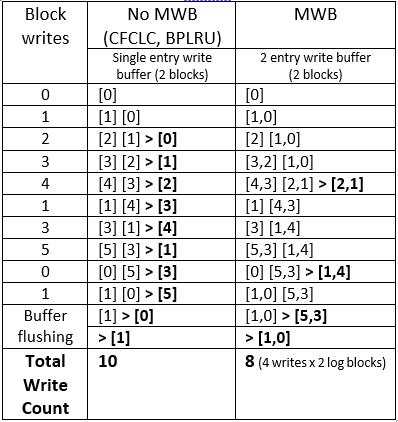

SEQUENTIAL-WRITE
RANDOM-WRITE
conclusion
&future work
merging write buffer management reduces the number of erase-write counts in a random-write but doesn't have an effect on sequential-write.
merging write buffer management algorithm could be extended to the other buffer-based algorithm such as CFLRU and BPLRU
END
Merging Write Buffer Management Algorithm
By Mylene King
Merging Write Buffer Management Algorithm
COE218 Advanced Computer Architecture
- 1,365



