Towards an All-IP-Based UMTS System Architecture
Authors: Lieve Bos and Suresh Leroy, Alcatel
Presented by: Neil Koul
Background
UMTS
- Universal Mobile Telecommunications System
- 3rd Generation cell communication
- Based on the GSM system, maintained by 3GPP
- Was in competition with the cdmaOne technology
Main Goal
Clarify Implications of IP-based core network on UMTS
Virtual Home Environment
Standardizing capabilities instead of services.
What is VHE?
- Intended to allow users to access services outside of home network
- Make the user feel "virtually at home"
- Automatic message adaptation depending on what the user is connected to
VHE Terminology
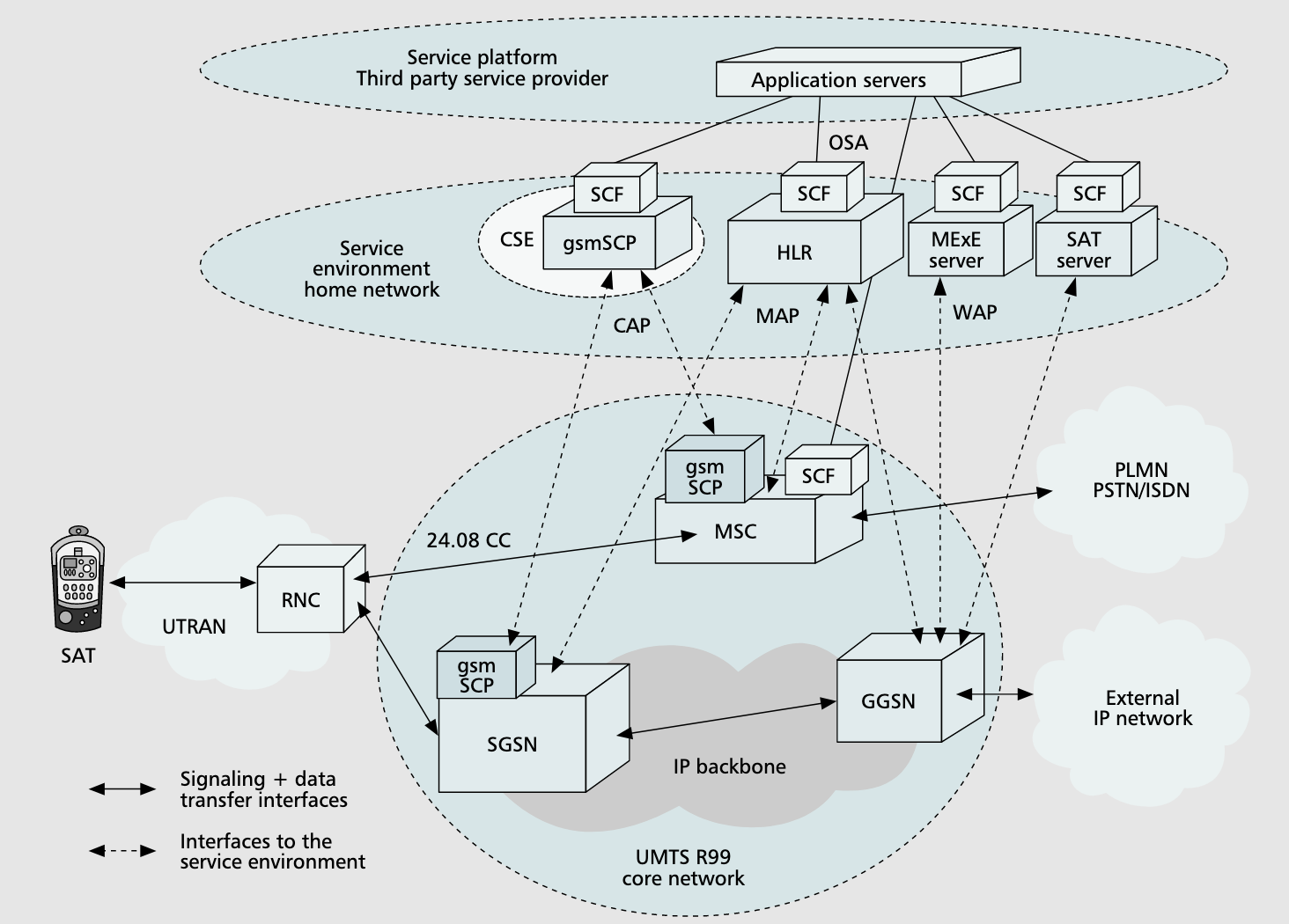
- Service Capability Servers (SCSs) - servers that allow for services to be constructed
- Service Capability Features (SCFs) - classes/services constructed by SCSs
- Their purpose is to raise abstraction of network interfaces in order to simplify app development
VHE SCSs
- UTMS call control servers- manage bearer/call control capabilities, R99 only allows circuit-switched telephony
- Home Location Register (HLR)- database that contains location and subscriber information
- Mobile Execution Environment (MExE)- a JVM or WAP browser, where value-added services are offered
- SIM application toolkit (SAT)- additional SIM features that allow for extra authentication information into terminals
- Customized Application for Mobile Networks Enhanced Logic (CAMEL)- extends traditional intelligent network scope.
R99 UMTS

Voice over IP
Is VoIP better than traditional telephony?
R00 Features
- IP-based multimedia services as extension of packet-switched services
- Circuit-switched transport is replaced by packet-based network transport
- IP transport on the Radio Access Network (RAN/UTRAN)
- Network architecture is independent of transport layer, can be ATM or IP
What it would take for all IP-based core
- Roaming and Handover to 2G support
- Support of 3G circuit-switched terminals (for backwards compatibility)
- Support of new speed, SMS and other services that are all legacy as well as new IP-based versions
R00 All-IP Architecture
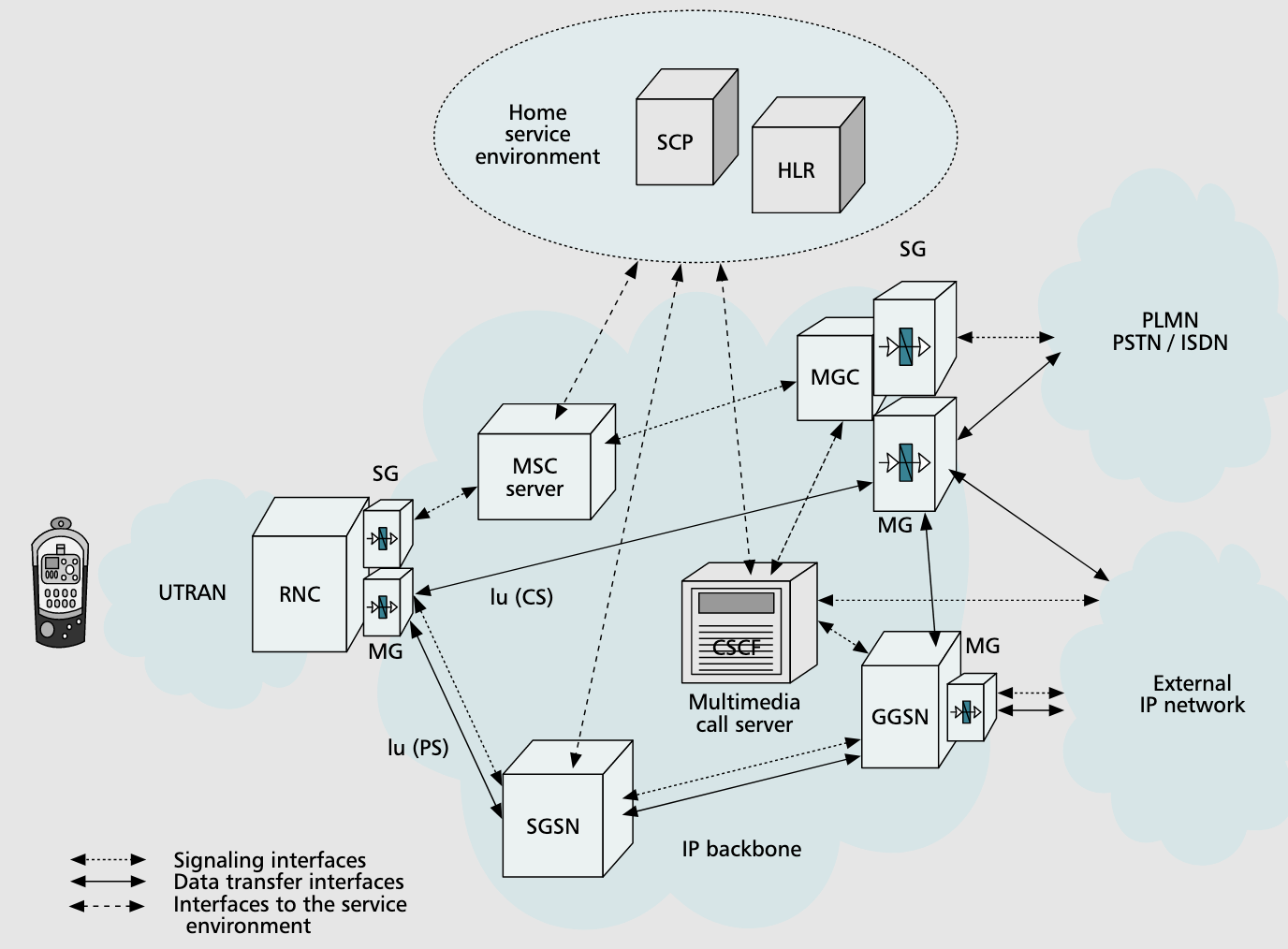
New Elements in IP Arch
- MSC- controls calls from circuit-switched terminals to mobile terminated calls, controls VoIP vs non VoIP
- Call state control function(CSCF)- provides/controls multimedia services for packet terminals
- MG at UTRAN side- transforms VoIP packets into UMTS frames
- MG at PTSN side- calls from PTSN converted into VoIP calls for transport in UMTS core network
- Signalling Gateway (SG)- relays all call-related signaling from PTSN/UTRAN on IP bearer and sends data to MGCF
- MGCF- control MGs, and provides translation
- Home Subscriber Server (HSS)- HLR extension with multimedia profile
VoIP in VHE
Two scenarios for providing VoIP in VHE
Scenario 1
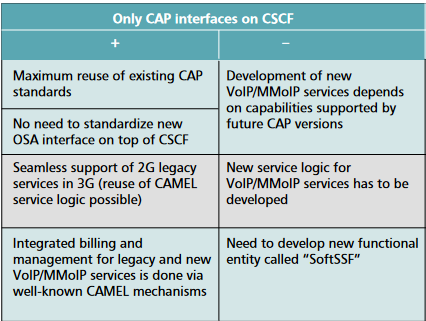
SoftSSP Concept INAP/CAP
- The IN Application Part (INAP) triggers Service Control Point (SCP) reliant on Service Switching Point (SSP)
- CAMEL Application Part (CAP) is the same as INAP but in CAMEL
- The "SoftSSP" is to be build on top of the Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) server, to ensure that services can be provided via IN/CAMEL
- Mapping between the SIP call state model and the state model of IN/CAMEL
Scenario 1
VoIP on CSCF
- CSCF-SoftSSP must carry sufficient call data for the SoftSSP to deliver data to the SCP so service logic can function
- It also must allow SCP with the SoftSSP to control VoIP calls, like changing party address, add/remove media components, and to manipulate call information
Scenario 1
Advantages of SoftSSP
- Helps existing operators since UMTS R99 or GSM is already in use
- The newer CAMEL service environment creation methods work on legacy systems
- Mapping between CAP and SIP call control allow for VoIP to act like traditional services
Scenario 1
Disadvantage of SoftSSP
- Third Party Service providers can get access to the operators network via only the SCP
- They cannot get access to the CSCF, which implies no way of access to manage VoIP services
Scenario 2
3rd Party Support via CGI/CPL/SIP
- Two possible gateways for Third Party to allow access and control of network entities
- The Common Gateway Interface (CGI) : a mechanism already used on the internet for dynamic web pages, In the SIP, CGIs are triggered when requests arrive at server
- The the Call Processing Languages (CPL): Scripting language for network servers, allowing for immediate instantiation, and report back to controller CPL
Scenario 2
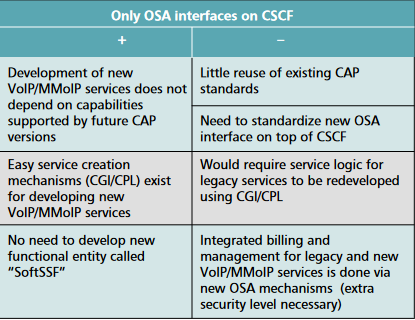
OSA arch for CGI and CPL
- Standardized representation for creating services in an order to enable multi vendor implementations
- Portability such that abstractions are defined and a high-level and are not SIP-specific, allowing portability between protocols
- Scripts are to be verified to ensure that it can run sucessfully
- Initiated services must be sure they can be terminated
- The integrity of other users must not be effected via the script run
OSA with SCP
vs
OSA with CSCF
Which is better?
Mobile Computing Paper presentation
By Neil Koul
Mobile Computing Paper presentation
- 120



