Valgrind
How it work?
Valgrind Component
- Valgrind core
- vgtool
- program
Valgrind Core
Valgrind Tool
Program
JIT
- simulated CPU
- x86 -> ucode
x86 Binary
UCode Binary
Emulator
Program
Valgrind Core
Host CPU
Intermediate Representation (IR)
ucode
Tools
Machine Code
System Call
-
system call may change process memory by kernel and valgrind want to know
- Pre
- Post
- copy all program's state to real CPU
- except program counter
PRE(sys_SYNOStat)
{
FUSE_COMPATIBLE_MAY_BLOCK();
PRINT("sys_SYNOStat ( %#lx(%s), %ld, %#lx)",ARG1,(char*)ARG1,ARG2,ARG3);
PRE_REG_READ3(long, "SYNOStat", const char *, file_name,
unsigned int, flags, struct SYNOSTAT64 *, statbuf);
PRE_MEM_RASCIIZ( "SYNOStat(file_name)", ARG1 );
if (ARG3 != 0)
PRE_MEM_WRITE( "SYNOStat(statbuf)", ARG3, sizeof(struct vki_SYNOSTAT) );
}
POST(sys_SYNOStat)
{
if (ARG3 != 0)
POST_MEM_WRITE( ARG3, sizeof(struct vki_SYNOSTAT) );
}Tools
MemCheck
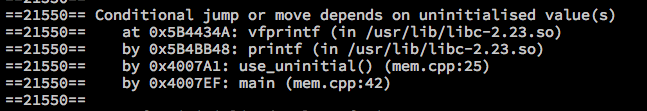
- Use of uninitialised memory
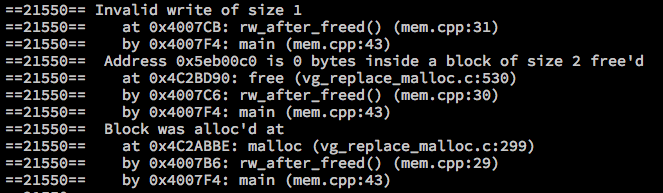
- RW after freed
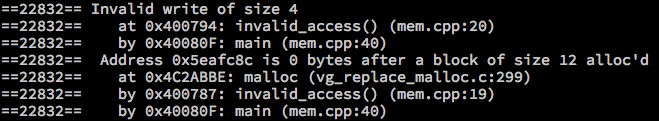
- RW over malloc space
- RW on wrong stack
- Not free
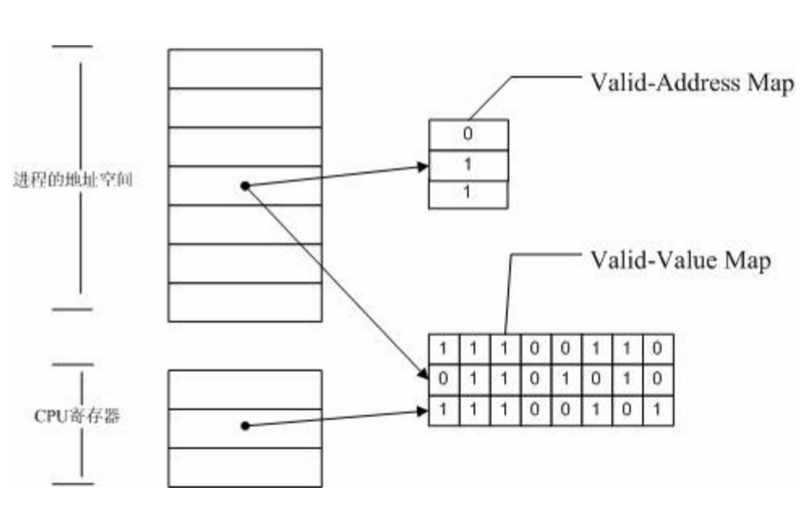
- Valid-Value table
- validity(defined) of the bit
- Valid-Address table
- accessble of the byte
void invalid_access() {
int *a = malloc(3 * sizeof(int));
a[3] = 3;
free(a);
}
void use_uninitial() {
int i;
printf("%d\n", i);
}
void rw_after_freed() {
char *a = (char *)malloc(2*sizeof(char));
free(a);
a[0] = '1';
}
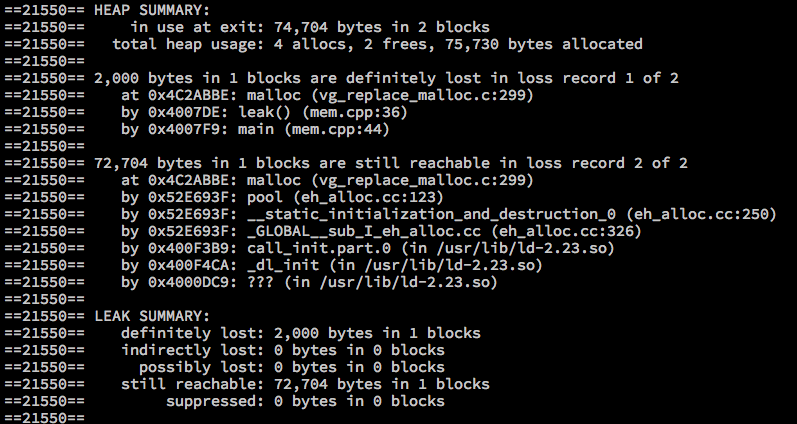
void leak()
{
malloc(2000);
}
int main(void)
{
invalid_access();
use_uninitial();
rw_after_freed();
leak();
return 0;
}
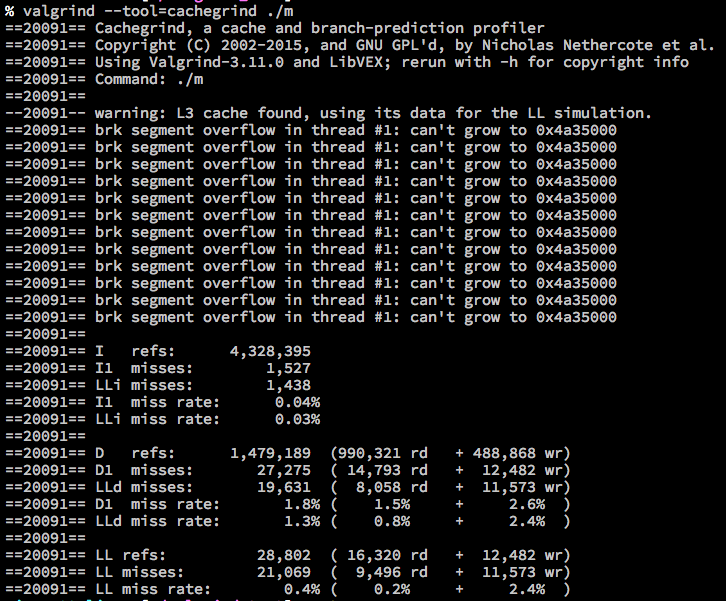
Cachegrind
- Simulate first and last cache
- l1: instruction cache
- D1: data cache
- LL: last level instruction cache
- Branch prediction
Callgrind
- record call history
- coolect number of instructions executed
% valgrind --tool=callgrind ./m
% python gprof2dot.py -f callgrind -n10 -s callgrind.out.19576 > valgrind.dot
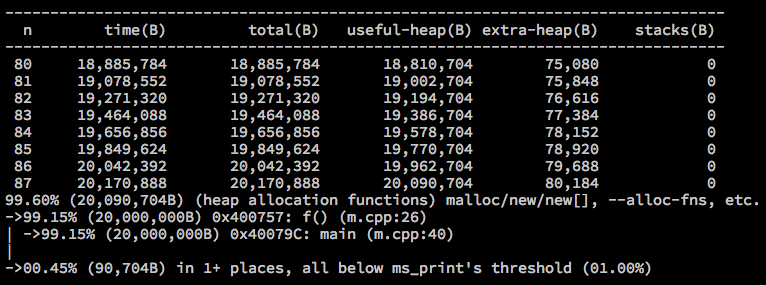
% dot -Tpng valgrind.dot -o valgrind.pngMassif
- Heap profiler
- mesures heap memory usage
void g(void)
{
malloc(4000);
}
void f(void)
{
for (int i=0; i < 10000; i++) {
malloc(2000);
}
g();
}
int main(void)
{
int i;
int* a[10];
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
a[i] = (int *)malloc(1000);
}
f();
g();
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
free(a[i]);
}
return 0;
}% valgrind --tool=massif ./m
% ms_print massif.out.18981
Helgrind/DRD
- Detect data races in mult-threads programs
- Inconsistent lock order
Monitor all access to memory location if accessed by different threads check if two accesses are ordered by happen-before relations.
Means there is some chain of inter-thread synchronisation operations only correctly handle POSIX condition variables. Ex: pthread_conf_wait, pthread_cond_signal ...
Demo
Valgrind
By nit nit
Valgrind
- 38



