Dovetail 2016 Architecture
Dovetail 2016 Architecture
(Single Sprint PoC)
Traditional Approach
Designing for Scale
Traditional Scaling
- Write code to handle web requests

Traditional Scaling
- Write code to handle web requests
- Deploy code to Amazon

Traditional Scaling
- Write code to handle web requests
- Deploy code to Amazon
- Create an Auto Scaling Group







Traditional Scaling
- Write code to handle web requests
- Deploy code to Amazon
- Create an Auto Scaling Group
- Front with an Elastic Load Balancer







Traditional Scaling
- Write code to handle web requests
- Deploy code to Amazon
- Create an Auto Scaling Group
- Front with an Elastic Load Balancer
- Instances come and go as traffic rises/lowers










Traditional Scaling
- Write code to handle web requests
- Deploy code to Amazon
- Create an Auto Scaling Group
- Front with an Elastic Load Balancer
- Instances come and go as traffic rises/lowers






Traditional Scaling
- Write code to handle web requests
- Deploy code to Amazon
- Create an Auto Scaling Group
- Front with an Elastic Load Balancer
- Instances come and go as traffic rises/lowers











Traditional Approach
Challenges
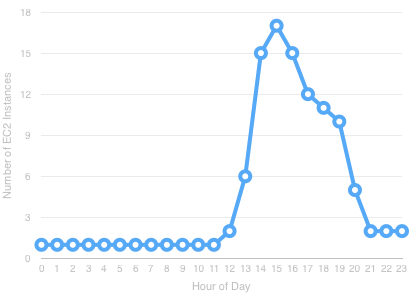
Difficult to Cost
- Costs are associated with number of instances
- How many requests per second can an instance handle?
- How many can 10 instances handle? 100?
Difficult to Cost
- Cost models require load testing
- As code changes, so does impact on load
- Architecture changes impact cost models
- Provisioning estimates impact cost models
- Calculate bandwidth per hour
- Extrapolate servers per hour
- Use hourly server cost to calculate daily cost
- Multiply by additional factors to determine monthly/annual costs
- Divide by number of events to get a per event cost
$76.92 per 1M events
Management Challenge
- Traditional architecture requires constant vigilance
- Configure CloudWatch to monitor, alert, and scale
- We lack dynamic instance monitoring capabilities
- Are we 24x7? Datapipe, GTS, Developers?
- Can we autoscale?
Maintenance Challenge
- Code is more complex
- Infrastructure management handled in code
- Per environment configuration has been a challenge
- Failover behavior mostly in code
A MaaP Approach
Designing for Scale
A MaaP Approach
Designing for Scale
(Microservice as a Platform)
Microservice Scaling
- Write code to handle web requests

Microservice Scaling
- Write code to handle web requests
- Deploy code to Amazon

Microservice Scaling
- Write code to handle web requests
- Deploy code to Amazon
- Profit!!!

Microservice Scaling
- Write code to handle web requests
- Deploy code to Amazon
-
API Gateway and Lambda
API Gateway
- Web request front end
- Receives inbound HTTP requests, forwards to Lambda (among other things)
- Handles authentication (Signature Version 4, pass through authentication coming soon)
- Throttling and caching provided
- Performance at any scale*
- No servers, no administration
- Monitoring via CloudWatch metrics
- Logging via CloudWatch logging
- Constant cost formula

AWS Lambda
- Runs your code without provisioning servers
- Pay only for the compute time consumes
- No charge when code is not running
- Triggered by API Gateway (among others)
- Continuous scaling
- Support for Java, Node JS and Python runtimes
- Deployment = Code Upload and Configuration
- Code and configuration is versioned and tagged
- Constant Cost Formula

A MaaP Approach
Challenges
On the Edge
- Developers are up to speed within a week
- Serverless Framework is the go-to development tool
- Serverless was conceived in October 2015, since funded and version 0.1.0 released. :)
- Remote debugging is difficult
- Amazon is confident in our load requests, but no order of magnitude support without workarounds
- Amazon is slow to increment language runtimes
- Will GTS be able to adopt APIG/Lambda?
- Management decision forthcoming
A Successful PoC
- Developers up to speed and productive with the new framework immediately
- Four of five services ported to APIG/Lambda
- 80% of Java code ported to Node JS
- Amount of code reduced by 80%
- Number of classes reduced by 95%
- Code is much cleaner and more easily maintained
- Implemented remote configuration of services
- Ability to scale to many thousands of request per second is done from the coding perspective
A MaaP Approach
Cost Model
MaaP Cost Model
- Cost for API Gateway and Lambda are constant and per request
- API Gateway Pricing
- $3.50 per 1M requests
- Lambda Pricing
- Request Fee - $0.20 per 1M requests
- Compute Fee - $16.67 per 1M seconds (1GB RAM)
MaaP Cost Model
- Per request calculations possible using MaaP model
- Cost is impacted by the operational time of Lambda functions and memory usage (should be constant)
Remember?
$76.92 per 1M Events - ELB/EC2 Instances
$6.20 per 1M Events - API Gateway/Lambda
MaaP Architecture
- Smaller code base
- More maintainable
- More scalable
- Less expensive (order of magnitude)
- Sub-minimal administration
PoC Accomplishments
- Port of Input API to APIG/Lambda
- Port of Reconcile API to APIG/Lambda
- Port of S3 Processor to APIG/Lambda
- Port of ES Processor to APIG/Lambda
- Standup of Kinesis stream in Test
- Standup of Event repository in Test
- Standup of Audit repository in Test
- Creation of rudimentary dashboard
- Generation of load test (1,000 events per second)
Dovetail 2016 Architecture
By James Cook
Dovetail 2016 Architecture
- 952



