State Management
What is State ?
舉例來說:
- 使用者登入狀態
- 購物車狀態
- 訊息狀態
所有可互動的都有狀態
feat. 冠群的 slide
What is State Management ?
先由使用者互動改變狀態
畫面會依據不同的狀態去顯示
管理 資料 和 使用者操作事件 的互動流程
Redux
一個可預測的狀態容器
Flux Pattern Based
單向資料流
將狀態視作一連串的狀態流
每次的事件都是產生一個新的狀態

Before Flux : Only MVC
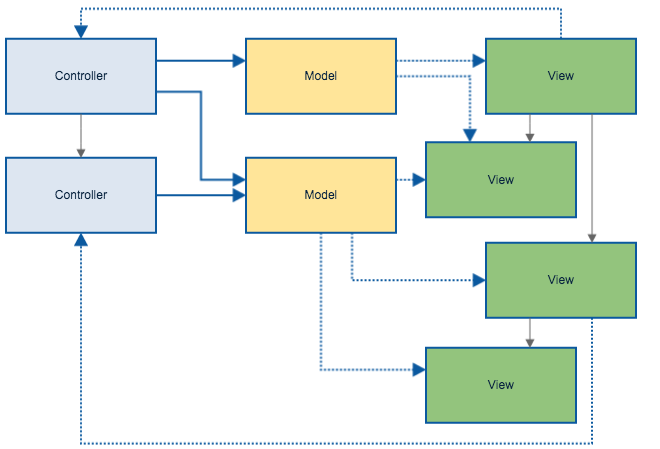
雙向資料綁定 → 連鎖更新
不容易去預測一個單一互動所造成的改變結果
MVC 只定義了三個角色的功能與關係
有了 FLUX 能更明確的定義「與資料互動的方式」
Single Store : Single Source of Truth
Redux
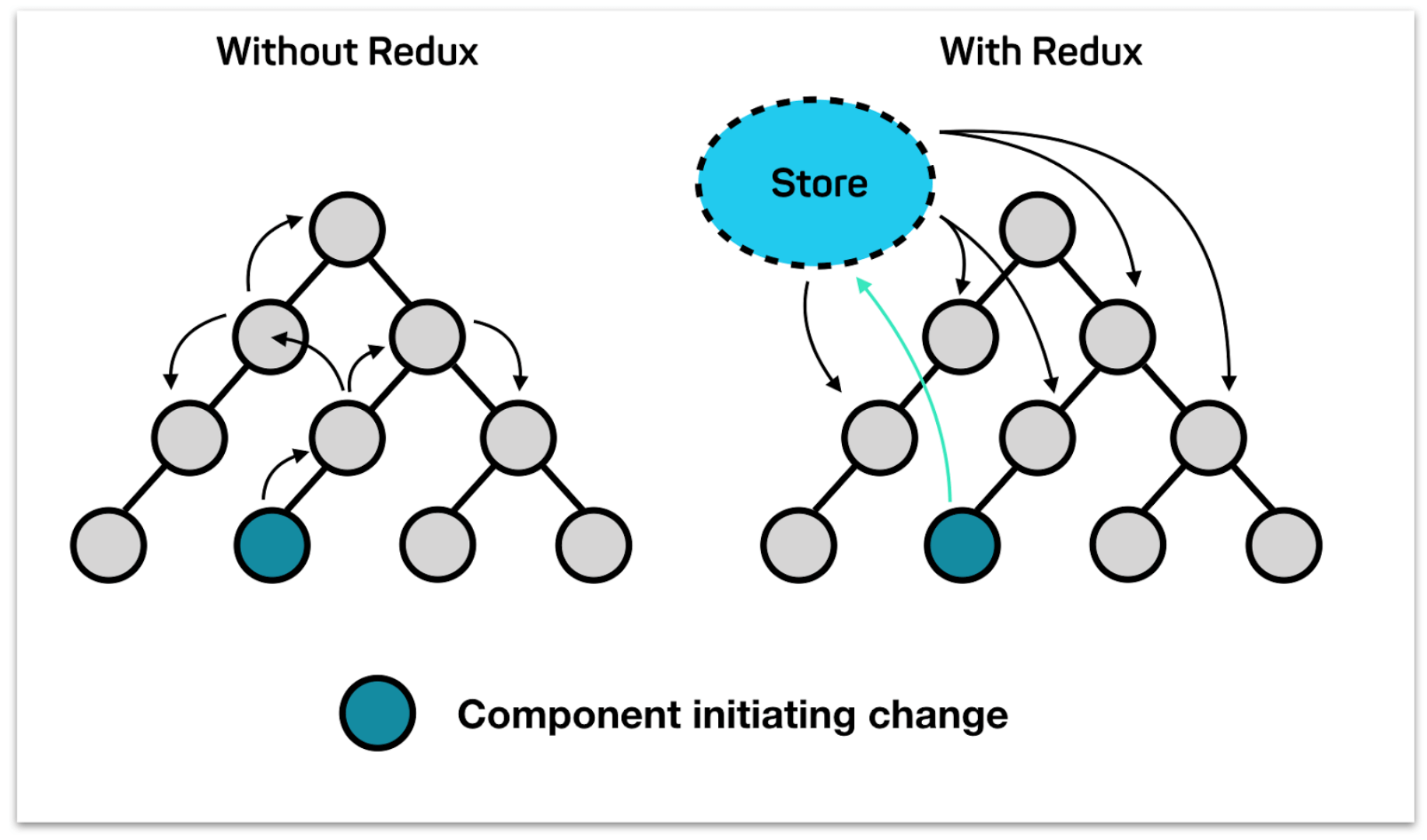
- Action 描述行為
- Reducer 通知改變
- Store 存值

Xstate
Finite State Machine (FSM) & Statechart based
Why Xstate ?
- 區分狀態 ( state ) 和 資料 ( context )
- 事先定義狀態(UI不會出現未知的狀態)
- XState Visualizer 可展示 StateChart
What is FSM ?
- 狀態總數(state)是有限的。
- 任一時刻,只處在一種狀態之中。
- 某種條件下,會從一種狀態轉變(transition)到另一種狀態。
有限個狀態以及在這些狀態之間的轉移和動作等行為的數學模型
例如:紅綠燈
( FSM 是很嚴謹的模型,這邊只是粗淺介紹 )
In Practice, we need ...
- 有限數量的狀態 (state)
- 有限數量的事件 (event)
- 一個初始狀態 (initial state)
- 一個轉換函式 (transition function)
- 具有 0 至 n 個最終狀態 (final state)
簡言之 就是 定義 各狀態 ( State ) 和 過渡方法 ( Action )
StateChart & Demo
import React from 'react';
import { useMachine } from '@xstate/react';
import { lightMachine } from './lightMachine';
function App() {
const [state, send] = useMachine(lightMachine);
return (
<div className="App">
{state.matches(LIGHT_STATES.RED) && <RedLight />}
{state.matches(LIGHT_STATES.GREEN) && <GreenLight />}
{state.matches(LIGHT_STATES.YELLOW) && <YellowLight />}
<button
onClick={() => {
send(LIGHT_EVENTS.CLICK);
}}
>
click me
</button>
</div>
);
}import { Machine } from 'xstate';
const LIGHT_STATES = {
RED: 'RED',
GREEN: 'GREEN',
YELLOW: 'YELLOW',
};
const LIGHT_EVENTS = {
CLICK: 'CLICK',
};
export const lightMachine = Machine({
initial: LIGHT_STATES.RED,
states: {
[LIGHT_STATES.RED]: {
on: {
[LIGHT_EVENTS.CLICK]: LIGHT_STATES.GREEN,
},
},
[LIGHT_STATES.GREEN]: {
on: {
[LIGHT_EVENTS.CLICK]: LIGHT_STATES.YELLOW,
},
},
[LIGHT_STATES.YELLOW]: {
on: {
[LIGHT_EVENTS.CLICK]: LIGHT_STATES.RED,
},
},
},
});- State & Action 統一在 Machine 處理
- View 用 useMachine 來取得 service
Effect Handle
What is Effect ?
資料改變 或 使用者觸發事件 後產生的後續影響
Side Effect
運算的過程中,改變了系統狀態或是對外部世界進行交互。
如:非同步請求( Network Request )而產生的資料不一致
Redux
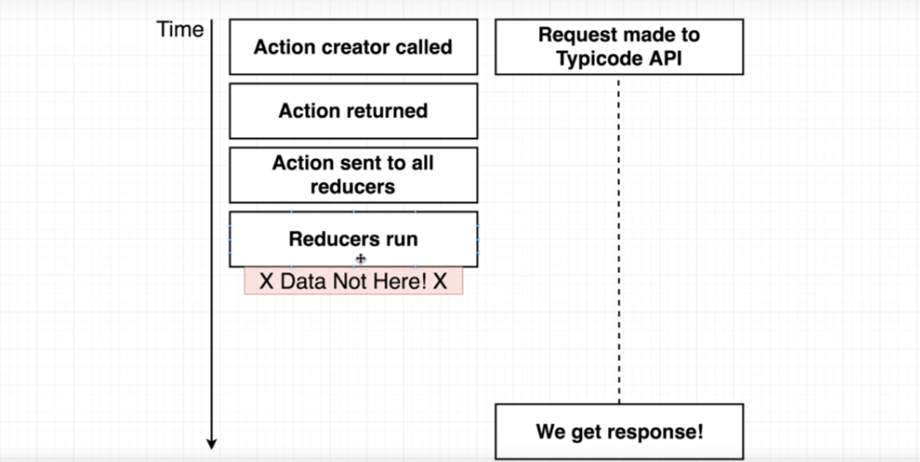
Redux Side Effect Management
本身自己不處理 Side Effect,依賴於 其他套件處理 ( middleware )
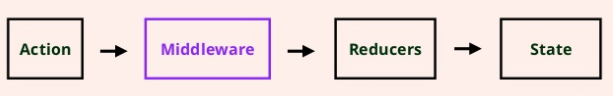
Redux thunk
import {
createStore,
combineReducers,
compose,
applyMiddleware,
} from 'redux';
import thunk from 'redux-thunk';
const store = createStore(combineReducers({
}), {}, compose(
applyMiddleware(
thunk,
),
));
export default store;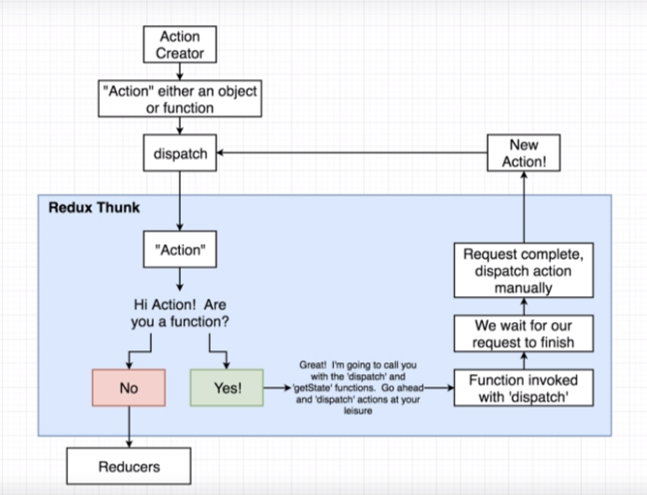
Xstate Effects
-
Fire-and-forget effects ( synchronously ) :
Real-time 操作,執行動作後,直接改變狀態。
-
Invoked effects ( asynchronously ):
可發送或接收非同步請求。
- entry : upon entering a state
- exit : upon exiting a state
- transition actions : when a transition is taken
- src : Promise handler
- resolve : onDone Transition
- reject : onError Transition
Redux
Xstate
- 生態系完整
- 僅需對資料流做控管
- State 和 context 定義清楚
- 使用情境可預測性高
- 可細拆分 machine
- 使用上較不直覺
- 狀態切換不明確
- 事先定義撰寫相對麻煩
- 狀態擴充複雜度易太高
優
優
缺
缺
One More Thing
Flow Control in FSM
By Routing
- " / commodity "
- " / commodity / : customerCode "
- " / commodity / : customerCode / shopping "
- " / commodity / : customerCode / payment "
- redirect to "/ commodity"
By Routing
- 傳遞資料不便
- 流程再多一點網址就會無限拉長
By FSM-Like Design
Shopping
Login
Payment
Pending
Success
idle
type Payload =
| {
step: 'idle';
}
| PayloadShopping
| PayloadLogin
| PayloadPayment
| PayloadPending
| PayloadSucess;interface PayloadShopping {
step: 'shopping';
customerInfo: CustomerInfo | undefined;
items: ShoppingCartItemData[];
}
interface PayloadLogin extends Omit<PayloadShopping, 'step'> {
step: 'login';
}
interface PayloadPayment extends Omit<PayloadLogin, 'step'> {
accessToken: string;
step: 'payment';
}
interface PayloadPending extends Omit<PayloadPayment, 'step'> {
receivedAmount: number;
step: 'pending';
}
interface PayloadSucess extends Pick<PayloadPending, 'receivedAmount'> {
payment: CheckoutCashPaymentMutation_payment;
step: 'success';
}{payload.step === 'idle' && (
<EnterCustomerNoModal
onNextStep={...}
/>
)}
{payload.step === 'shopping' && (
<Shopping
payload={...}
onGoBack={...}
onCheckout={...}
/>
}
{payload.step === 'login' && (
<Login
payload={...}
onGoBack={...}
onCheckout={...}
/>
)}
{payload.step === 'payment' && (
<Payment
payload={...}
onGoBack={...}
onPayment={...}
/>
)}
{payload.step === 'pending' && (
<Pending
payload={...}
onGoBack={...}
onSuccess={...}
/>
)}
{payload.step === 'success' && (
<Success
payload={...}
onGoBack={...}
onOk={...}
/>
)}Flow Control
- 定義 state 和 context,好預測
- Component 採用依賴抽離模式
- 可讀性高,方便Debug & 測試
THANKS FOR LISTENING
State Management
By parkerhiphop
State Management
- 541



