CVAT-BWV
— Parsa Hejabi, Akshay Kiran Padte, Preni Golazizian, Rajat Hebbar, Jackson Trager, Yiorgos Chochlakis, Aditya Kommineni, Ellie Graeden, Shrikanth Narayanan,
Benjamin A.T. Graham, Morteza Dehghani
A Web-Based Video Annotation Platform for Police Body-Worn Video



Introduction




Introduction
-
High-Quality Policing and Community Impact
- Essential government service, yet impacts communities unevenly [1]
- Influences public trust with over 20 million traffic stops annually [2]
-
Challenges with BWV Data
- Limited data analysis due to technical and resource challenges
- Often underutilized, primarily for crisis management
-
Potential of ML Tools
- Enables scalable analysis of BWV footage
- Promotes transparency and accountability
-
Studies on BWV Footage
- Revealed racial disparities in officer-civilian interactions [3,4,5]
- Underscore the importance of effective analysis
- Requirement for Extensive and Diverse Human Annotation [6]
Photo by David McNew/Getty Images, 2017. Retrieved from here.
Photo by David Paul Morris/Bloomberg via Getty Images, June 2020. Retrieved from here.
Photo by Bruno Martins on Unsplash, n.d.
Photo by Scott Rodgerson on Unsplash, n.d.
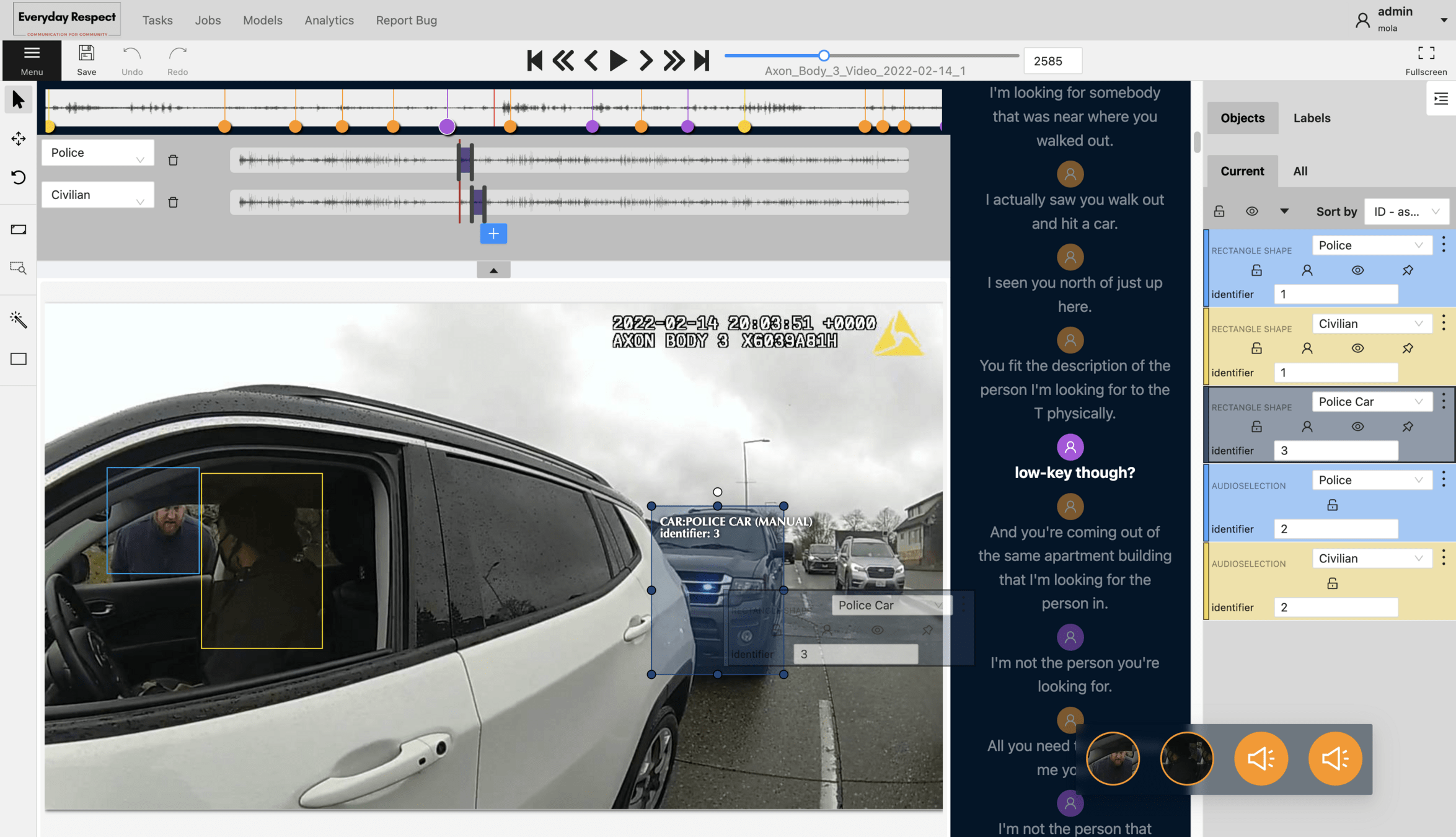

Introducing CVAT-BWV
CVAT-BWV Advantages
- Secure, local hosting for sensitive BWV data
- Open-source flexibility in customization
- Integrated AI-assisted annotation tools
-
Support for multimodal annotations
(text, audio, and video) - Based on Computer Vision Annotation Tool¹
Limitations of Other Tools
(e.g., Labelbox², or Prodigy³)
- Problems with Software as a Service platforms
- Cloud-based; raise data security concerns
- Closed-source; therefore, not customizable
- Limited AI-assisted annotation features
- Do not supporting all modalities
² https://labelbox.com
³ https://prodi.gy
Platform
Description
AI-Assisted Annotation Tools
ASR and Speaker Diarization Module
- Uses the WhisperX model [10]
1.
Object Detection Module
- Automated bounding box creation for people and vehicles
- Integrates YOLOv8 model, a SOTA object detection model [11]
2.
Face Recognition Module
- Prevents creation of duplicate bounding boxes for each individual
- Employs LightFace framework [12] with RetinaFace [13] and FaceNet [14] models
3.
Using Human-in-the-Loop components can reduce the annotators' workload and enhance data quality [7,8,9]
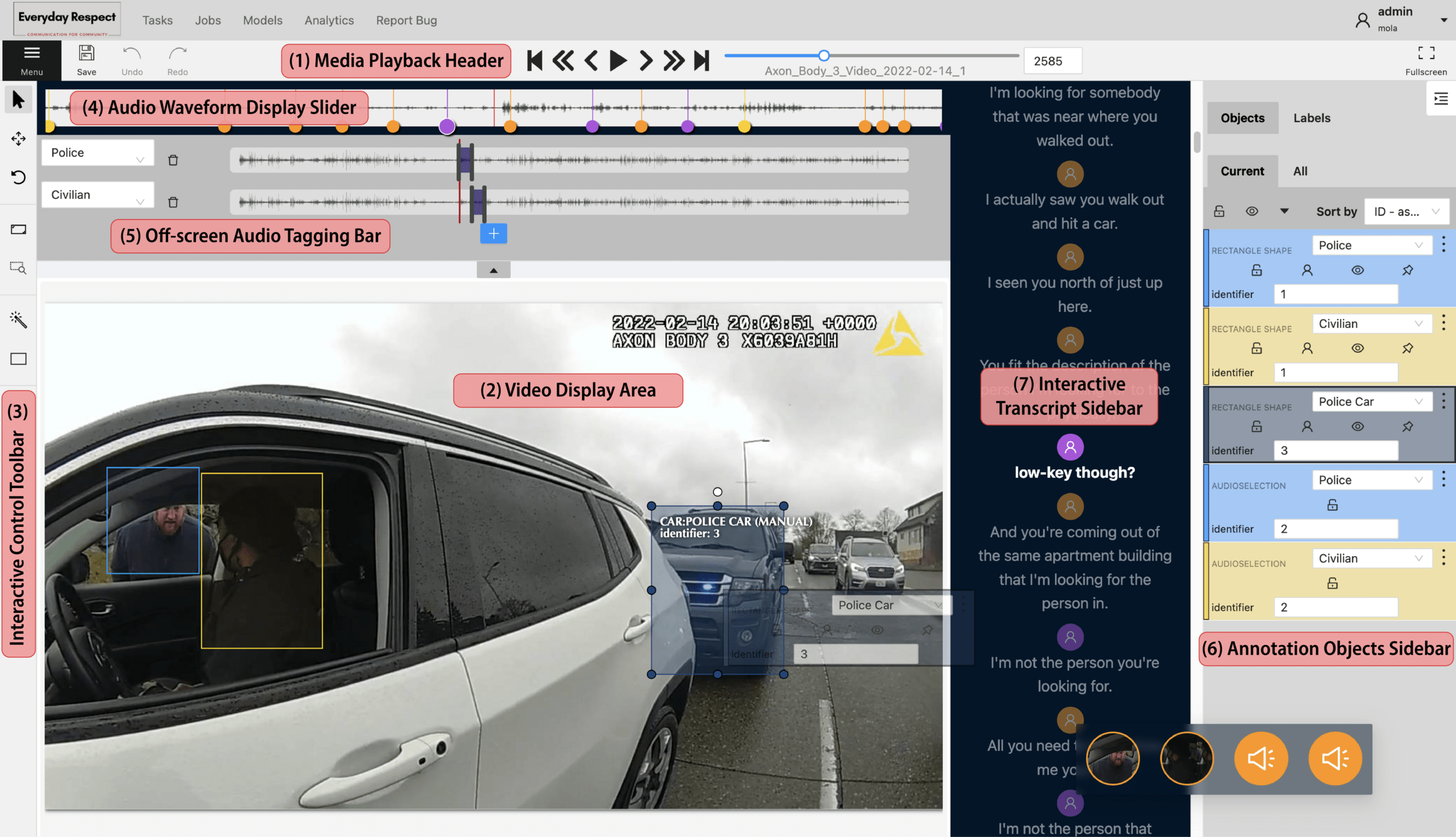








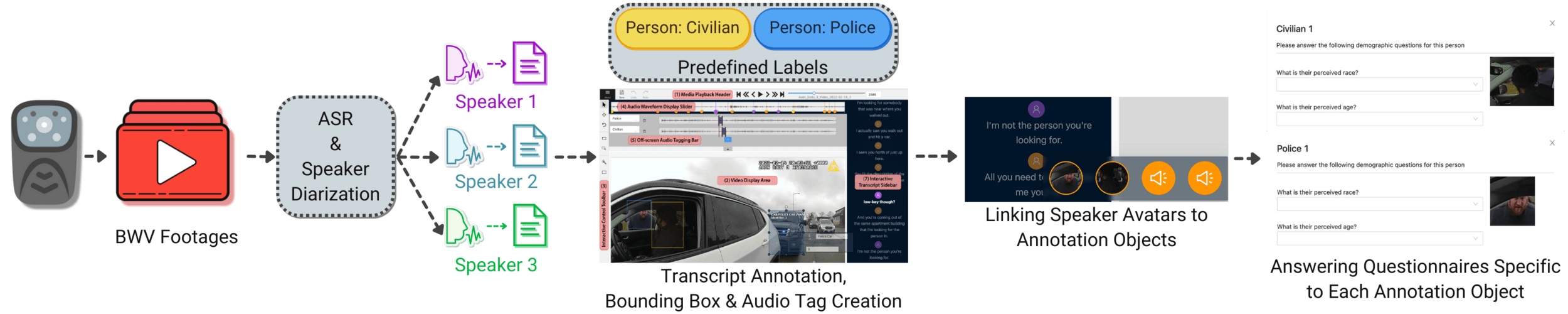
Workflow
1.
Task Creation and Assignment
2.
Transcript Annotation
3.
Creation of Bounding Boxes and Audio Tags
5.
Annotation Object Questionnaires
4.
Linking Transcripts to Annotation Objects





Demo
References
-
[1] California Department of Justice. (2024). RIPA Board Report 2024. Retrieved from https://oag.ca.gov/system/files/media/ripa-board-report-2024.pdf
-
[2] Camp, N. P., Voigt, R., Jurafsky, D., & Eberhardt, J. L. (2021). The thin blue waveform: Racial disparities in officer prosody undermine institutional trust in the police. Journal of personality and social psychology, 121(6), 1157–1171. https://doi.org/10.1037/pspa0000270
-
[3] Voigt, R., Camp, N. P., Prabhakaran, V., Hamilton, W. L., Hetey, R. C., Griffiths, C. M., Jurgens, D., Jurafsky, D., & Eberhardt, J. L. (2017). Language from police body camera footage shows racial disparities in officer respect. In Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (Vol. 114, Issue 25, pp. 6521–6526). Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1702413114
-
[4] Rho, E. H., Harrington, M., Zhong, Y., Pryzant, R., Camp, N. P., Jurafsky, D., & Eberhardt, J. L. (2023). Escalated police stops of Black men are linguistically and psychologically distinct in their earliest moments. In Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (Vol. 120, Issue 23). Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2216162120
-
[5] Prabhakaran, V., Griffiths, C., Su, H., Verma, P., Morgan, N., Eberhardt, J. L., & Jurafsky, D. (2018). Detecting Institutional Dialog Acts in Police Traffic Stops. In Transactions of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Vol. 6, pp. 467–481). MIT Press - Journals. https://doi.org/10.1162/tacl_a_00031
-
[6] Graham, B., Brown, L., Chochlakis, G., Dehghani, M., Delerme, R., Friedman, B., Graeden, E., Golazizian, P., Hebbar, R., Hejabi, P., & others (2024). A Multi-Perspective Machine Learning Approach to Evaluate Police-Driver Interaction in Los Angeles. arXiv preprint arXiv:2402.01703.
-
[7] van der Wal, D., Jhun, I., Laklouk, I., Nirschl, J., Richer, L., Rojansky, R., Theparee, T., Wheeler, J., Sander, J., Feng, F., Mohamad, O., Savarese, S., Socher, R., & Esteva, A. (2021). Biological data annotation via a human-augmenting AI-based labeling system. In npj Digital Medicine (Vol. 4, Issue 1). Springer Science and Business Media LLC. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41746-021-00520-6
-
[8] Franco Marchesoni-Acland, & Gabriele Facciolo. (2023). IAdet: Simplest human-in-the-loop object detection.
-
[9] Weber, L., & Plank, B. (2023). ActiveAED: A Human in the Loop Improves Annotation Error Detection. In Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: ACL 2023 (pp. 8834–8845). Association for Computational Linguistics.
-
[10] Bain, M., Huh, J., Han, T., & Zisserman, A. (2023). WhisperX: Time-Accurate Speech Transcription of Long-Form Audio. In INTERSPEECH 2023. INTERSPEECH 2023. ISCA. https://doi.org/10.21437/interspeech.2023-78
-
[11] Jocher, G., Chaurasia, A., & Qiu, J.. (2023). Ultralytics YOLO.
-
[12] Serengil, S. I., & Ozpinar, A. (2020). LightFace: A Hybrid Deep Face Recognition Framework. In 2020 Innovations in Intelligent Systems and Applications Conference (ASYU). 2020 Innovations in Intelligent Systems and Applications Conference (ASYU). IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/asyu50717.2020.9259802
-
[13] Deng, J., Guo, J., Ververas, E., Kotsia, I., & Zafeiriou, S. (2020). RetinaFace: Single-Shot Multi-Level Face Localisation in the Wild. In 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) (pp. 5202-5211).
-
[14] Schroff, F., Kalenichenko, D., & Philbin, J. (2015). Facenet: A unified embedding for face recognition and clustering. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (pp. 815-823).
Thanks to our Funders



Thank you!

Parsa Hejabi

Akshay Kiran Padte

Preni Golazizian

Rajat Hebbar

Jackson Trager
Yiorgos Chochlakis

Aditya Kommineni

Shrikanth Narayanan

Benjamin A.T. Graham

Ellie Graeden

Morteza Dehghani
CVAT-BWV: A Web-Based Video Annotation Platform for Police Body-Worn Camera Footage
By Parsa Hejabi
CVAT-BWV: A Web-Based Video Annotation Platform for Police Body-Worn Camera Footage
- 379



