Views
Drupal 8
Complete guide
Views
Overview
Views
Using the Views module, you can fetch content from the database of your site and present it to the user as lists, posts, galleries, tables, maps, graphs, menu items, blocks, reports, forum posts etc.
Different content types including nodes, users, and other bundles can be displayed.
Views
Views UI, a submodule within Views, provides a graphical interface underneath which lies a powerful SQL query builder that can access virtually any information in your database and display it in any format.
Views
Different displays can present the query results as pages with fixed URLs on your site (or URLs accepting arguments), blocks, feeds, or panel panes.
Views
You can also use Views to present related content or implement contextual filters.
An example of presenting related content is when you want to display a list of users along with links to the content they have created. To do this, you need to create a relationship linking two nodes.
Views
Interfaces
Interfaces
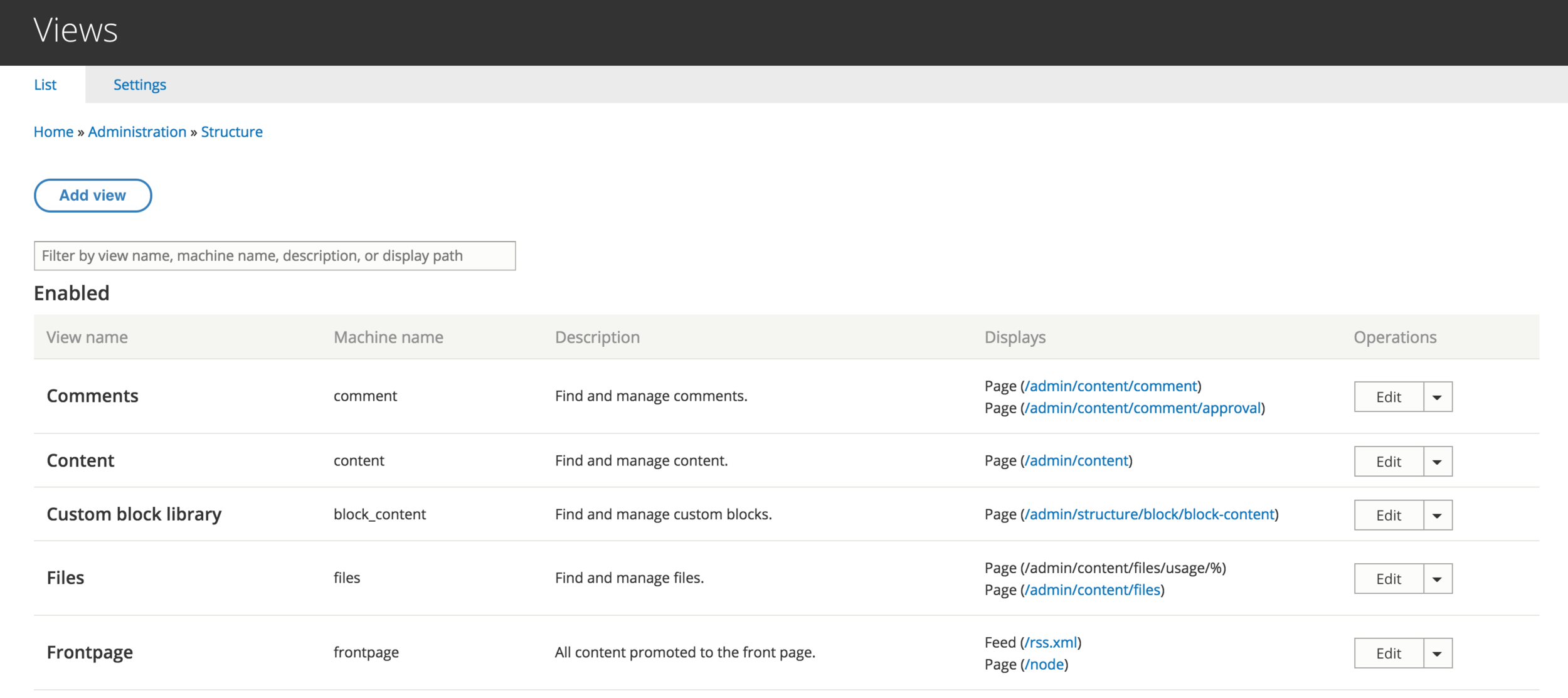
The Views Overview can be found under Structure > Views.
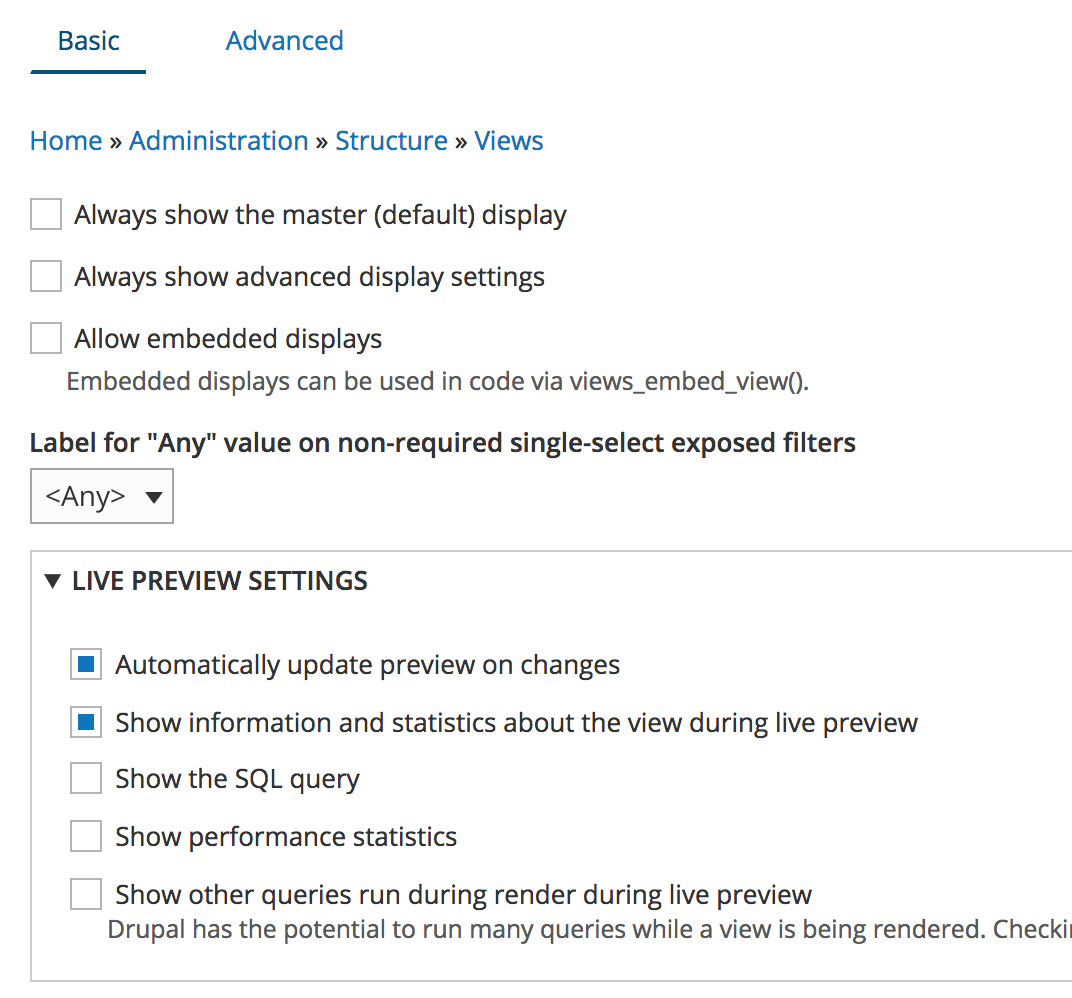
Views have some basic settings than can be found under Structure > Views > Settings
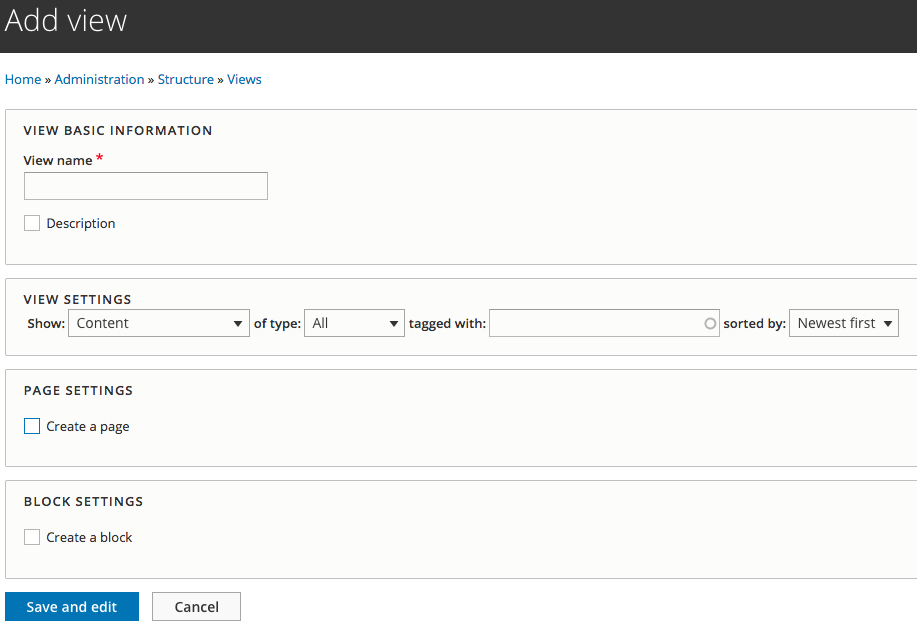
When creating a new view you start with the Creation Wizard.
Once a view has been created you can edit it using the normal View UI.
Views Overview
Views Settings
Creation Wizard
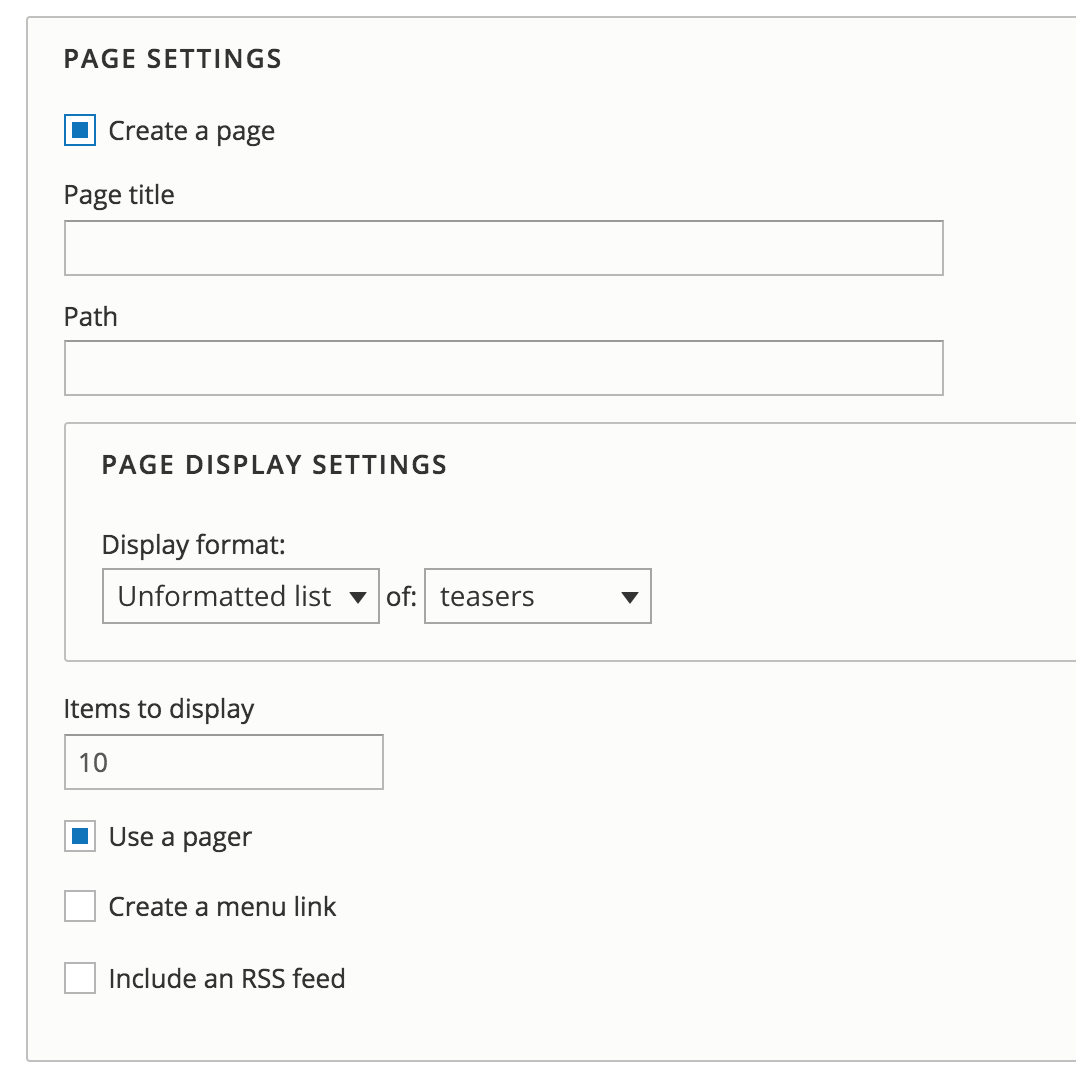
Wizard - Page
Wizard - Block
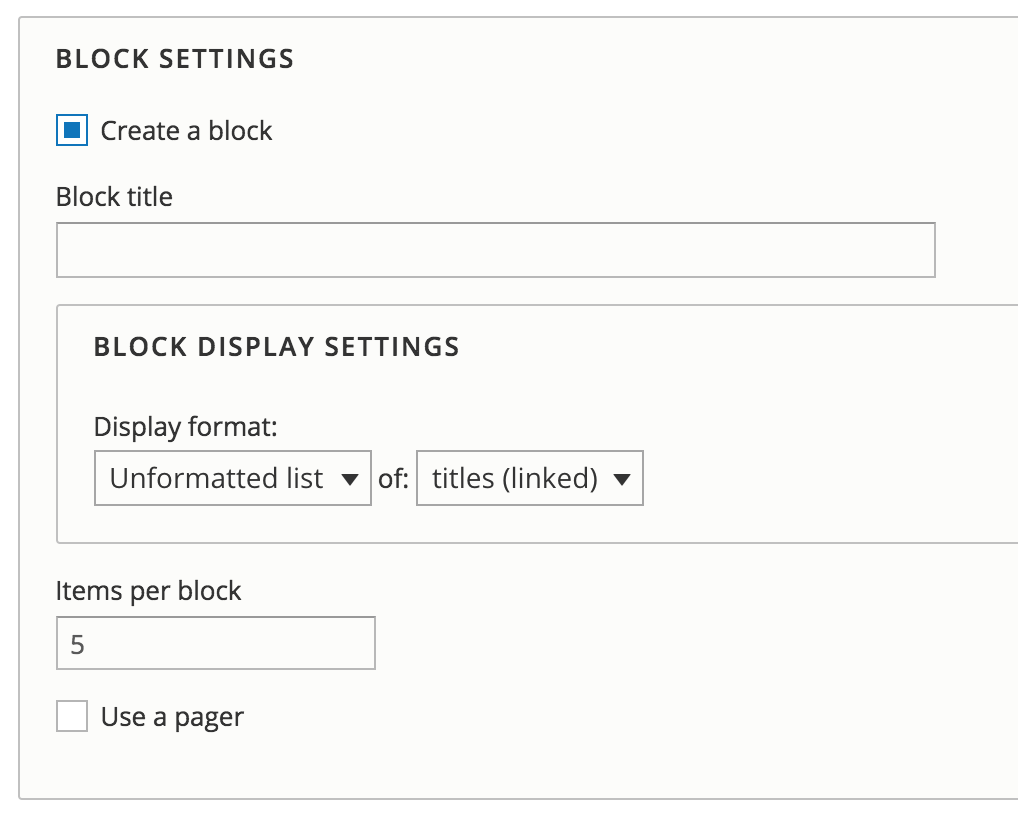
Wizard - Block

Views UI
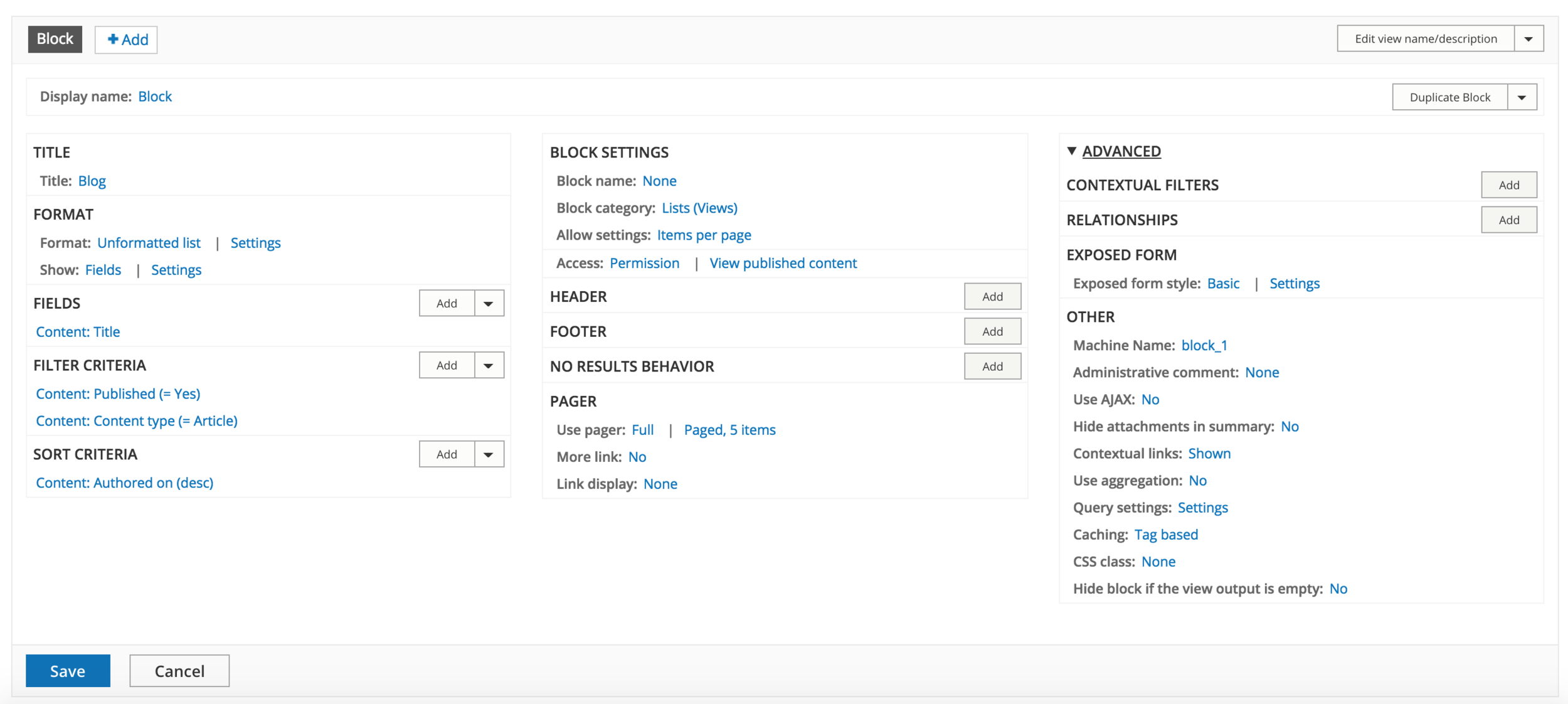
Views
Edit UI
UI
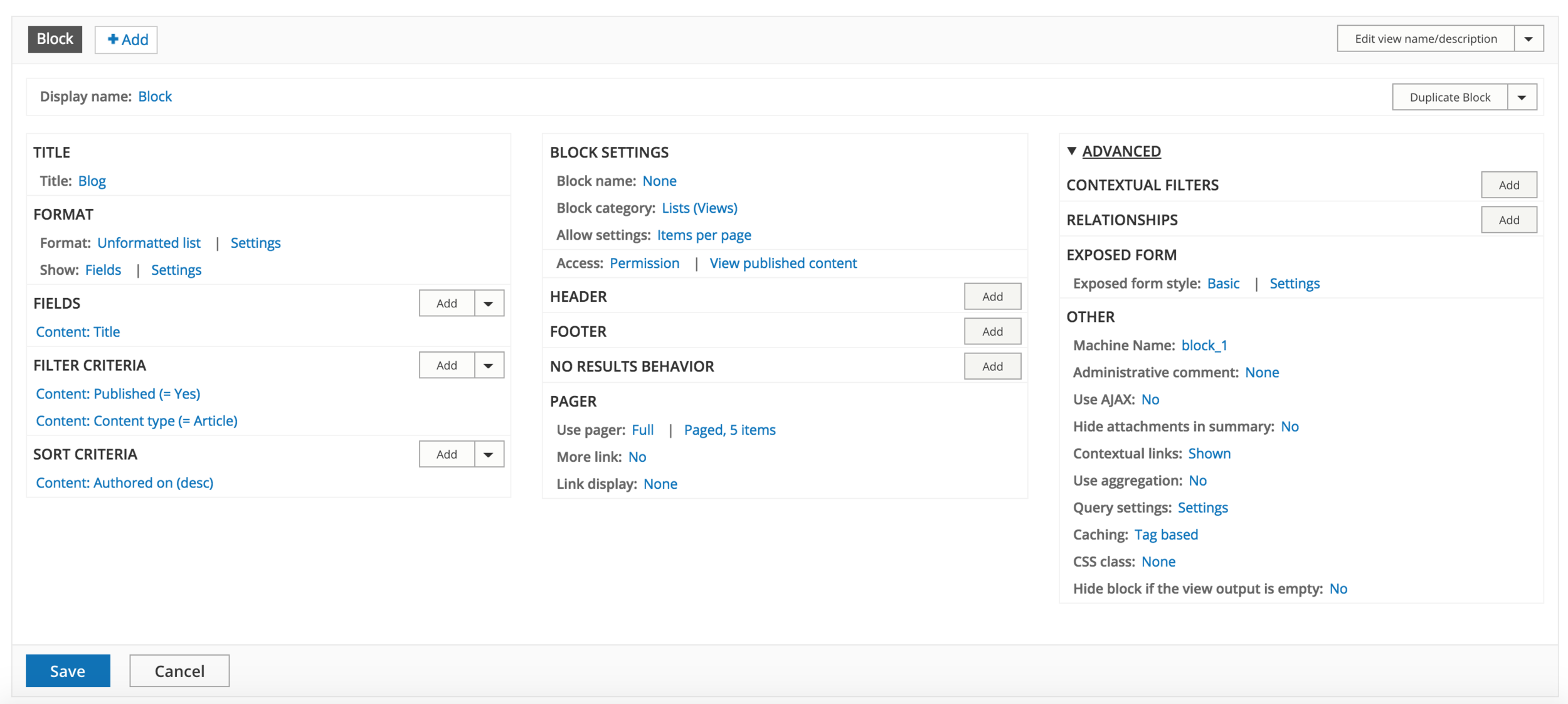
Displays
View Operations
Display Operations
Basic settings
Display settings
Advanced settings
UI - Displays
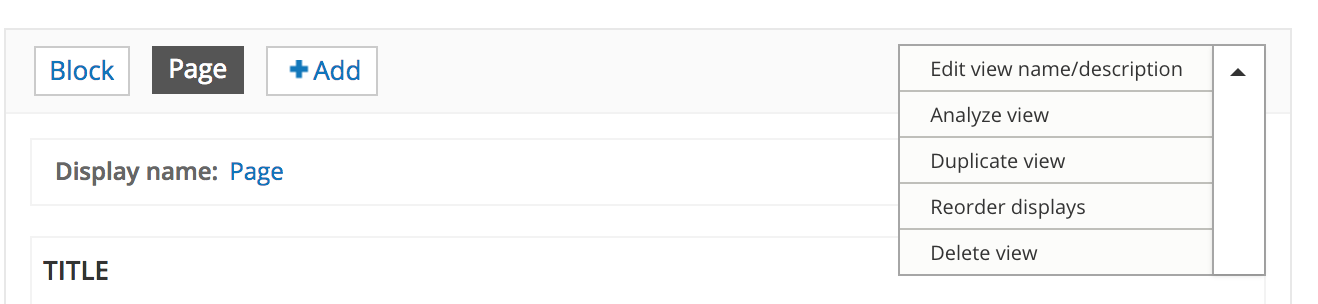
Choose/add display
View operations
edit/copy/delete
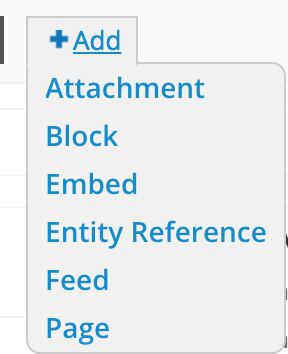
UI - Displays
"inline" view, attached to other views

view available as a block
to embed with code/php
feeds: rss, json, etc
view available as a page
create custom admin search filters
for references to taxonomies & other entitites
UI - Displays
Display operations
edit/copy/delete

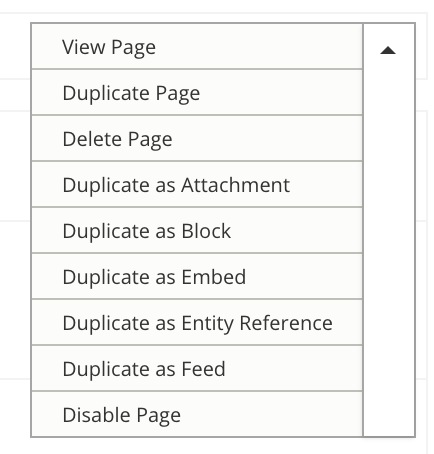
UI - Displays
When making changes, make sure to choose the correct display!
Views
Basic settings
UI - Basic settings

UI - Format
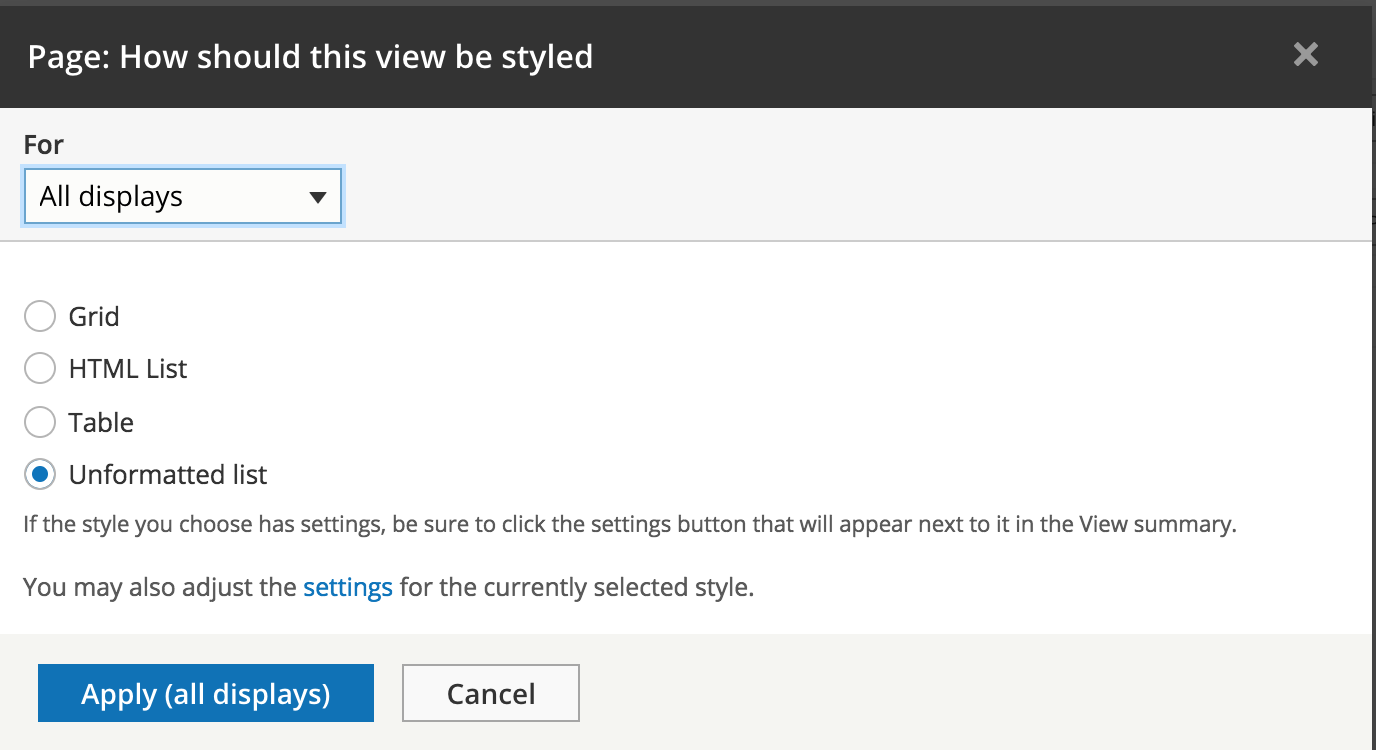
HTML grid with custom grid classes
HTML list <ul><li></li></ul>
HTML table <table><tr><td>
HTML divs <div class="views-row"></div>>
UI - Format
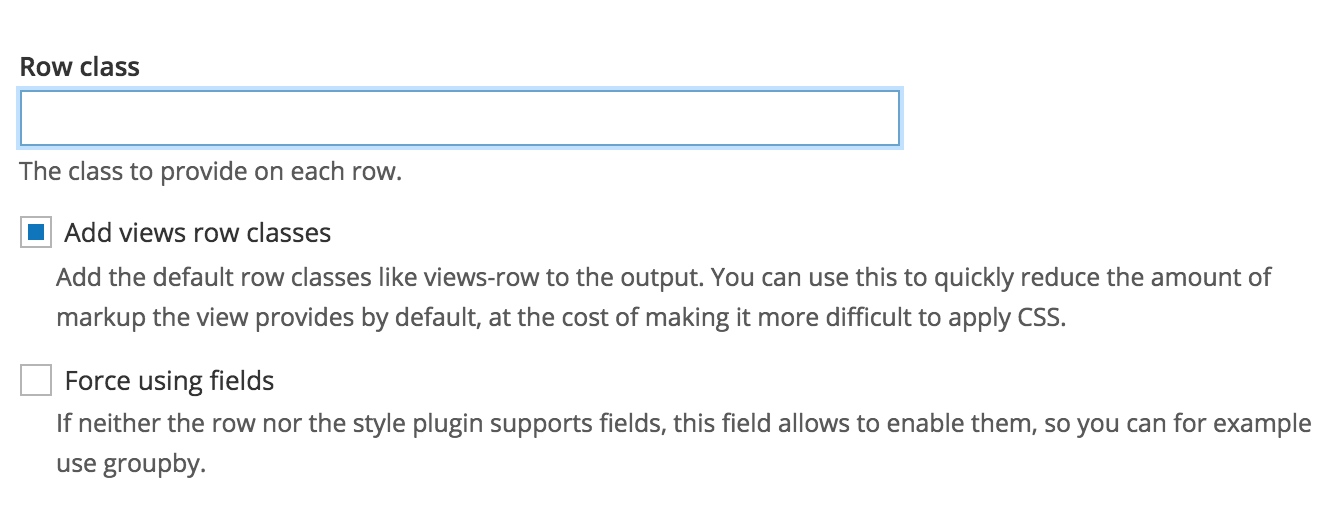
Unformatted list - settings
UI - Format
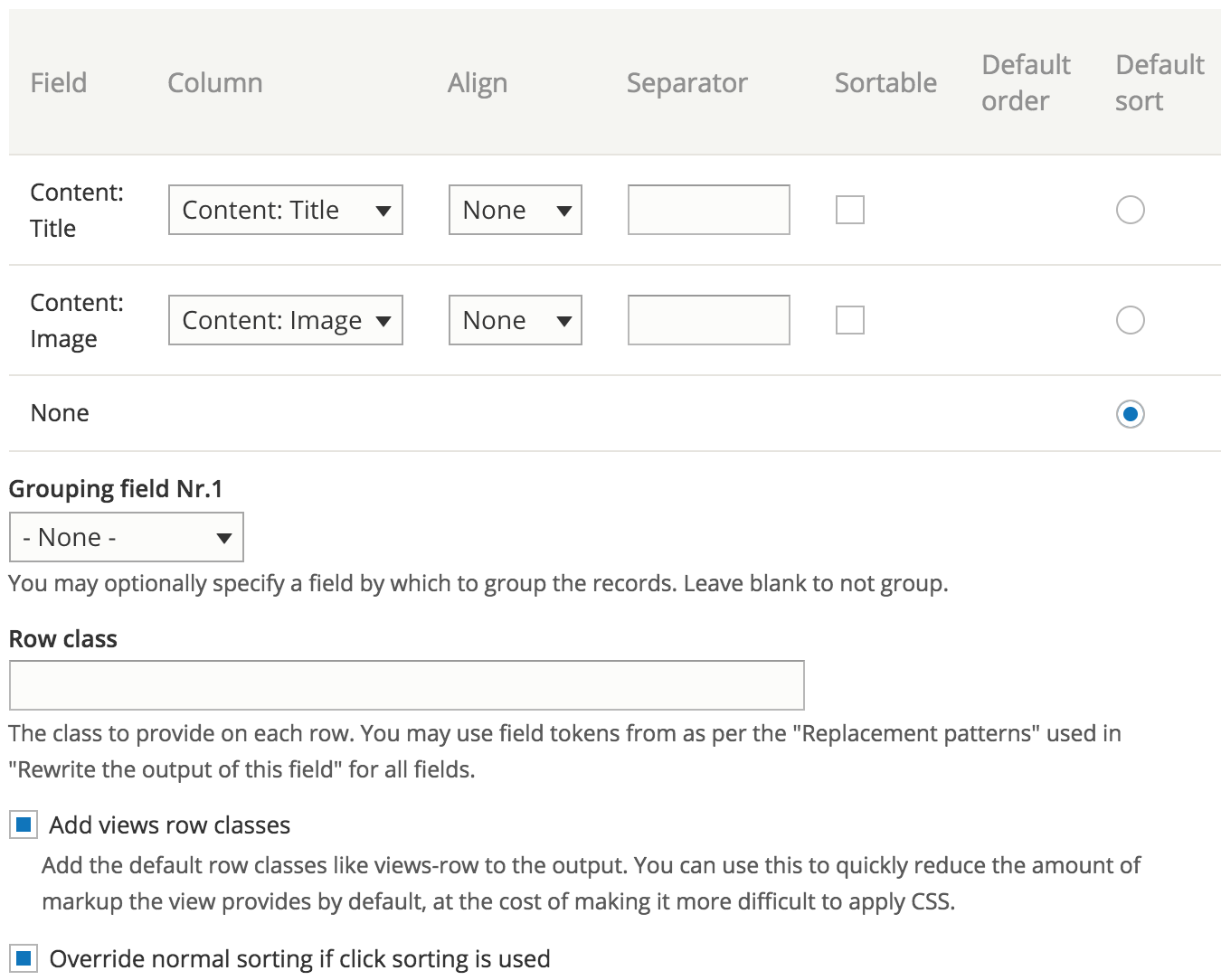
Table - settings
UI - Format
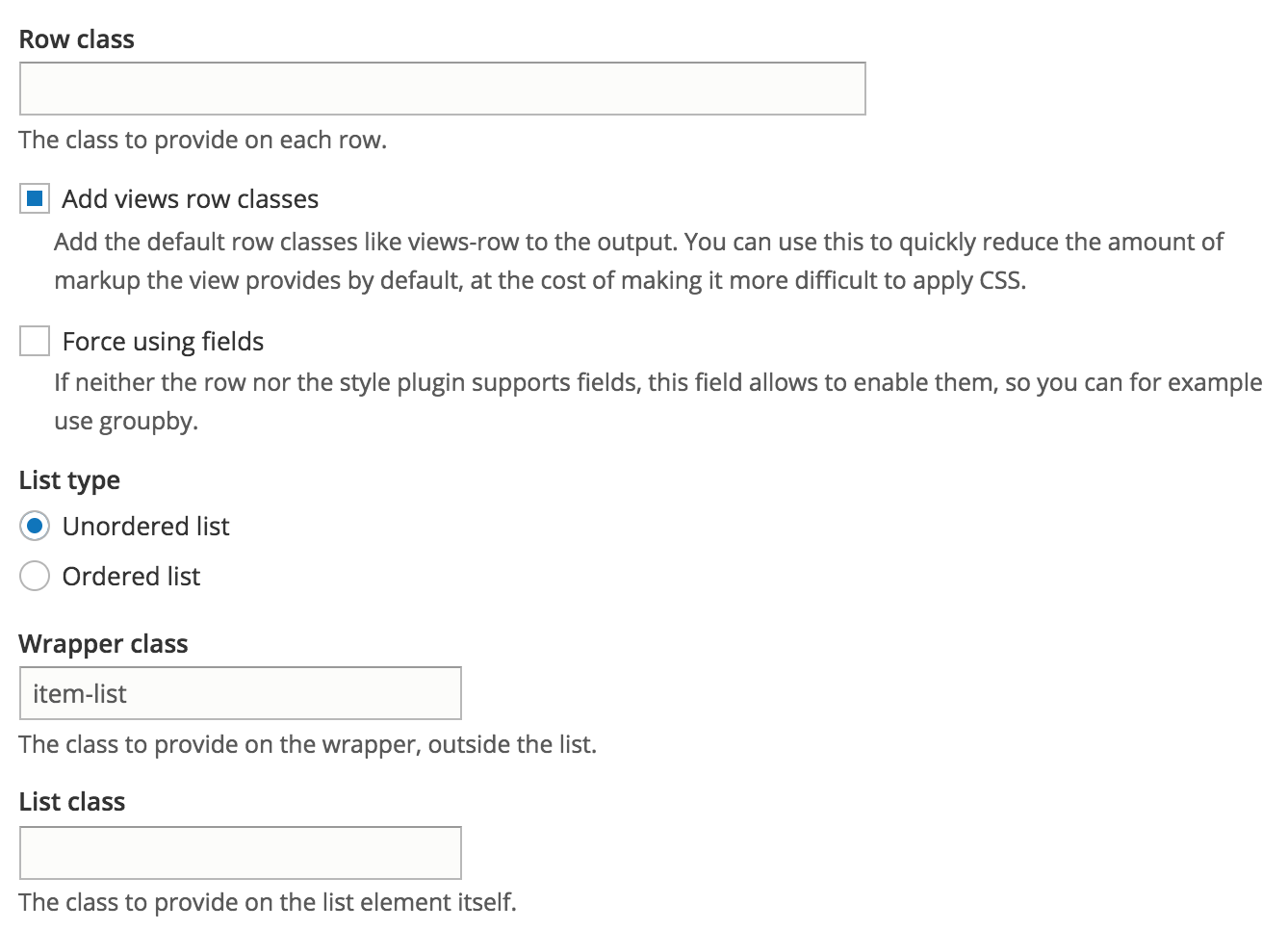
HTLM List - settings
UI - Format
Grid - settings

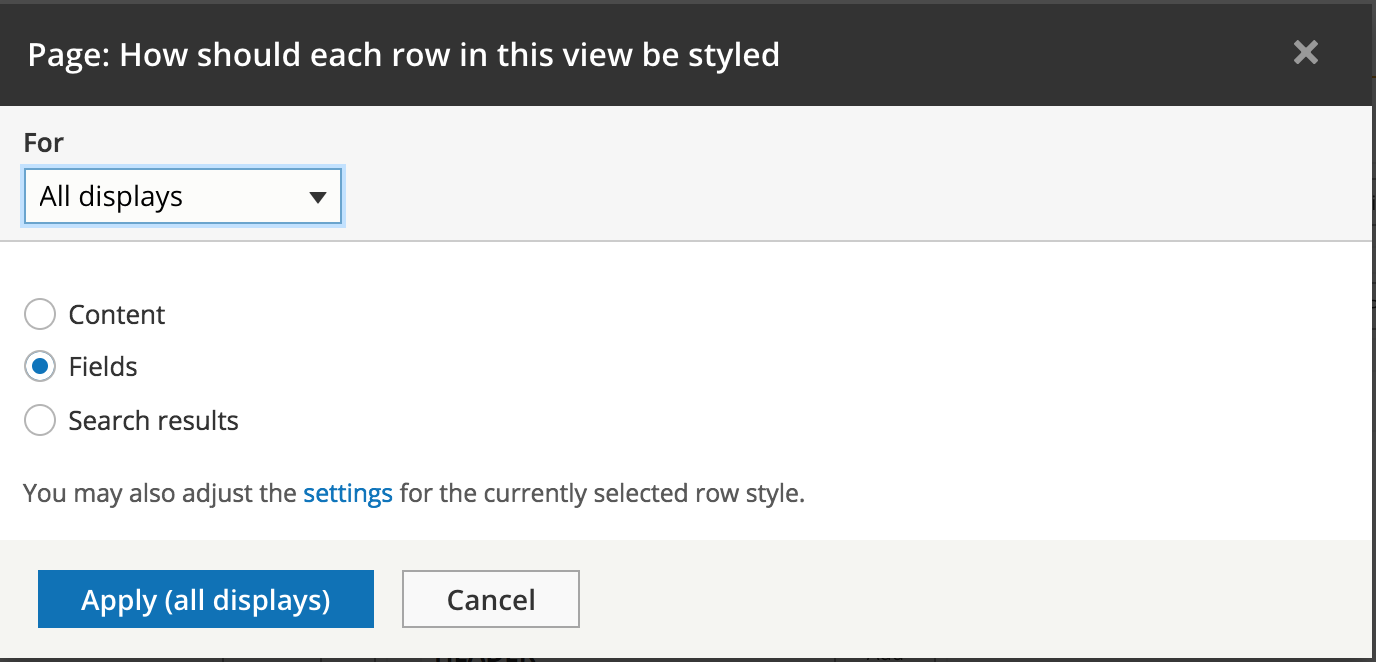
UI - Format show
Uses content displays: Default, Full, Teaser
Choose fields
Content snippet
UI - Format show
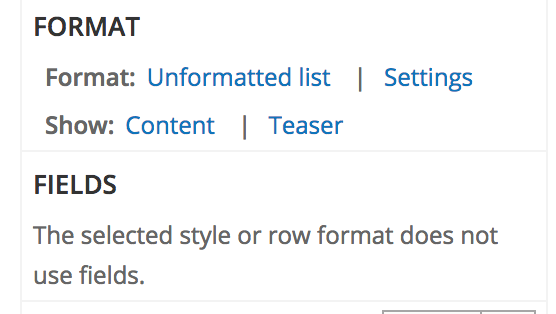
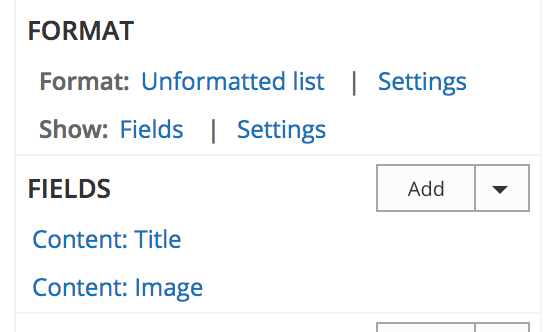
Fields
Content
UI - Format show
Field settings
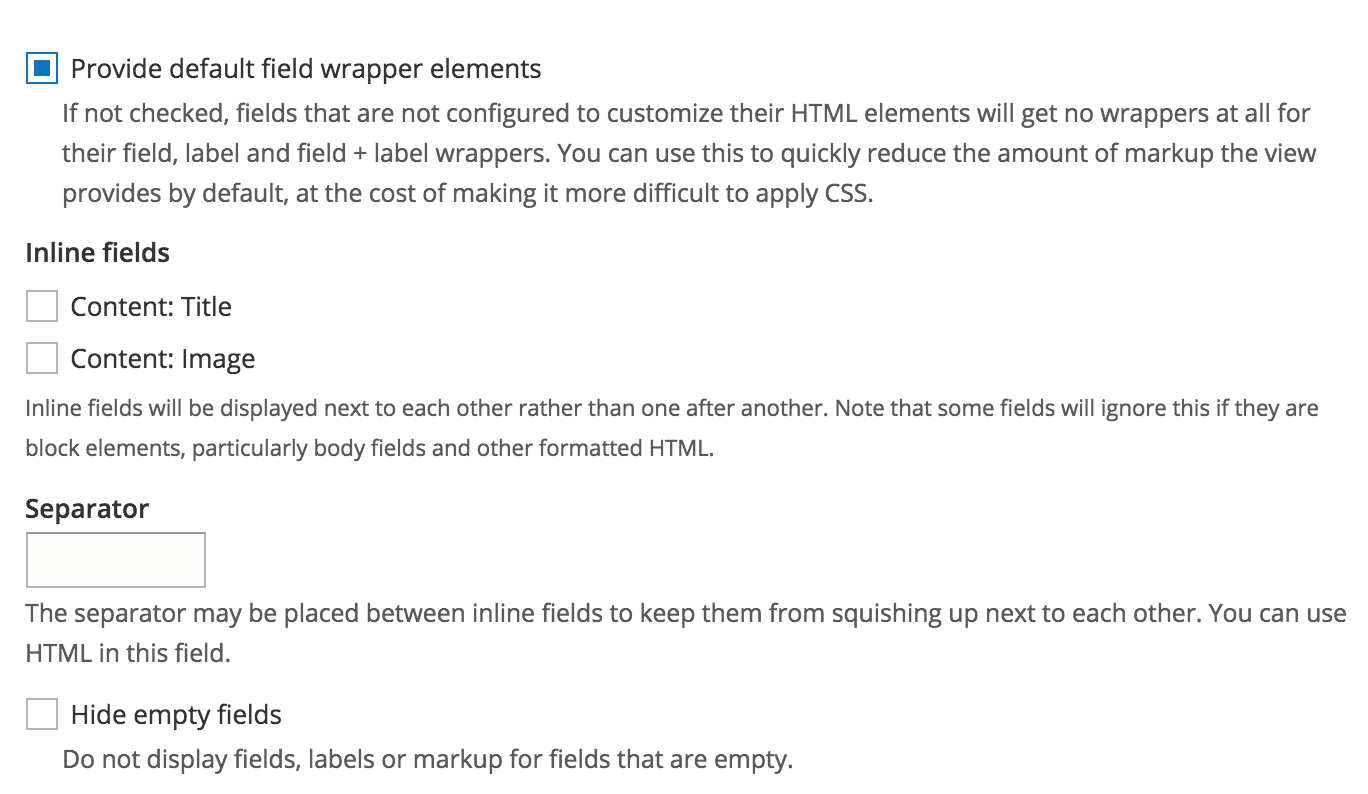
UI - Format show
Content settings
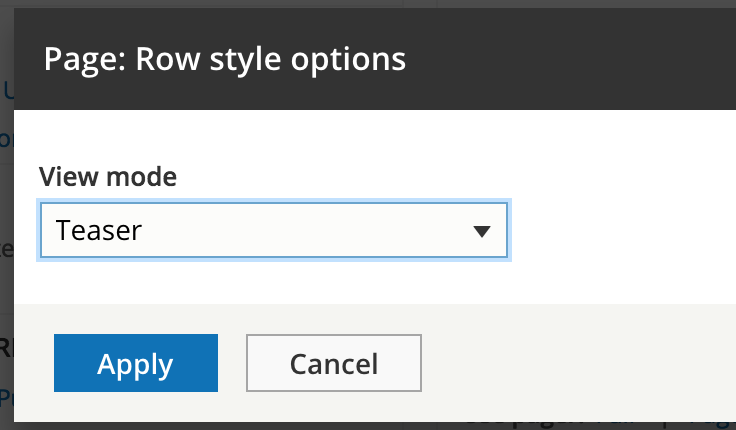
UI - Fields
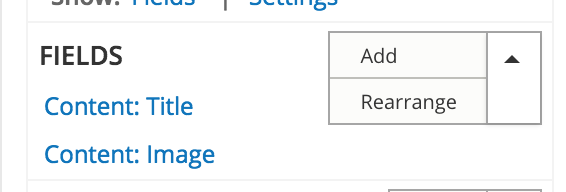
UI - Fields add
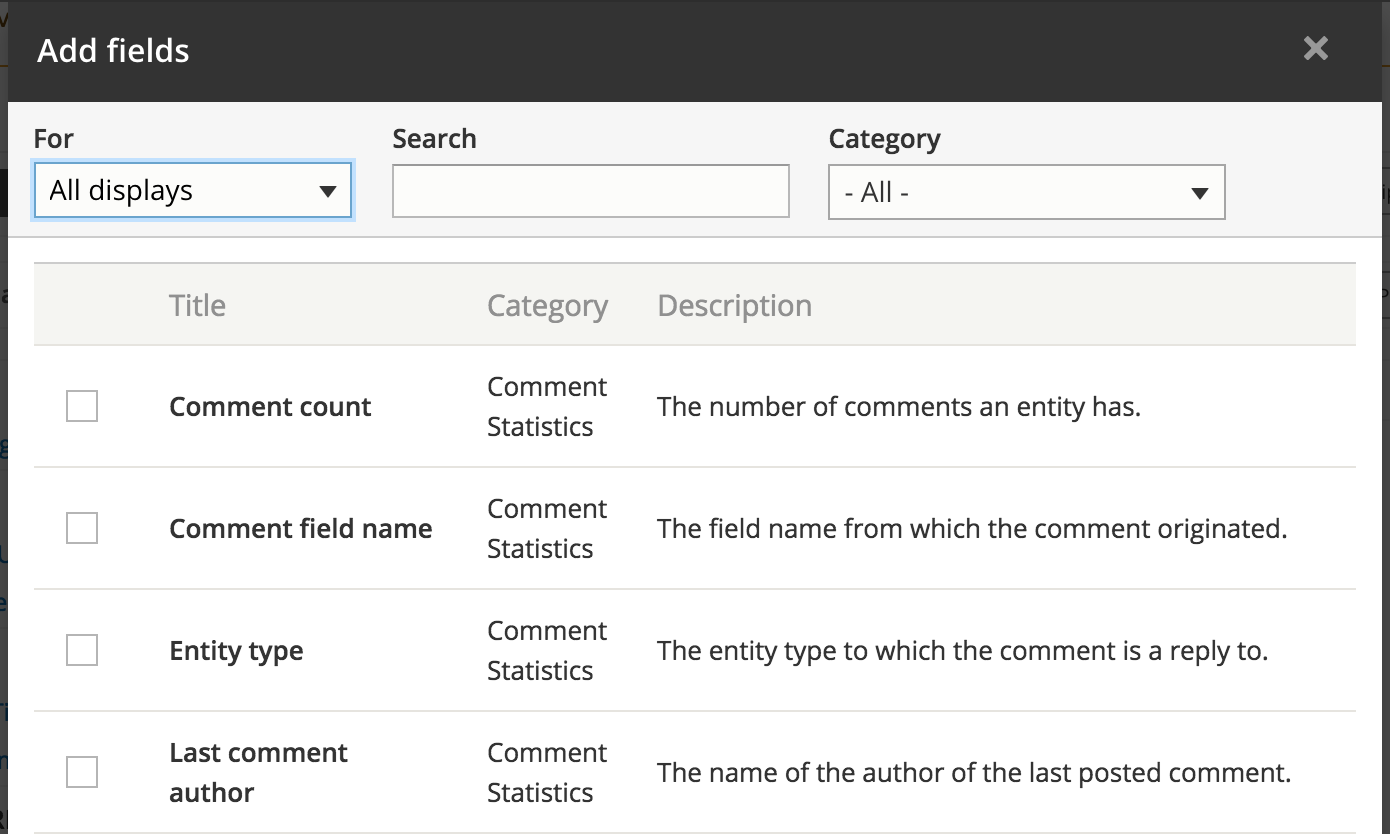
UI - Fields rearrange
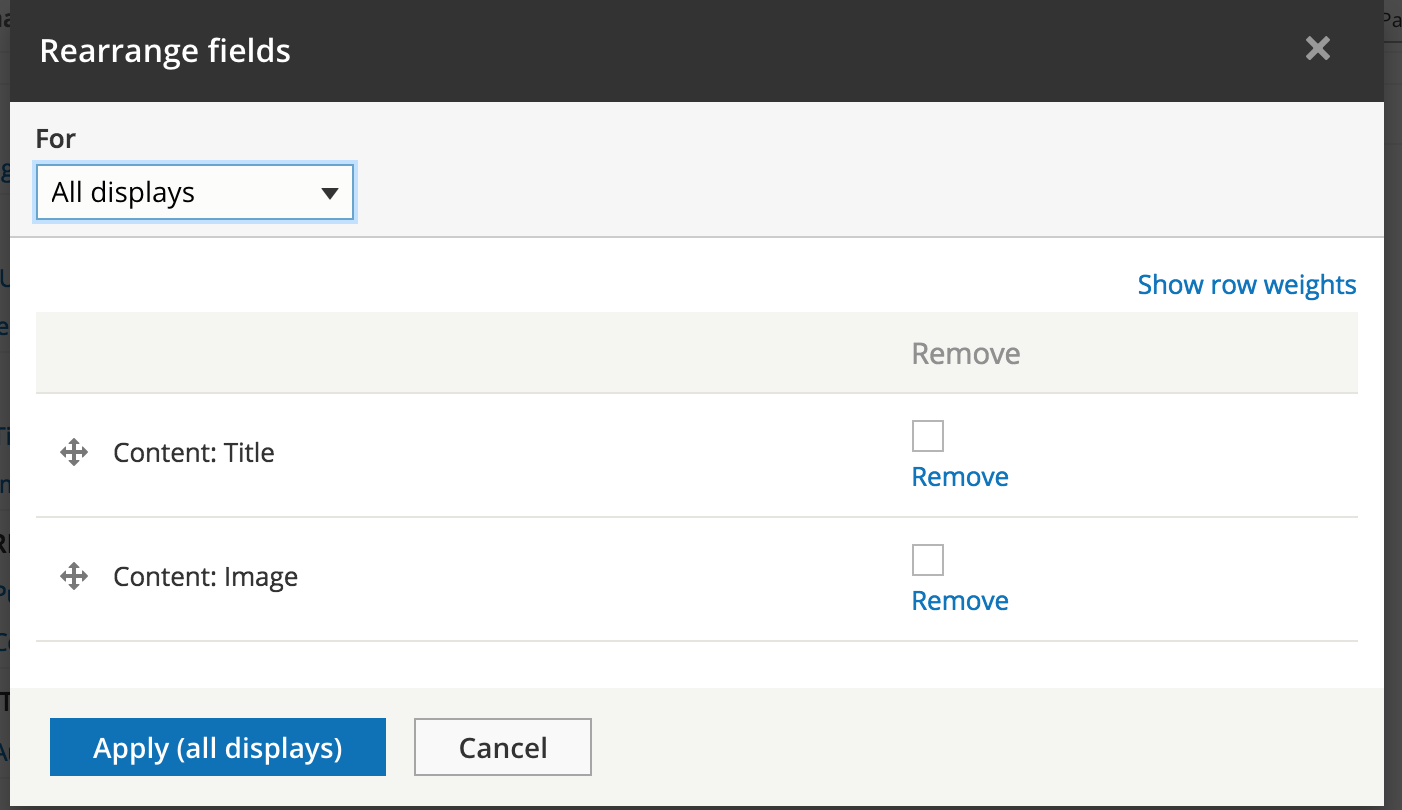
UI - Field settings
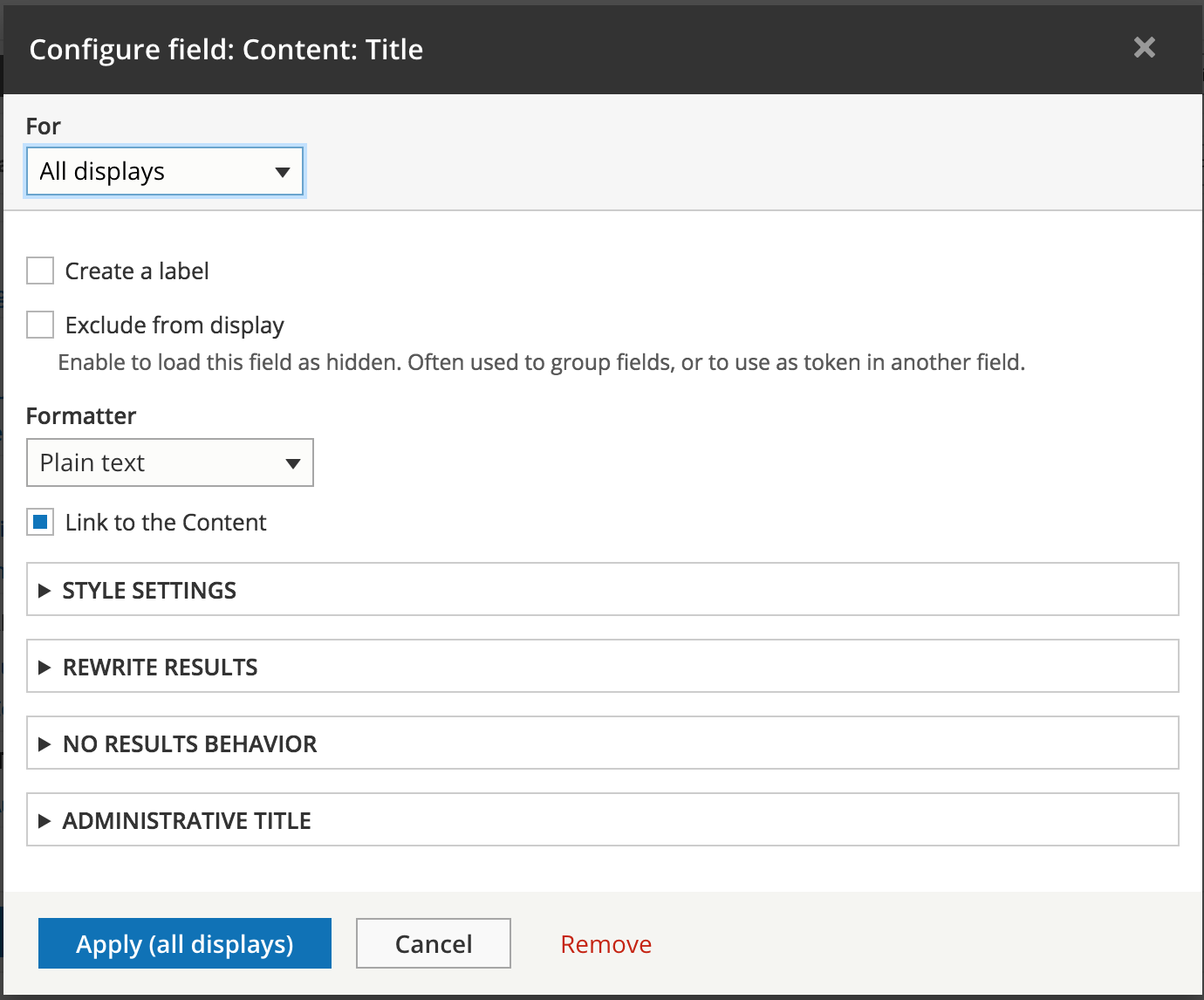
Settings relative to field type
UI - Field settings

UI - Field settings

UI - Field settings
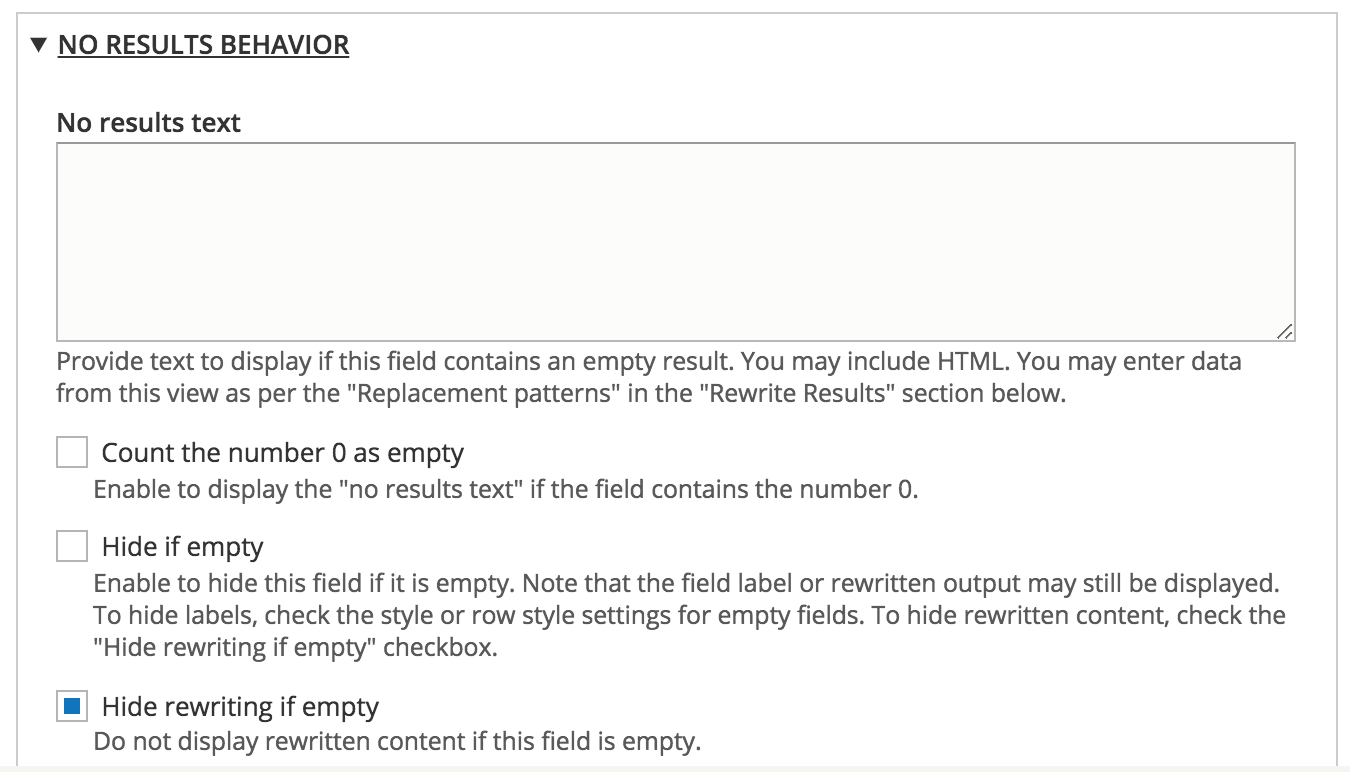
UI - Field settings
UI - Filters
UI - Filters add
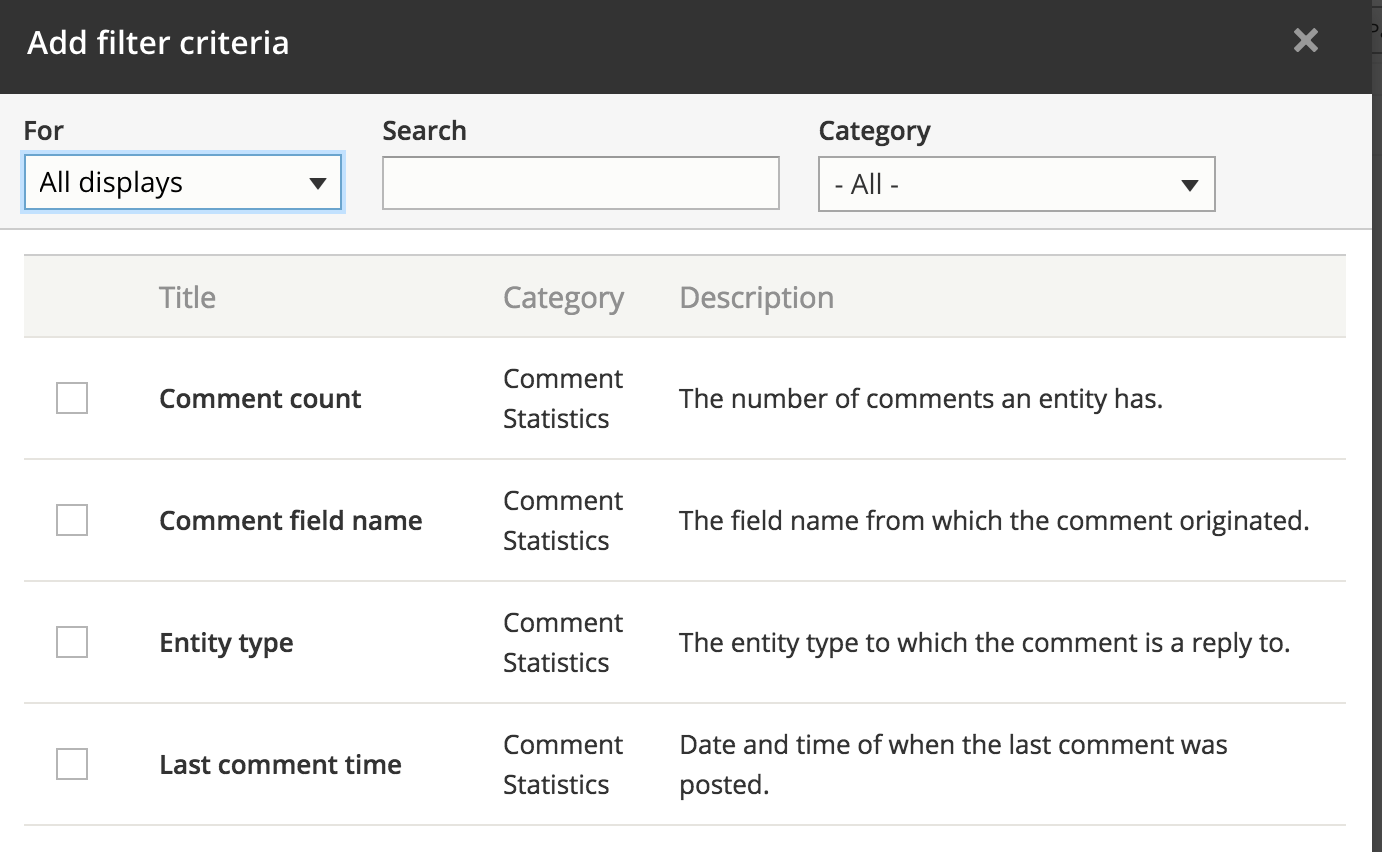
UI - Filters rearrange
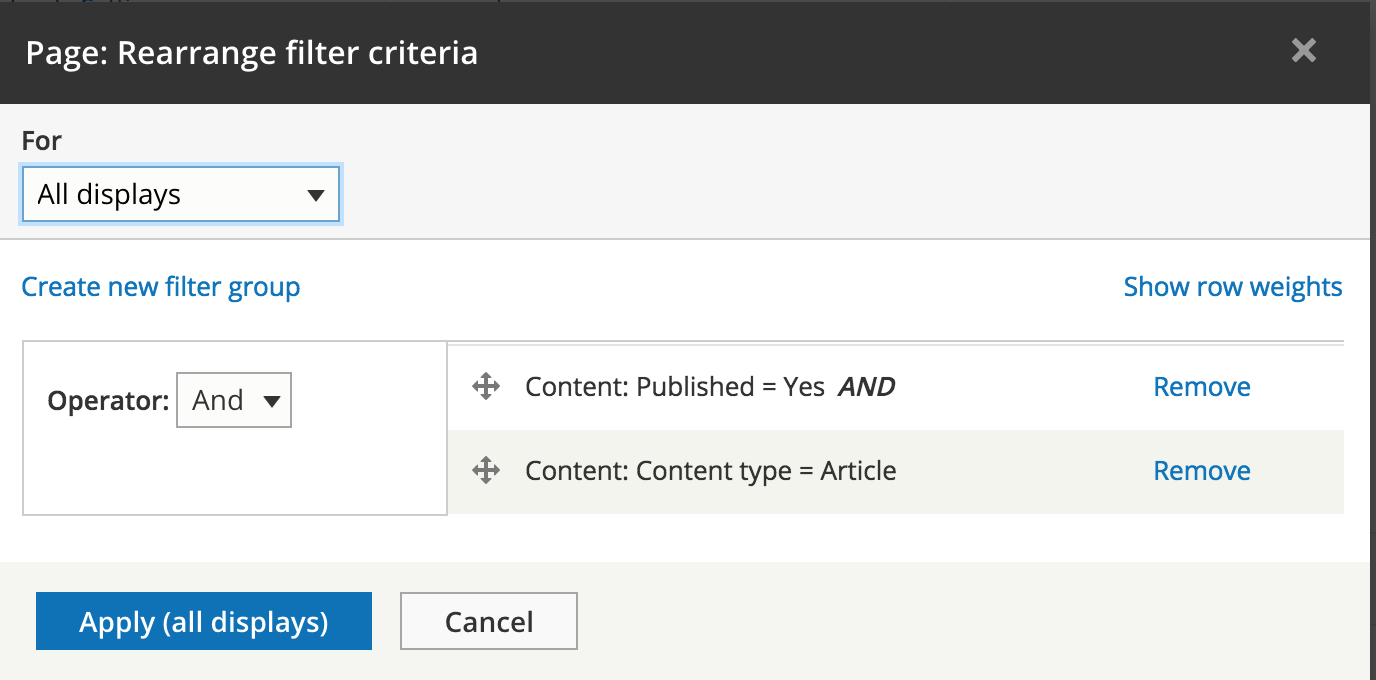
UI - Filter settings
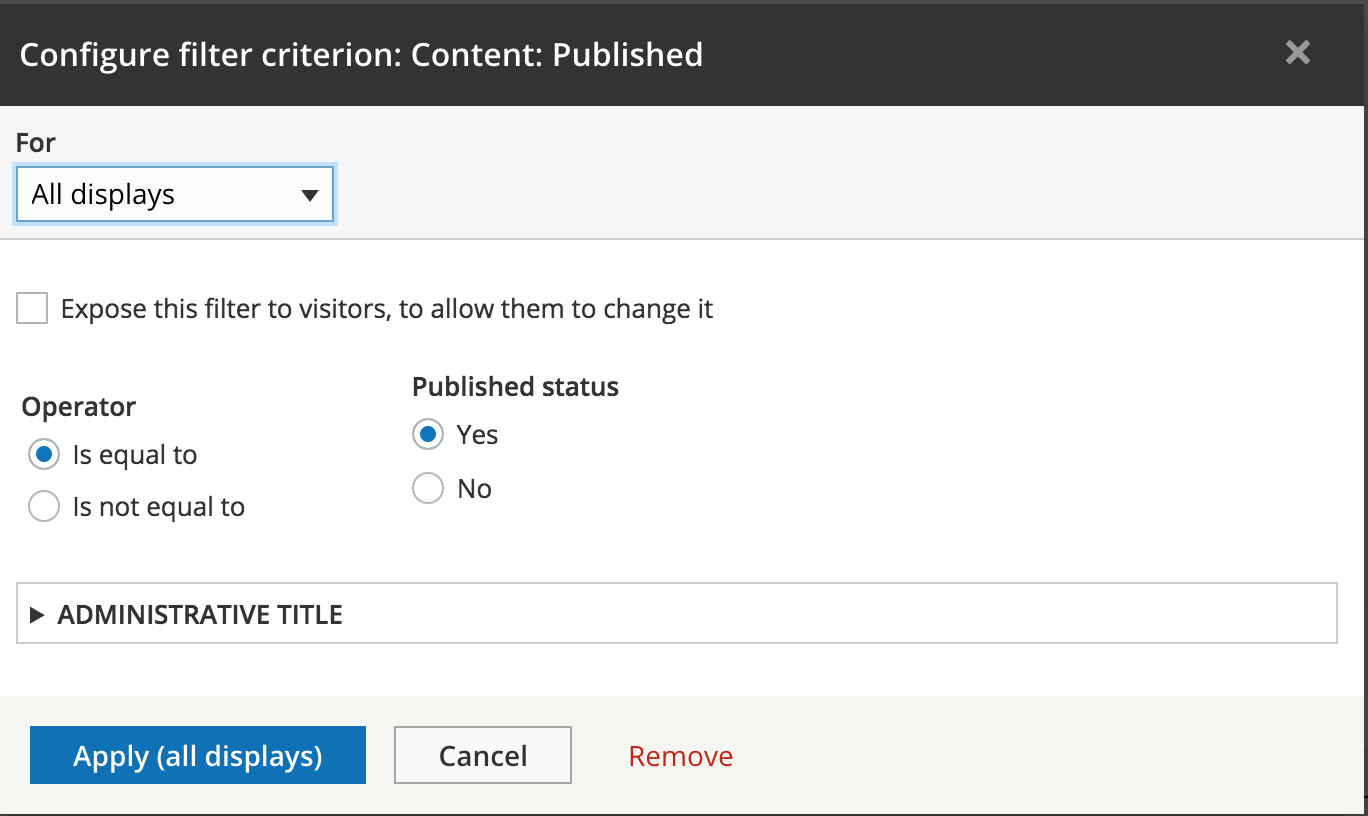
UI - Filter settings
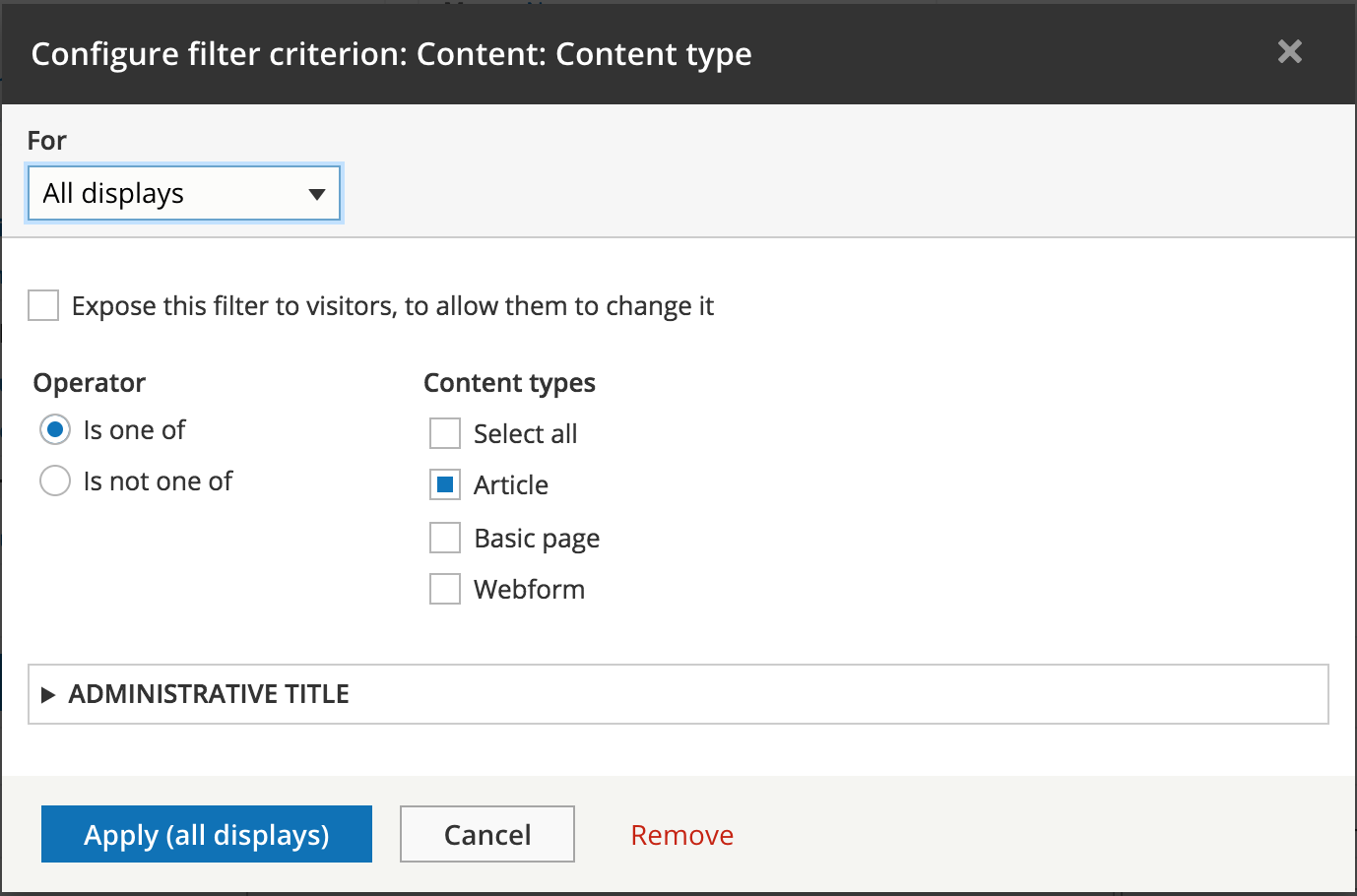
UI - Filter expose
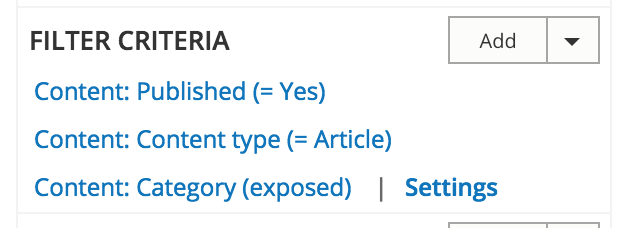
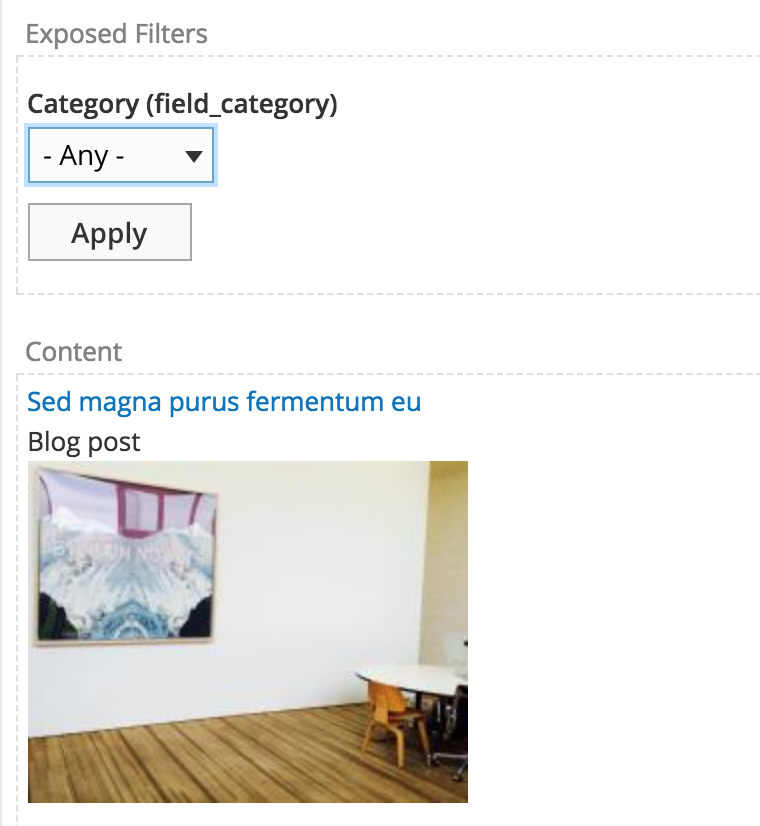
UI - Filter expose
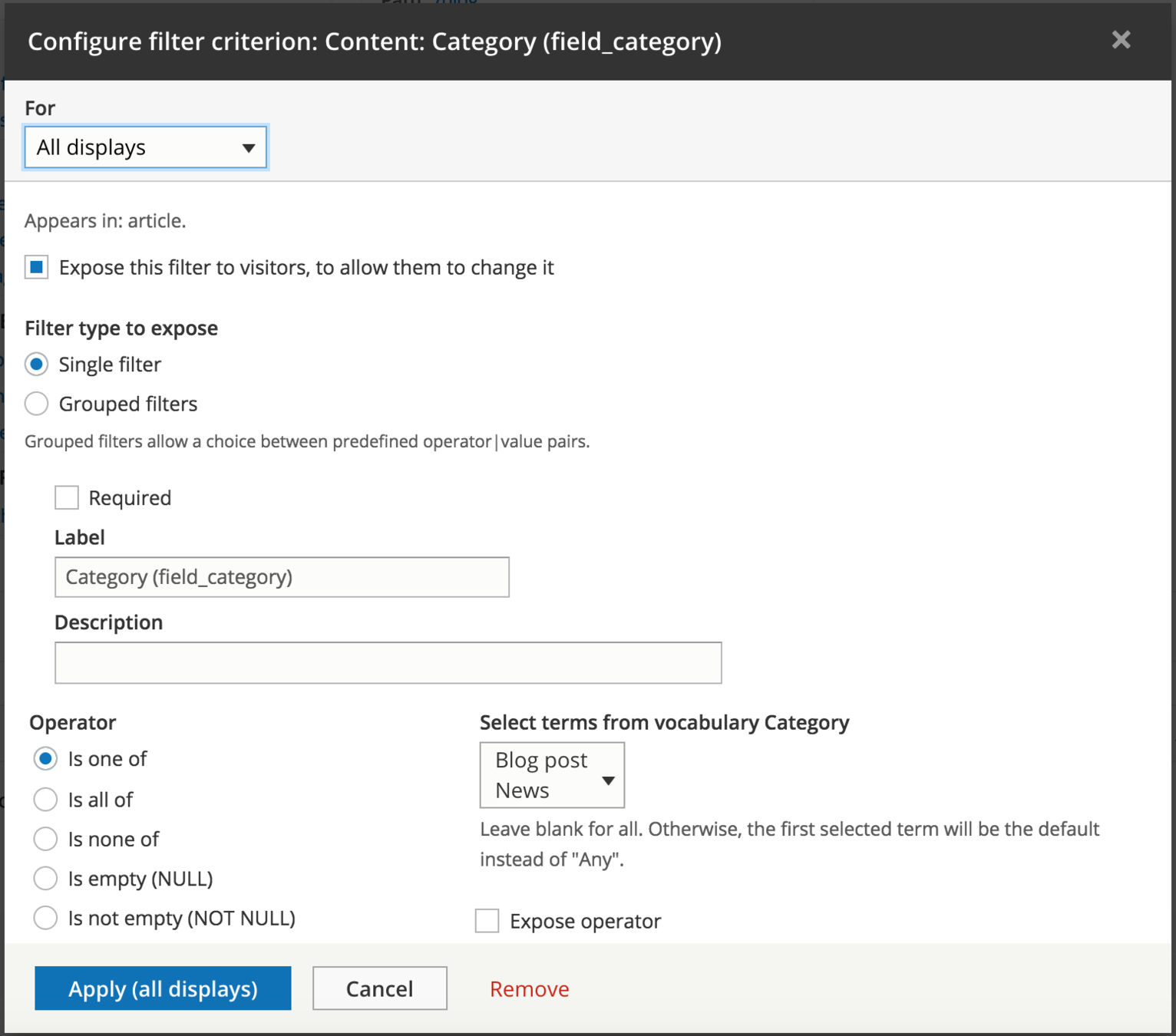
UI - Filter expose
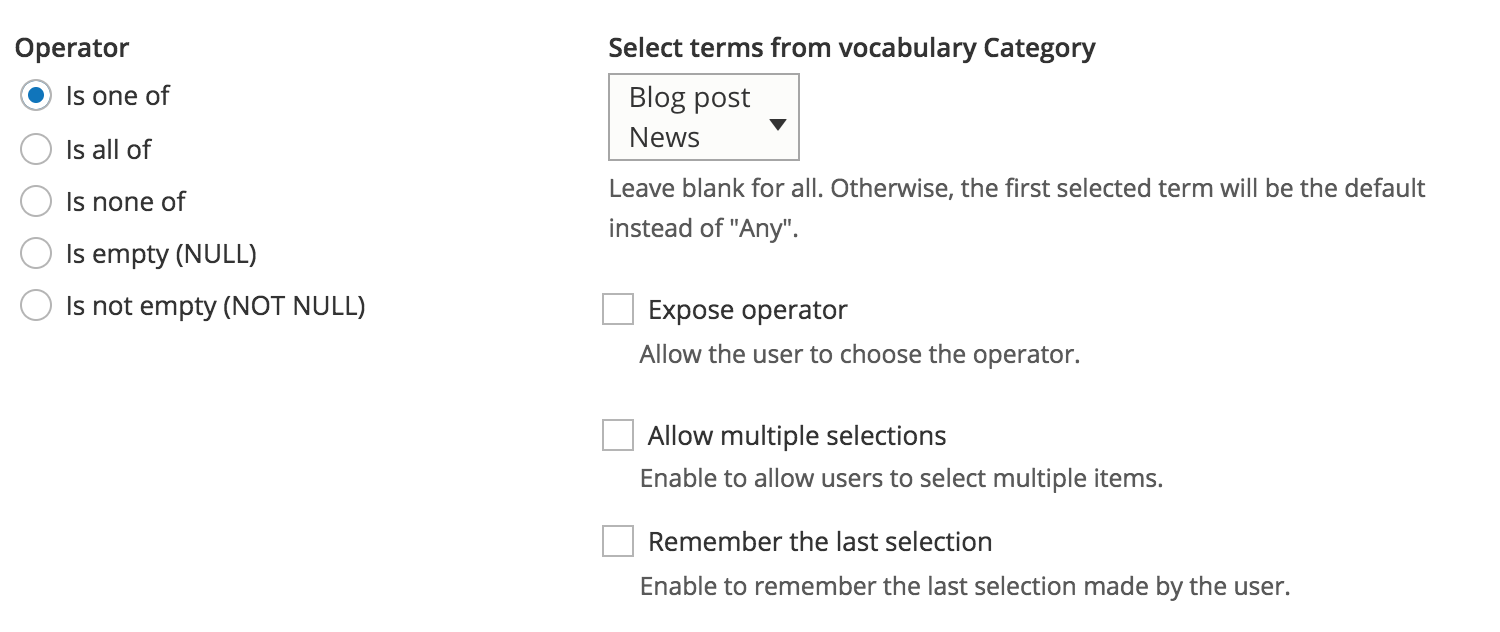
UI - Filter expose

UI - Filter expose

UI - Sort criteria
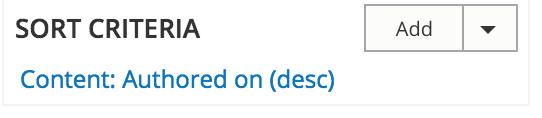
UI - Sort add
UI - Sort rearrange
UI - Sort settings

Views
Display settings
Page settings
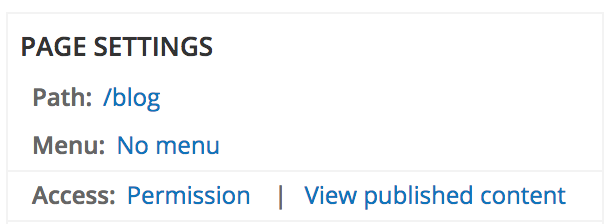
Page settings
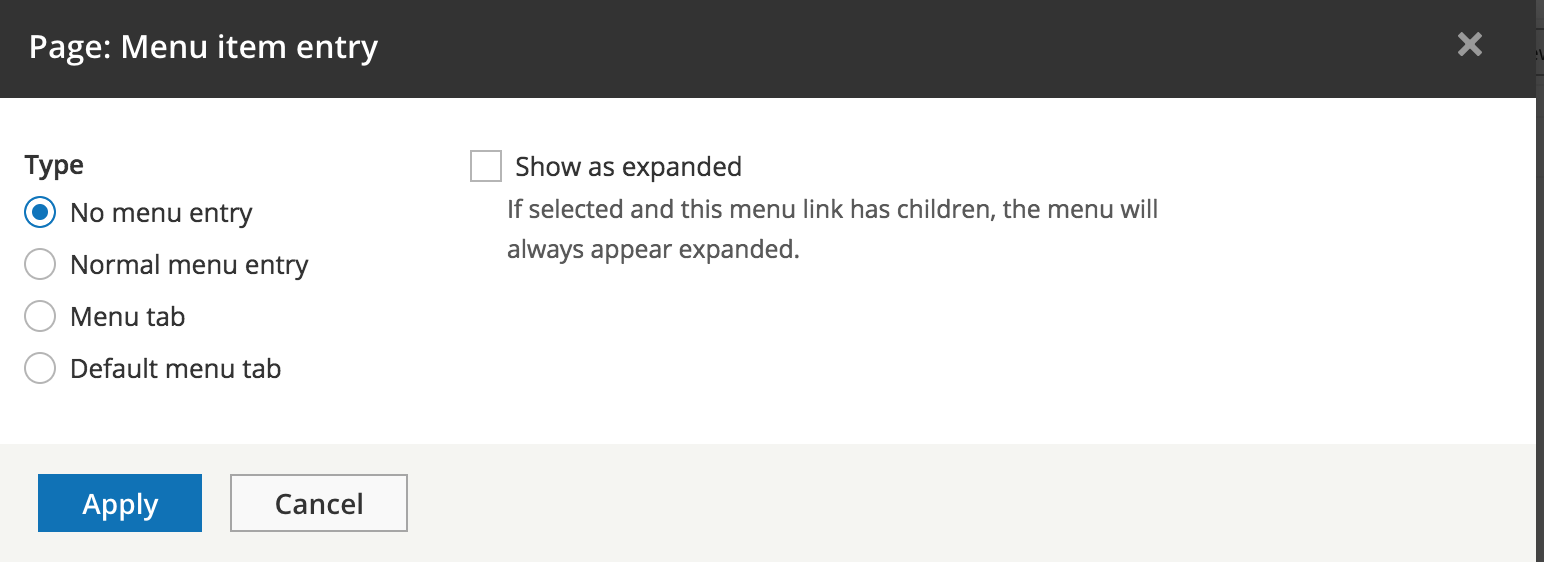
Menu item - none
Page settings
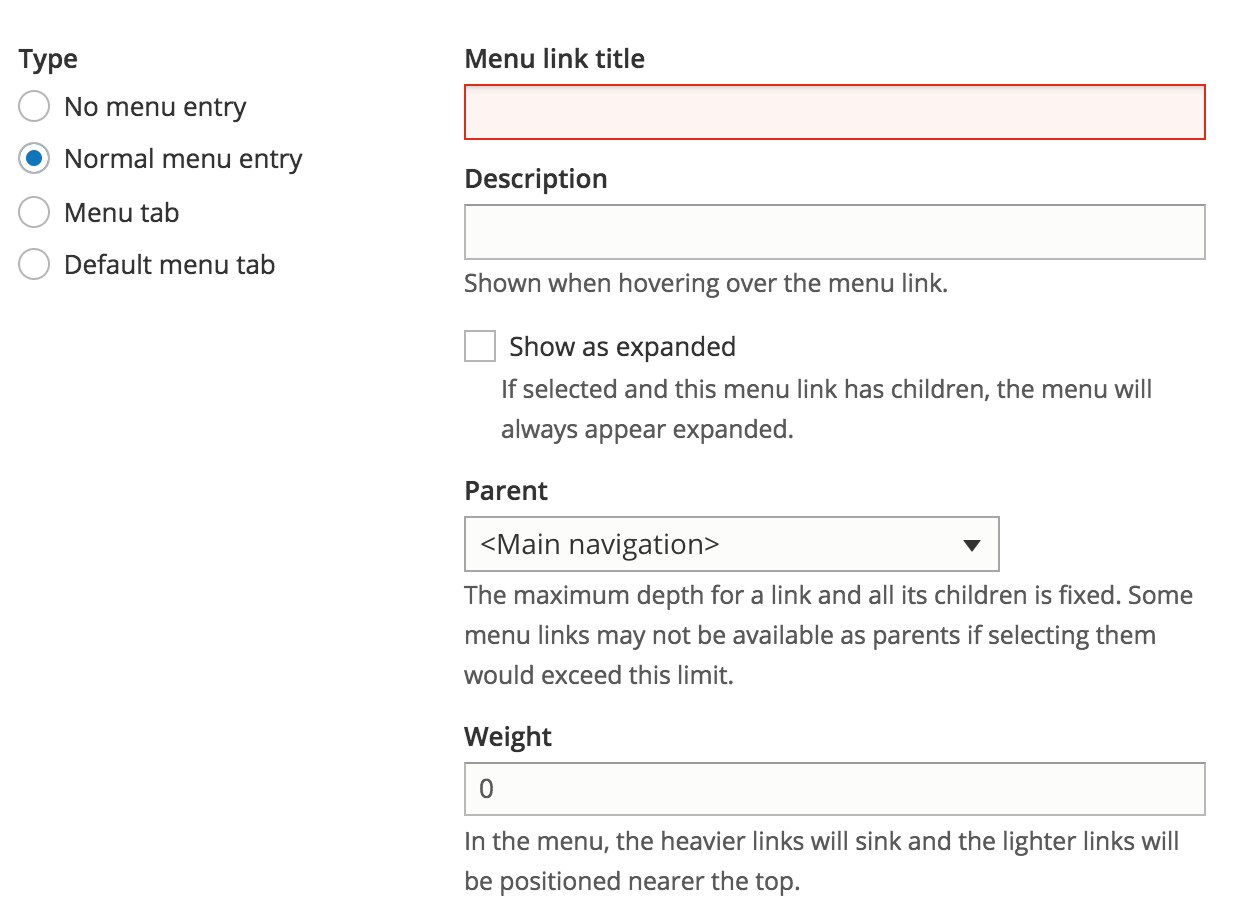
Menu item - normal menu entry
Page settings
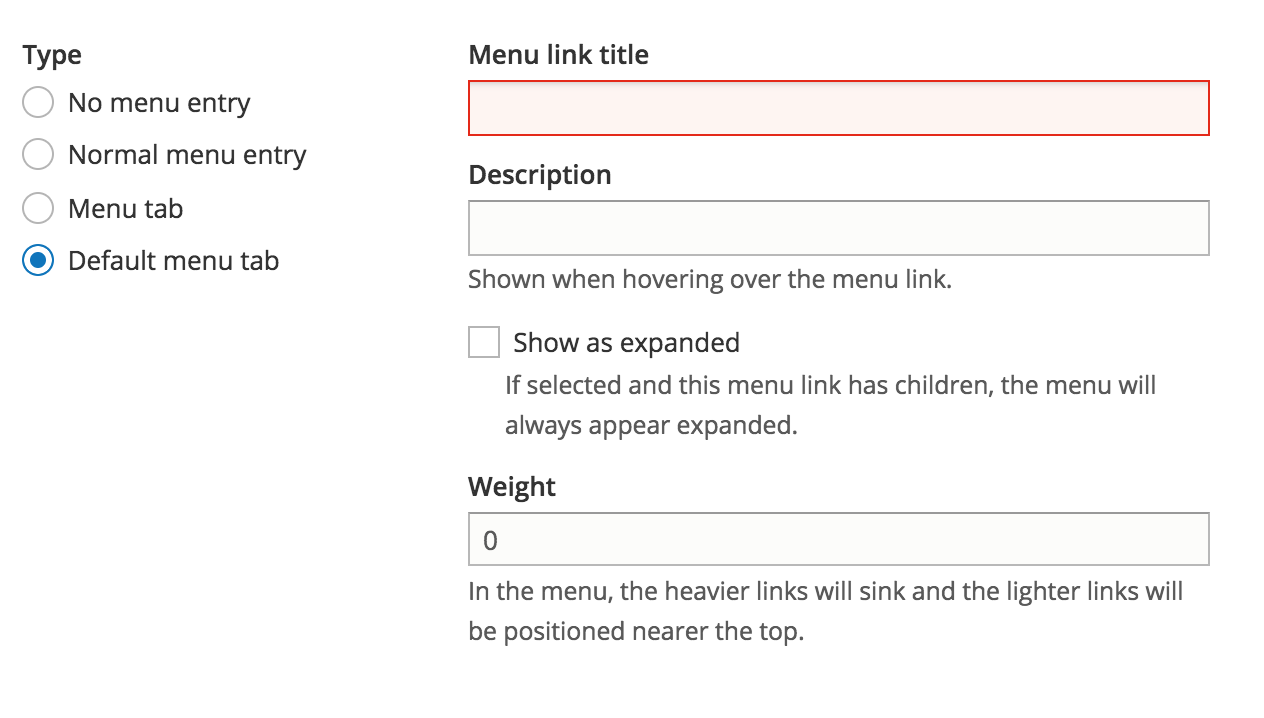
Menu item - menu tab
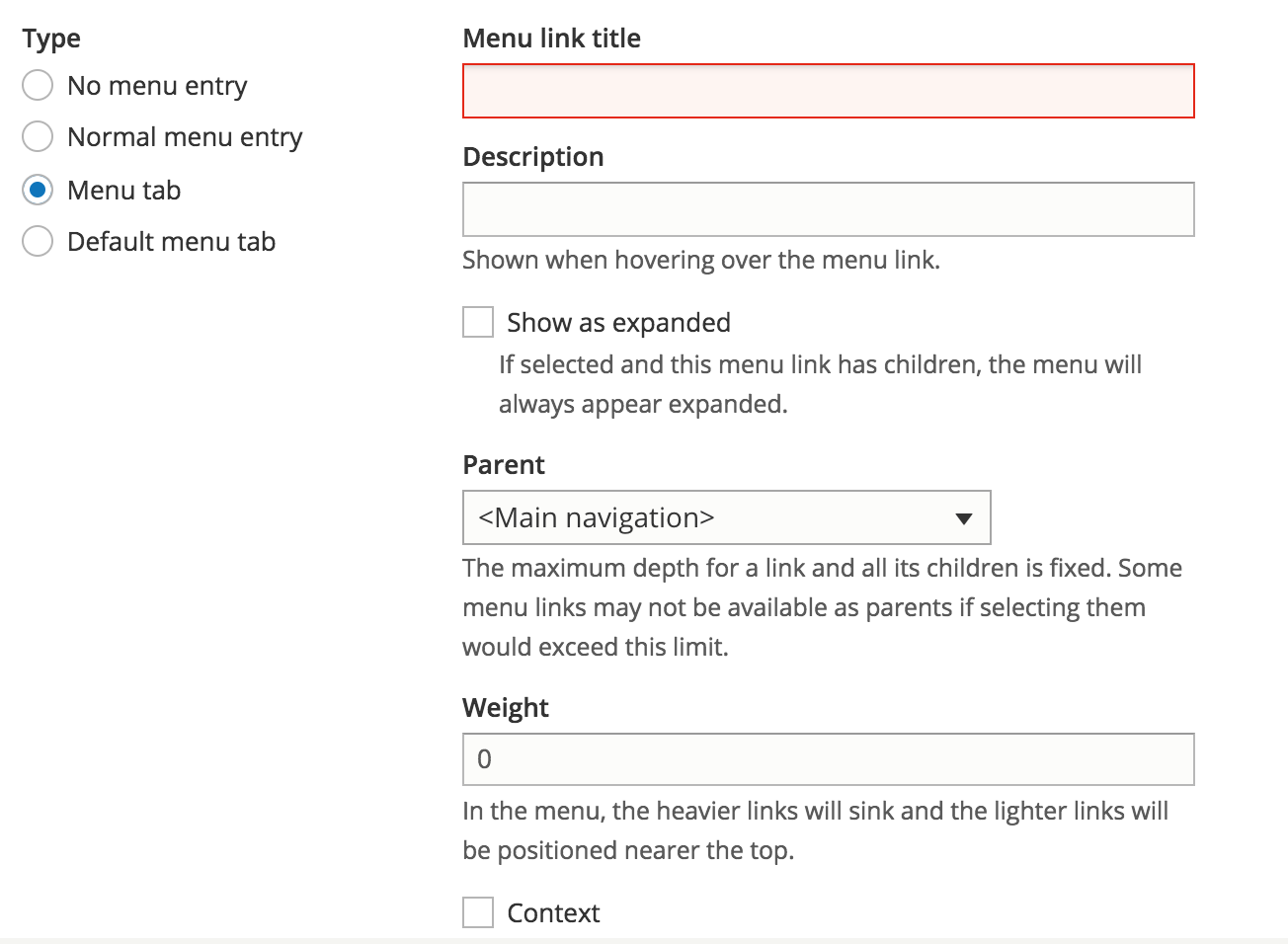
Menu items of this kind will be visible as tabs on a given path, here called the tab's main page, rather than being displayed as normal menu items.
Page settings
Menu item - default menu tab
Creating default menu tabs is similar to creating regular menu tabs, but at the same time you are creating the main page for the tab.
Block settings
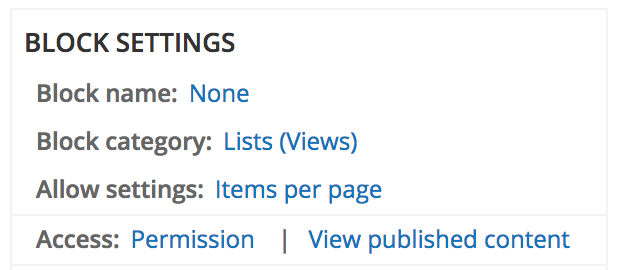
Block name: This will appear as the name of this block in administer >> structure >> blocks.
Block category: The category this block will appear under on the blocks placement page.
General settings

Header/Footer/NR

Header, Footer and No results behavior can be configured to display custom markup, a different view, a block, content and other entities.
Header/Footer/NR
Header/Footer/NR
Header/Footer/NR
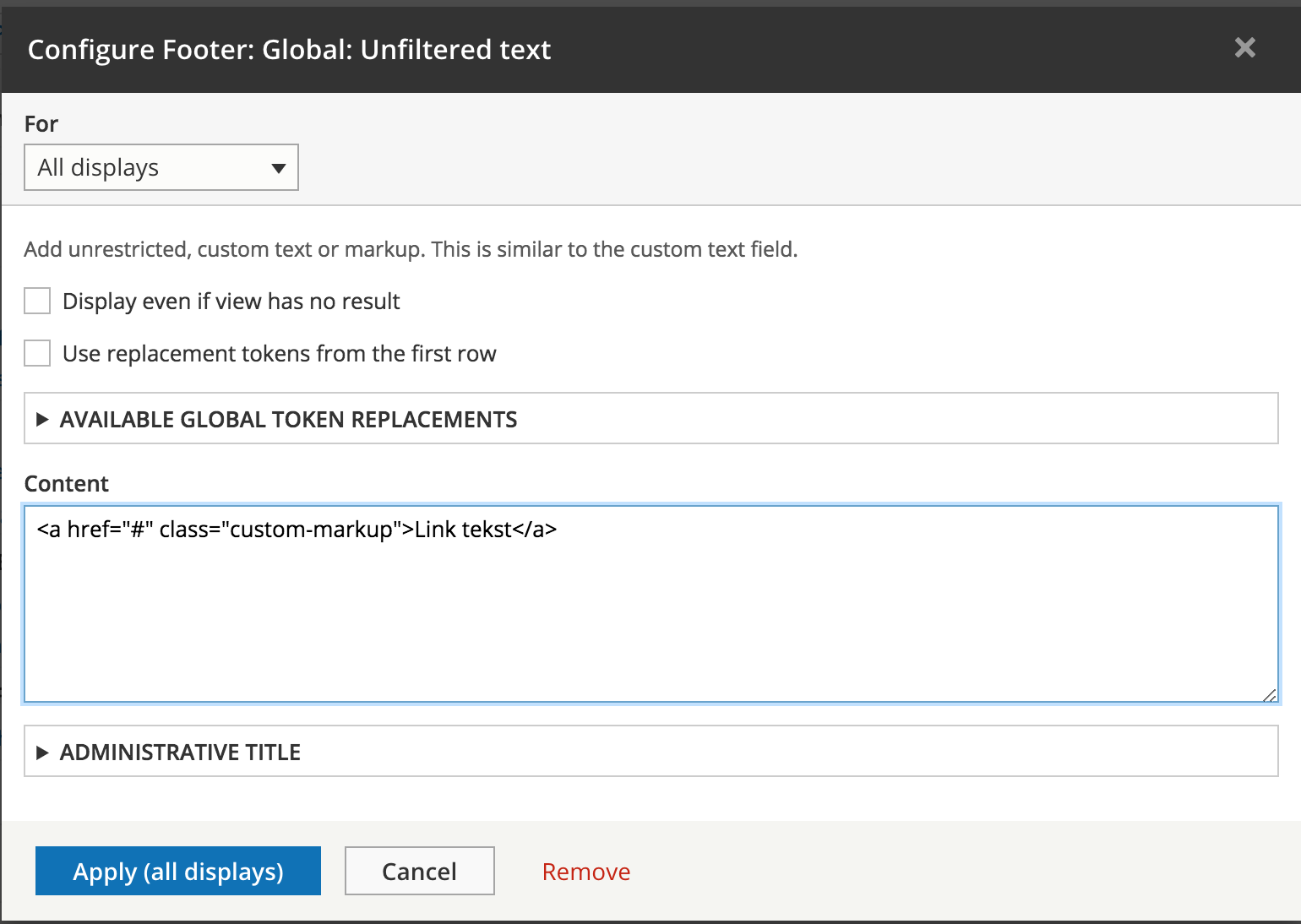
Pager
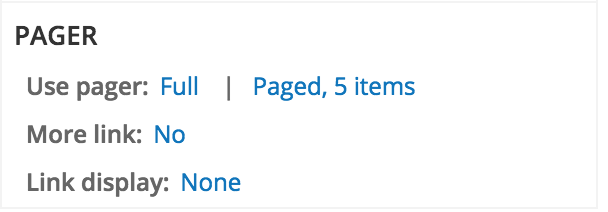
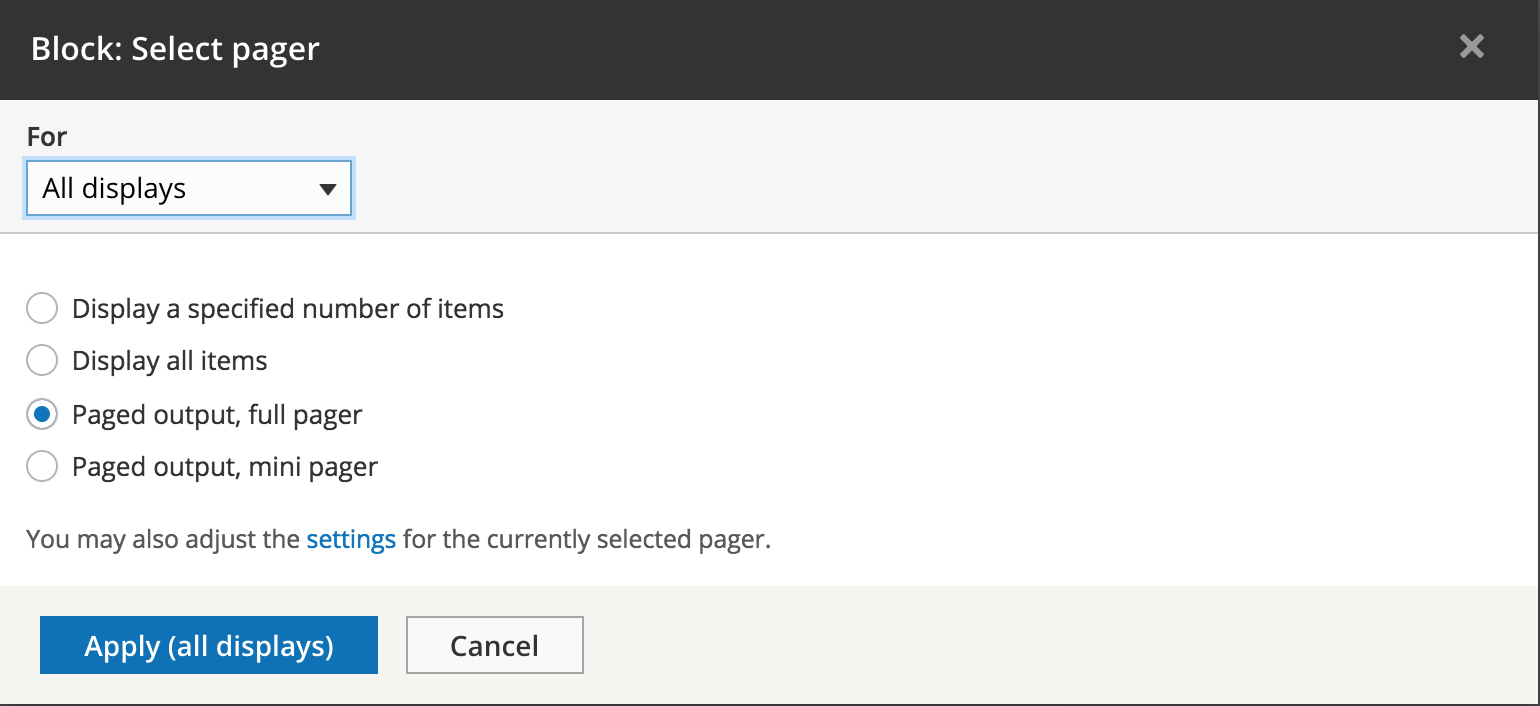
Pager - type
first, previous, 1, ..., 5, 6, 7, ..., 9, next, last
previous, 5, 6, 7, next
Pager - type

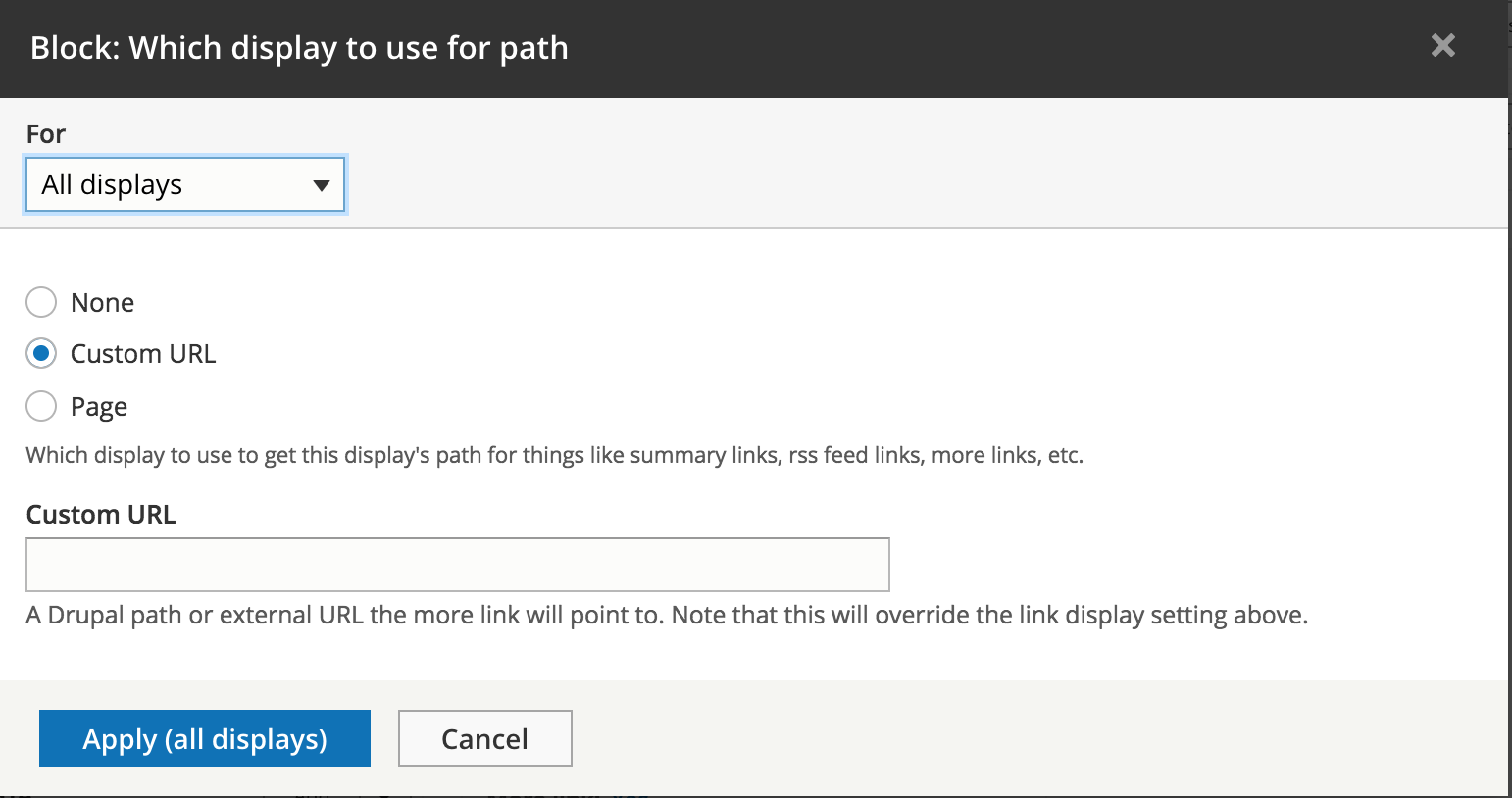
Pager - more link

Pager - link display
Views
Advanced settings
Advanced settings
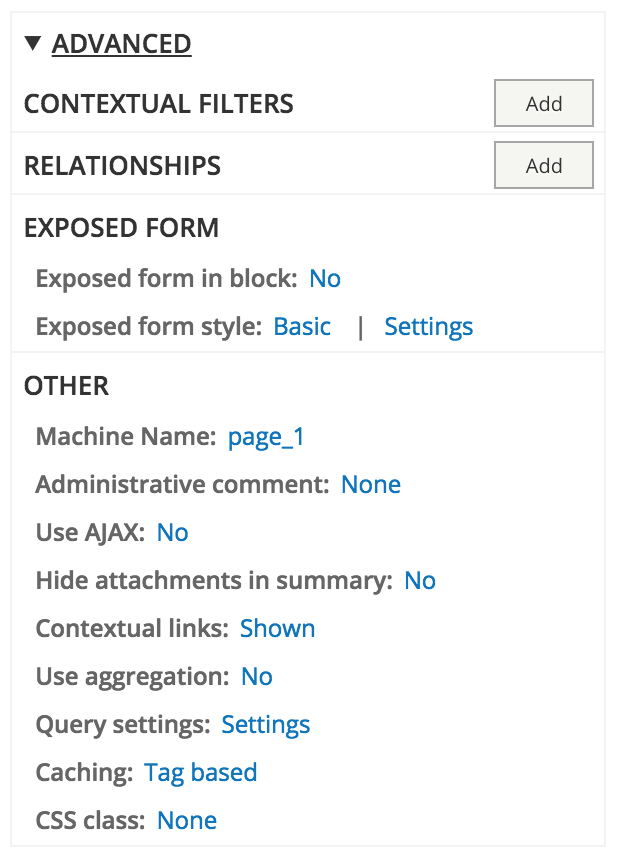
Relationships
A relationship is like making a JOIN in SQL.
You relate different types of content and/or entities through fields with the same value.
When you add a relationship, you can start using the fields of the related entity. This way you can create more advanced views, or filter based on related content.
Relationships
When you first create a view you select the base table from options such as Comments, Content, and Taxonomy terms. This cannot be changed later.
After that selection you will only be able to select fields from that base table. For example, with a Content view, you can get the User ID of the author, but not the author's username.
To get that information you will need to create a Relationship to join those two tables. With the connection of User ID, you can get the author's username from the User table.
Relationships

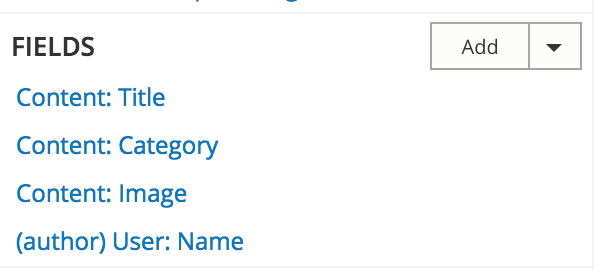
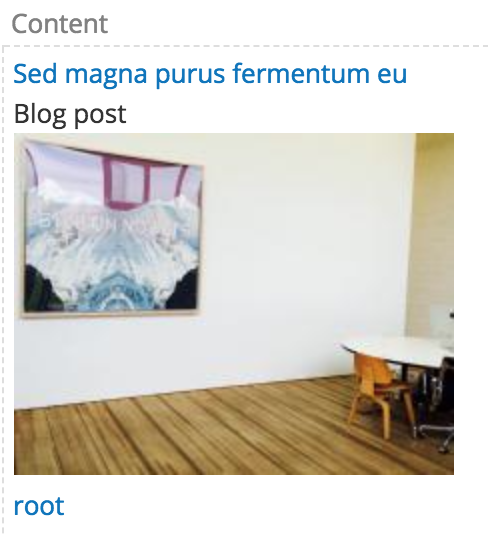
Contextual Filters
You can configure a view so that it is filtered dynamically, depending on the context.
For example, you could use a contextual filter to add a block that contains related content or that presents a list of articles by the same author.
Prerequisite: To create a contextual filter that is based on a context other than the information in the URL, you may need to create a relationship. For more information, see previous slides relationships.
Contextual Filters
Basic guide:
https://www.drupal.org/docs/8/core/modules/views/add-a-contextual-filter-to-a-view
Create view that shows content made by the logged in user:
http://redcrackle.com/blog/adding-contextual-filter-view-drupal-8
Creating a related articles block view:
http://www.pixelwrapped.com/blog/related-articles-block-view-nodes-common-taxonomy-terms
More docs at the end of slides
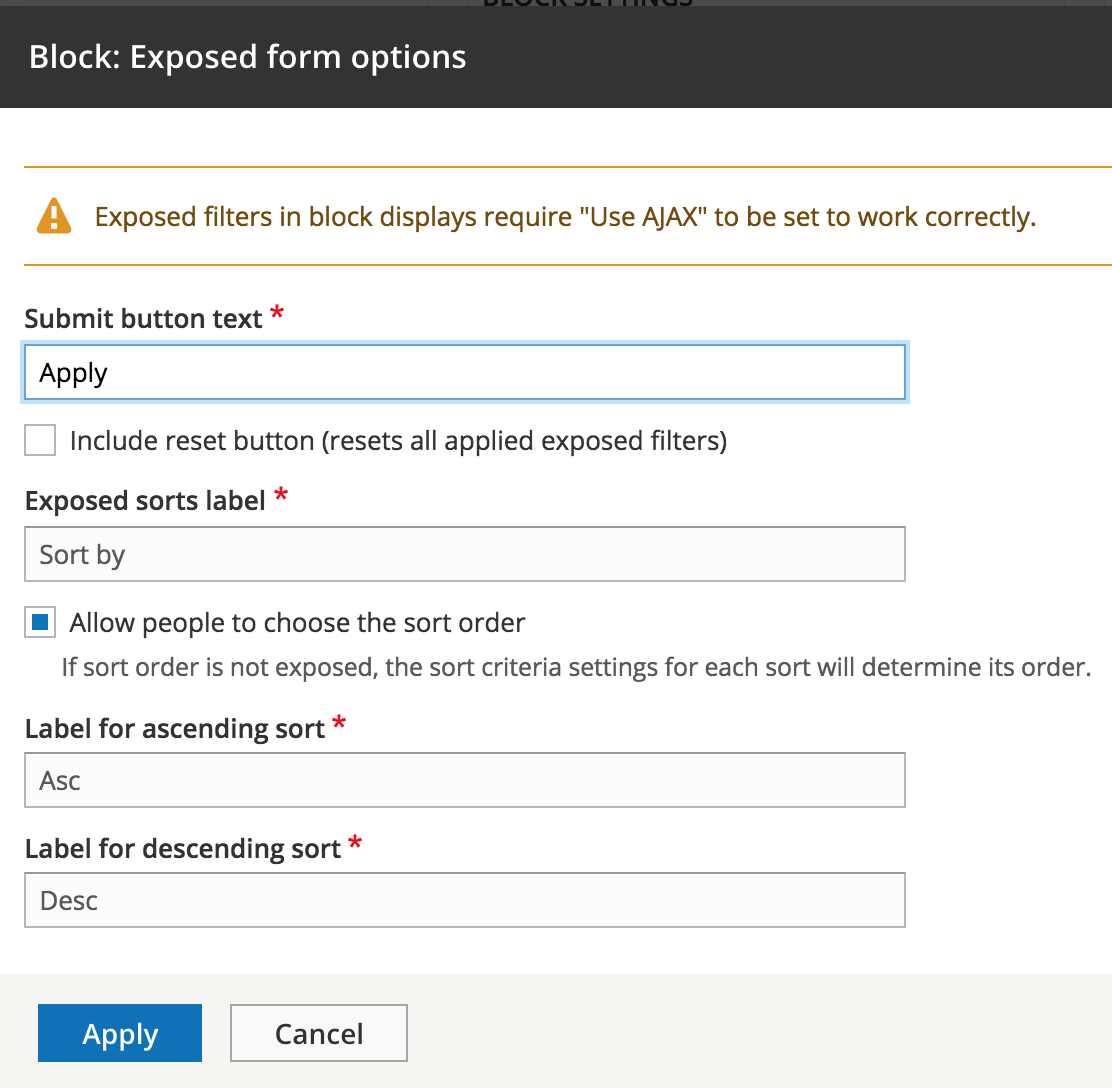
Exposed form
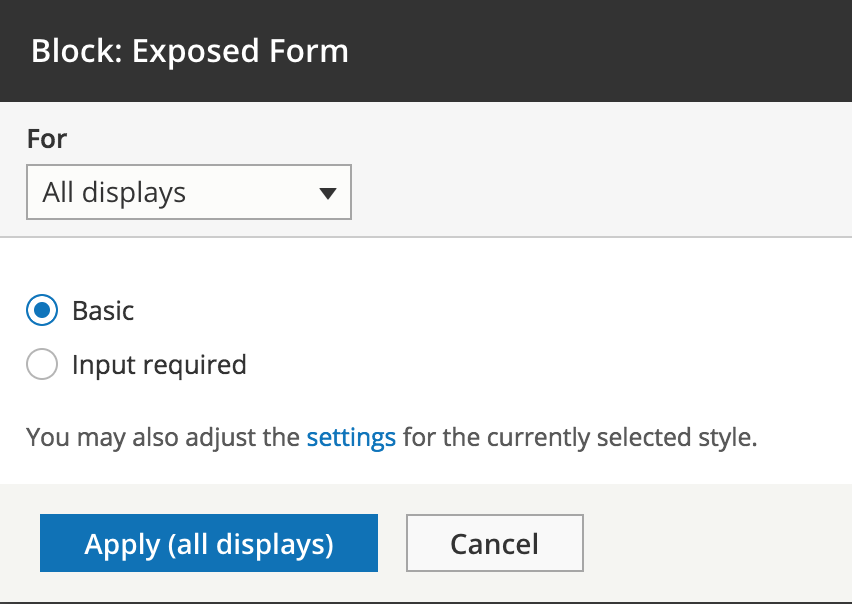
Exposed form settings
Other
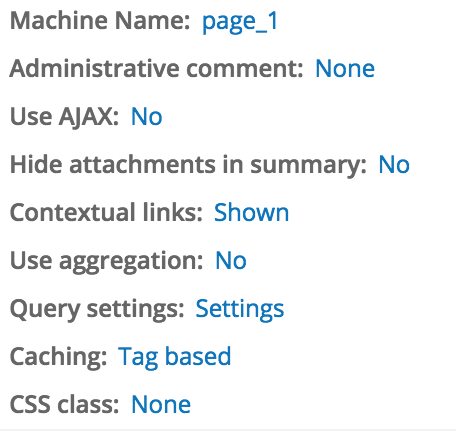
admin description
Other - query settings

Views
Docs
Docs
- Official guides & tutorials
- Video tutorials
* D8 Views is very similar to D7 Views, so you can use D7 Views documentation aswel.
Docs
-
Contextual Filters
CMS1 - D8 Views
By Pieter Mathys
CMS1 - D8 Views
Complete guide
- 595



