strategies to identify strongly lensed type Ia supernovae in the rubin LSST
Prajakta Mane
Final year, Integrated BS-MS,
Indian Institute of Science Education and Research (IISER) Mohali, India
LSST TDWG Meeting
Anupreeta More, Surhud More
Inter-University Centre for Astronomy and Astrophysics (IUCAA), India
March 26, 2024
Time delay cosmography:
accurate time delays, surface mass distribution and redshift of lens
Hubble constant with strong lensing time delays
well-constrained Hubble Constant!

Hubble constant constraints from 6 lensed quasars, Wong et al., 2019
Time delay cosmography:
accurate time delays, surface mass distribution and redshift of lens
Hubble constant with strong lensing time delays
well-constrained Hubble Constant
What makes SNeIa a better source for TDC?
-
well-studied light curves -> more accurate time delay measurements
-
transient source -> improved constraints on the lens galaxy model
-
standard candle nature -> help overcome degeneracies
How to find lensed SNeIa?
DIA: run LSST Stack's difference imaging pipeline to identify multiply imaged SNe
CMA: study outliers in the colour-magnitude space for transients to identify lensed SNeIa
- Raw exposures from Subaru Hyper-Suprime Cam (HSC) -> Public Data Release 1
- UltraDeep Survey's COSMOS region, Tract number 9813 (~1.7 deg wide)
- 149 visits in grizy from 10 nights in 2014 and 2015: 16,688 CCD images
- LSST Science Pipeline w_2022_12
- Strong lensing positions, magnifications, and time delays simulated using a code adapted from More & More, 2022
- SNe light curves: SALT2 (Guy et al., 2007, 2010) template built in SNCosmo (Barbary et al., 2017) manually incorporating strong lensing observables
SNe light curve simulations
Sky data for DIA
Difference imaging analysis
Preliminary results

Difference imaging analysis
Preliminary results
- Total recovery fraction ~70%
- Slightly higher for quads
- Decreases significantly for the y-band
| Injected | Detected | % recovery | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 74k | 51.5k | 70 |
| Doubles | 70k | 48.3k | 70 |
| Quads | 4.1k | 3.2k | 78 |
| g | 310 | 260 | 83 |
| r | 5.4k | 4.7k | 86 |
| i | 14k | 11k | 80 |
| z | 21k | 16k | 76 |
| y | 34k | 20k | 58 |
Difference imaging analysis


Preliminary results
Recovery fraction variation with injected unresolved magnitude
Recovery fraction variation with maximum injected angular separation
- Recovery fraction decreases for fainter systems.
- Expected variation across different bands both with magnitude and angular separation.
Color-magnitude analysis
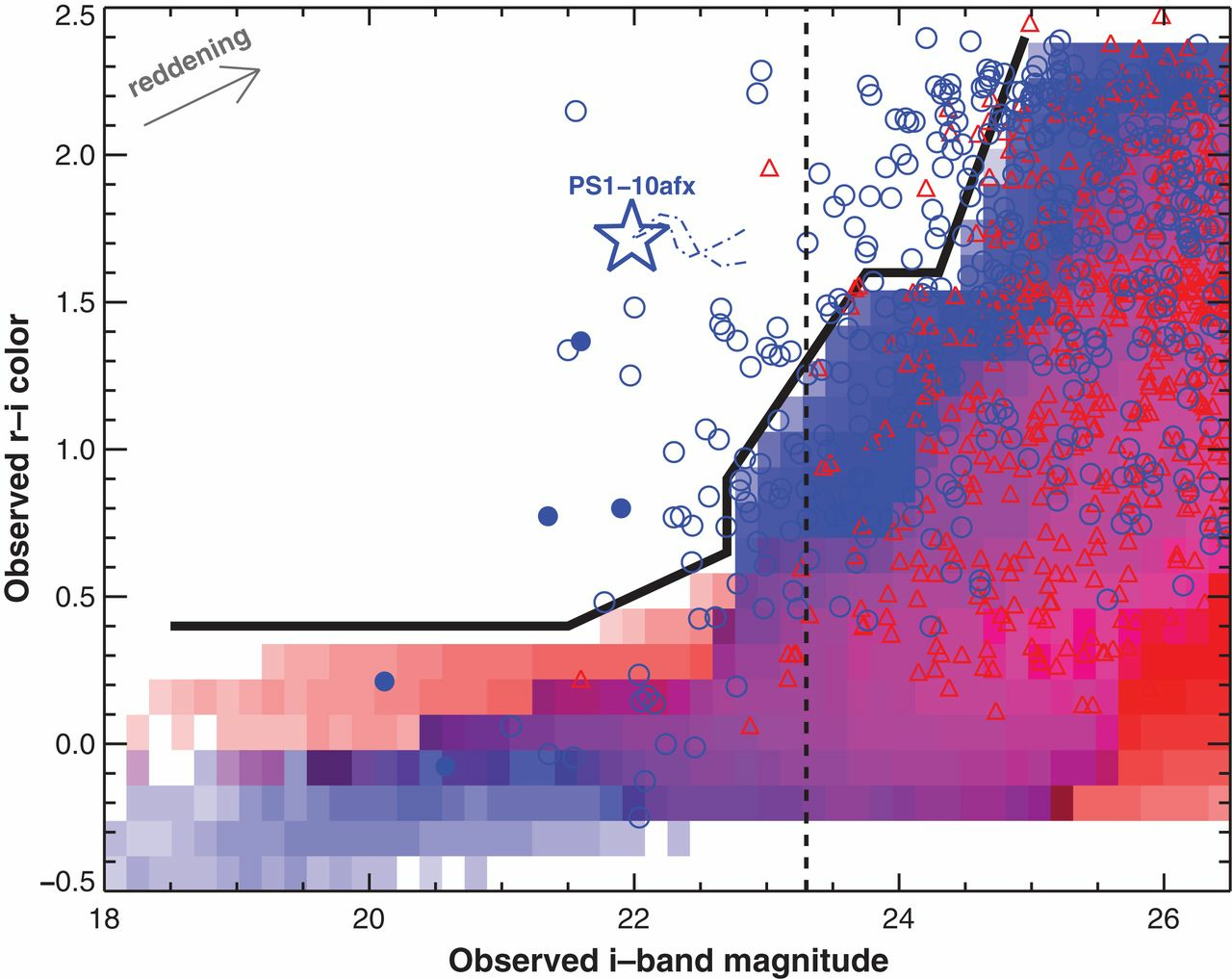
Quimby et al. 2014
: Unlensed SNIa
: Unlensed core collapse
: Lensed SNIa
: Lensed core collapse
The redder supernovae for given i-band magnitude are more likely to be lensed SNeIa


High redshift: 1.64 < z < 2.4
CM diagram for simulated SNeIa
The black bold curve separates the lensed SNeIa from unlensed both on the rising and the falling edge of light curve for z < 2.4!
Low redshift: z < 1.64

Comparison with observed SNeIa
The criteria hold well for the observed unlensed and lensed SNeIa!

Contamination from SNcc (Simulated)

Unlensed
Lensed
Not too much! Lensed Ib and Ic are majority of contaminants
Summary of current results
- Employed differece imaging pipeline recovers ~70% of the injected data of lensed SNeIa.
- Colour-magnitude criteria hold well for simulated and observed (un-)lensed SNeIa till redshift 2.4, both on rising and falling edge. Contamination from (un-)lensed SNeCC is low.
Thank you!
Ongoing work
- Separate DIA sources detected as resolved and unresolved by the pipeline and study their recovery properties.
- Study extended DIA sources to check if extendedness can be used as a marker for a lensed system.
- Study contamination by superluminous SNe in the CM space of lensed SNeIa.
Time delay cosmography:
accurate time delays, surface mass distribution and redshift of lens
Hubble constant with strong lensing time delays
well-constrained Hubble Constant
What makes SNeIa a better source for TDC?
well-studied light curves -> more accurate time delay measurements
transient source -> improved constraints on the lens galaxy model
standard candle nature -> help overcome degeneracies

Current lensed supernova sample
SNIa
SNIa
better constraints expected
Time delay cosmography:
accurate time delays, surface mass distribution and redshift of lens
Hubble constant with strong lensing time delays
well-constrained Hubble Constant
What makes SNeIa a better source for TDC?
-
well-studied light curves -> more accurate time delay measurements
-
transient source -> improved constraints on the lens galaxy model
-
standard candle nature -> help overcome degeneracies
How to find lensed SNeIa?
DIA: run LSST Stack's difference imaging pipeline to identify multiply imaged SNe
CMA: study outliers in the colour-magnitude space for transients to identify lensed SNeIa
better constraints expected

Current lensed supernova sample
SNIa
SNIa
LSST_TDWG_Mar26
By Prajakta
LSST_TDWG_Mar26
Presentation made for IDC451: Seminar Delivery course on the topic Gravitational Lensing and the Most Powerful Explosions in the Space
- 214



