Programming in JAVA 🚀
Binary Number System

We humans use a decimal, or base-10, numbering system, presumably because people have 10 fingers
Early computers were designed around the decimal numbering system. This approach made the creation of computer logic capabilities unnecessarily complex and did not make efficient use of resources. (For example, 10 vacuum tubes were needed to represent one decimal digit.)

Story behind
To deal with the basic electronic states of on and off, Von Neumann suggested using the binary numbering system

Conversions
- Binary Number to Decimal
- Decimal Number to Binary
Quiz Time 🔥
Programming in JAVA
What happens behind the scenes?
Why Java is Platform independent.

.java file
(source code)
.class file
(byte code)


Machine Code (0s & 1s)
compiler
interpreter
What happens behind the scenes?
Why Java is Platform independent.

.java file
(source code)
.class file
(byte code)


Machine Code (0s & 1s)
compiler
interpreter
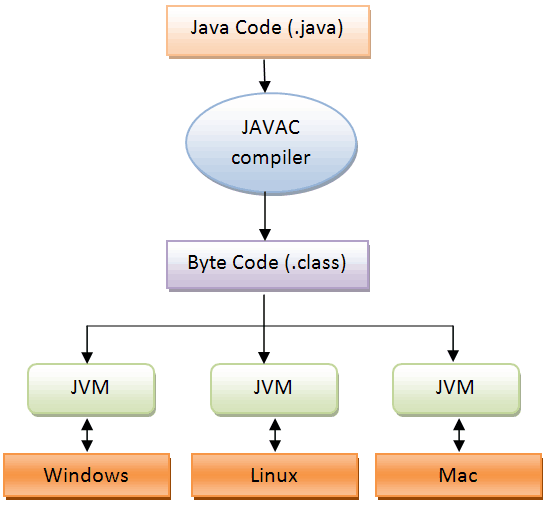
Byte Code doesn't run directly, we need a JVM (Java Virtual Machine) to run this code
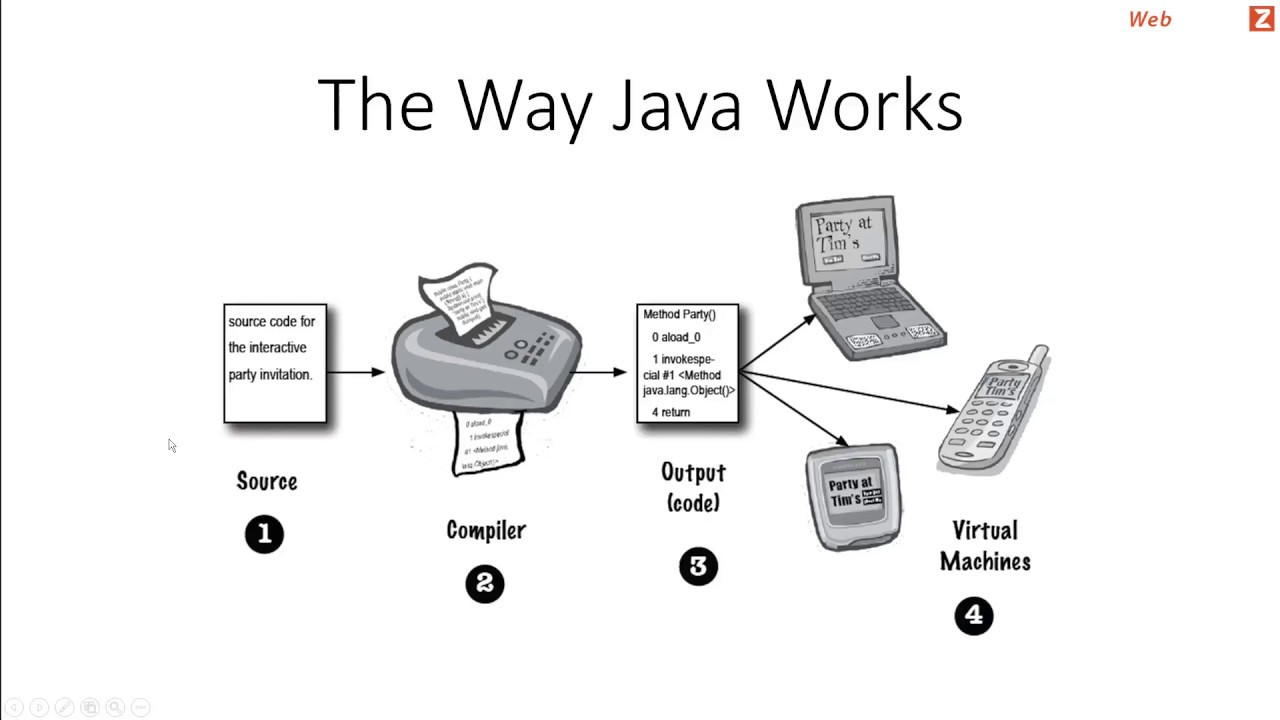
Platform Independence?
Byte-Code can run all operating systems
C++
C/C++ Compiler generates a .exe file which is platform dependent.
Java
In Java we get bytecode, JVM converts this bytecode into machine code.
To run byte-code, we need a JVM installed on a machine.
Java is platform independent but JVM is platform dependent.
Software Tools [Recommended] 🤔
IntelliJ Idea (IDE)
https://www.jetbrains.com/idea/download
(Free Community Edition)
JDK
https://www.oracle.com/java/technologies/downloads/#java16
JVM 🤔
Java Virtual Machine
JVM

Java Virtual Machine, or JVM, loads, verifies and executes Java bytecode. It is known as the interpreter or the core of Java programming language because it executes Java code.
First Java Program
Boilerplate Code
//Boilerplate Code
class Main
{
public static void main (String[] args)
{
}
}First Java Program
Boilerplate Code
//Boilerplate Code
class Main
{
public static void main (String[] args)
{
//Your Code goes here
}
}First Java Program
Boilerplate Code
//Boilerplate Code
class Main
{
public static void main (String[] args)
{
//Your Code goes here
System.out.println("Hello World");
}
}Let's learn Java syntax!
1. Hello Java
2. Variables & Data types
3. Typecasting
4. Branching
Next Class
3. Loops
4. More constructs
Variables & Datatypes
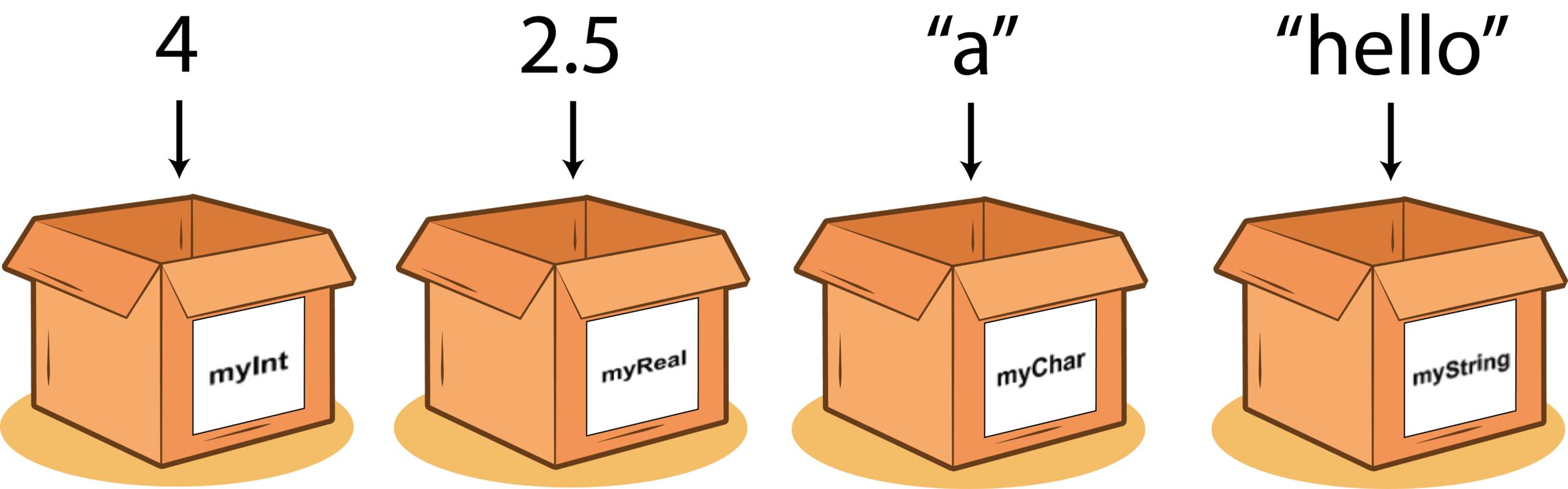
Variables come in two types
- Primitives
- Object References
Boolean - boolean
Character - char
Integer – int
Floating Point – float
Double Floating Point – double
Primitive Data Types

Buckets come in different Sizes!
You can't put a large value into a small cup.

Range of Data Types
Lil bit about Objects!
Read Principal, Rate & Time and print Simple Interest.
Sample Input
P = 100
R = 5
T = 2
Sample Output
SI = 10
Simple Interest Calculator


Read 3 Numbers and find their largest.
Sample Input
10
50
40
Sample Output
50
Largest of 3 Numbers


Learning Outcomes🦸🏻♂️
'float' data type used to define
numeric values
with floating decimal points.
'int' divided by 'int' gives a
integer output due to a
concept called Implicit Typecasting.
Branching
if/else tests - do something under this condtion
if ( weather == "rainy"){
System.out.print("Take an Umbrella");
}
Conditional Statements
Single If
// Single If
int marks = 90;
if (marks > 80) {
cout << “Let's Party!”;
}
Conditional Statements
// If-Else Block
int marks = 70;
if (marks > 80) {
cout << “Let's Party”;
}
else{
cout<< “Work hard next time“;
}

Conditional Statements
If-else-if-else block
// If-Else Block
int marks = 70;
if (marks > 80) {
cout << “Let's Party”;
}
else if(marks>60){
cout<<"Good Job";
}
else{
cout<<"Work hard next time";
}
Homework Challenge 🔥
Electricity Bill Calculator : Given total consumption of a
household in units, write a program to estimate the total bill amount as per the table.
| Units | Charges |
|---|---|
| 1 to 100 units | Free |
| 100 to 200 units | Rs. 5/unit |
| 200 to 300 units | Rs.10/unit |
| 300+ units | Rs.12/unit |
[Java 03] Introduction to Java, Number Systems
By Prateek Narang
[Java 03] Introduction to Java, Number Systems
- 21



