Programming in JAVA 👨💻
Binary Number System

We humans use a decimal, or base-10, numbering system, presumably because people have 10 fingers
Early computers were designed around the decimal numbering system. This approach made the creation of computer logic capabilities unnecessarily complex and did not make efficient use of resources. (For example, 10 vacuum tubes were needed to represent one decimal digit.)

Story behind
To deal with the basic electronic states of on and off, Von Neumann suggested using the binary numbering system

Conversions
- Binary Number to Decimal
- Decimal Number to Binary
Programming in JAVA
What happens behind the scenes?
Why Java is Platform independent.

.java file
(source code)
.class file
(byte code)


Machine Code (0s & 1s)
compiler
interpreter
What happens behind the scenes?
Why Java is Platform independent.

.java file
(source code)
.class file
(byte code)


Machine Code (0s & 1s)
compiler
interpreter
Byte Code doesn't run directly, we need a JVM (Java Virtual Machine) to run this code
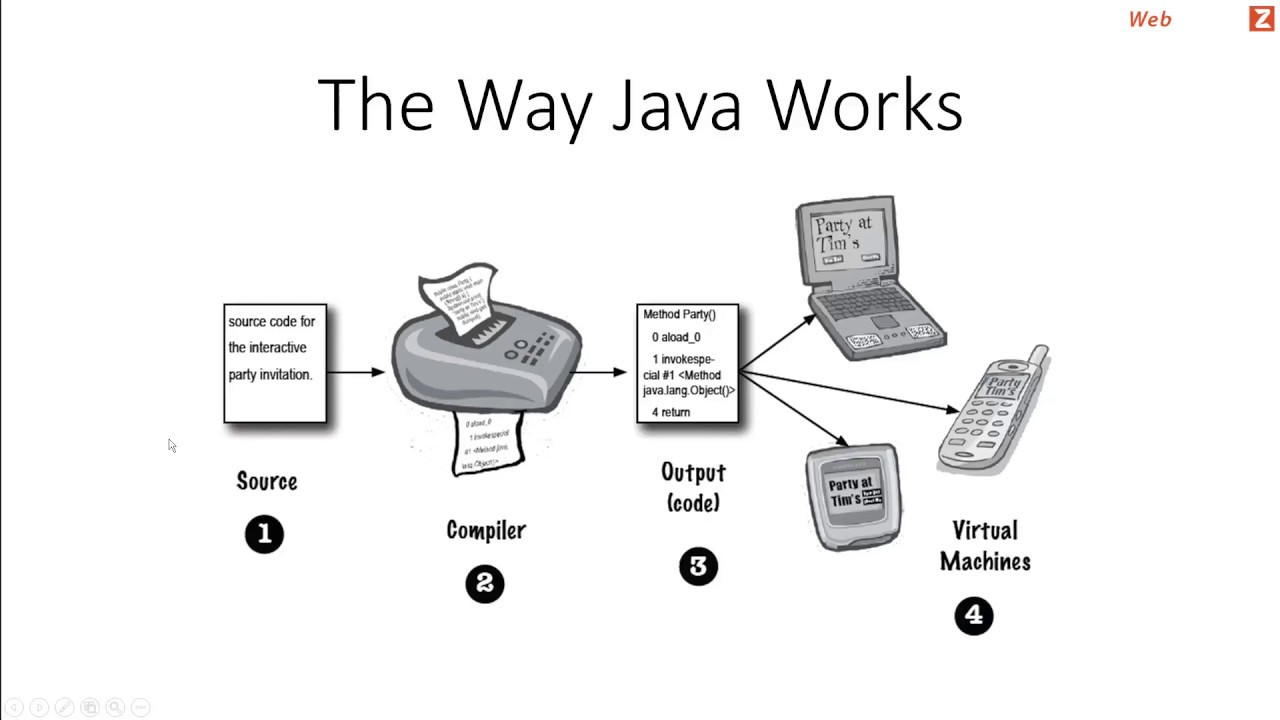
Platform Independence?
Byte-Code can run all operating systems
C++
C/C++ Compiler generates a .exe file which is platform dependent.
Java
In Java we get bytecode, JVM converts this bytecode into machine code.
To run byte-code, we need a JVM installed on a machine.
Java is platform independent but JVM is platform dependent.
Python
Python is interpreted language, instructions are executed line by line.
Software Tools [Recommended] 🤔
IntelliJ Idea (IDE)
https://www.jetbrains.com/idea/download
(Free Community Edition)
JDK
https://www.oracle.com/java/technologies/downloads/#java16
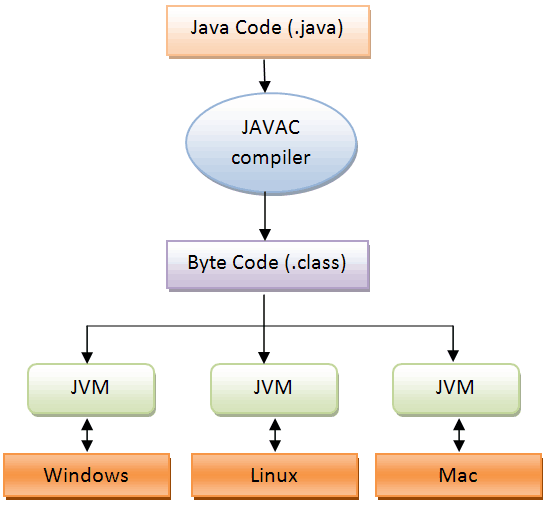
Architecture
JDK = JRE + Development Tools
JRE = JVM + Library Classes
JDK = JRE + Development Tools
Java Virtual Machine (JVM)
JIT Compiler
(Just In Time)
JDK

Consists of Development tools & environment to run the Java program.
1. Development Tools
2. Compiler (javac)
3. Archiver (jar)
4. docs generator (javadoc)
5. interpreter / loader
JRE

Provides environment to only run the program.
JRE = JVM + Additional technologies & features
1. Deployment solutions
2. Development toolkits & libraries
3. Integration libraries
4. Language and utility libraries
(such as collections framework)
JVM 🤔
Java Virtual Machine
JVM

Java Virtual Machine, or JVM, loads, verifies and executes Java bytecode. It is known as the interpreter or the core of Java programming language because it executes Java code.
- Class Loader Subsystem is responsible for loading, linking and initializing a Java class file (i.e., “Java file”), otherwise known as dynamic class loading.
- Runtime Data Areas contain method areas, PC registers, stack areas and threads.
- Execution Engine contains an interpreter, compiler and garbage collection area.
Summary

The JRE combines Java code created using the JDK with the necessary libraries required to run it on a JVM and then creates an instance of the JVM that executes the resulting program.
JVMs are available for multiple operating systems, and programs created with the JRE will run on all of them. In this way, the Java Runtime Environment is what enables a Java program to run in any operating system without modification.
Coding Minutes IDE
ide.codingminutes.com

No Installation Required!
Directly Run | Save | Share Codes!
Recommended for beginners
First Java Program
Boilerplate Code
//Boilerplate Code
class Main
{
public static void main (String[] args)
{
}
}First Java Program
Boilerplate Code
//Boilerplate Code
class Main
{
public static void main (String[] args)
{
//Your Code goes here
}
}First Java Program
Boilerplate Code
//Boilerplate Code
class Main
{
public static void main (String[] args)
{
//Your Code goes here
System.out.println("Hello World");
}
}Bookmark this Link
bit.ly/javaOct21
Let's Solve Problems & learn Java syntax!
1. Hello Java
2. Variables
3. Loops
4. Typecasting
5. Problems - Prime Numbers, Patterns, Simple Interest
variable = (condition) ? expressionTrue : expressionFalse;
Ternary Operator
[Java 03] Introduction to Java, Number Systems
By Prateek Narang
[Java 03] Introduction to Java, Number Systems
- 10



