
C++ Operators, Expressions & Statements
Prateek Narang
Topics

-
Expressions
-
Statements
-
Operators
-
Associativity & Precedence


Expressions vs Statements




int total_marks = physics + chem + maths;


Expressions & Statements
- Any variable name (x, y, z, . . . ), constant, or literal is an expression.
- One or more expressions combined by an operator constitute an expression, e.g., x + y or x * y + z
int x = 10;
// Expression
x
10
"hello"
x + y - z


Expressions
int x = 10, y=20, z=30;
// Expressions
x = y = z + 10
// Statement
x = y = z;
In C++, assignment is also an expression, e.g., x = y + z. As a consequence, it can be used within another assignment: x2= x= y + z. Assignments are evaluated from right to left.

Any of the expressions above followed by a semicolon is a statement.
The variable and constant declarations we have seen before are also statements. As the initial value of a variable or constant, we can use any expression
A single semicolon is an empty statement, and we can thus put as many semicolons after an expression as we want.

Statements
int marks = 10; //statement
5 + 3 // expression
5 + 3; //statement
int z = 5 + 3; // statement
int total = marks; // statement
// Control Statements
if(...){
}

Operators




Operators
Arithmetic Operators
Relational Operators
Logical Operators
Bitwise Operators
Assignment Operators
Misc Operators

Arithmetic operators are used to perform arithmetic operations on variables and data.

1. Arithmetic Operators
a + b
a + b - c * d + 24| + | Addition |
| - | Subtraction |
| * | Multiplication |
| / | Division |
| % | Modulo |

Arithmetic operators are used to perform arithmetic operations on variables and data.

1. Arithmetic Operators
a + b
a + b - c * d + 24| + | Addition |
| - | Subtraction |
| * | Multiplication |
| / | Division |
| % | Modulo |

/ Division Operator
Note the operation (a / b) in our program. The / operator is the division operator.If an integer is divided by another integer, we will get the quotient.
However, if either divisor or dividend is a floating-point number, we will get the result in decimals
% Modulo Operator
The modulo operator % computes the remainder. When a = 9 is divided by b = 4, the remainder is 1.


Also known as compound assignment operators (combine binary operator with assignment operator)

2. Assignment Operators
| = | Assignment |
| += | Compound Addition |
| -= | Compound Substraction |
| *= | Compound Multiplication |
| /= | Compound Division |
| %= | Compound Modulo |

Arithmetic operators are used to perform arithmetic operations on variables and data.

Increment Decrement
int a = 10;
a++ ; //postincrement
++a; // preincrement
a--; //post decrement
--a; // pre decrement
| ++ | Increment |
| -- | Decrement |

A relational operator is used to check the relationship between two operands

3. Relational Operators
| == | isEqual to |
| != | Not Equal To |
| > | Greater than |
| < | Less than |
| >= | Greater than or Equal to |
| <= | Less than or equal to |

Logical operators are used to check whether an expression is true or false. If the expression is true, it returns 1 whereas if the expression is false, it returns 0.

4. Logical Operators
| && | Logical AND |
| || | Logical OR |
| ! | Logical NOT |

In C++, bitwise operators are used to perform operations on individual bits. They can only be used alongside char and int data types

5. Bitwise Operators
| & | Binary AND |
| | | Binary OR |
| ^ | Binary XOR |
| ~ | Binary One Compliment |
| << | Left Shift |
| >> | Right Shift |

Here's a list of some other common operators available in C++. We will learn about them in later tutorials.

6. Other Operators
| sizeof | returns size of datatype |
| ? : | Ternary Operator |
| & | Address Of Operator |
| . | Dot Operator |
| * | Dereference Operator |
| -> | Access members of objects |
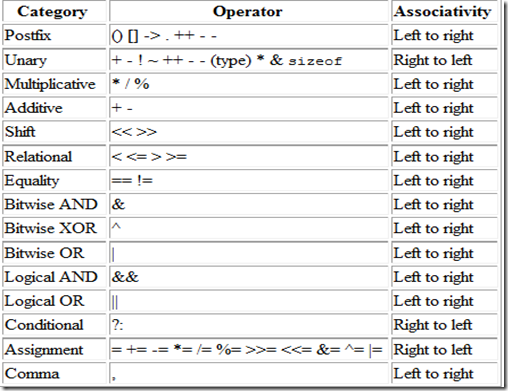
Operator Precedence



[Topics 06] Operators
By Prateek Narang
[Topics 06] Operators
- 13



