Review
講義連結(高一上)
講義連結(高一下)
字串與字元陣列
String vs Char Array
String
#include <string>
int main(){
std::string s = "hello";
return 0;
}Char Array
#include <iostream>
int main(){
char s1[] = {'h', 'e', 'l', 'l', 'o'};
char s2[] = "hello";
return 0;
}Iterator
迭代器
| s.begin() | s.begin()+1 | s.begin()+2 | s.begin()+3 | s.begin()+4 | s.end() |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| h | e | l | l | o |
#include <string>
int main(){
std::string s = "hello";
return 0;
}| [ ] | 取出/修改其中的字元 | s[0] | h |
| size() | 回傳字串長度 | s.size() | 5 |
| empty() | 判斷是否為空 | s.empty() | 0 |
| insert() | 插入字串 | s.insert(0,"ko") | kohello |
| erase() | 清除字串 | s.erase(s.begin()+2, s.end()) | he |
| find() | 回傳字串位置 | s.find("ll") | 2 |
#include <string>
int main(){
std::string s = "hello";
return 0;
}String常用語法
遞迴
Recursion
Dynamic Programming
將已計算過的放在陣列裡(像做筆記)
long long f[100000];
long long factorial(long long N){
f[0] = 0;
f[1] = 1;
for (int i=2; i<=N; ++i){
f[i] = f[i-1] * i;
}
return f[N];
}| 0 | 1! | 2! | 3! | 4! |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 6 | 24 |
Tower of Hanoi
河內塔
void hanoi(int from, int to, int temp, int n)
{
if(n==1){
cout<<"Ring "<<n<<" from "<<from<<" to "<<to<<'\n';
return;
}
hanoi(from,temp,to,n-1);
cout<<"Ring "<<n<<" from "<<from<<" to "<<to<<'\n';
hanoi(temp,to,from,n-1);
}
//hanoi( 1 , 3 , 2 , n個環)Sort
SelectSort
選擇排序法
BubbleSort
泡沫排序法
InsertSort
插入排序法
把每個元素放在正確的位置
先把最大/最小的值放到末端
取出未比較的元素插入已比較過的元素當中
0
1
2
3
4
0
1
2
3
4
0
1
2
3
4
0
1
2
3
4
SelectSort
BubbleSort
0
1
2
3
4
0
1
2
3
4
0
1
2
3
4
0
1
2
3
4
0
1
2
3
4
....
0
1
2
3
4
InsertSort
0
1
2
3
4
0
1
2
3
4
0
1
2
3
4
0
1
2
3
4
0
1
2
3
4
0
1
2
3
4
由小排到大
程式:
int main()
{
int arr[5] = {4,1,3,0,2};
for(int i=0;i<4;i++){
for(int j=0;j<4-i;j++){
if(arr[j]>arr[j+1]){
swap(arr[j],arr[j+1]);
}
}
}
for(int i=0;i<5;i++){
cout << arr[i] << " ";
}
return 0;
}
SelectSort
BubbleSort
InsertSort
int main()
{
int arr[5] = {4,1,3,0,2};
for(int i=0;i<5;i++){
int small=arr[i], select=i;
for(int j=i;j<5;j++){
if(arr[j]<small){
small=arr[j];
select=j;
}
}
swap(arr[i],arr[select]);
}
for(int i=0;i<5;i++){
cout << arr[i] << " ";
}
return 0;
}int main()
{
int arr[10] = {4,1,3,0,2};
for(int i=1;i<5;i++){
int k=arr[i], j=i-1;
while(j>=0 && arr[j] > k){
swap(arr[j],arr[j+1]);
j--;
}
}
for(int i=0;i<5;i++){
cout << arr[i] << " ";
}
return 0;
}MergeSort
合併排序法
先把所有元素分割成兩兩一組後各自排列,接著相鄰組別比較後合併成一組,直至剩下一組
0
1
2
3
4
0
1
2
3
4
1
4
0
3
2
1
4
0
3
2
0
1
2
3
4
程式:
int arr[5]={4,1,3,0,2};
void mergeSort(int arr[],int begin,int end){
if(begin+1>=end){
return;
}
int mid=(begin+end)/2;
mergeSort(arr,begin,mid);
mergeSort(arr,mid,end);
int wait[end-begin],j=mid,k=0;
for(int i=begin;i<mid;i++){
while(j<end && arr[j]<arr[i]){
wait[k++]=arr[j++];
}
wait[k++]=arr[i];
}
for(k=begin;k<j;k++){
arr[k]=wait[k-begin];
}
return;
}
int main()
{
mergeSort(arr,0,5);
for(int i=0;i<5;i++){
cout << arr[i] << " ";
}
return 0;
}BinarySort
二分搜
把已排序序列切一半,若相同即停止,若較大,往上尋找,反之則往下
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
找1
0
1
2
int arr[7] = {0,1,2,3,4,5,6};
int binarySort(int n){
int s = 0, e = 7, i;
do{
i = (e + s) / 2;
if(arr[i] == n){
return i;
}else if(arr[i] > n)
e = i;
else if(arr[i] < n){
s = i;
}
}while(e - s > 0);
}
int main(){
cout << binarySort(1) ;
return 0;
}
//1程式版本:
std::sort()
std::binary_search()
std::sort(迭代器的頭,迭代器的尾,升冪或降冪)std:binary_search(迭代器的頭,迭代器的尾,要尋找的數字)Vector
std::vector<型態> 名稱 (內容)//宣告.push_back(值):從後方加入
.pop_back():把最後一個刪除
.erase(迭代器頭,(迭代器尾)):消除
.insert(迭代器位置,(數量),值):插入值
向量(名稱)+
char arr[11]="chikichiki";
vector<char>k(arr,arr+10);
k.pop_back();//刪除最後的i
k.push_back('i');//加入i到最後
k.erase(k.end()-5,k.end());//刪除'chiki'
k.insert(k.begin()+3,'~');//插入'~'
int length=k.size();
for(int i=0;i<k.size();i++){
cout << k[i];
}
//chi~ki[索引值] :回傳索引指向的值
.at(索引值):搜尋索引值
.front():回傳第一個值
.back():回傳最後一個值
向量(名稱)+
char arr[]="chikichiki";
vector<char>k(arr,arr+10);
cout << k[0] << endl;
cout << k.at(0) << endl;
cout << k.front() << endl;
cout << k.back() << endl;
//c c c i.size():計算長度
.empty():是否為空
*是則輸出1
向量(名稱)+
c h i k i '\0'
.begin()
.end()
.rend()
.rbegin()
.begin() .end()
.rbegin() .rend()
向量(名稱)+
.assign(數量,值):初始化向量並放入等同於數量的值
(其他迭代器頭,其他迭代器尾):把此指定區域的值成為此 向量的初始值
.swap(其他向量):交換
.clear():清空
char arr[11]="chikichiki";
vector<char>k(arr,arr+10);
vector<char>U;
U.assign(k.begin()+3,k.end()-3);
U.swap(k);
k.clear();
if(k.empty()){
cout << 1;
}else if(U.empty()){
cout << -1;
}
//1std::vector<型態>::iterator 名稱=值//宣告char arr[11]="chikichiki";
vector<char>k(arr,arr+10);
for(vector<char>::iterator i=k.begin();i!=k.end();i++){
cout << *i;
}
//chikichikiAP325
優化輸入輸出之速度
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
//萬用標頭檔
using namespace std;
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
//優化cin/cout速度
// 其餘程式碼
return 0;
}BIG O
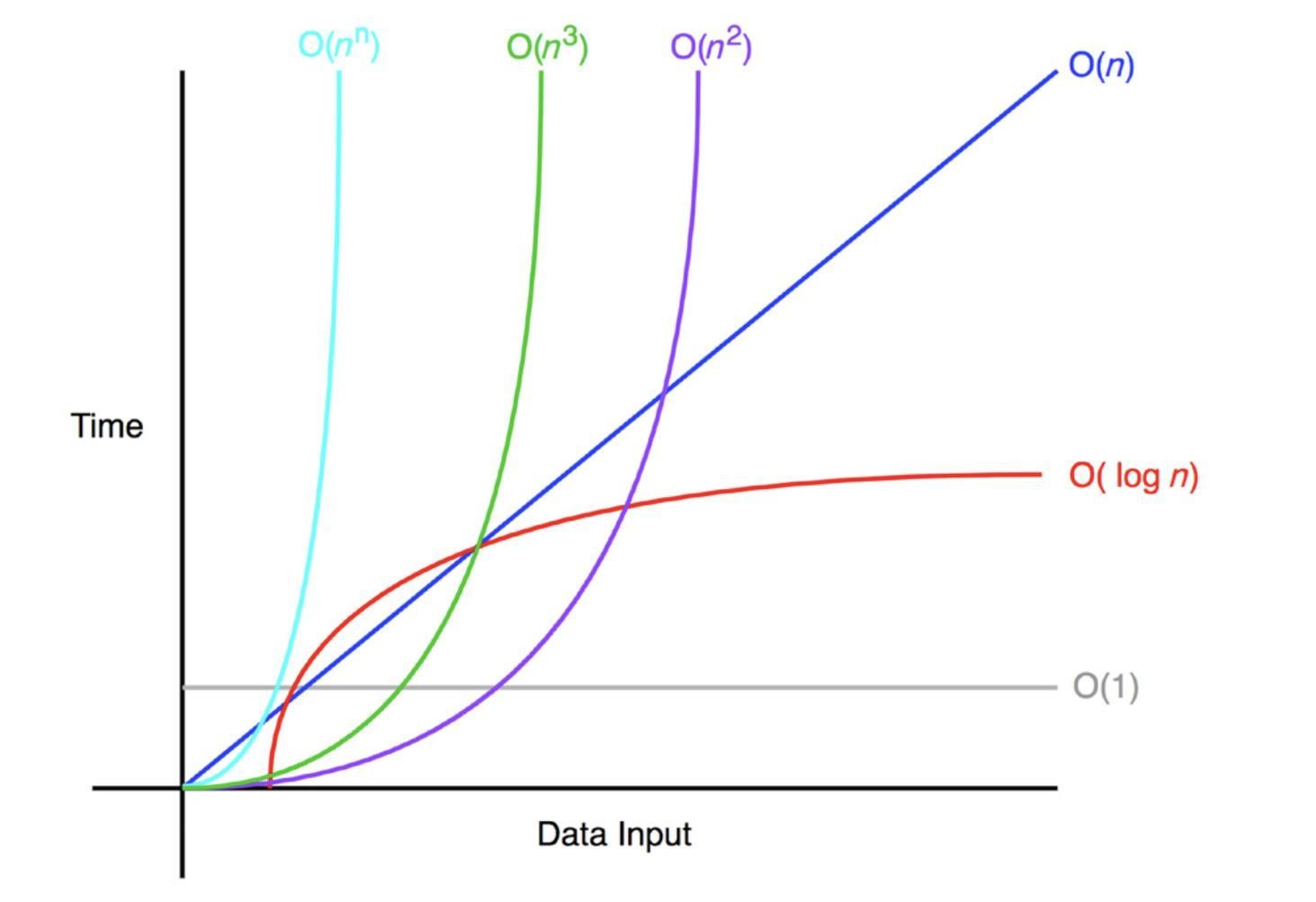
O(f(n))
- 不計算常數倍數 like:O(2n), O(4n)
- 兩函式相加時看大的 O(f(n)+g(n)) if f(n)>g(n), 則O(f(n)+g(n))==O(f(n))
- 若O(f(n))執行g(n)次, 則速度為O(f(n)*g(n))
- 一般的複雜度指的是WORST-CASE 複雜
//O(1)
char a[100];
std::cin >> a;
std::cout << a;
//O(n)
int n;
char a[100];
std::cin >> n >> a;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
std::cout << a[i];
//O(log(n))
int a = 2, arr[5] = {2, 5, 7, 9, 25};
int s = 0, e = 4, i;
do{
i = (e + s) / 2;
if(arr[i] == a){
std::cout << "find it at " << i << ".\n";
break;
}else if(arr[i] > a)
e = i;
else
s = i;
}while(e - s > 0);
std::cout << "end";需要注意的地方
Attention!
-
整數溢位
- 可用long long解決
- 可用取餘數解決
-
判斷式短路求值
-
編譯器優化
while(i < 5 && a[i] != 0)
//&&若前面條件已不符合,則直接回傳false
for(int i = 0, len = a.size(); i < len; i++)
//這樣就不用每跑一次迴圈,取一次大小了Stack & Queue
堆疊與佇列
Stack & Queue
- 一種容器
Stack(堆疊)
Queue(佇列)
LIFO(last-in-first-out)
FIFO(first-in-first-out)
Stack & Queue
S
Q
S.push(t)
t
S.pop()
S.top()
n
Q.push(n)
Q.pop()
Q.front()
是否為空?
S.empty()
Q.empty()
Stack
Queue
輸入與輸出
#include <iostream>
#include <stack>
//#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
stack<int> S;
int n,put;
cin>>n;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
cin>>put;
S.push(put);
}
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
cout<<S.top()<<endl;
S.pop();
}
return 0;
}#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
//#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
queue<int> Q;
int n,put;
cin>>n;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
cin>>put;
Q.push(put);
}
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
cout<<Q.front()<<endl;
Q.pop();
}
return 0;
}Priority _queue
優先佇列
Priority_queue
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
//宣告:priority_queue<型態> 名稱;
priority_queue<int> pq;
//放入t的值:pq.push(t);
int t=1;
pq.push(t);
pq.push(3);
cout<<pq.top()<<endl;//輸出最上層的值
pq.pop();//刪除最上層的值
cout<<pq.top()<<endl;
return 0;
}
//3
//1- 會將內容物由大到小排列
- 英文先比字母順序再比字母數
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
priority_queue<string> pq;
pq.push("abc");
pq.push("abcd");
pq.push("acbd");
pq.push("adc");
for(int i=0;i<4;i++){
cout<<pq.top()<<" ";
pq.pop();
}
return 0;
}
//adc acbd abcd abcGreedy Algorithm
貪心演算法
- 由大開始選數值
- 不適用於所有情況
Structure
結構
Structure
- 一種可以在裡面放不同型態的變數的容器
- 包括函式
struct 結構名稱(可以無){
型態 名稱 = 初始值(可以無);
型態 函式名稱(型態 參數1;型態 參數2){
內容
}
...
};(記得要加這很重要)struct 結構名稱{
...
}結構變數名稱1,名稱2...;
struct 結構名稱{
....
};
結構名稱 變數名稱;//可事先賦值//如何賦值
結構變數名稱.成員=值;
//如何取值
變數=結構變數名稱.成員;
//宣告一個指標變數
結構名稱 *指標變數名稱 = new 結構名稱;
//後面記得delete他
//將指標用在結構理
(*指標結構變數名稱).成員 = 值;
指標結構變數名稱->成員 = 值;#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct jujutsu{
string a;
string b;
void say(){
cout<<a<<" "<<b;
}
};
int main(){
jujutsu *ryouikitennkai = new jujutsu;
if(ryouikitennkai==NULL){
return -1;
}
(*ryouikitennkai).a="muryoukuusyo";
ryouikitennkai->b="fukumamizushi";
ryouikitennkai->say();
delete ryouikitennkai;
return 0;
}
//muryoukuusyo fukumamizushi舉例
Object Oriented Programming
物件導向
Class(類別)
- 可能包含資料(data),屬性(attribute),與處理的方法(method)
Object(物件)
- 為類別的實例
- 獨立存在
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class SPYxFAMILY{
public: string Name;
public: int Strength;
public: int Intelligence;
public:
void information(){
cout<<"Name: "<<Name<<" Strength: "<<Strength<<" Intelligence: "<<Intelligence<<endl;
}
};
int main(){
SPYxFAMILY *Anya = new SPYxFAMILY;
SPYxFAMILY *Loid = new SPYxFAMILY;
SPYxFAMILY *Yor = new SPYxFAMILY;
Anya->Name="Anya";
Anya->Strength=20;
Anya->Intelligence=10;
Loid->Name="Loid";
Loid->Strength=70;
Loid->Intelligence=100;
Yor->Name="Yor";
Yor->Strength=100;
Yor->Intelligence=20;
Anya->information();
Loid->information();
Yor->information();
delete Anya;
delete Loid;
delete Yor;
return 0;
}
//Name: Anya Strength: 20 Intelligence: 10
//Name: Loid Strength: 70 Intelligence: 100
//Name: Yor Strength: 100 Intelligence: 20三大特性
- 封裝(Encapsulation)
- 繼承(Inheritance)
- 多型(Polymorphism)
Class VS Structure
| Class | Structure |
|---|---|
| 成員預設是private | 成員預設為public |
| reference(參考)類型的資料型態 | value(價值)類型的資料型態 |
| 用class為關鍵字宣告 | 用struct為關鍵字宣告 |
封裝Encapsulation
- 把物質內部的資料隱藏只能透過物質本身提供的介紹了解其內部資料
繼承Inheritance
- 許可權
| public | protected | private | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 可被繼承 | O | O | X |
| 存取權 | 大家都有 | 僅限子類別 | X |
Example
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
struct parent{
private:
void papri(){
cout << "This is parent's private.\n";
}
protected:
void papro(){
cout << "This is parent's protected.\n";
}
public:
void papub(){
cout << "This is parent's public.\n";
}
};
struct child : parent{
private:
void chpri(){
//papri();
cout << "This is child's private.\n";
}
protected:
void chpro(){
papro();
cout << "This is child's protected.\n";
}
public:
void chpub(){
papub();
cout << "This is child's public.\n";
}
};
int main(){
parent A;
child B;
//A.papri();
//A.papro();
A.papub();
//B.chpri();
//B.chpro();
B.papub();
B.chpub();
return 0;
}
//This is parent's public.
//This is parent's public.
//This is parent's public.
//This is child's public.- 同個類型內同名的方法,參數不同,可依參數之類型選擇
多型Polymorphism
多載
複寫
- 當子類別中有與父類別名稱相同的方法,子類別會覆蓋他
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct anime{
void character(string a,string b){
cout<<"My favorite character in Haikyu is "<<a<<", and second is "<<b<<"\n";
}
void character(string a,string b,string c){
cout<<"My favorite characters in MHA are "<<a<<", "<<b<<", "<<c<<"\n";
}
};
struct child : anime{
void character(){
cout<<"I love Bakugo, Bakugo is true love!!"<<"\n";
}
};
int main(){
anime haikyuMHA;
child mylove;
haikyuMHA.character("Tsuki","Kuroo");
haikyuMHA.character("Bakugo","Shoto","Denki");
mylove.character();
return 0;
}
//My favorite character in Haikyu is Tsuki, and second is Kuroo
//My favorite characters in MHA are Bakugo, Shoto, Denki
//I love Bakugo, Bakugo is true love!Constructor & Destructor
建構式與解構式
建構式
struct 名稱{
public:
名稱(){ //建構式
...
}
~名稱(){ //解構式
...
}
...
};- 進行物件初始化的成員函式
解構式
- 比建構式多一個~
- 幫建構式擦屁股(like釋放動態配置的記憶體)
- 不具參數
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
struct phy{
public:
int *score;
char *level;
phy(){
score = new int;
level = new char;
cout << "created"<<endl;
}
~phy(){
delete score;
delete level;
cout << "deleted\n";
}
};
int main(){
phy sad;
*sad.score = 63;
*sad.level = 'D';
cout << *sad.score <<" "<<*sad.level << '\n';
return 0;
}
//created
//63 D
//deletedKahooooooot!
110-2review
By problemsolvemaster_kaitochiang
110-2review
- 106



