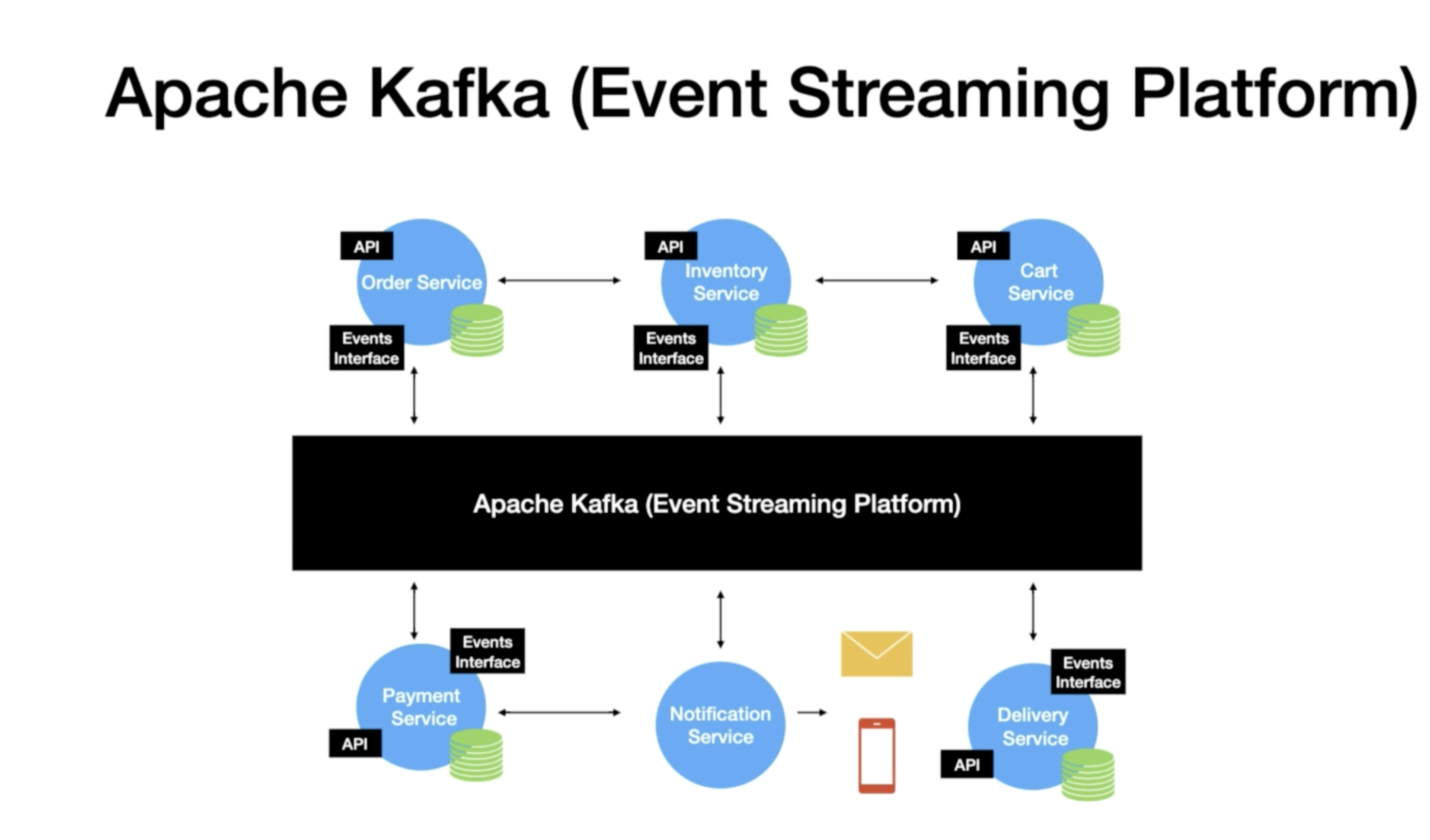
Kafka with Spring Boot
What is an Event Streaming platform ?
- Producers and Consumers Subscribe to a stream of records.
- Store stream of Events
- Analyze and Process Events as they occur
| Traditional Messaging System | Kafka Streaming Platform |
|---|---|
| Transient Message Persistence. | Stores Events based on Retention time. Events are Immutable. |
| Brokers Responsibility to keep track of consumed messages. | Consumers Responsibility to keep track of consumed messages. |
| Target a specific Consumer. | Any consumer can access message from the broker. |
| Not a distributed system. | It's a distributed streaming system. |
Kafka use cases
- Transportation
- Driver rider notifications
- Food delivery notifications
- Retail
- Sales notifications
- Real time purchase recommendations
- Tracking online order deliveries
- Banking
- Fraud transactions
- New feature/product notifications
Downloading apache kafka
- Go to https://kafka.apache.org/downloads
- Look for the recommended version of kafka.
- Go to the download link and click it.
- Once you extract zip file you will see that it has bin and config folders.
- We will use the shell scripts inside bin directory for setting up kafka.
- To change the configuration we will use server.properties file inside the config folder
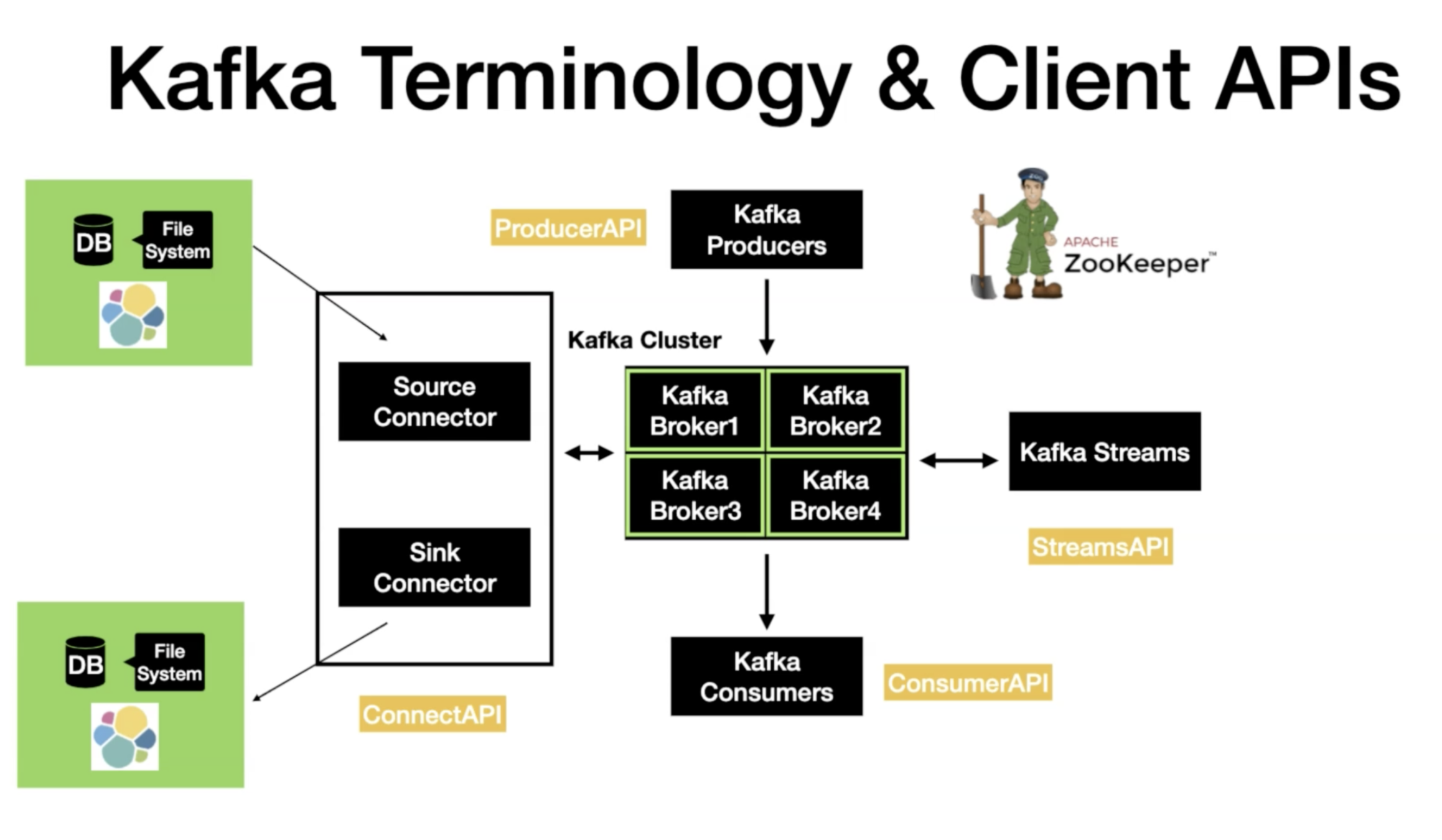
Kafka Topics
- Topic is an Entity in Kafka with a name.
- Even if a record is read by the Consumer the message reside inside the kafka for the defined retention time.
Kafka Producer
Kafka Consumer
Topic A
Sends to Topic A
Poll Topic A
Topics and Partitions
- Partition is where message lives inside the topic.
- Each topic will be creates with one or more partitions.
- Each partition is ordered immutable sequence of record.
- Each record is assigned a sequential number called offset.
- Each partition is independent of each other.
- Ordering is guaranteed only at the partition level.
- Partition continuously grow as new records are produced.
- All the records are persisted in a commit log in the file system where kafka is installed.
Setting up Zookeeper and kafka broker
- Start up the Zookeeper: inside bin directory run the command below
- Add the below properties in the server.properties file inside config folder of kafka
- Start up kafka broke
./zookeeper-server-start.sh ../config/zookeeper.propertieslisteners=PLAINTEXT://localhost:9092
auto.create.topics.enable=false./kafka-server-start.sh ../config/server.properties-
How to create a topic ?
./kafka-topics.sh --create --topic test-topic -zookeeper localhost:2181
--replication-factor 1
--partitions 4-
How to instantiate a Console Producer ?
./kafka-console-producer.sh --broker-list localhost:9092 --topic test-topic-
How to instantiate a Console Consumer?
./kafka-console-consumer.sh --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --topic test-topic
--from-beginningNote : If we do not specify --from-beginning then our consumer will fetch only new messages and not the once which already exists in kafka
Kafka Messages
- Kafka messages send from consumer has 2 properties:
- Key (Optional)
- Value (Mandatory)
- If we do not send key with Kafka message than Kafka partitioner will distribute the messages to all the partitions in round robin manner.
- If we pass a key with a message than Kafka partitioner will generate a hash for the key and place messages with same key in same partition.
-
How to instantiate a Console Producer?
Key separator parameter is used to provide delimiter which separates the key from value and parse.key property is used to print the key on the console
-
How to instantiate a Console Consumer?
./kafka-console-producer.sh --broker-list localhost:9092 --topic test-topic
--property "key.separator=-"
--property "parse.key=true"./kafka-console-consumer.sh --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --topic test-topic
--from-beginning
--property "key.separator=-"
--property "print.key=true"Consumer Offset
- Consumer have three options to read
- from-beginning
- latest
- specific offset (This option can only be done programatically)
- Consumer offset is stored inside an internal topic which is automatically created by broker called __consumer_offset.
- Consumer offset behaves like a bookmark for the consumers to start reading messages from the point it left off.
- List the topics inside a cluster and you can see -__consumer_offset topic.
./kafka-topics.sh --zookeeper localhost:2181 --listConsumer Group
- Consumer groups are used for scalable message consumption.
- Different applications will need to have a unique consumer group.
- Who manages consumer group ?
- Kafka broker manages the consumer group
- In case if the producer is producing messages at a very fast rate than it might be possible that producer may over overwhelm consumer.
Partition1
Partition4
Partition3
Partition2
Producer
Consumer A
group.id=group1
- We can increase the consumers distribute the partitions among the consumers in case one cosumer is overwhelm.
Partition1
Partition4
Partition3
Partition2
Consumer A
Consumer A
group.id=group1
group.id=group1
- Spin up a consumer
- View the consumer groups ?
- the output of the command will be in the format console-consumer-<some-number> e.g console-consumer-39300
-
Now spin up another consumer with the same group
- Now spin up a producer
- Now if you produce messages you will observe that messages are read by both the consumers from kafka
./kafka-console-consumer.sh --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --topic test-topic./kafka-consumer-groups.sh --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --list./kafka-console-consumer.sh --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --topic test-topic
--group console-consumer-39300./kafka-console-producer.sh --broker-list localhost:9092 --topic test-topic Commit Log
- When producer sends the message to the topic the very thing that happens is that the message is stored in the file system.
- The file system is where the Kafka broker is installed.
- The record is always stored in the file system as bytes.
- The file system where the files needs to be written is configured using the log.dir=/tmp/kafka-logs property. This property is stored in the server.properties file.
- It creates the file with the extension of .log.
- Each partition has its own log file.
- Consumer can only see the messages which are recorded in the log file.
- Use the following command to view the logs of one of the partition of test-topic:
./kafka-run-class.sh kafka.tools.DumpLogSegments --deep-iteration
--files /tmp/kafka-logs/test-topic-0/00000000000000000000.logRetention Policy
- Determines how long the message is retained.
- Configured using the property log.retention.hours in server.properties file.
- Default retention period is 168 hours.
Kafka as a distributed system
- Apache Kafka is a distributed streaming platform.
- Distributed systems are a collection of system working together to deliver a value.
- Characteristics of a distributed system:
- Availability and fault tolerance
- Reliable work distribution
- Easily scalable
Producer 1
Producer 5
Producer 4
Producer 3
Producer 2
Consumer 1
Consumer 5
Consumer 4
Consumer 3
Consumer 2
Broker
Producer 1
Producer 6
Producer 5
Producer 4
Producer 3
Producer 2
Consumer 6
Consumer 5
Consumer 4
Consumer 3
Consumer 2
Consumer 1
Broker 1
Broker 2
Broker 3
- Client requests are distributed between brokers.
- Easy to scale by adding more brokers based on the need.
- Kafka handles data loss using replication.
Creating a Kafka cluster
- We have create one broker already. Now we will make 2 copies of the server.properties file which is inside config folder and will name it server-1.properties and server-2.properties.
-
Configuration changes in server-1.properties
-
listeners=PLAINTEXT://localhost:9093
-
auto.create.topics.enable=false
-
log.dirs=/tmp/kafka-logs-1
-
broker.id=1
-
- Configuration changes in server-2.properties
-
listeners=PLAINTEXT://localhost:9094
-
auto.create.topics.enable=false
-
log.dirs=/tmp/kafka-logs-2
-
broker.id=2
-
- Spin up Kafka broker with server-1.properties file
- Spin up Kafka broker with server-2.properties file
- Create a new topic
- Create a producer for the topic
- Create a consumer for the topic
./kafka-server-start.sh ../config/server-1.properties./kafka-server-start.sh ../config/server-2.properties ./kafka-topics.sh --create --topic test-topic-replicated -zookeeper localhost:2181
--replication-factor 3 --partitions 3./kafka-console-producer.sh --broker-list localhost:9094 --topic test-topic-replicated./kafka-console-consumer.sh --bootstrap-server localhost:9094 --topic test-topic-replicated
--from-beginning- Get details of a topic
- Bring one broker down and run the describe command again
./kafka-topics.sh --zookeeper localhost:2181 --describe --topic test-topic-replicatedExercise 1
- Spin up zookeeper and kafka broker.
- Create a topic, produce and consumer message from topic.
- Create a topic, produce and consumer message from topics using keys with messages.
- Create a kafka cluster with 3 brokers
- Create a kafka topic with 3 partitions
- Produce and consume messages for the topic which you have created for the cluster
- Bring one of the cluster down and run describe topic command to see its impact.
Set up Spring Boot application for kafka Producer
- Go to https://start.spring.io/ and add the following dependencies in the project
- Spring for Apache Kafka
- Lombok
- Spring Web
- Choose gradle project option for build tool
- Download the zip file extract it an import it in intellij idea.
In the application.properties mention the following properties
spring.kafka.producer.bootstrap-servers=localhost:9092,localhost:9093,localhost:9094
spring.kafka.template.default-topic=library-events
spring.kafka.producer.key-serializer=org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.IntegerSerializer
spring.kafka.producer.value-serializer=org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringSerializer
spring.kafka.admin.properties.bootstrap.servers=localhost:9092,localhost:9093,localhost:9094
Note : Please make sure that your zookeeper and brokers are up and running
Create 2 domain classes Book and Libraryevent
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Builder;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
@NoArgsConstructor
@Data
@Builder
@AllArgsConstructor
public class Book {
private Integer bookId;
private String bookName;
private String bookAuthor;
}
package com.springkafkademo.spring.kafkaproducer.domain;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Builder;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
@Data
@Builder
public class LibraryEvent {
private Integer libraryEventId;
private Book book;
}
Creating topic via Spring boot
package com.springkafkademo.spring.kafkaproducer.config;
import org.apache.kafka.clients.admin.NewTopic;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.kafka.config.TopicBuilder;
@Configuration
public class AutoCreateConfig {
@Bean
public NewTopic libraryEvents(){
return TopicBuilder.name("library-events")
.partitions(3).replicas(3)
.build();
}
}
./kafka-topics.sh --zookeeper localhost:2181 --listUse the command below to check the created topic after running the application
Createing EventProducer
@Component
@Slf4j
public class LibraryEventProducer {
@Autowired
KafkaTemplate<Integer,String> kafkaTemplate;
@Autowired
ObjectMapper objectMapper;
String topic = "library-events";
public void sendLibraryEvent(LibraryEvent libraryEvent) throws JsonProcessingException {
Integer key = libraryEvent.getLibraryEventId();
String value = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(libraryEvent);
ListenableFuture<SendResult<Integer,String>> listenableFuture
= kafkaTemplate.sendDefault(key,value);
listenableFuture.addCallback(
new ListenableFutureCallback<SendResult<Integer, String>>() {
@Override
public void onFailure(Throwable ex) {
log.error("...Failure..."+ex);
}
@Override
public void onSuccess(SendResult<Integer, String> result) {
log.info("...onSuccess..."+result.getProducerRecord().value());
}
});}}Create a Rest API with POST request to produce the event
@RestController
public class LibraryEventController {
@Autowired
LibraryEventProducer libraryEventProducer;
@PostMapping("/v1/libraryevent")
public ResponseEntity<LibraryEvent> postLibraryEvent(@RequestBody LibraryEvent libraryEvent)
throws JsonProcessingException {
libraryEventProducer.sendLibraryEvent(libraryEvent);
return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.CREATED).body(libraryEvent);
}
}
Now run the Application and hit the following request with the help of postman
Url : localhost:8080/v1/libraryevent
RequestBody :
{
"libraryEventId":4 ,
"book":{
"bookId":3,
"bookName":"Kafka Tutorial 3",
"bookAuthor":"Venkat 3"
}
}
Approach 2 - Synchronous way of producing event
public void sendLibrarySyncEvent(LibraryEvent libraryEvent) throws JsonProcessingException {
Integer key = libraryEvent.getLibraryEventId();
String value = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(libraryEvent);
try {
SendResult<Integer,String> sendResult
= kafkaTemplate.sendDefault(key,value).get(1, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
} catch (InterruptedException | ExecutionException | TimeoutException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}Approach 3 - Produce event using ProduceRecord
public void sendLibraryEventViaProducerRecord(LibraryEvent libraryEvent)
throws JsonProcessingException {
Integer key = libraryEvent.getLibraryEventId();
String value = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(libraryEvent);
List<Header> headerList = List.of(new RecordHeader("source","scanner".getBytes()));
ProducerRecord<Integer, String> producerRecord
= new ProducerRecord<>(topic, null, key, value, headerList);
ListenableFuture<SendResult<Integer, String>> listenableFuture
= kafkaTemplate.send(producerRecord);
listenableFuture.addCallback(
new ListenableFutureCallback<SendResult<Integer, String>>() {
@Override
public void onFailure(Throwable ex) {
log.error("...Failure..." + ex);
}
@Override
public void onSuccess(SendResult<Integer, String> result) {
log.info("...onSuccess..." + result.getProducerRecord().value());
}
});
}Put request for Library Event
@PutMapping("/v1/libraryevent")
public ResponseEntity<?> putLibraryEvent(@RequestBody LibraryEvent libraryEvent)
throws JsonProcessingException {
if(Objects.isNull(libraryEvent.getLibraryEventId()) ){
return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST)
.body("Please provide the library event id");
}
libraryEvent.setLibraryEventType(LibraryEventType.UPDATE);
libraryEventProducer.sendLibraryEvent(libraryEvent);
return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.OK).body(libraryEvent);
}public enum LibraryEventType {
NEW,UPDATE
}
Exercise 2
- Create a spring boot app which auto generates a topic
-
Produce Events for the topic using ProduceRecord approach for a StudentEvent with following details:
- studentEventId
- student (studentId, studentName, studentClass)
- studentEventId
- Create a Rest API which triggers event generation.
- Run a consumer from console to consume the events for the topic.
Create Kafka Consumer using spring boot
- Go to https://start.spring.io/
- Add following dependencies for the project
- Spring for Apache Kafka
- Lombok
- Download the zip project and import it in Intellij Idea
application.properties
spring.kafka.producer.bootstrap-servers=localhost:9092,localhost:9093,localhost:9094
spring.kafka.consumer.key-serializer=org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.IntegerSerializer
spring.kafka.consumer.value-serializer=org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringSerializer
spring.kafka.consumer.group-id=library-events-listener-group
server.port=8081
Might need to add following dependencies in build.gradle
implementation 'com.fasterxml.jackson.core:jackson-databind:2.10.0'
implementation 'com.fasterxml.jackson.core:jackson-core:2.10.0'Enable Kafka
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableKafka
public class KafkaConsumerApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(KafkaConsumerApplication.class, args);
}
}Create Library Event Consumer
package com.springkafkademo.kafkaconsumer.consumer;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.apache.kafka.clients.consumer.ConsumerRecord;
import org.springframework.kafka.annotation.KafkaListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@Slf4j
public class LibraryEventConsumer {
@KafkaListener(topics = {"library-events"})
public void onMessage(ConsumerRecord<Integer,String> consumerRecord){
log.info("Consumer Record :: {}",consumerRecord);
}
}
Rebalancing with Consumer groups
- Consumer groups : Multiple instances of same application with same group id.
- Consumer groups are the foundation of scalable message consumption.
- Rebalancing : Changing the partition ownership from one consumer to another.
- Group coordinator triggers rebalancing when new consumers are added to the consumer group.
- Try to run multiple instances of the Consumer app and on producing events you will observe that the partitions are divided among consumers.
Manual Consumer Offset Management
- We need to override the bean
kafkaListenerContainerFactory which is inside KafkaAnnotationDrivenConfiguration.java
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(name = "kafkaListenerContainerFactory")
ConcurrentKafkaListenerContainerFactory<?, ?> kafkaListenerContainerFactory(
ConcurrentKafkaListenerContainerFactoryConfigurer configurer,
ObjectProvider<ConsumerFactory<Object, Object>> kafkaConsumerFactory) {
ConcurrentKafkaListenerContainerFactory<Object, Object> factory =
new ConcurrentKafkaListenerContainerFactory<>();
configurer.configure(factory,kafkaConsumerFactory.getIfAvailable());
factory.getContainerProperties().setAckMode(ContainerProperties.AckMode.MANUAL);
return factory;
}import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.apache.kafka.clients.consumer.ConsumerRecord;
import org.springframework.kafka.annotation.KafkaListener;
import org.springframework.kafka.listener.AcknowledgingMessageListener;
import org.springframework.kafka.support.Acknowledgment;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@Slf4j
public class LibraryEventConsumerOffsetManual
implements AcknowledgingMessageListener<Integer,String> {
@Override
@KafkaListener(topics = {"library-events"})
public void onMessage(ConsumerRecord<Integer, String> data, Acknowledgment acknowledgment) {
log.info("Consumer : {}",data);
acknowledgment.acknowledge();
}
}
If we do not mention the acknowledge statement then every time we spin up our Consumer it will start reading messages from the beginning
Concurrent Consumers
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(name = "kafkaListenerContainerFactory")
ConcurrentKafkaListenerContainerFactory<?, ?> kafkaListenerContainerFactory(
ConcurrentKafkaListenerContainerFactoryConfigurer configurer,
ObjectProvider<ConsumerFactory<Object, Object>> kafkaConsumerFactory) {
ConcurrentKafkaListenerContainerFactory<Object, Object> factory =
new ConcurrentKafkaListenerContainerFactory<>();
configurer.configure(factory,kafkaConsumerFactory.getIfAvailable());
factory.setConcurrency(3);
return factory;
}In the above code we have set Concurrency level to 3 so Consumer will create 3 thread to consume the events and partitions will be distributed among the threads
Custom error handling
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(name = "kafkaListenerContainerFactory")
ConcurrentKafkaListenerContainerFactory<?, ?> kafkaListenerContainerFactory(
ConcurrentKafkaListenerContainerFactoryConfigurer configurer,
ObjectProvider<ConsumerFactory<Object, Object>> kafkaConsumerFactory) {
ConcurrentKafkaListenerContainerFactory<Object, Object> factory = new ConcurrentKafkaListenerContainerFactory<>();
configurer.configure(factory,kafkaConsumerFactory.getIfAvailable());
factory.getContainerProperties().setAckMode(ContainerProperties.AckMode.MANUAL);
factory.setConcurrency(3);
factory.setErrorHandler((exception,data)->{
log.info("exception : {} data : {}",exception,data);
});
return factory;
}We can use setErrorHandler method to handle the situation where an exception has been generated while reading the record
import com.fasterxml.jackson.core.type.TypeReference;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.apache.kafka.clients.consumer.ConsumerRecord;
import org.springframework.kafka.annotation.KafkaListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.HashMap;
@Component
@Slf4j
public class LibraryEventConsumer {
ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
@KafkaListener(topics = {"library-events"})
public void onMessage(ConsumerRecord<Integer,String> consumerRecord){
log.info("Consumer Record :: {}",consumerRecord);
TypeReference<HashMap<String,Object>> typeRef
= new TypeReference<HashMap<String,Object>>() {};
try {
HashMap<String,Object> map= objectMapper.readValue(consumerRecord.value().getBytes(),typeRef);
Integer id=(Integer)map.get("libraryEventId");
if(id<0){
throw new IllegalArgumentException("id cannot be less than 0");
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
Throw a Runtime exception for negative id of library event
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(name = "kafkaListenerContainerFactory")
ConcurrentKafkaListenerContainerFactory<?, ?> kafkaListenerContainerFactory(
ConcurrentKafkaListenerContainerFactoryConfigurer configurer,
ObjectProvider<ConsumerFactory<Object, Object>> kafkaConsumerFactory) {
ConcurrentKafkaListenerContainerFactory<Object, Object> factory = new ConcurrentKafkaListenerContainerFactory<>();
configurer.configure(factory,kafkaConsumerFactory.getIfAvailable());
factory.setConcurrency(3);
factory.setErrorHandler((exception,data)->{
log.info("exception : {} data : {}",exception,data);
});
factory.setRetryTemplate(retryTemplate());
return factory;
}
RetryTemplate retryTemplate(){
RetryTemplate retryTemplate = new RetryTemplate();
retryTemplate.setRetryPolicy(retryPolicy());
FixedBackOffPolicy fixedBackOffPolicy = new FixedBackOffPolicy();
fixedBackOffPolicy.setBackOffPeriod(1000);
retryTemplate.setBackOffPolicy(fixedBackOffPolicy);
return retryTemplate;
}
RetryPolicy retryPolicy(){
SimpleRetryPolicy simpleRetryPolicy = new SimpleRetryPolicy();
simpleRetryPolicy.setMaxAttempts(3);
return simpleRetryPolicy;
}Configuring retry mechanism
Retrying for particular exception
RetryPolicy retryPolicy(){
Map<Class<? extends Throwable>,Boolean> exceptionMap=new HashMap();
exceptionMap.put(IllegalArgumentException.class,true);
SimpleRetryPolicy simpleRetryPolicy = new SimpleRetryPolicy(3,exceptionMap,true);
return simpleRetryPolicy;
}Recovering from exception
factory.setRecoveryCallback(context -> {
if(context.getLastThrowable().getCause() instanceof IllegalArgumentException){
log.info("This is recoverable exception");
ConsumerRecord<Integer,String> consumerRecord = (ConsumerRecord<Integer, String>)context.getAttribute("record");
log.info("Recoverable Record : {}",consumerRecord);
}else{
log.info("This is non recoverable exception");
}
return null;
});Exercise 3
- Create a Spring boot App which consumes the Events for the topic StudentEvent.
- Split the event distribution among multiple consumer by using the same groupId.
- Acknowledge consumed events manually.
- Run concurrent consumers
- Implement Custom error handling and Retry mechanism fro Consumer.

Kafka with Spring Boot
By Pulkit Pushkarna
Kafka with Spring Boot
- 1,359



