RAG Benchmarking
Input
Data
Data processing
Embedding
Vector db
Output
Question
Fetch context
Prompt
LLM
Input
Data processing
Embedding
Vector db
Output
Fetch context
Prompt
LLM
How does it affect RAG?
Input
Data processing
Embedding
Vector db
Output
Context fetch
Prompt
LLM
Splitting method, chunk size, overlap, appending title
Embedding model, dimensions, sparse vectors
Metric, search type
Model, quantization level
Prompt size, prompt template (order, multi step)
Similarity threshold, top k, reranking
Example
Data: Particle network
Question: What is error 40101 in particle network?
We only change the embedding model.
Same input data, same vector dimensions but 3 different OpenAI embedding models
Example - returned sections
large

small

ada

Answer to the question
Some other error
Some other error
Not relevant
Many many different RAG approaches
Simple - Add surrounding context


Complicated - Create "synthetic" answer -> retrieve context
How to benchmark RAG?
Manually - A/B testing by us or users
Automatically - using combination of embeddings and LLMs
Evaluation framework for your Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) pipelines
RAGAS
Query types
- Single-hop query
- Multi-hop query
- Specific
- Abstract
Query types
Single-hop
Specific
Abstract
Multi-hop
What is the default port number for HTTP?
If a TCP connection fails to establish, what are possible causes, and which protocol helps diagnose such issues?
Why is HTTP considered a stateless protocol?
How has the evolution of IPv6 addressed scalability challenges in modern networks?
Knowledge graph
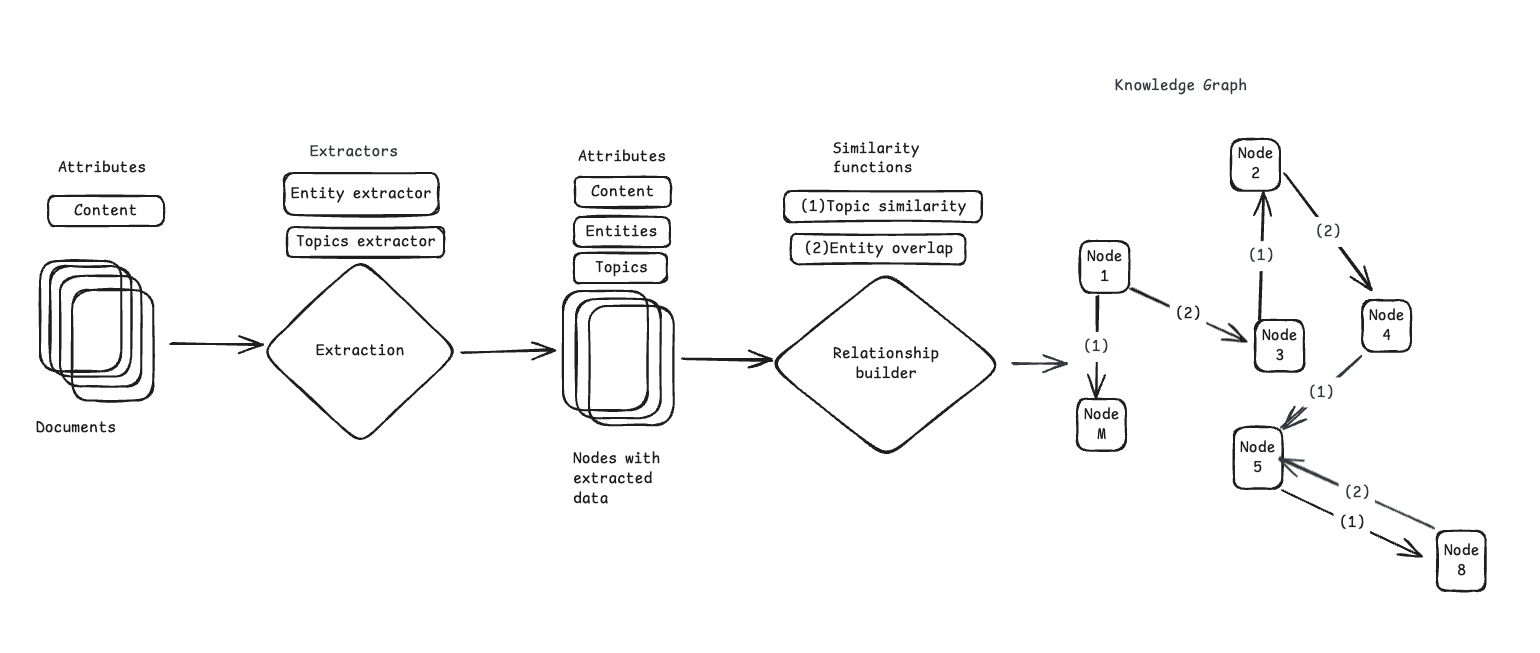
Scenario generation
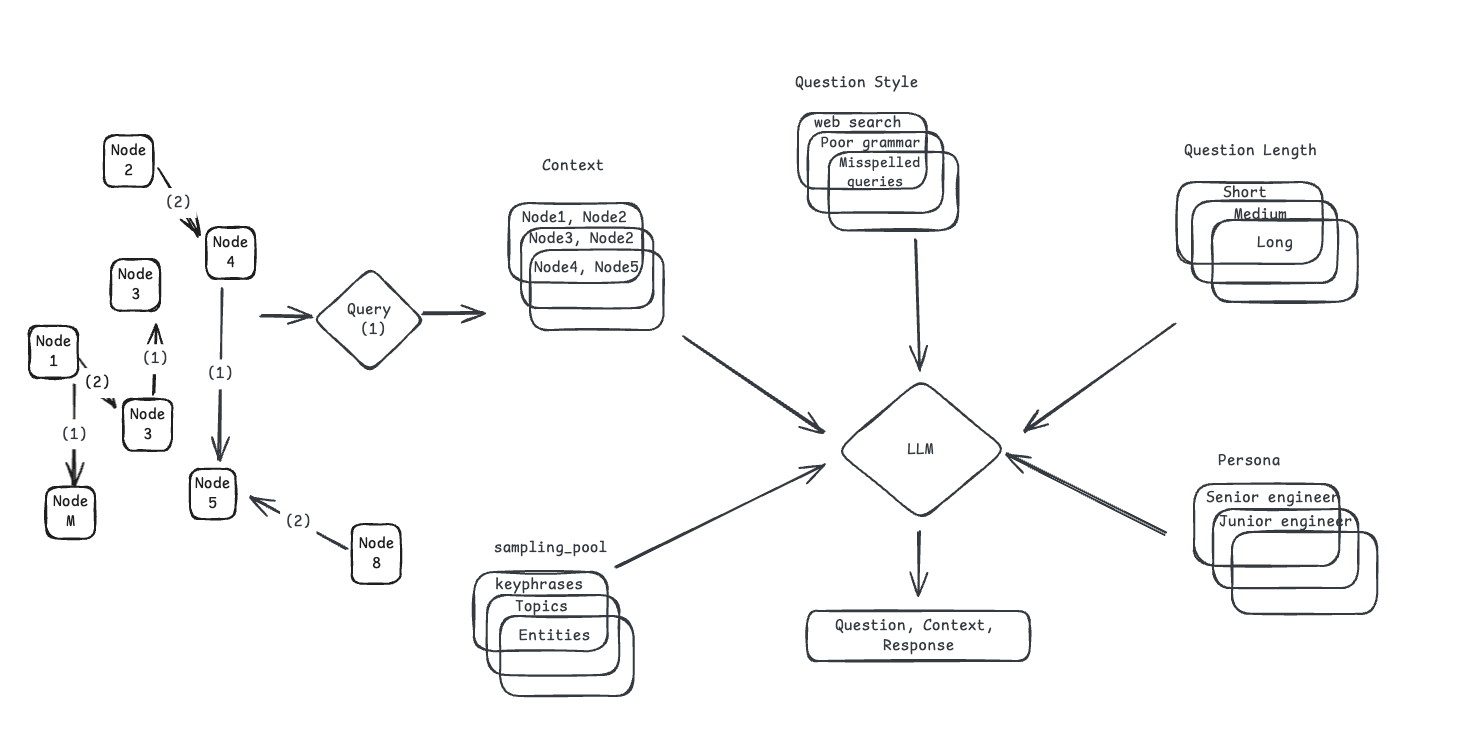
Scenario generation
Each Scenario has:
- Data/Knowledge nodes
- Persona (eg, Senior Engineer, Junior Engineer, etc),
- Query length (Short, Long, etc)
- Query style (Formal, Informal, etc)
Test set generation
from langchain_community.document_loaders import DirectoryLoader
from ragas.llms import LangchainLLMWrapper
from ragas.embeddings import LangchainEmbeddingsWrapper
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from langchain_openai import OpenAIEmbeddings
from ragas.testset import TestsetGenerator
path = "Sample_Docs_Markdown/"
loader = DirectoryLoader(path, glob="**/*.md")
docs = loader.load()
generator_llm = LangchainLLMWrapper(ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-4o"))
generator_embeddings = LangchainEmbeddingsWrapper(OpenAIEmbeddings())
generator = TestsetGenerator(llm=generator_llm, embedding_model=generator_embeddings)
dataset = generator.generate_with_langchain_docs(docs, testset_size=10)
Without the knowledge graph
Test set generation
kg = KnowledgeGraph()
for doc in docs:
kg.nodes.append(
Node(
type=NodeType.DOCUMENT,
properties={"page_content": doc.page_content, "document_metadata": doc.metadata}
)
)
transformer_llm = LangchainLLMWrapper(ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-4o"))
embedding_model = LangchainEmbeddingsWrapper(OpenAIEmbeddings())
transformer = default_transforms(documents=docs, llm=transformer_llm, embedding_model=embedding_model)
apply_transforms(kg, transformer)
generator = TestsetGenerator(llm=generator_llm, embedding_model=embedding_model, knowledge_graph=kg)
query_distribution = [
(SingleHopSpecificQuerySynthesizer(llm=generator_llm), 0.5),
(SingleHopAbstractQuerySynthesizer(llm=generator_llm), 0.25),
(MultiHopSpecificQuerySynthesizer(llm=generator_llm), 0.25),
]
testset = generator.generate(testset_size=10, query_distribution=query_distribution)
Adding knowledge graph
Test set generation
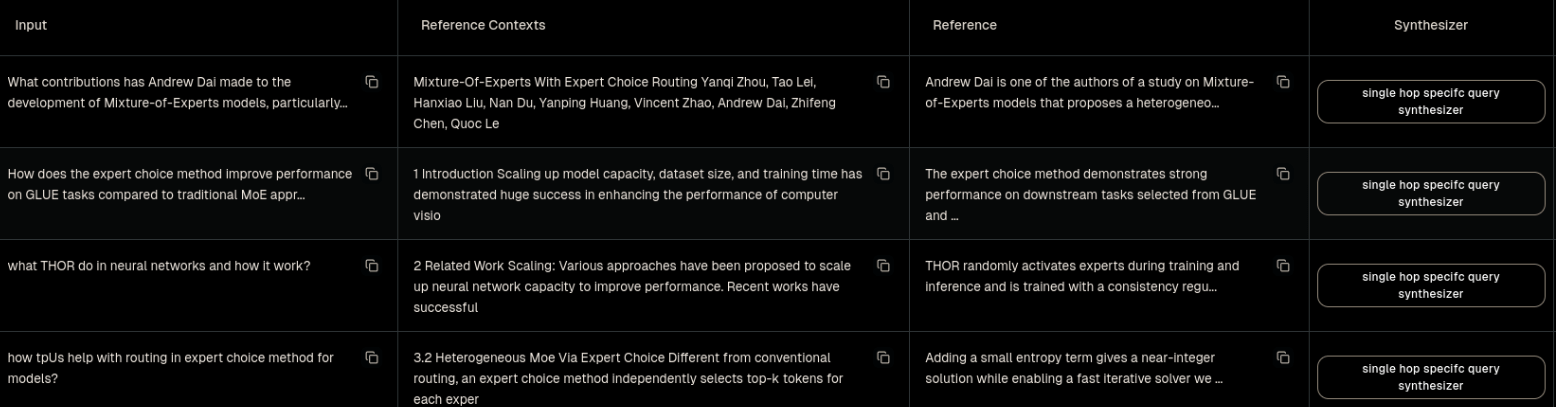
Example (previous Ragas version)
Usage:
- GPT-4o-mini: ~760k tokens input, 36k tokens output
- Embeddings: 110k tokens
- Cost: $ 0.14
- Pay attention to the language. Generated questions will be in English. (They added guide for this)
Dataset: Particle network
50 questions (simple: 0.5, reasoning: 0.25, multi_context: 0.25)
Evaluation metrics
LLM based metrics
- Faithfulness
- Answer relevance
- Context precision
- Context recall
- Context entities recall
- Answer correctness
Many different metrics available and also possible to modify or create custom metrics.
Evaluation metrics
Natural language comparison
- Answer semantic similarity
- Exact match
- String presence
- BLUE score
- String similarity
Faithfulness

Total faithfulness score is the average of this
Factual consistency of the generated answer against given context.
Example - generating statements
{
"question": "Who was Albert Einstein and what is he best known for?",
"answer": "He was a German-born theoretical physicist, widely acknowledged to be one of the greatest and most influential physicists of all time. He was best known for developing the theory of relativity, he also made important contributions to the development of the theory of quantum mechanics.",
"sentences": {
"0": "He was a German-born theoretical physicist, widely acknowledged to be one of the greatest and most influential physicists of all time.",
"1": "He was best known for developing the theory of relativity, he also made important contributions to the development of the theory of quantum mechanics."
}
}LLM input
{
"sentence_index": 0,
"simpler_statements": [
"Albert Einstein was a German-born theoretical physicist.",
"Albert Einstein is recognized as one of the greatest and most influential physicists of all time.",
],
},
{
"sentence_index": 1,
"simpler_statements": [
"Albert Einstein was best known for developing the theory of relativity.",
"Albert Einstein also made important contributions to the development of the theory of quantum mechanics.",
],
}LLM output
Example - calculating faithfulness
Context: Albert Einstein (born 14 March 1879) was a German-born theoretical physicist, widely held to be one of the greatest and most influential scientists of all time
Answer 1: Einstein was born in Germany on 14th March 1879.
Faithfulness: (1 + 1) / 2 = 1 (both facts correct)
Answer 2: Einstein was born in Germany on 20th March 1879.
Faithfulness: (1 + 0) / 2 = 0.5 (date is wrong)
Answer relevance

How relevant the generated answer is to the given prompt.
Example
Question: Where is France located?
Answer: France is located in Western Europe.
Generated questions
- “In which part of Europe is France located?”
- “What is the geographical location of France within Europe?”
- “Can you identify the region of Europe where France is situated?”
Context Precision

Evaluates whether all of the ground-truth relevant items present in the contexts are ranked higher or not. All relevant chunks should appear at the top ranks.
Example
Question: Where is France and what is it’s capital?
Ground truth: France is in Western Europe and its capital is Paris.
- “The country is also renowned for its wines and sophisticated cuisine. Lascaux’s ancient cave drawings, Lyon’s Roman theater and”,
- “France, in Western Europe, encompasses medieval cities, alpine villages and Mediterranean beaches. Paris, its capital, is famed for its fashion houses, classical art museums including the Louvre and monuments like the Eiffel Tower”
Contexts returned (low precision):
Example - calculate context precision
Precision@2 = 1/2 = 0.5
“The country is also renowned for its wines and sophisticated cuisine. Lascaux’s ancient cave drawings, Lyon’s Roman theater and”,
Precision@1 = 0/1 = 0
“France, in Western Europe, encompasses medieval cities, alpine villages and Mediterranean beaches. Paris, its capital, is famed for its fashion houses, classical art museums including the Louvre and monuments like the Eiffel Tower”
Context precision = 0.5/1 = 0.5
Context recall

Alignment between retrieved context and ground truth.
0-1, higher is better.
Context entities recall

Measure of the recall of the retrieved context, based on the number of entities present in both ground_truths and contexts relative to the number of entities present in the ground_truths alone.
Example
{
"Ground truth": "The Taj Mahal is an ivory-white marble mausoleum on the right bank of the river Yamuna in the Indian city of Agra. It was commissioned in 1631 by the Mughal emperor Shah Jahan to house the tomb of his favorite wife, Mumtaz Mahal.",
"High entity recall context": "The Taj Mahal is a symbol of love and architectural marvel located in Agra, India. It was built by the Mughal emperor Shah Jahan in memory of his beloved wife, Mumtaz Mahal. The structure is renowned for its intricate marble work and beautiful gardens surrounding it.",
"Low entity recall context": "The Taj Mahal is an iconic monument in India. It is a UNESCO World Heritage Site and attracts millions of visitors annually. The intricate carvings and stunning architecture make it a must-visit destination."
}
{
"Entities in ground truth (GE)": ["Taj Mahal", "Yamuna", "Agra", "1631", "Shah Jahan", "Mumtaz Mahal"],
"Entities in context (CE1)": ["Taj Mahal", "Agra", "Shah Jahan", "Mumtaz Mahal", "India"],
"Entities in context (CE2)": ["Taj Mahal", "UNESCO", "India"]
}
- context entity recall 1 = 4/6 = 0.67
- context entity recall 2 = 1/6 = 0.17
Answer semantic similarity

Answer correctness

Answer correctness
Factual similarity:
-
TP (True Positive): Facts that are present in both
answerand theground_truth - FP (False Positive): Facts in the
answerbut not in theground_truth - FN (False Negative): Facts present in the
ground_truthbut not in theanswer
Answer semantic similarity + factual similarity
Answer correctness

CORRECTNESS_INSTRUCTIONS = """\
Given a ground truth and an answer statements, analyze each statement and classify them in one of the following categories:
- TP (true positive): statements that are present in answer that are also directly supported by the one or more statements in ground truth,
- FP (false positive): statements present in the answer but not directly supported by any statement in ground truth,
- FN (false negative): statements found in the ground truth but not present in answer.
Each statement can only belong to one of the categories. Provide a reason for each classification.
"""Example - instructions
"question": """What powers the sun and what is its primary function?""",
"answer": [
"The sun is powered by nuclear fission, similar to nuclear reactors on Earth.",
"The primary function of the sun is to provide light to the solar system.",
],
"ground_truth": [
"The sun is powered by nuclear fusion, where hydrogen atoms fuse to form helium.",
"This fusion process in the sun's core releases a tremendous amount of energy.",
"The energy from the sun provides heat and light, which are essential for life on Earth.",
"The sun's light plays a critical role in Earth's climate system.",
"Sunlight helps to drive the weather and ocean currents.",
],Example
"TP": [
{
"statement": "The primary function of the sun is to provide light to the solar system.",
"reason": "This statement is somewhat supported by the ground truth mentioning the sun providing light and its roles, though it focuses more broadly on the sun's energy."
}
],
"FP": [
{
"statement": "The sun is powered by nuclear fission, similar to nuclear reactors on Earth.",
"reason": "This statement is incorrect and contradicts the ground truth which states that the sun is powered by nuclear fusion."
}
],
"FN": [
{
"statement": "The sun is powered by nuclear fusion, where hydrogen atoms fuse to form helium.",
"reason": "This accurate description of the sun’s power source is not included in the answer."
}
]BLEU score
- made for translation benchmarking but can be used here
- compares 2 texts - candidate and reference
- takes into account repetition and adds brevity penalty
String similarity
- Levenshtein distance, Hamming distance,...
- Character level comparison between ground truth and RAG produced answer
Running Ragas
- Data: Particle network docs
- 50 questions and ground truths generated by GPT-4o-mini (slide 13)
- Rag method: chunks using sections, OpenAI embeddings small 1536 dimensions, cosine metric
- Answers generated by GPT-4o-mini
- Rating for metrics GPT-4o-mini



Cost
| LLM in | LLM out | Embeddings | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Generating questions | 760 | 36 | 110 |
| Generating answers | 400 | 17 | 1 |
| Evaluating | 1300 | 80 | 3 |
| Total | 2460 | 133 | 114 |
Roughly, in thousands of tokens
Thanks for listening.
Questions?
RAG benchmarks
By Sasa Trivic
RAG benchmarks
- 250



