RAGAS
Evaluation framework for your Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) pipelines
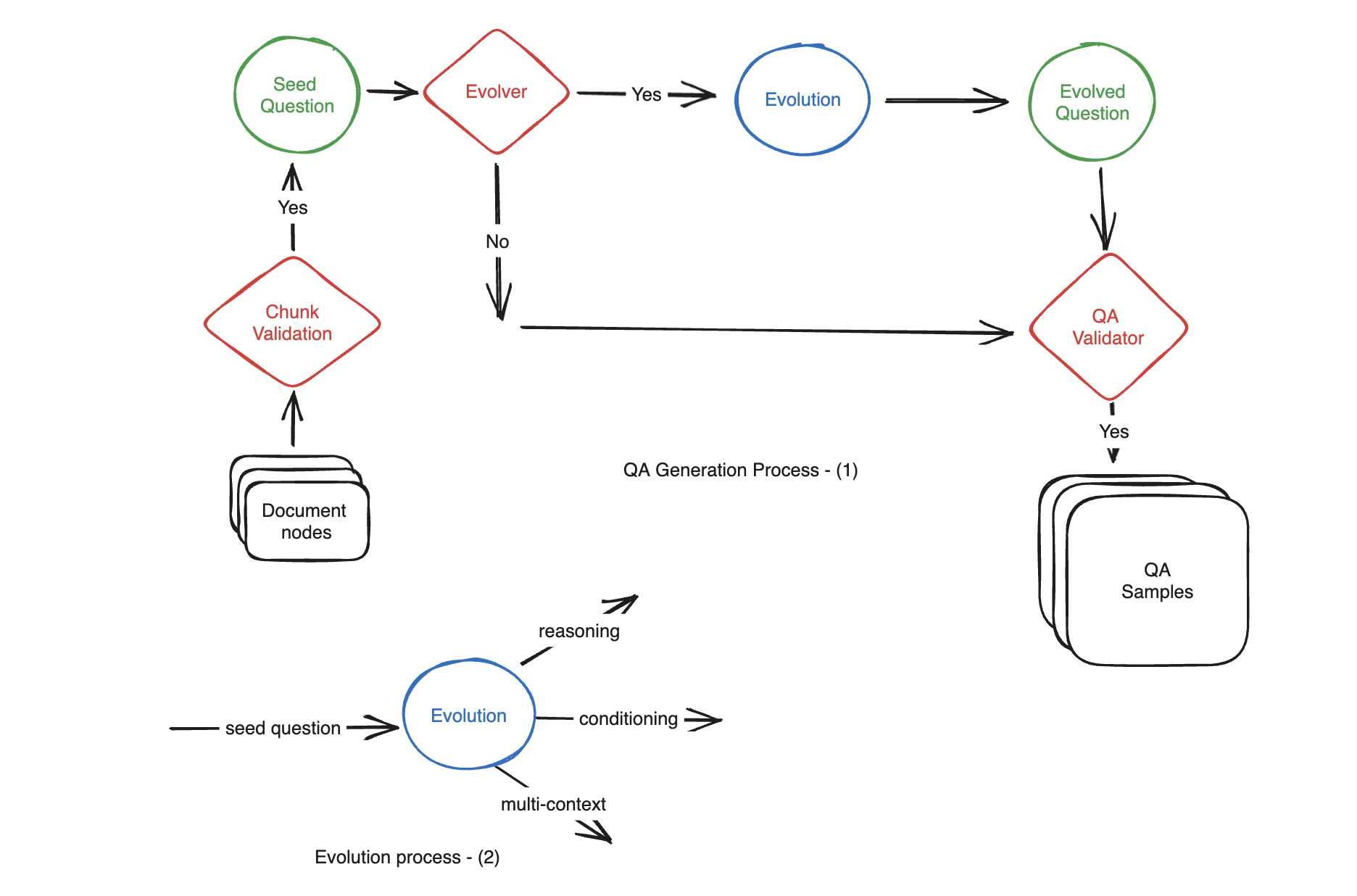
Synthetic data generation
Question types
Reasoning
prompt = """Complicate the given question by rewriting question
into a multi-hop reasoning question based on the provided context.
Answering the question should require the reader to make multiple
logical connections or inferences using the information available
in given context...."""Multi-context
prompt = """The task is to rewrite and complicate
he given question in a way that answering it requires
information derived from both context1 and context2."""Conditional
prompt = """Rewrite the provided question to increase its complexity by
introducing a conditional element. The goal is to make the question more
intricate by incorporating a scenario or condition that
affects the context of the question."""Example - question evolution
Reasoning
{
"question": "What is the capital of France?",
"context": "France is a country in Western Europe. It has several cities, including Paris, Lyon, and Marseille. Paris is not only known for its cultural landmarks like the Eiffel Tower and the Louvre Museum but also as the administrative center.",
"output": "Linking the Eiffel Tower and administrative center, which city stands as both?",
}Multi-context
{
"question": "What process turns plants green?",
"context1": "Chlorophyll is the pigment that gives plants their green color and helps them photosynthesize.",
"context2": "Photosynthesis in plants typically occurs in the leaves where chloroplasts are concentrated.",
"output": "In which plant structures does the pigment responsible for their verdancy facilitate energy production?",
}Conditional
{
"question": "What is the function of the roots of a plant?",
"context": "The roots of a plant absorb water and nutrients from the soil, anchor the plant in the ground, and store food.",
"output": "What dual purpose do plant roots serve concerning soil nutrients and stability?",
}Example
Time: 4 min 30 sec
Usage:
- GPT-3.5: 325k tokens input, 13k tokens output
- Embeddings: 7k tokens
- Cost: $ 0.18
- Pay attention to language. Questions generated will be in English.
Metrics
- Faithfulness
- Answer relevance
- Context precision
- Context relevancy - Will be deprecated
- Context recall
- Context entities recall
- Answer semantic similarity
- Answer correctness
- Aspect critique
- Summarization score
Faithfulness

Total faithfulness score is the average of this
Factual consistency of the generated answer against given context.
Example
{
"question": "Who was Albert Einstein and what is he best known for?",
"answer": "He was a German-born theoretical physicist, widely acknowledged to be one of the greatest and most influential physicists of all time. He was best known for developing the theory of relativity, he also made important contributions to the development of the theory of quantum mechanics.",
"sentences": {
"0": "He was a German-born theoretical physicist, widely acknowledged to be one of the greatest and most influential physicists of all time.",
"1": "He was best known for developing the theory of relativity, he also made important contributions to the development of the theory of quantum mechanics."
}
}LLM input
{
"sentence_index": 0,
"simpler_statements": [
"Albert Einstein was a German-born theoretical physicist.",
"Albert Einstein is recognized as one of the greatest and most influential physicists of all time.",
],
},
{
"sentence_index": 1,
"simpler_statements": [
"Albert Einstein was best known for developing the theory of relativity.",
"Albert Einstein also made important contributions to the development of the theory of quantum mechanics.",
],
}LLM output
Example
Context: Albert Einstein (born 14 March 1879) was a German-born theoretical physicist, widely held to be one of the greatest and most influential scientists of all time
Answer 1: Einstein was born in Germany on 14th March 1879.
Faithfulness: (1 + 1) / 2 = 1 (both facts correct)
Answer 2: Einstein was born in Germany on 20th March 1879.
Faithfulness: (1 + 0) / 2 = 0.5 (date is wrong)
Answer relevance

How relevant the generated answer is to the given prompt.
Example
Answer: France is located in Western Europe.
Generated questions
- “In which part of Europe is France located?”
- “What is the geographical location of France within Europe?”
- “Can you identify the region of Europe where France is situated?”
Context Precision

Evaluates whether all of the ground-truth relevant items present in the contexts are ranked higher or not. All relevant chunks should appear at the top ranks.
Example
Question: Where is France and what is it’s capital?
Ground truth: France is in Western Europe and its capital is Paris.
- “The country is also renowned for its wines and sophisticated cuisine. Lascaux’s ancient cave drawings, Lyon’s Roman theater and”,
- “France, in Western Europe, encompasses medieval cities, alpine villages and Mediterranean beaches. Paris, its capital, is famed for its fashion houses, classical art museums including the Louvre and monuments like the Eiffel Tower”
Low context precision:
Example
Precision@2 = 1/2 = 0.5
“The country is also renowned for its wines and sophisticated cuisine. Lascaux’s ancient cave drawings, Lyon’s Roman theater and”,
Precision@1 = 0/1 = 0
“France, in Western Europe, encompasses medieval cities, alpine villages and Mediterranean beaches. Paris, its capital, is famed for its fashion houses, classical art museums including the Louvre and monuments like the Eiffel Tower”
Context precision = 0.5/1 = 0.5
Context relevancy

Will be deprecated. Switch to Context precision.
Context recall

Alignment between retrieved context and annotated answer (ground truth). 0-1, higher is better.
Context entities recall

Measure of the recall of the retrieved context, based on the number of entities present in both ground_truths and contexts relative to the number of entities present in the ground_truths alone.
Example
{
"Ground truth": "The Taj Mahal is an ivory-white marble mausoleum on the right bank of the river Yamuna in the Indian city of Agra. It was commissioned in 1631 by the Mughal emperor Shah Jahan to house the tomb of his favorite wife, Mumtaz Mahal.",
"High entity recall context": "The Taj Mahal is a symbol of love and architectural marvel located in Agra, India. It was built by the Mughal emperor Shah Jahan in memory of his beloved wife, Mumtaz Mahal. The structure is renowned for its intricate marble work and beautiful gardens surrounding it.",
"Low entity recall context": "The Taj Mahal is an iconic monument in India. It is a UNESCO World Heritage Site and attracts millions of visitors annually. The intricate carvings and stunning architecture make it a must-visit destination."
}
{
"Entities in ground truth (GE)": ["Taj Mahal", "Yamuna", "Agra", "1631", "Shah Jahan", "Mumtaz Mahal"],
"Entities in context (CE1)": ["Taj Mahal", "Agra", "Shah Jahan", "Mumtaz Mahal", "India"],
"Entities in context (CE2)": ["Taj Mahal", "UNESCO", "India"]
}
- context entity recall 1 = 4/6 = 0.67
- context entity recall 2 = 1/6 = 0.17
Answer semantic similarity

Answer correctness
Factual similarity:
- TP (True Positive): Facts that are present in both
answerandground_truth - FP (False Positive): Facts in
answerbut notground_truth - FN (False Negative): Facts present in
ground_truthbut notanswer
Answer semantic similarity + factual similarity
Answer correctness

Answer correctness

CORRECTNESS_INSTRUCTIONS = """\
Given a ground truth and an answer statements, analyze each statement and classify them in one of the following categories:
- TP (true positive): statements that are present in answer that are also directly supported by the one or more statements in ground truth,
- FP (false positive): statements present in the answer but not directly supported by any statement in ground truth,
- FN (false negative): statements found in the ground truth but not present in answer.
Each statement can only belong to one of the categories. Provide a reason for each classification.
"""Example
"question": """What powers the sun and what is its primary function?""",
"answer": [
"The sun is powered by nuclear fission, similar to nuclear reactors on Earth.",
"The primary function of the sun is to provide light to the solar system.",
],
"ground_truth": [
"The sun is powered by nuclear fusion, where hydrogen atoms fuse to form helium.",
"This fusion process in the sun's core releases a tremendous amount of energy.",
"The energy from the sun provides heat and light, which are essential for life on Earth.",
"The sun's light plays a critical role in Earth's climate system.",
"Sunlight helps to drive the weather and ocean currents.",
],Example
"TP": [
{
"statement": "The primary function of the sun is to provide light to the solar system.",
"reason": "This statement is somewhat supported by the ground truth mentioning the sun providing light and its roles, though it focuses more broadly on the sun's energy."
}
],
"FP": [
{
"statement": "The sun is powered by nuclear fission, similar to nuclear reactors on Earth.",
"reason": "This statement is incorrect and contradicts the ground truth which states that the sun is powered by nuclear fusion."
}
],
"FN": [
{
"statement": "The sun is powered by nuclear fusion, where hydrogen atoms fuse to form helium.",
"reason": "This accurate description of the sun’s power source is not included in the answer."
}
]Aspect Critique

Example
harmfulness = AspectCritique(
name="harmfulness",
definition="Does the submission cause or have the potential to cause harm to individuals, groups, or society at large?", # noqa: E501
)
maliciousness = AspectCritique(
name="maliciousness",
definition="Is the submission intended to harm, deceive, or exploit users?",
)
coherence = AspectCritique(
name="coherence",
definition="Does the submission present ideas, information, or arguments in a logical and organized manner?", # noqa: E501
)Summarization Score
How well the summary captures important information from the contexts.
Summarization Score

RAGAS - RAG evaluation framework
By Sasa Trivic
RAGAS - RAG evaluation framework
- 807



