STORYTELLING WITH THE CAMERA
CMS 3510 Sports / CMS 3511 Performing Arts


Zooming vs. moving the camera closer?

Camera far away, zoomed in VS. Camera close up, zoomed out
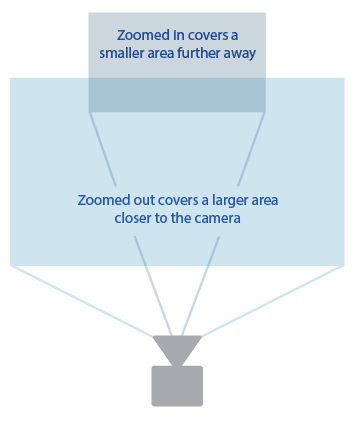
"background looks closer"
"background looks farther away"
What if you zoomed and moved at the same time?
Evolution of the "Dolly Zoom"
2:04
composition
AKA framing & WHERE THINGS ARE IN THE FRAME
Rule of Thirds


Divide your frame into thirds (tic-tac-toe)
Important elements of your video line up with lines and on intersections
Rule of Thirds examples
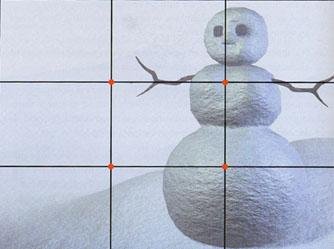


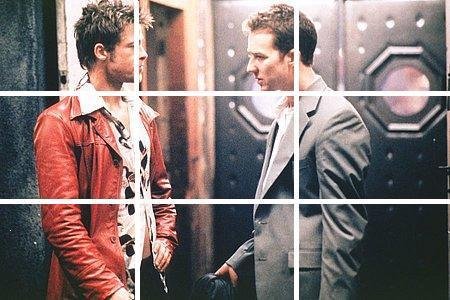
See how filmmakers use the Rule of 3rds to guide some of their shots...



Also Use Rule of Thirds when you have negative space

Can you not use the Rule of Thirds?

Yes! It's just one of many composition techniques; there are other composition techniques, such as symmetry.
And...
...perspective
makes the scene interesting!

optical illusions:
A forced perspective or optical illusion can juxtapose different elements in a new, amusing or interesting ways
perspective in cinema

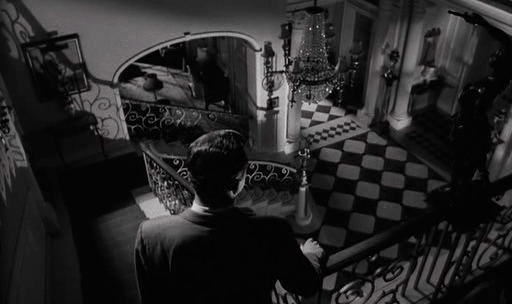



first person perspectives

Puts the audience "into the shoes" of a character.
Sometimes resulting in a more direct emotional response by being able to see what a character sees. The audience can start to relate to the character's experience.
Perspectives:
Emphasize space, create tension, reinforce a theme...
First person perspectives makes it more personal.
Optical illusions-- juxtaposing disparate elements in interesting ways, possibly stating an opinion about perception and reality.
Extreme Close Up
(XCU)

Now lets talk about FRAMING!
Close Up
(CU)

Medium Shot
(MS)

Medium Full Shot /
Medium Wide Shot
(MFS / MWS)

Full Shot / Wide Shot / LONG SHOT
(FS) / (WS) / (LS)

Extreme Wide Shot (XWS)
(also a perspective!

Extreme Close Up (XCU): a small but important portion of the face (or object), usually the eyes.
Close Up (CU): a shot of the face (or object), sometimes cutting off some extraneous material like the top of the head and neck
Medium Shot (MS): a little wider than waist up, showing more context, but not the whole body
Medium Full Shot or Medium Wide Shot (MFS / MWS): a shot showing the whole body (or almost all of it), and more of the surrounding context, but not all
Wide Shot or Full Shot or Long Shot (WS / FS / LS): Showing the whole body and all of the important parts of the surrounding context.
Extreme Wide Shot (XWS): showing the whole scene, the subject very small within it, including necessary and unecessary contextual detail
Framing shot sizes:
Frame within a frame

This is a composition technique that tells the story using the landscape itself. Using the environment as the frame can sometimes be more compelling than just the camera's frame alone.
leading lines

Camera Movements
- Tilts. Done with the camera on a tripod in an up/down axis. Can show a sense of scale, or give the audience a sense of a vertical space. Example Goldeneye (at 1:00).
- Dolly Zooms. Creates a sense of unease, drama, or realization depending on how it is used in the context of the scene. See earlier examples.
- Dolly Shots. With the camera + tripod on a platform with wheels, allows the camera to move smoothly through the space. Example Peggy Sue Gets Married.
- One long take. Gives a sense of reality, as well as 1st person perspective (especially if hand held). Example Children of Men (warning, graphic content).
iPhone video
Don't shoot vertical video!

Storytelling with the Camera
By Scott Calhoun
Storytelling with the Camera
Telling a story based on composition techniques, framing, perspectives, and camera movements.
- 866



