C++基礎語法
C++
- 高階語言
- 編譯語言
安裝開發環境
第一個程式
一個C++程式的空殼
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
return 0;
}#include<iostream>
引入函式庫
using namespace std;
使用std命名空間
int main()
程式進入的地方
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
cout << "hello, world";
return 0;
}Hello, world!
d483
分號
-
分號是一行程式的結尾
- 換行和縮排不影響程式的執行
(但會影響人的閱讀)
cout << "hello" << endl << "world" << endl;可以把多個輸出用<<串起來
endl是換行
cout << (2 + 4) * 10 << endl;也可以直接輸出數字運算結果
變數
變數
一個存放資料的空間
int
整數變數
宣告變數
初始化
int x;
int y, z;int x = 27, y = 10;int
整數變數
宣告變數
int x;
int y, z;初始化
int x = 27, y = 10;指定運算子
x = 1;
x = x + 1int
整數變數
整數變數可以把它當成數字去做計算
也可以用cout輸出
int x = 5;
int y = 10;
int z = x + y;
cout << x + y - 10 << '\n';輸入
int x;
cin >> x;int x, y;
cin >> x >> y;將輸入存入變數中
也可以連續輸入
a002
d049
變數命名規則
- 只能使用英文大小寫、數字、和底線(_)
- 大小寫視為不同字
- 不能以數字開頭 e.g. int 1x
- 不能與c++ 保留字相同 e.g. int int
更大範圍的整數變數
int
可儲存整數
範圍:\(-2^{31}\) ~ \(2^{31}-1\)
long long int
可儲存更大的整數
範圍:\(-2^{63}\) ~ \(2^{63}-1\)
有小數點的變數
float
可儲存有小數點的數字
精度:6~7位數
double
可儲存更多位數
精度:14~15位數
有小數點的變數
float
可儲存有小數點的數字
精度:6~7位數
double
可儲存更多位數
精度:14~15位數
更多不同種類的變數
char
可儲存字元
一個字元的表示方式:'a'
string
可儲存字串
字串表示方式:"abc"
bool
只儲存真假值
true or false
a001
怎麼交換兩個數
錯誤作法
int x = 5, y = 7;
x = y;
y = x;要開一個暫存空間
int x = 5, y = 7;
int tmp = x;
x = y;
y = tmp;也有一些其他做法
int x = 5, y = 7;
y = x + y;
x = y - x;
y = y - x;運算子
+-*/
指定運算子
- =
- 把等號右邊的運算結果存到左邊的變數
int x;
x = 10 + (2 + 5) * 2;
x = x + 1;算術運算子
- +,-,*,/,%
- %是取餘數
- 13 % 4會得到1
cout << 13 % 4 << endl;判斷奇數偶數
判斷奇數偶數
x % 2
算術運算子
++ 遞增
x = x + 1
int x = 1;
x++;
cout << x << endl;
cout << x++ << endl;
cout << ++x << endl;
-- 遞減
x = x - 1
括號
- C++中可以使用小括號進行優先計算
cout << ((5 + 2) * 2 + 3) / 3 << endl;d050
比較運算子
- >, >=, ==, <=, <, !=
- ==用來比較相等
- 運算結果為布林值
cout << (13 < 4) << endl;邏輯運算子
- &&, ||, !
- and, or, not
- 判斷5 < x < 13
cout << (5 < x && x < 13) << endl;型別轉換
- 以下程式的計算結果?
cout << 5 / 2 << endl;2
隱含型別轉換
- 運算式中有float
cout << 5.0 / 2 << endl;2.5
隱含型別轉換
- 指定運算子=,以左邊變數的型別為準
int x = 5.0 / 2;
cout << x << endl;強制型別轉換
- 直接告訴他要轉成什麼型別
- (型別)變數
int x = 5;
cout << (double)5 / 2 << endl;
cout << (double)x / 2 << endl;b757
註解
- 註解是給人看的,電腦會忽略
- // 代表單行註解
- /*註解內容*/ 會把中間的都當成註解
int x = 5; //我是註解
/*
我是註解
*/
選擇結構
if, else if, else
選擇結構
看情況決定要不要執行
if(判斷條件){
要執行的程式碼;
}範例
int x;
cin >> x;
if(x >= 90){
cout << x << ">= 90" << endl;
}用邏輯運算子做多個條件的判斷
int x;
cin >> x;
if(x >= 90 && x <= 95){
cout << "90 <= " << x << " <= 95" << endl;
}else
int x;
cin >> x;
if(x >= 90){
cout << x << " >= 90" << endl;
}else{
cout << x << " < 90" << endl;
}不符合條件要做的事
d064
這會輸出什麼
int x = 95;
if(x >= 90){
cout << "A+" << endl;
}
if(x >= 80){
cout << "A" << endl;
}else if
int x = 95;
if(x >= 90){
cout << "A+" << endl;
}else if(x >= 80){
cout << "A" << endl;
}前一個情況不符合,再做判斷
else if
int x = 95;
if(x >= 90){
cout << "A+" << endl;
}else if(x >= 80){
cout << "A" << endl;
}else if{x >= 70}{
cout << "B" << endl;
}else{
cout << "C" << endl;
}可以接很多個else if
a003
迴圈
把重複的工作交給電腦
for迴圈
for(int i = 0; i < 執行次數; i++){
cout << i << ' ';
}
cout << endl;for迴圈
for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++){
cout << i << ' ';
}
cout << endl;0 1 2 3 4
d498
int n;
cin >> n;
int x;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
cin >> x;
cout << x * 2 << '\n';
}for迴圈
for(迴圈一開始要做的事; 每一次迴圈執行條件; 每次迴圈結束時要做的事){
cout << i << ' ';
}
cout << endl;int n;
cin >> n;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i = i + 2){
cout << i << ' ';
}
cout << endl;這個程式的執行結果是什麼
int n;
cin >> n;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i = i + 2){
cout << i << ' ';
}
cout << endl;這個程式的執行結果是什麼
輸出1~n之間的奇數
int n;
cin >> n;
for(int i = 1; i * i <= n; i++){
cout << i << ' ';
}
cout << endl;這個程式的執行結果是什麼
int n;
cin >> n;
for(int i = 1; i * i <= n; i++){
cout << i << ' ';
}
cout << endl;這個程式的執行結果是什麼
輸出1~\(\sqrt{n}\)
變數作用範圍
- 一個變數只在當前這個程式區塊內有效
if(5 > 0){
int x = 5;
}
cout << x << '\n';Compile Error
變數作用範圍
- 一個變數只在當前這個程式區塊內有效
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
int x;
cin >> x;
}
cout << i << '\n';Compile Error
巢狀迴圈
在迴圈裡面放迴圈
例題:矩形
輸入 \(n, m\) 兩個正整數
用*輸出一個 \(n\times m\) 的正方形
範例輸入
3 5
範例輸出
*****
*****
*****
c418
迴圈常見使用方式
- 總和
- 記數
- 最大值
總和
輸入一個n,接著輸入n個整數,輸出這n個數的總和
總和
輸入一個n,接著輸入n個整數,輸出這n個數的總和
int n, x;
cin >> n;
int sum = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
cin >> x;
sum += x;
}b294
記數
輸入一個n代表學生數量
接著輸入n個整數,代表每個人的成績
輸出這n個數中有幾個人不及格(小於60)
int n, x;
cin >> n;
int cnt = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
cin >> x;
if(x < 60){
cnt++;
}
}
cout << cnt << '\n';記數
輸入一個n代表學生數量
接著輸入n個整數,代表每個人的成績
輸出這n個數中有幾個人不及格(小於60)
a058
最大值
d074
最大值
用一個變數儲存目前的最大值
d074
while迴圈
- while(判斷式)
- 通常用於不確定執行次數的迴圈
int x;
cin >> x;
int i = 0;
while(i < x){
cout << i << ' ';
i++;
}
3n+1猜想
- 對於任意n
- 若 n 是奇數,則將n 改為 3n+1
- 若 n 是偶數,則將n改為 n / 2
3n+1猜想
int x;
cin >> x;
while(x > 1){
if(x % 2 == 1){
x = 3 * x + 1;
}else{
x = x / 2;
}
}
cout << x << '\n';
- 對於任意n
- 若 n 是奇數,則將n 改為 3n+1
- 若 n 是偶數,則將n改為 n / 2
while迴圈
- 得到十進位的每個位數
- 怎麼得到目前的個位數
- 怎麼讓把現在的個位數刪掉
- 什麼時候停止
a038
迴圈的中斷和跳過
break; 直接結束目前這層迴圈
continue; 跳回迴圈開頭繼續執行
break
int n;
while(true){
cin >> n;
if(n == 0){
cout << "stop the loop\n";
break;
}
cout << n << '\n';
}d070
continue
for(int i = x; i < y; i++){
if(i % 2)
continue;
cout << i << '\n';
}讀入到EOF(檔案結尾)
a004
int year;
while(cin >> year){
//你的程式
}陣列
一次宣告很多個變數
一次宣告很多個變數
宣告陣列
int a[5];一次宣告很多個變數
宣告陣列
int a[5];陣列初始化
int a[5] = {1, 3, 5, 2, 4};一次宣告很多個變數
宣告陣列
int a[5];用索引值取變數
int a[5];
cin >> a[3];陣列要注意的地方
- 陣列是從0開始
- 陣列到範圍減一結束
- 陣列宣告要是固定大小
可以與迴圈一起使用
用for迴圈的變數當作索引值
int n;
int a[50];
cin >> n;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
cin >> a[i];
}
可以與迴圈一起使用
用for迴圈的變數當作索引值
int n;
int a[50];
cin >> n;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
cin >> a[i];
}
g595
字串也是一種陣列
- s[i]代表第i+1個字元
a022
排序
把一堆數字照順序排好
選擇排序
泡沫排序
a104
二維陣列
宣告二維陣列
int a[2][4];使用二維陣列
int a[2][4];
a[1][3] = 5;int a[2][4]={
{1, 4, 2, 3},
{2, 3, 4, 1}
};例題:矩陣翻轉
a015
b367
字串處理
string 的功能
- 字串的長度可以用s.size() 來獲得
- string是一種陣列 e.g. s[3]是s的第4個字串
ASCII
char變數是使用ASCII來儲存
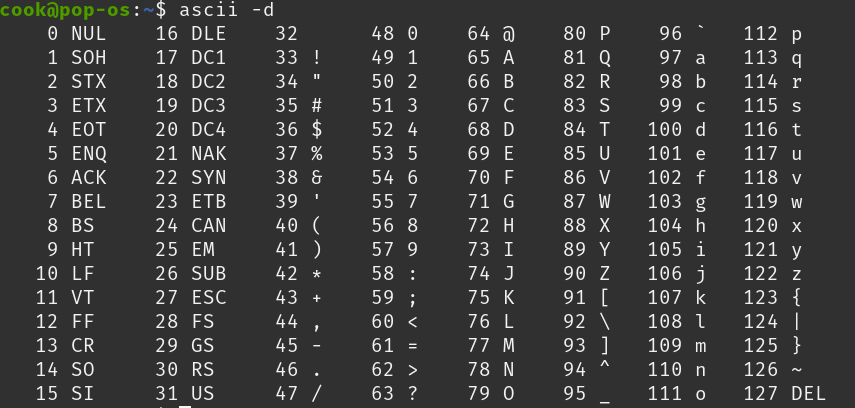
特殊字元
跳脫字元
特殊字元
跳脫字元
以反斜線開始
特殊字元
跳脫字元
以反斜線開始
換行 \n
tab \t
\ \\
" \"
' \'
一些字元處理的技巧
- 怎麼知道一個字元是不是小寫英文字母
- 怎麼得到一個數字字元的數值
把一個字串的英文字母都改成小寫
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
string s;
cin >> s;
int n = s.size();
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
if(s[i] >= 'A' && s[i] <= 'Z'){
s[i] = s[i] - 'A' + 'a';
}
}
cout << s << '\n';
}a224
short-circuit evaluation
(判斷式1) && (判斷式2)
當判斷式1的結果是false
那就不會執行判斷式2
因為 && 的結果一定是 false
short-circuit evaluation
(判斷式1) || (判斷式2)
當判斷式1的結果是 true
那就不會執行判斷式2
因為 || 的結果一定是 true
int a[10] = {1, 5, 2, 3, 6, 7, 1, 2, 3, 9};
cin >> x;
if(x >= 0 && a[x] < 5){
cout << a[x] << endl;
}else{
cout << 0 << endl;
}函式
將不同功能的程式分開擺放
- 函式宣告
- 函式回傳型別
- 函式名稱
- 參數
宣告函式
回傳型別 函數名稱(參數型別 參數名稱){
//程式
}int f(int x){
return 2 * x;
}int f(int x){
int a = 1;
for(int i = 1; i <= x; i++){
a = a * i;
}
return a;
}可以把重複的工作放到函式裡面
int add(int x, int y){
return x + y;
}可以傳入多個參數
void hello_world(){
cout << "Hello, world!" << endl;
}void型別代表不回傳值
傳入參數的方式
參數會整個複製一份到新的變數裡
b513
試著把判斷質數的地方寫成函式
指標
指標儲存的是變數存放的地方
指標變數宣告
變數型別 *指標變數名稱;
int *ptr;取變數的位址
&變數;
int a = 10;
int *ptr = &a;從記憶體位址得到原本的變數
*(指標);
int a = 10;
int *ptr = &a;
cout << ptr << endl;
cout << *ptr << endl;從記憶體得到的是變數本身
不是複製品
*(指標);
int a = 10;
int *ptr = &a;
*ptr = *ptr + 5;
cout << *ptr << endl;指標可以幹嘛
讓函式可以直接更改原本變數的值
void add(int *x){
*x = *x + 1;
}
int main(){
int x;
cin >> x;
int *ptr = &x;
add(ptr);
cout << x << '\n';
}練習
寫一個可以將兩個變數交換的函式
提示:傳指標進去
struct
自己定義變數型別
我想要一個學生變數
- 學生姓名
- 學生年齡
- 學生成績
struct 型別名稱{
//想要包在裡面的變數
int x;
string s;
};
struct Student{
string name;
int age, score;
};struct Student{
string name;
int age, score;
};
int main(){
Student a;
a.name = "Scott";
a.age = 20;
a.score = 30;
}d550
c++基礎語法
By scottchou
c++基礎語法
- 80



