
Exploring the system-level impacts of urban parcel deliveries using synthetic data
Results from the project H2020 LEAD
Sebastian Hörl
2 March 2023

IRT SystemX

- Public/private research institute situated in Paris
- Focus on fostering digital transition in a range of fields from transport, cybersecurity to circular economy
- Transferring research results and tools into active application by development and provision of industry platforms
- Various collaborative projects with multiple French companies (Renault, SNCF, ...) and academic partners (Université Paris Saclay, CentraleSupélec, Université Gustave Eiffel)
- Participation in European projects

Transport Modeling @ IRT SystemX

- First/last mile mobility simulation
- Grand Paris Express
Passenger transport


- On-demand mobility simulation
Passenger transport

Transport Modeling @ IRT SystemX

European projects



Social Innovation to foster inclusive cooperative connected and automated mobility
Low-Emission Adaptive last mile logistics supporting on-demand economy through Digital Twins

Data-driven, Integrated, Synchromodal, Collaborative and Optimized urban freight meta-system for new generation of urban logistics and planning
- ERTICO Member
- Various European projects on transport
- Most EU projects of French institutions in the transport domain

Safe, Efficient and Autonomous: Multimodal Library of European Shortsea and inland Solutions

LEAD Project

Low-emission Adaptive last-mile logistics supporting on-demand economy through Digital Twins
- H2020 Project from 2020 to 2023
- Six living labs with different innovative logistics concepts
- Lyon, The Hague, Madrid, Budapest, Porto, Oslo
- One partner for implementation and one for research each
- Development of a generic modeling library for last-mile logistics scenario simulation and analysis


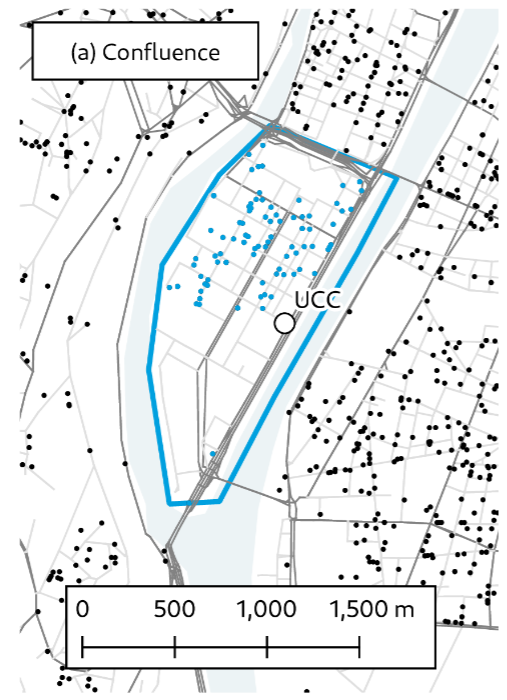
Lyon Living Lab

- Peninsula Confluence between Saône and Rhône
- Interesting use case as there are limited access points
- Implementation of an urban consolidation center (UCC) to collect the flow of goods and organize last-mile distribution
- using cargo-bikes
- using electric robots
- and others
- Analysis and modeling through
- Flow estimation through cameras
- Simulation of future scenarios
- Focus on parcel deliveries due to data availability

Modeling methodology

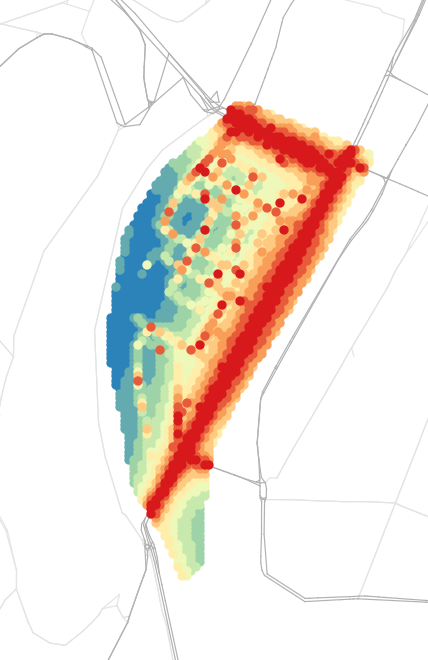
- Main question: What is the impact on traffic and population of implementing an Urban Consolidation Center in Confluence?
- Focus on B2C parcel deliveries due to data availability

Modeling methodology

Agent-based simulation of Lyon
- Main question: What is the impact on traffic and population of implementing an Urban Consolidation Center in Confluence?
- Focus on B2C parcel deliveries due to data availability

Modeling methodology

Agent-based simulation of Lyon
Demand in parcel deliveries
- Main question: What is the impact on traffic and population of implementing an Urban Consolidation Center in Confluence?
- Focus on B2C parcel deliveries due to data availability

Modeling methodology



Agent-based simulation of Lyon
Demand in parcel deliveries
Distribution by operators
- Main question: What is the impact on traffic and population of implementing an Urban Consolidation Center in Confluence?
- Focus on B2C parcel deliveries due to data availability

Modeling methodology





Agent-based simulation of Lyon
Demand in parcel deliveries
Distribution by operators
KPI Calculation
- Main question: What is the impact on traffic and population of implementing an Urban Consolidation Center in Confluence?
- Focus on B2C parcel deliveries due to data availability



Population census (RP)

Income data (FiLoSoFi)

Commuting data (RP-MOB)
National HTS (ENTD)

Enterprise census (SIRENE)

OpenStreetMap

GTFS (SYTRAL / SNCF)

Address database (BD-TOPO)
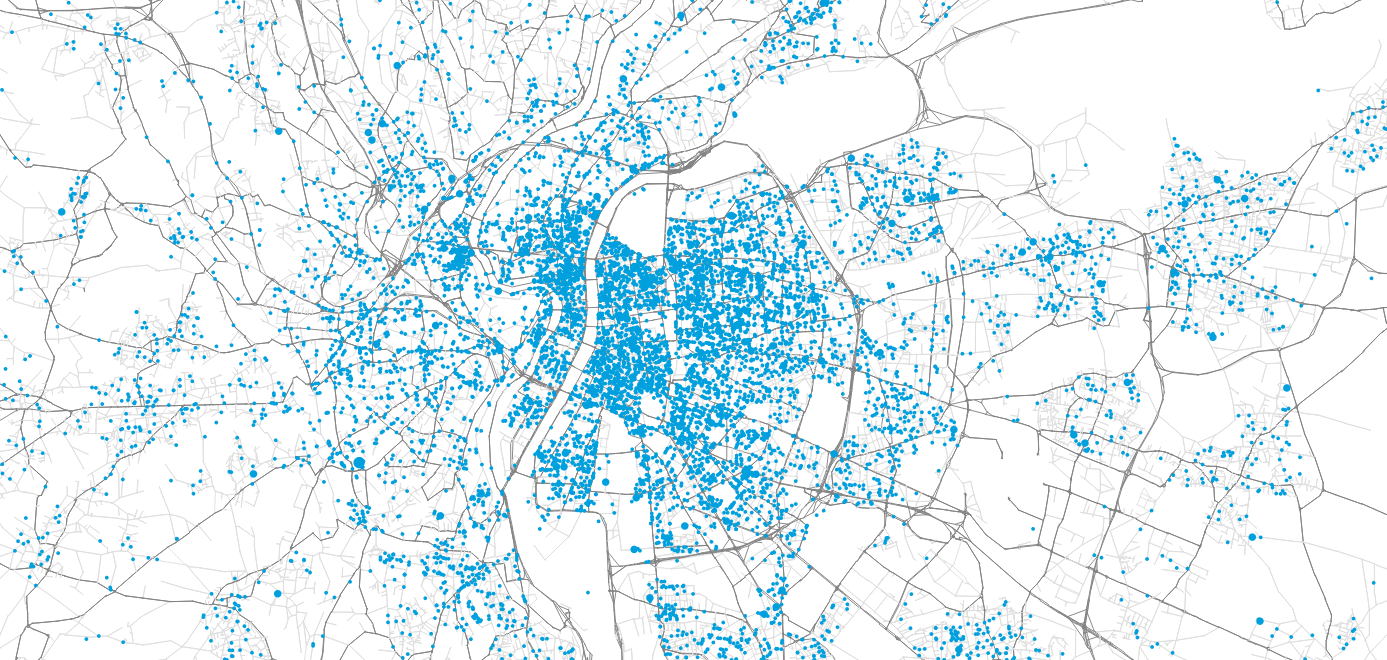
Methodology: Synthetic travel demand


EDGT
Synthetic travel demand has been generated for Lyon in order to perform agent-based mobility simulation of all residents' movements.











0:00 - 8:00
08:30 - 17:00
17:30 - 0:00
0:00 - 9:00
10:00 - 17:30
17:45 - 21:00
22:00 - 0:00







Population census (RP)

Income data (FiLoSoFi)

Commuting data (RP-MOB)
National HTS (ENTD)

Enterprise census (SIRENE)

OpenStreetMap

GTFS (SYTRAL / SNCF)

Address database (BD-TOPO)
Methodology: Synthetic travel demand


EDGT
Synthetic travel demand has been generated for Lyon in order to perform agent-based mobility simulation of all residents' movements.


Methodology: Synthetic travel demand
Open
Data


Open
Software
+
=
Reproducible research
Integrated testing

Population census (RP)

Income data (FiLoSoFi)

Commuting data (RP-MOB)
National HTS (ENTD)

Enterprise census (SIRENE)

OpenStreetMap

GTFS (SYTRAL / SNCF)

Address database (BD-TOPO)


EDGT
Synthetic travel demand has been generated for Lyon in order to perform agent-based mobility simulation of all residents' movements.


Methodology: Synthetic travel demand

Open
Software
=
Reproducible research
Integrated testing
Open
Data


Open
Software
+
=
Reproducible research
Integrated testing

Population census (RP)

Income data (FiLoSoFi)

Commuting data (RP-MOB)
National HTS (ENTD)

Enterprise census (SIRENE)

OpenStreetMap

GTFS (SYTRAL / SNCF)

Address database (BD-TOPO)


EDGT
Synthetic travel demand has been generated for Lyon in order to perform agent-based mobility simulation of all residents' movements.


Methodology: Synthetic travel demand













Methodology: Parcel demand


Synthetic population

+
Synthetic population
Out-of-home purchase survey
Achats découplés des ménages

Based on sociodemographic attributes of the households, parcels are generated for the city on an average day.
Gardrat, M., 2019. Méthodologie d’enquête: le découplage de l’achat et de la récupération des marchandises par les ménages. LAET, Lyon, France.
Methodology: Parcel demand


Synthetic population

+
Synthetic population
Out-of-home purchase survey
Achats découplés des ménages

Based on sociodemographic attributes of the households, parcels are generated for the city on an average day.

Gardrat, M., 2019. Méthodologie d’enquête: le découplage de l’achat et de la récupération des marchandises par les ménages. LAET, Lyon, France.
Methodology: Parcel demand


Synthetic population

+
Synthetic population
Out-of-home purchase survey
Achats découplés des ménages

Based on sociodemographic attributes of the households, parcels are generated for the city on an average day.


Gardrat, M., 2019. Méthodologie d’enquête: le découplage de l’achat et de la récupération des marchandises par les ménages. LAET, Lyon, France.
Methodology: Parcel demand


Synthetic population

Gardrat, M., 2019. Méthodologie d’enquête: le découplage de l’achat et de la récupération des marchandises par les ménages. LAET, Lyon, France.
+
Synthetic population
Out-of-home purchase survey
Achats découplés des ménages

Based on sociodemographic attributes of the households, parcels are generated for the city on an average day.



Gardrat, M., 2019. Méthodologie d’enquête: le découplage de l’achat et de la récupération des marchandises par les ménages. LAET, Lyon, France.
Methodology: Parcel demand


Synthetic population

Gardrat, M., 2019. Méthodologie d’enquête: le découplage de l’achat et de la récupération des marchandises par les ménages. LAET, Lyon, France.
+
Synthetic population
Out-of-home purchase survey
Achats découplés des ménages

Based on sociodemographic attributes of the households, parcels are generated for the city on an average day.
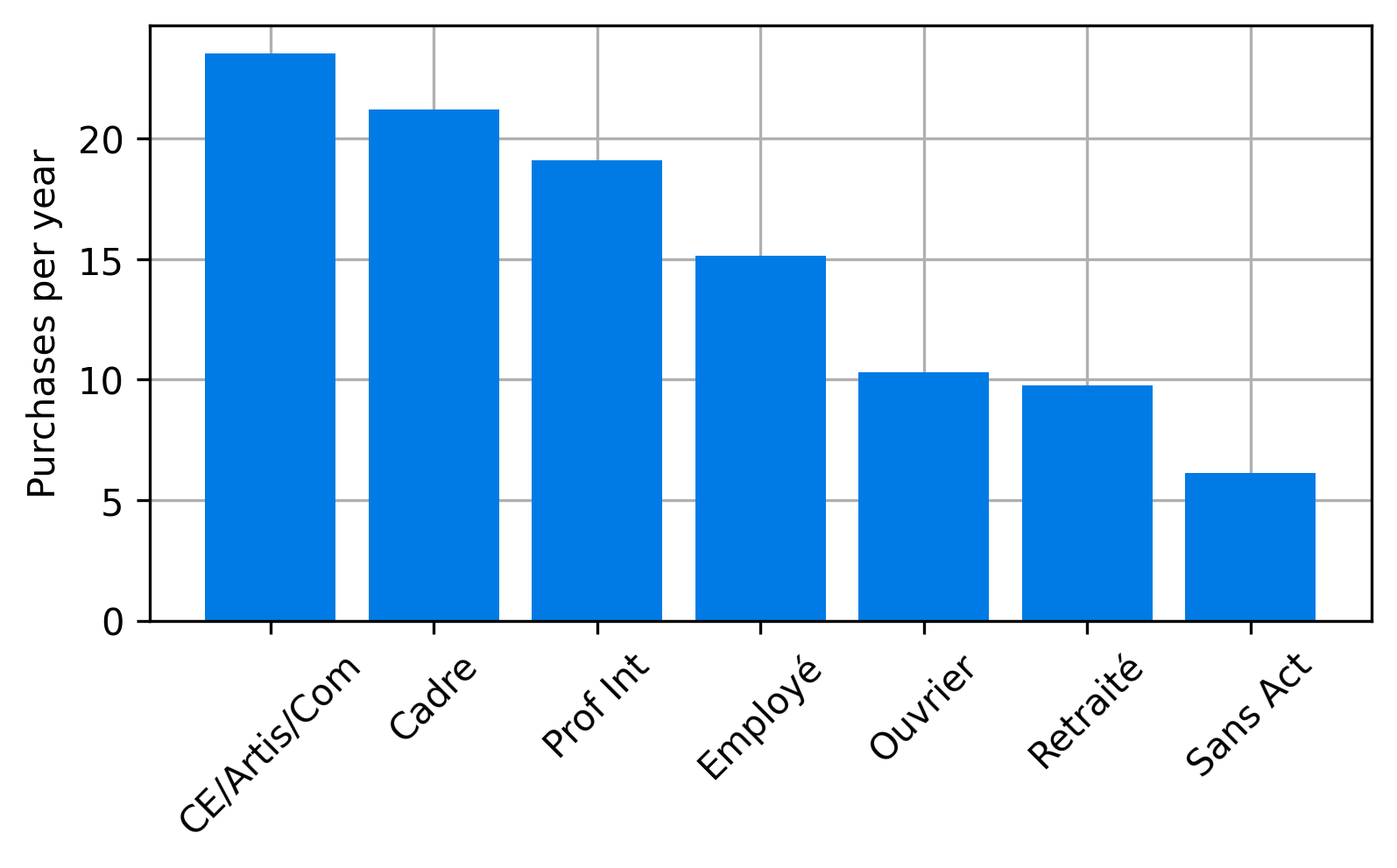
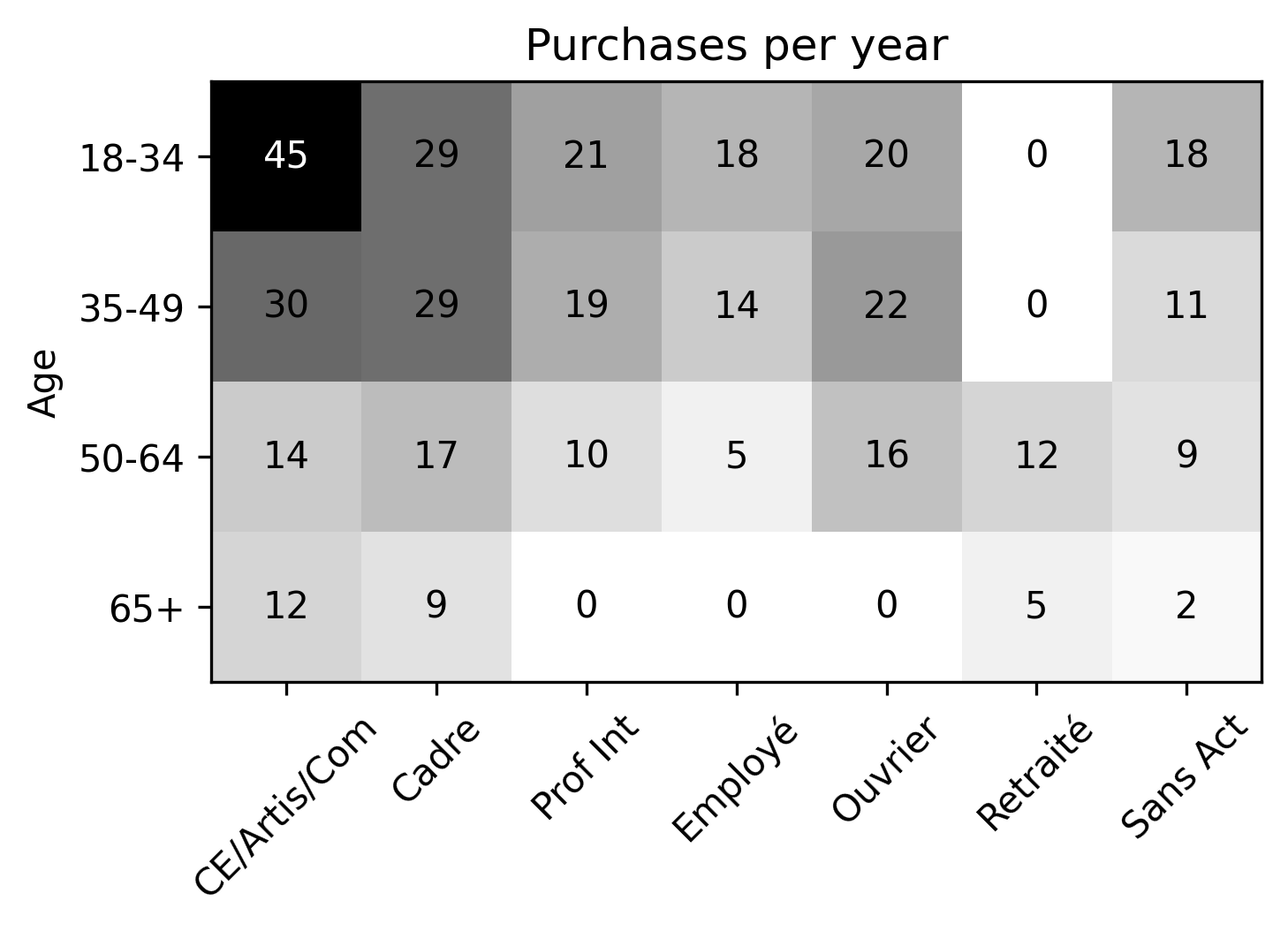
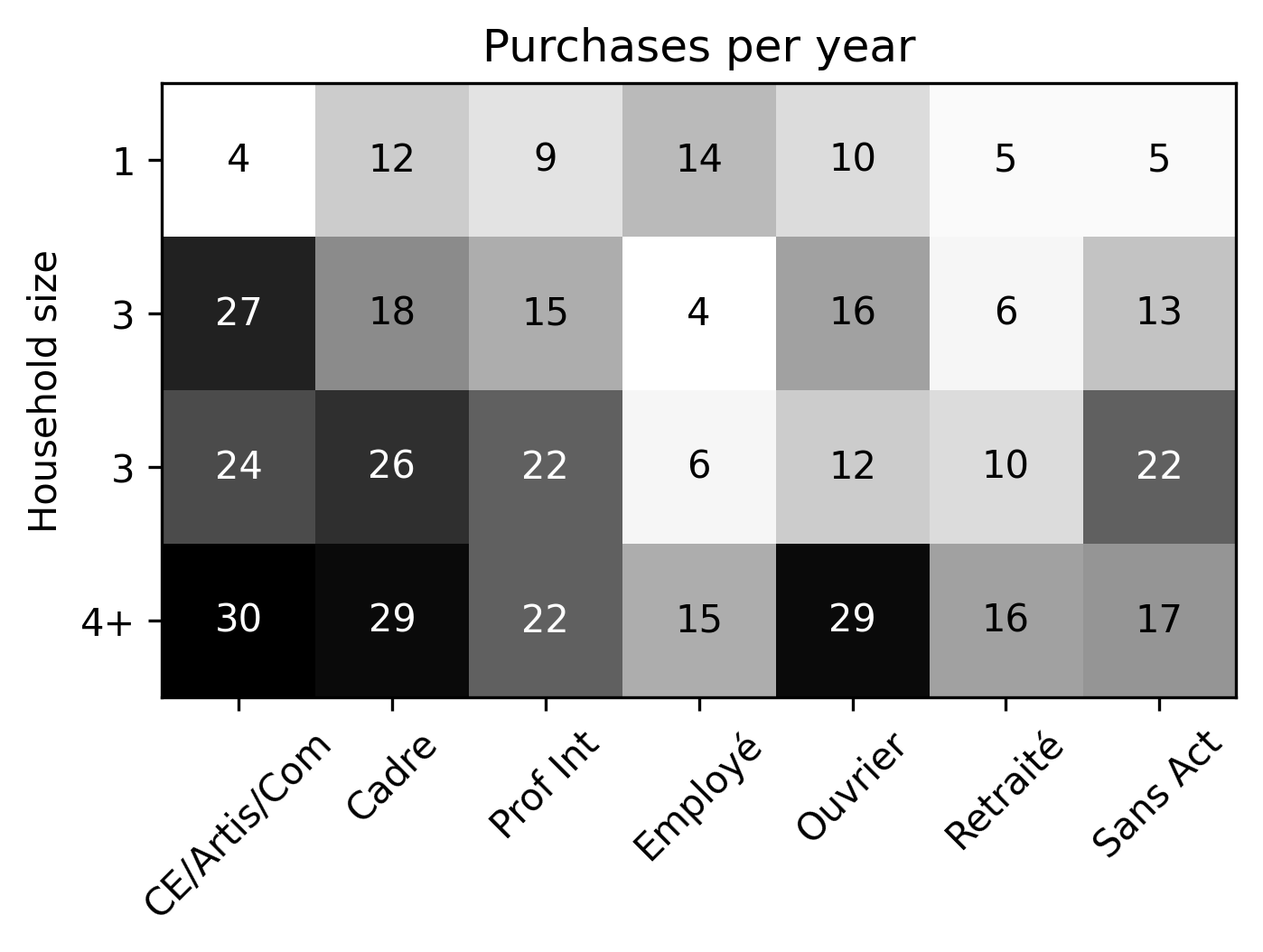
Iterative proportional fitting (IFP)
- Based on synthetic population, find average number of purchases delivered to a household defined by socioprofesional class, age of the reference person and household size per day.
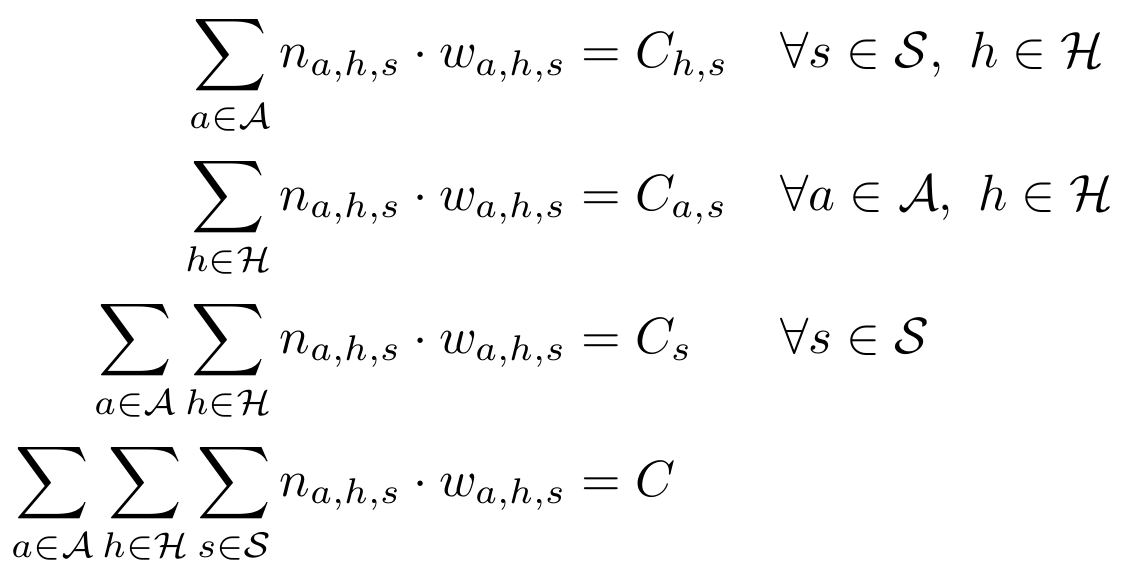
Methodology: Parcel demand


Synthetic population

Gardrat, M., 2019. Méthodologie d’enquête: le découplage de l’achat et de la récupération des marchandises par les ménages. LAET, Lyon, France.
+
Synthetic population
Out-of-home purchase survey
Achats découplés des ménages

Based on sociodemographic attributes of the households, parcels are generated for the city on an average day.
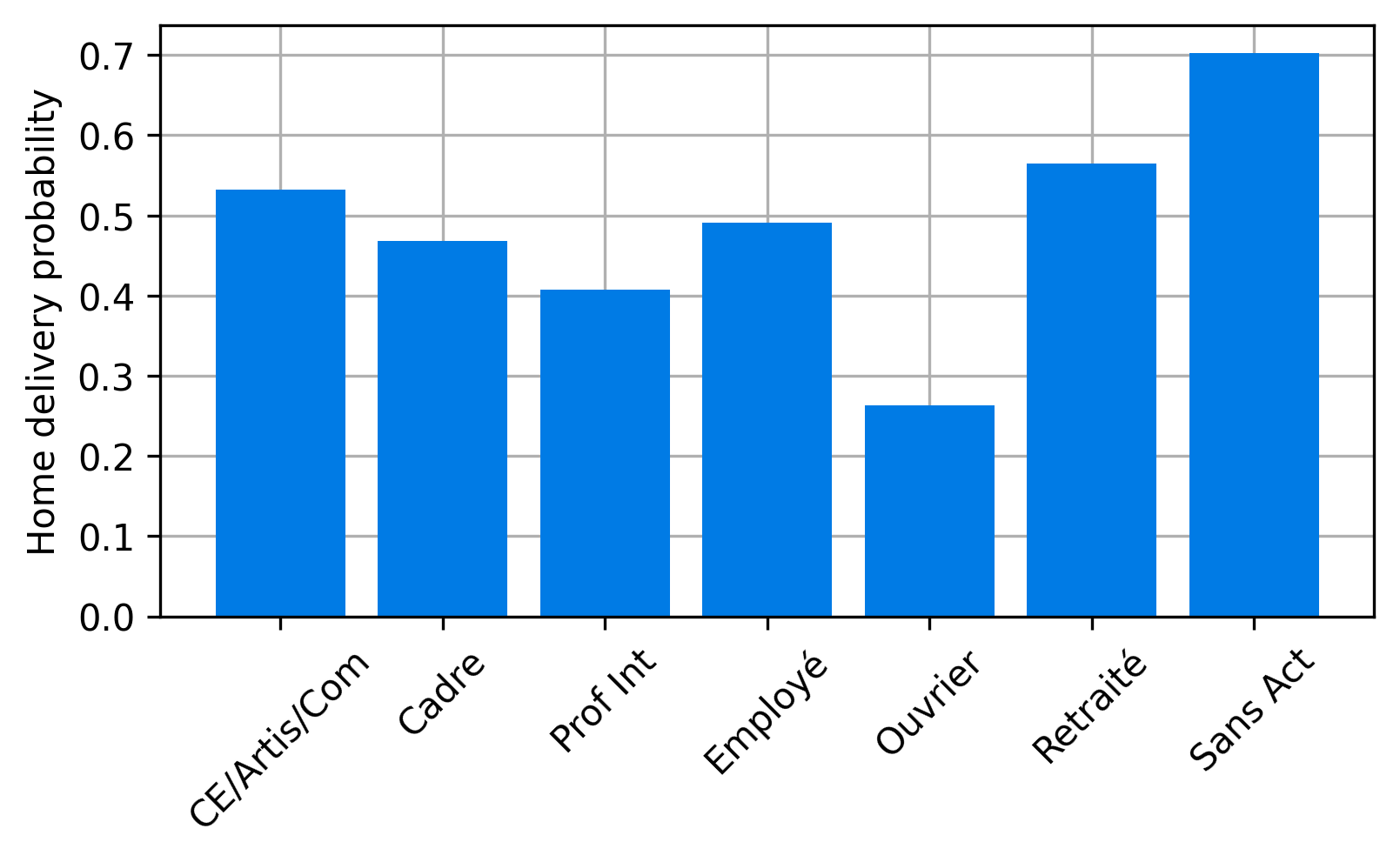
Maximum entropy approach
- We now the average number of parcels, but we do not now the distribution of the number of parcels for a household on an average day.
- We know it must be non-negative, and we know the mean.
- Without additional data, we assume maximum entropy distribution, which is Exponential in this case.
Methodology: Parcel demand


Synthetic population

Gardrat, M., 2019. Méthodologie d’enquête: le découplage de l’achat et de la récupération des marchandises par les ménages. LAET, Lyon, France.
+
Synthetic population
Out-of-home purchase survey
Achats découplés des ménages

Based on sociodemographic attributes of the households, parcels are generated for the city on an average day.
Methodology: Parcel demand


Synthetic population

Gardrat, M., 2019. Méthodologie d’enquête: le découplage de l’achat et de la récupération des marchandises par les ménages. LAET, Lyon, France.
+
Synthetic population
Out-of-home purchase survey
Achats découplés des ménages

Based on sociodemographic attributes of the households, parcels are generated for the city on an average day.

Methodology: Parcel demand


Synthetic population

Gardrat, M., 2019. Méthodologie d’enquête: le découplage de l’achat et de la récupération des marchandises par les ménages. LAET, Lyon, France.
+
Synthetic population
Out-of-home purchase survey
Achats découplés des ménages

Based on sociodemographic attributes of the households, parcels are generated for the city on an average day.
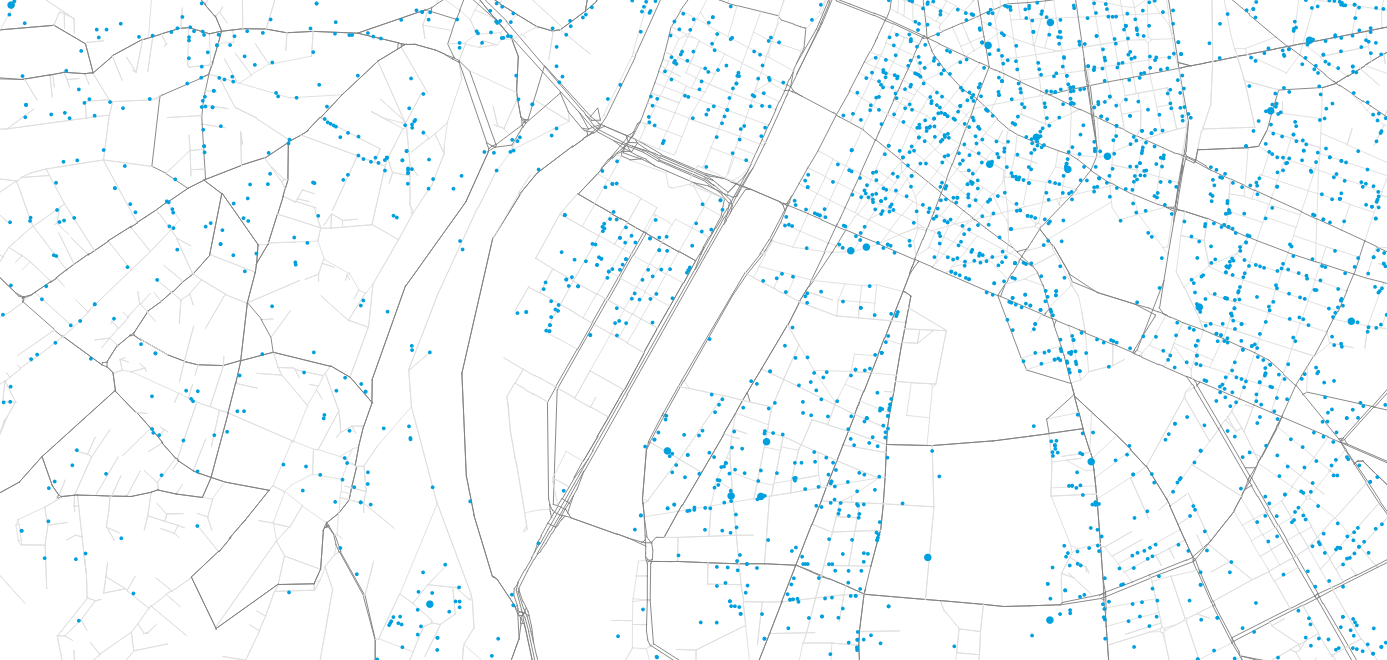
First case study


Hörl, S. and J. Puchinger (2022) From synthetic population to parcel demand: Modeling pipeline and case study for last-mile deliveries in Lyon, TRA 2022, Lisbon.
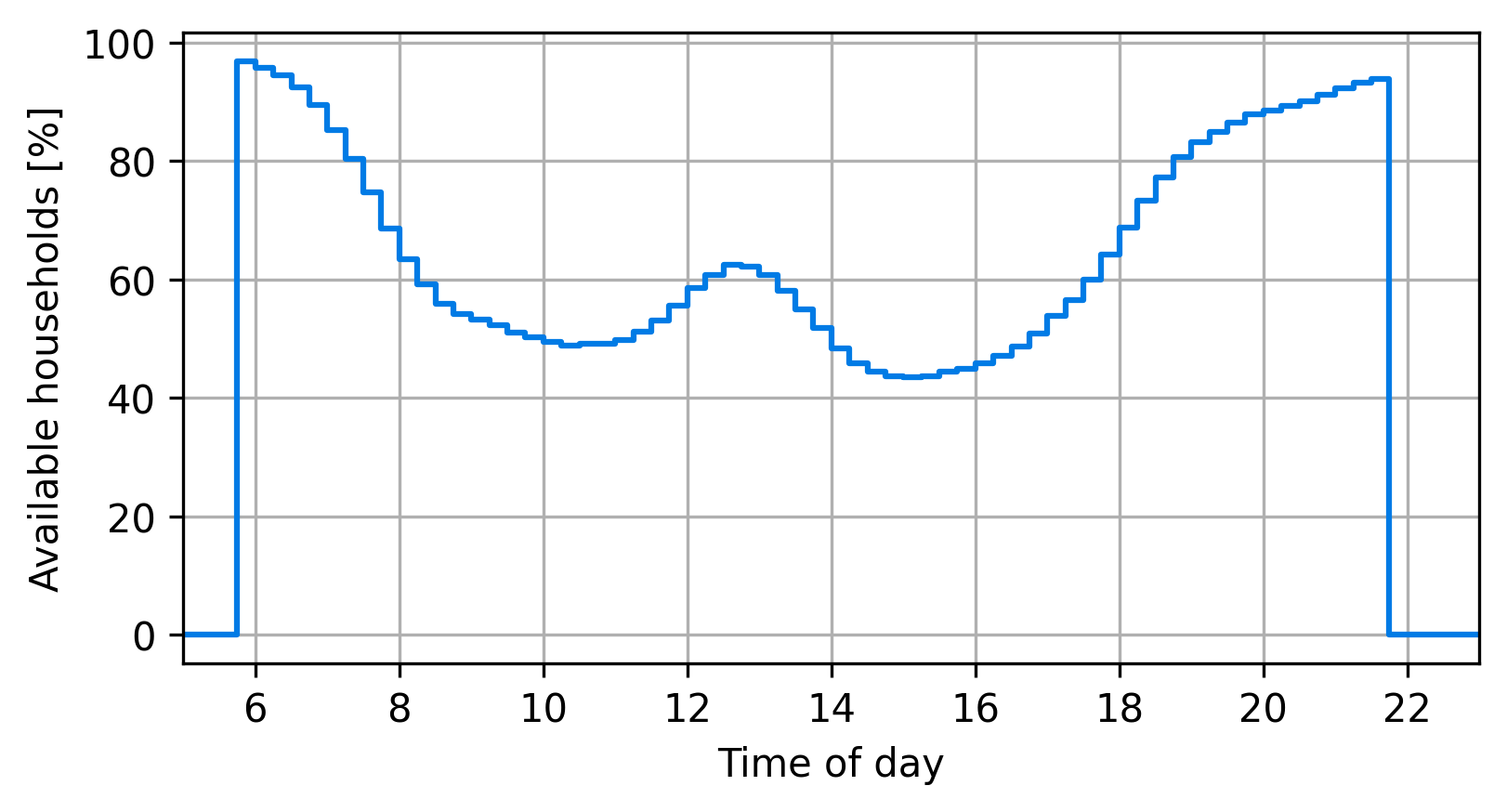
Presence of household members

First case study


Hörl, S. and J. Puchinger (2022) From synthetic population to parcel demand: Modeling pipeline and case study for last-mile deliveries in Lyon, TRA 2022, Lisbon.











JSprit
First case study



Hörl, S. and J. Puchinger (2022) From synthetic population to parcel demand: Modeling pipeline and case study for last-mile deliveries in Lyon, TRA 2022, Lisbon.
Solve VRP-TW based on generated parcels and household presence
JSprit
First case study



Solve VRP-TW based on generated parcels and household presence
JSprit
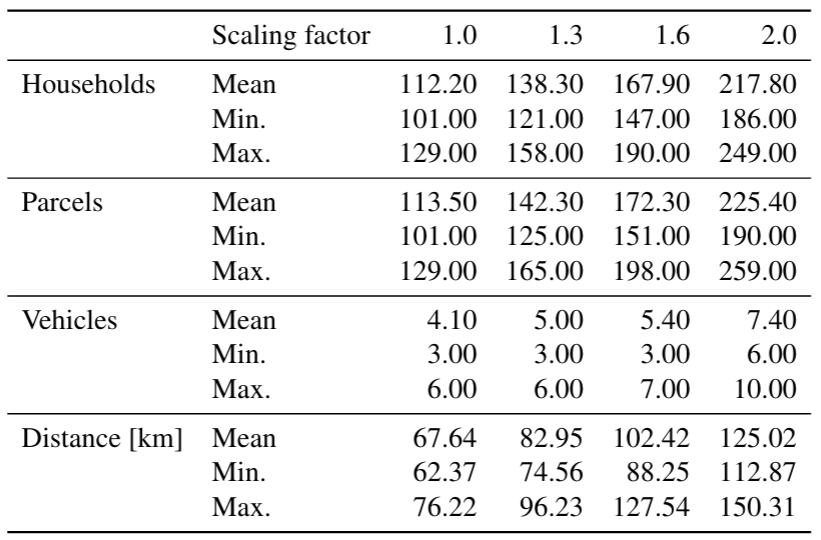
Hörl, S. and J. Puchinger (2022) From synthetic population to parcel demand: Modeling pipeline and case study for last-mile deliveries in Lyon, TRA 2022, Lisbon.
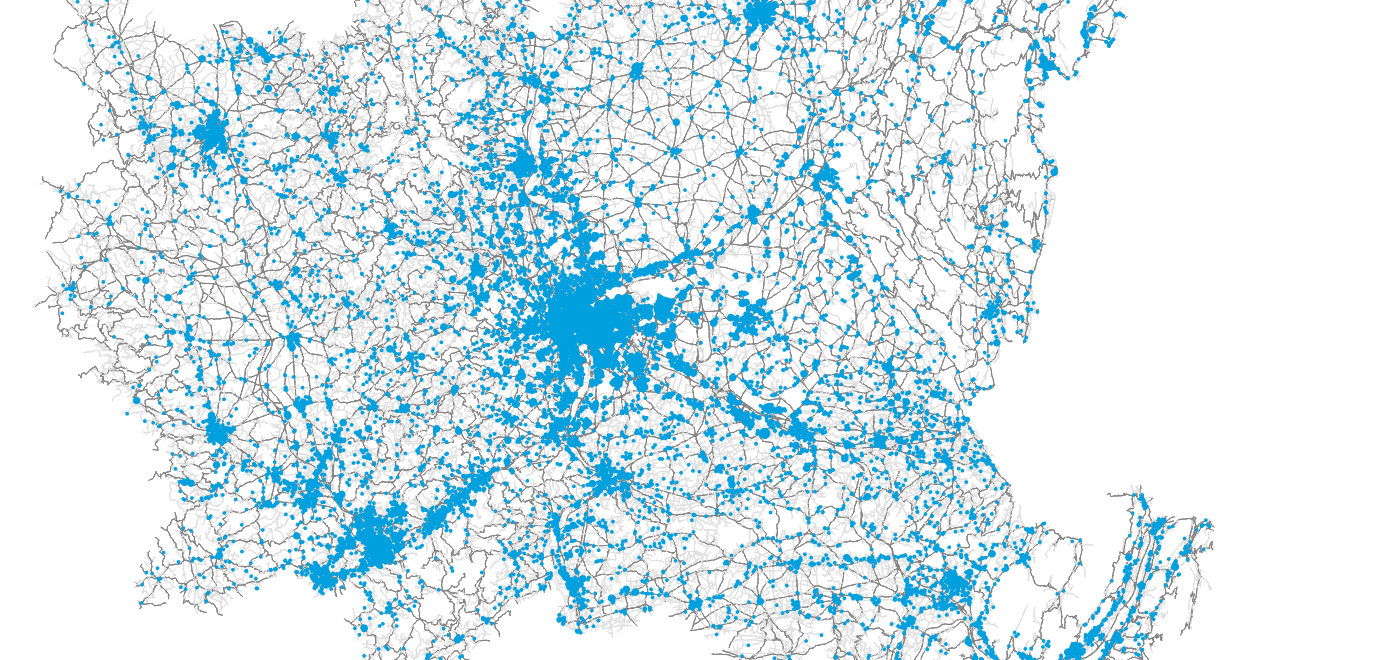
Methodology: Study area


How many parcels need to be delivered on one day?
Methodology: Study area


Perimeter
- City of Lyon
- Grand Lyon metropolitan region (dashed)
- Bordering municipalities including relevant logistics infrastructure
Demand
- 1.6M personas
- 790k households
- 16,252 parcels
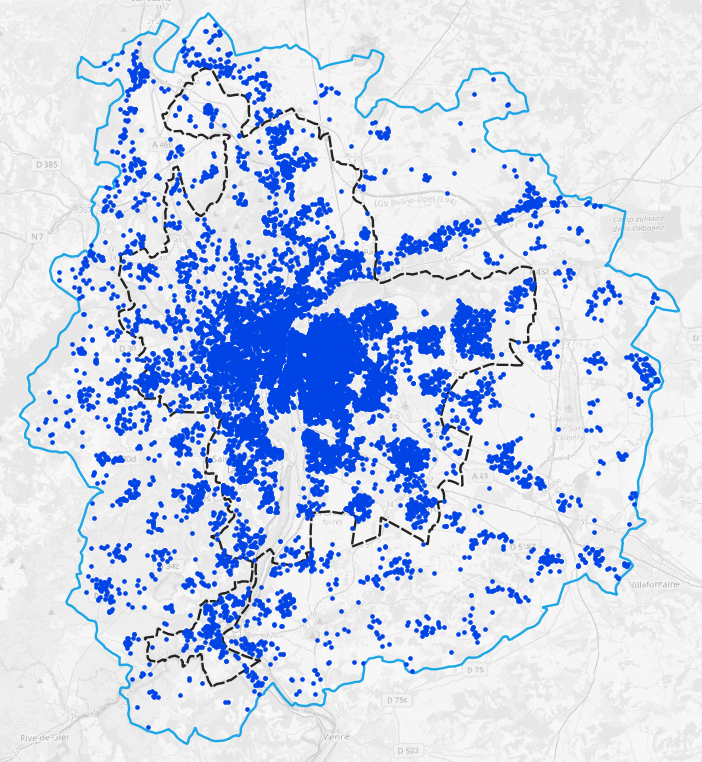
How many parcels need to be delivered on one day?
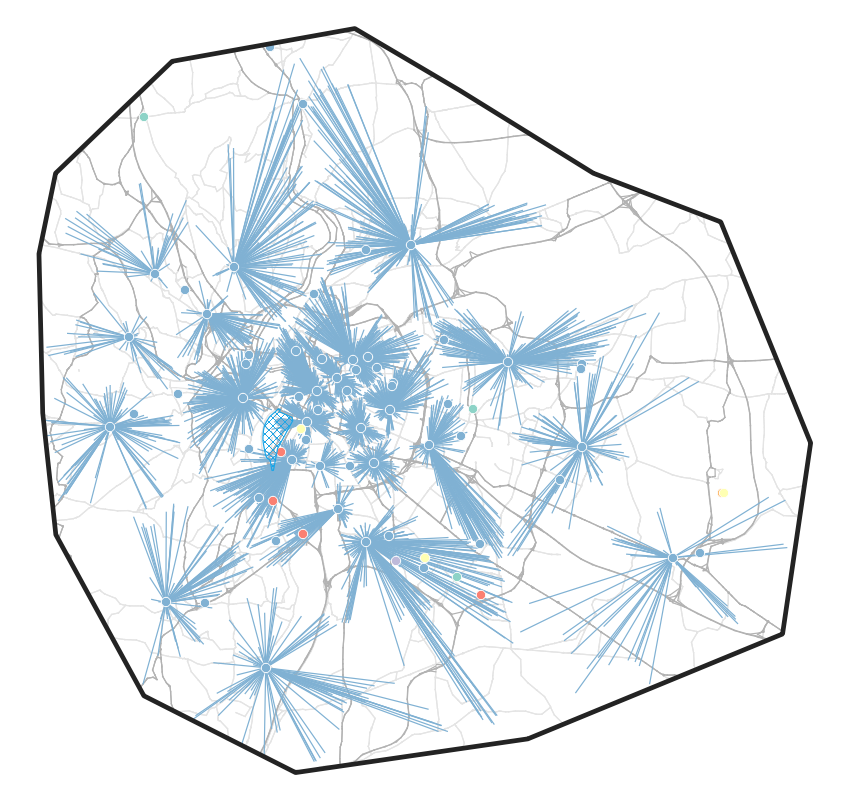
Methodology: Distribution centers


From where do operators delivery the parcels?
Methodology: Distribution centers


Approach
- Facilities per operator extracted from SIRENE
- Geolocated using public BAN API
- La Poste: Facilities with 20+ employees

From where do operators delivery the parcels?
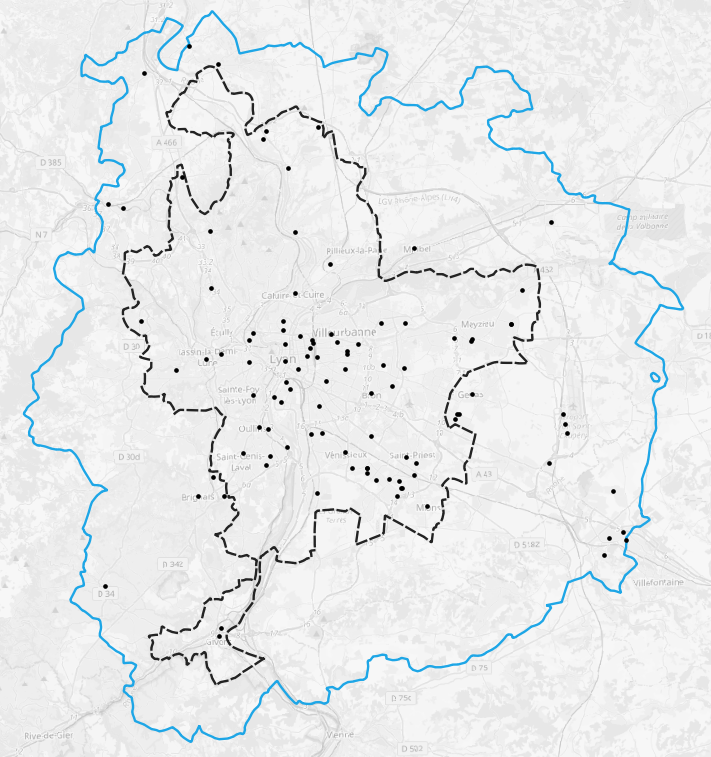
Methodology: Market shares


How many parcels are delivered by each operator?
Methodology: Market shares


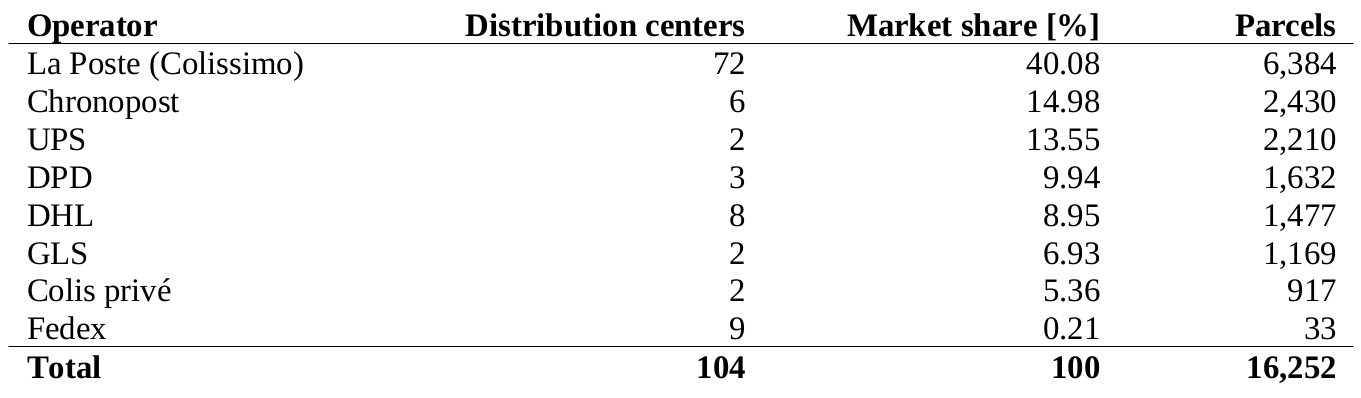
How many parcels are delivered by each operator?
Approach
- For some operators, we know the annual national volumes from gray literature
- We know that La Poste (Colissimo + DPD + Chronopost) add up to about 65% of all parcels in France
- For the rest, we approximate their market share using their annual turnover values

Methodology: Market shares


How many parcels are delivered by each operator?
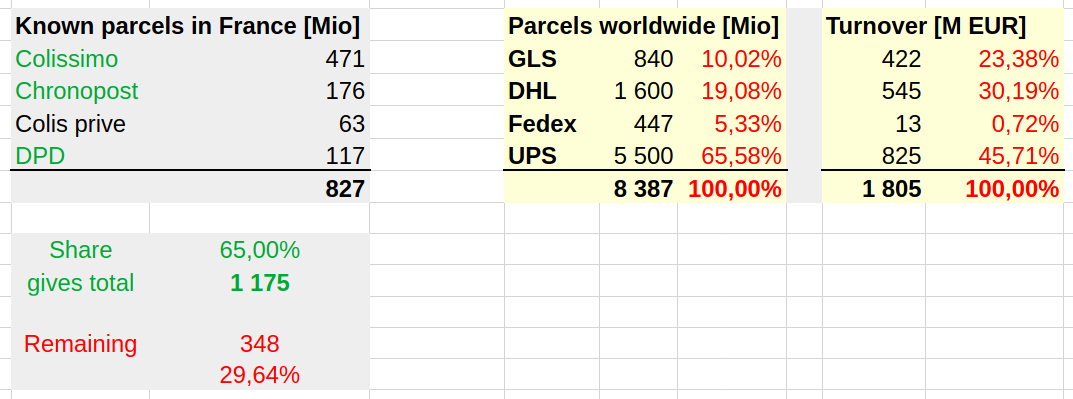
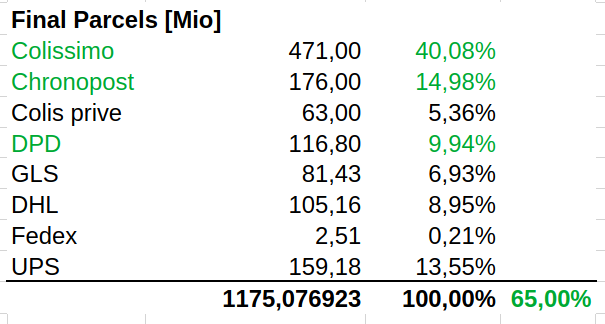
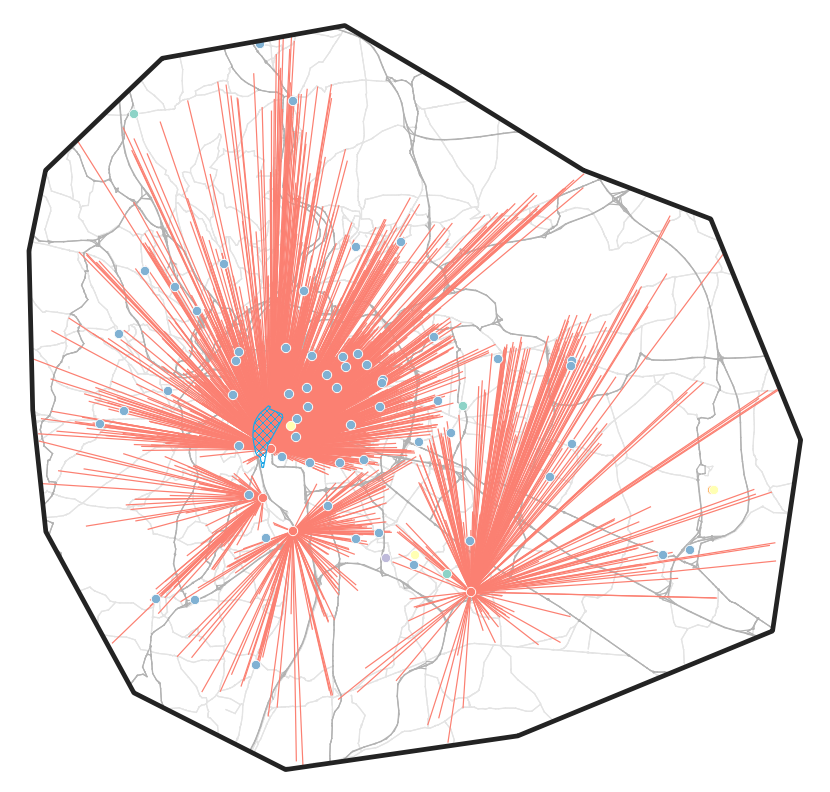
Methodology: Assignment


How many parcels are delivered by each distribution center?
Methodology: Assignment


How many parcels are delivered by each distribution center?
Approach
- For each parcel, sample an operator
- Find the operator's distribution center that is closest (shortest distance) to the parcel


Methodology: Assignment


Approach
- For each parcel, sample an operator
- Find the operator's distribution center that is closest (shortest distance) to the parcel
Outcome
- Nine centers with 300+ parcels
- Remaining centers with less than 300
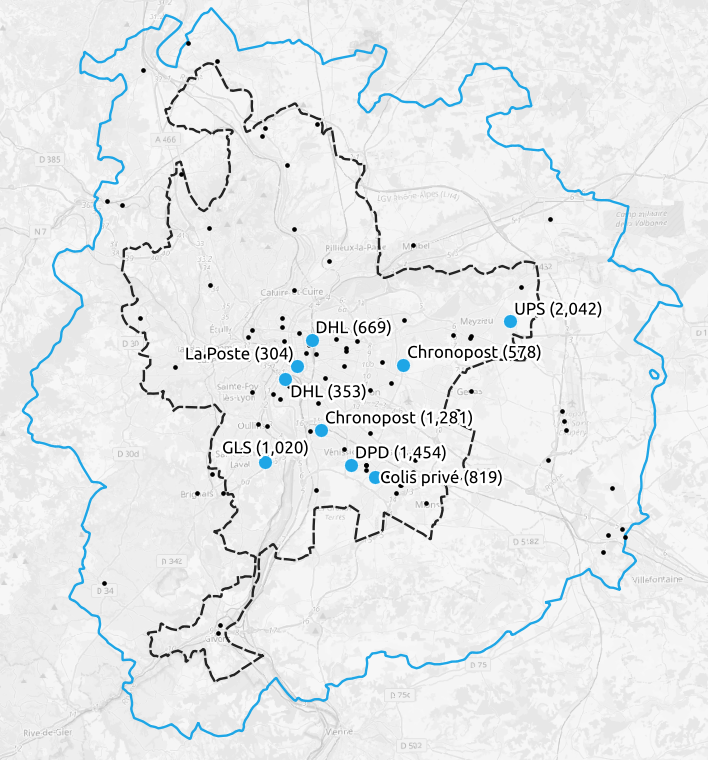
How many parcels are delivered by each distribution center?
Methodology: Cost structures


What influences operators decisions?
Methodology: Cost structures


What influences operators decisions?
Salaries
Vehicles
Distance
Daily cost
+
+
=
Methodology: Cost structures


What influences operators decisions?
Assumption (from grey literature)
- 1,300 EUR net per month
- 1,700 EUR gross per month
- 3,400 EUR staff cost per month
- 25 active days per month
- 136 EUR per day
Salaries
Vehicles
Distance
Daily cost
+
+
=
Methodology: Cost structures


What influences operators decisions?
Salaries
Distance
Daily cost
+
+
=
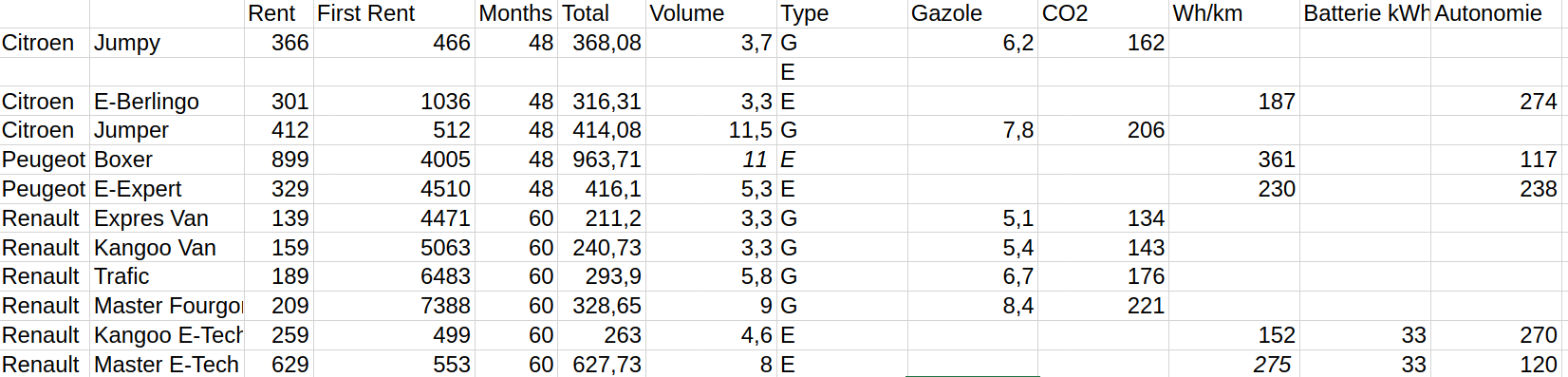
- We examined long-duration rental offers (LLD) of French vehicle manufacturers
Vehicles
Methodology: Cost structures


What influences operators decisions?
Daily cost
=
- Insight: Rental costs depend linearly on the transport volume
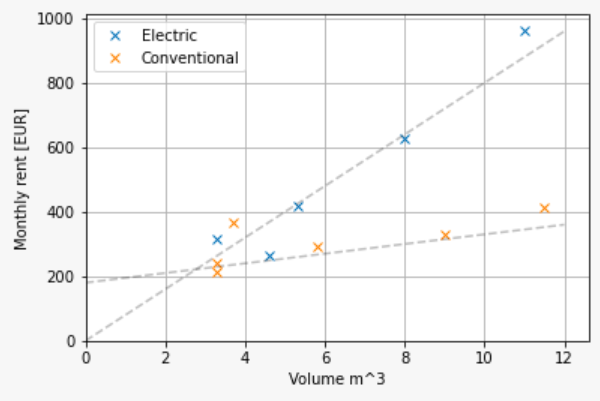
Salaries
Distance
+
+
Vehicles
Methodology: Cost structures


What influences operators decisions?
Daily cost
=
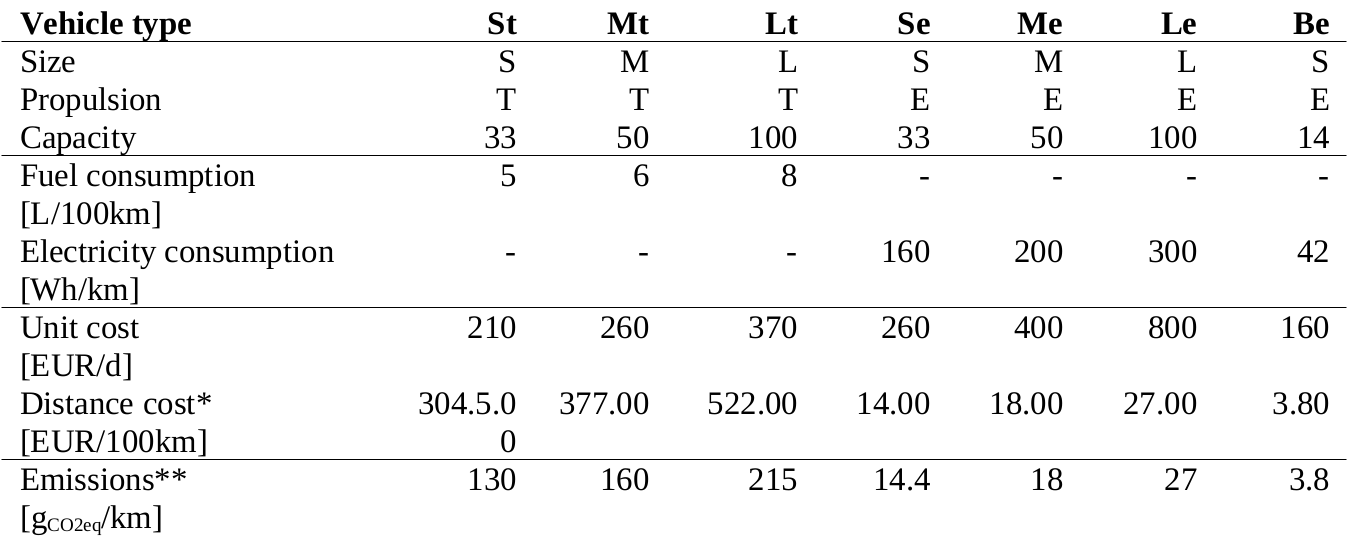
- Seven prototypical vehicle types: 3 sizes thermal or electric plus cargo-bike

Salaries
Distance
+
+
Vehicles
Methodology: Cost structures


What influences operators decisions?
Daily cost
=
- Distance-costs depend on consumption of fuel and electricity
- Multiplied by fuel or electricity prices (example 1.45 EUR/L and 9ct/kWh)



Salaries
Distance
+
+
Vehicles
Methodology: Cost structures


What influences operators decisions?
Daily cost
=
- Additional information from our manufacturer analysis: Emissions
- Assuming 90 gCO2eq/kWh for electric vehicles


Salaries
Distance
+
+
Vehicles
Methodology: Optimization


Minimize costs
Methodology: Optimization


Heterogeneous Vehicle Routing Problem
- Minimize cost per distribution center
- Operator can choose vehicles (7 types) and routes
- Operator must deliver all assigned parcels
- Maximum active time per day 10h
- Active time is travel time + 120s delivery + 60s pick-up per parcel
- Vehicles can not exceed capacity (we assume 10 parcels per m3)
- Multiple tours per vehicle are allowed
- Vehicles start and end the day at the distribution center
Minimize costs
Methodology: Optimization


Heterogeneous Vehicle Routing Problem
- Minimize cost per distribution center
- Operator can choose vehicles (7 types) and routes
- Operator must deliver all assigned parcels
- Maximum active time per day 10h
- Active time is travel time + 120s delivery + 60s pick-up per parcel
- Vehicles can not exceed capacity (we assume 10 parcels per m3)
- Multiple tours per vehicle are allowed
- Vehicles start and end the day at the distribution center
Minimize costs
Data
- OpenStreetMap network
- Extracted using osmnx
- Distance matrix between parcels and depot
- Travel time matrix using congestion factors
Solver
- Open-source
- VROOM
Visualisation platform


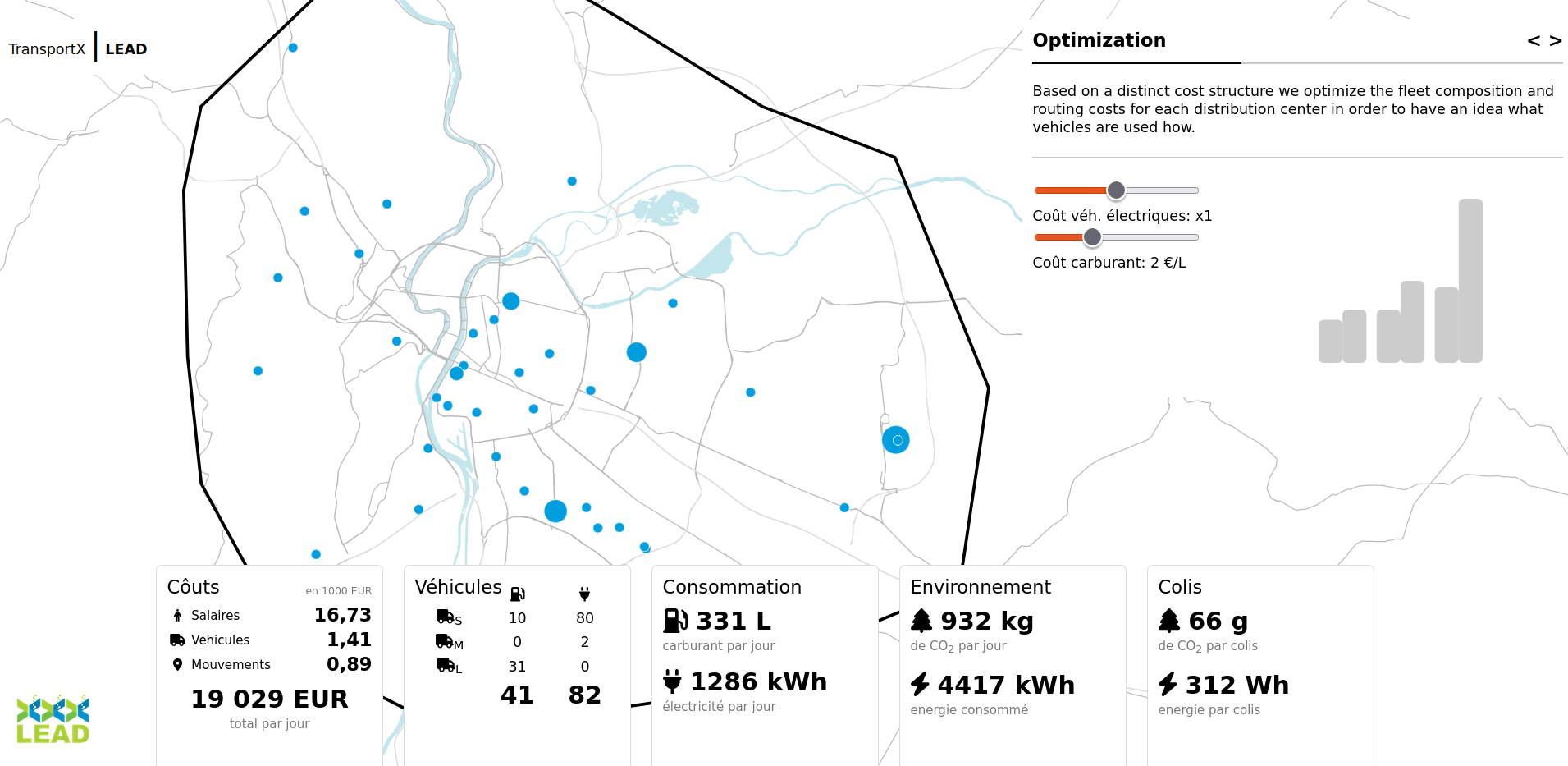
UCC platform


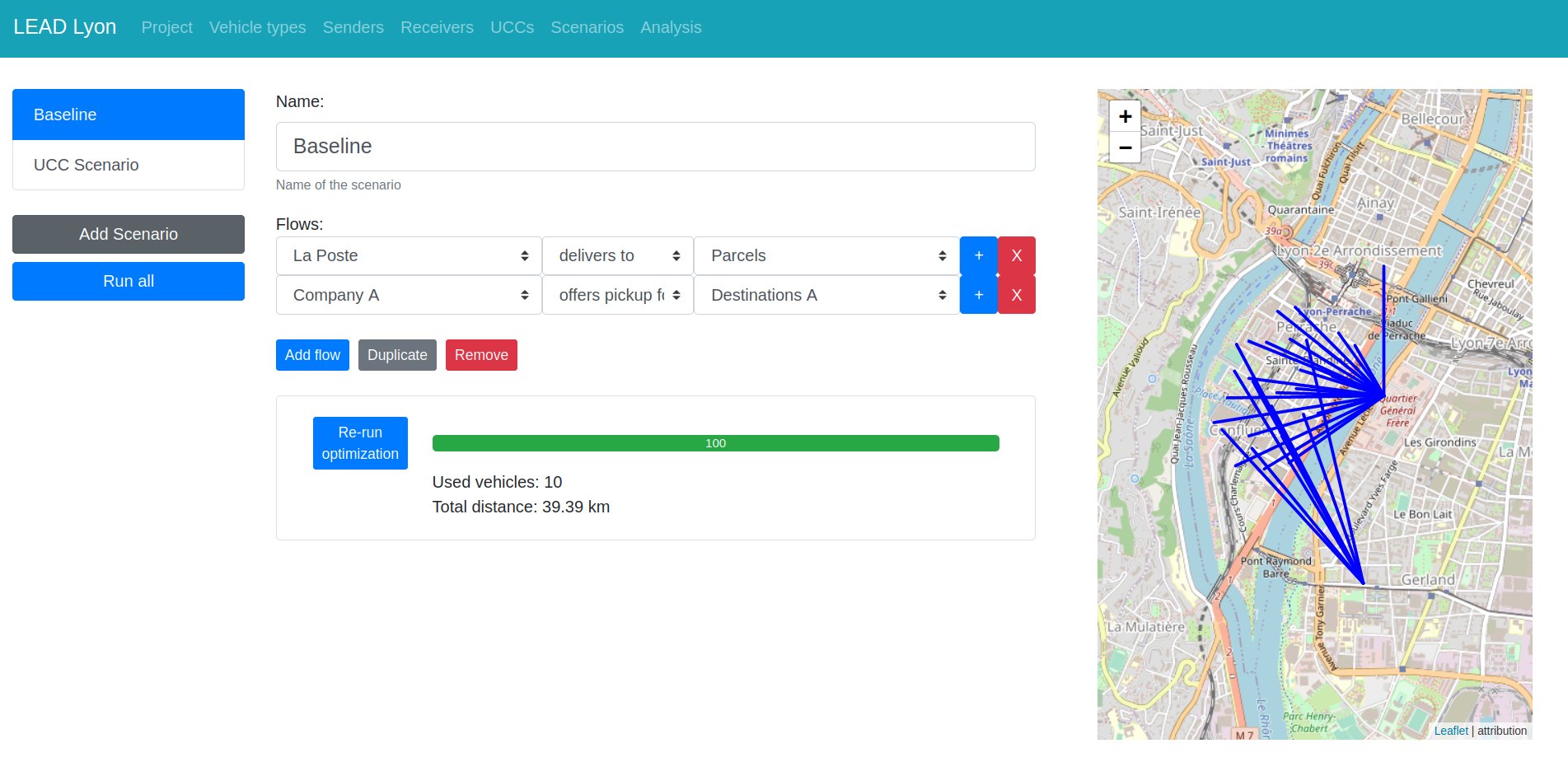
Discussion & Open questions


-
Validation
- What data can we use to validate the model?
- Validation of individual operators?
-
Coherence
- Are our cost structures coherent? Did we miss some aspects?
- Are our cost structures coherent? Did we miss some aspects?
-
Replicability
- Data available anywhere in France (but ADM survey only for Lyon)
- Theoretically applicable anywhere in France
Next steps


-
Scenarios
- Define more interesting and detailed scenarios
- Especially in terms of policies
-
Integration of new components
- Parcel lockers
- ZFE
-
Approximation model
- VRPs show specific structure
- Possibility to approximate solutions
- Allows for in-the-loop optimization (optimally placing UCCs, ...)


Questions?




Exploring the system-level impacts of urban parcel deliveries using synthetic data
By Sebastian Hörl
Exploring the system-level impacts of urban parcel deliveries using synthetic data
LAET, 2 March 2023, Séminaire d'Economie des Transports
- 618



