

K-matrix formalism in light-meson spectroscopy
Sebastián Ordóñez
Email: jsordonezs@unal.edu.co
Supervisor: Diego A. Milanés
Email: damilanesc@unal.edu.co
Phenomenology of High Energy Physics Group
Departamento de Física
Universidad Nacional de Colombia


Outline
- Introduction
- Dalitz plot and K-matrix formalism (The issue)
- Analysis
- Implementation of K-matrix formalism in D-decays
- Examples
- Results and Conclusions
- What we have learnt so far


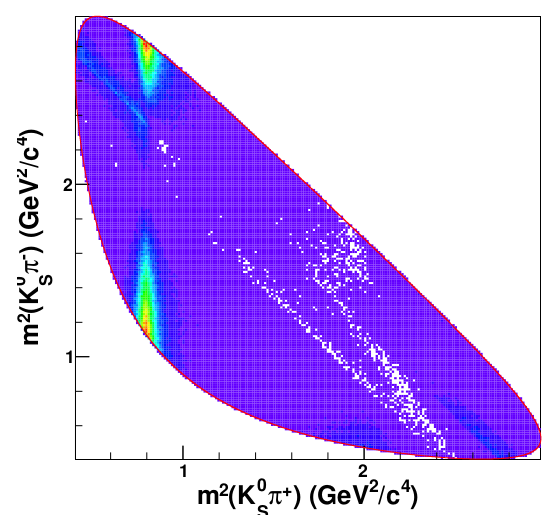
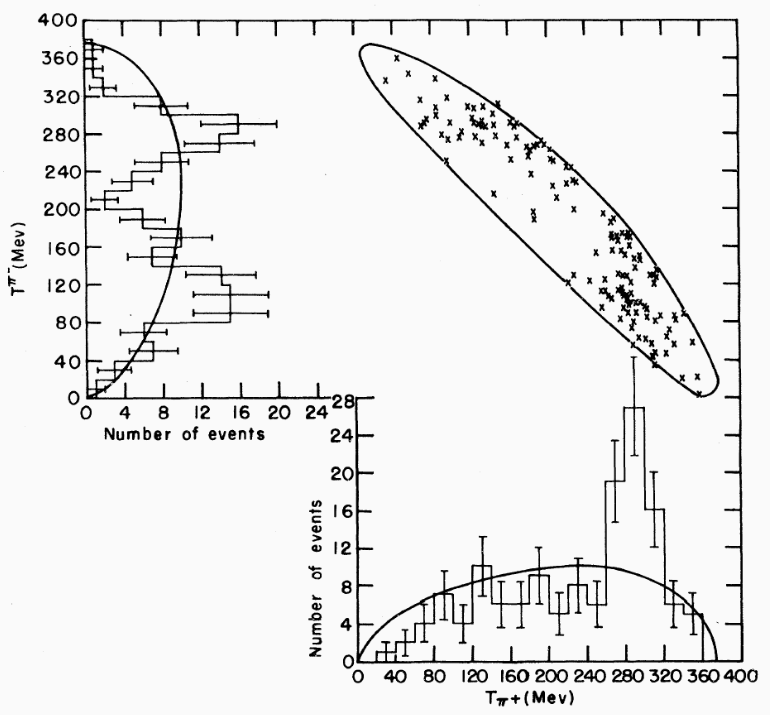
Dalitz plots
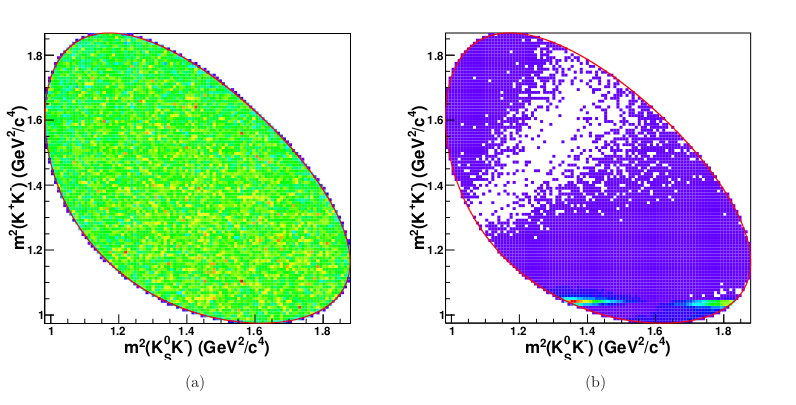
-
What are Dalitz Plots? Representations of a three-body decay
- DP allow us to extract dynamical information from deviations of a "homogeneous event distribution" (phase-space).
D. Milanés, Measurement of D 0 − D̄ 0 mixing in the BABAR experiment. PhD thesis,
Universidad de Valencia, Departmento de Física Teórica, 2010.


... and a question
- A model for decay is needed, i.e.
- How to deal with the underlying strong dynamics effects?
The S-wave is characterized by broad, overlapping resonances


Isobar Model
-
Typically for describing resonances is employed a sum of Breit-Wigner functions (Isobar Model).
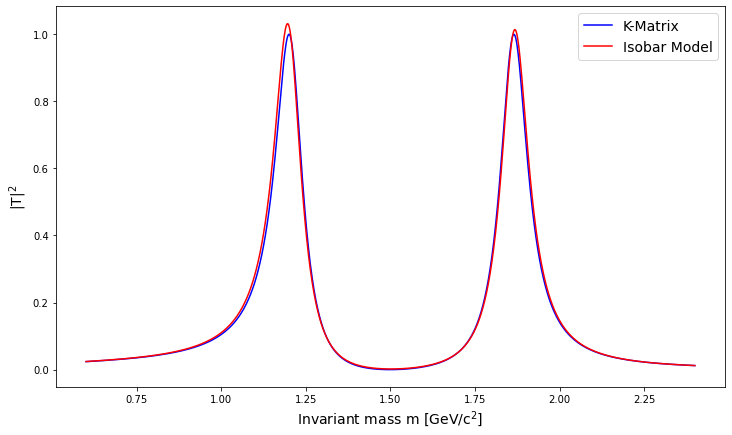
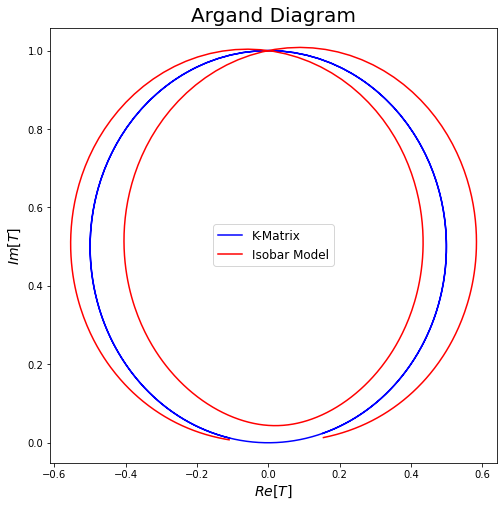


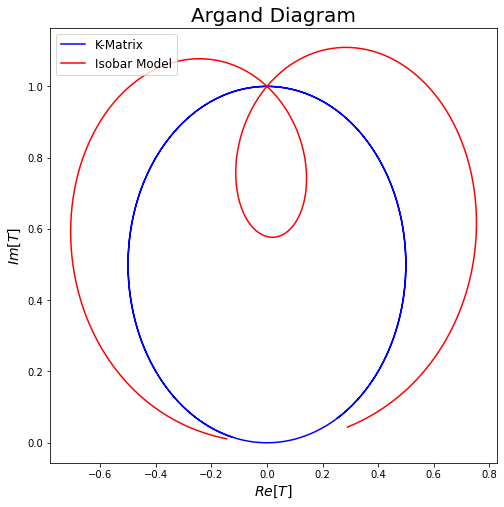
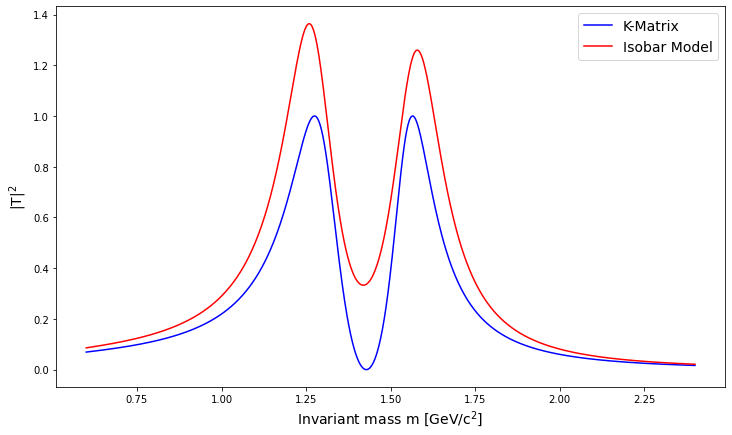
The issue
-
Why is this so problematic? Unitarity is not explicitly guaranteed by a simple sum of Breit-Wigner functions (Isobar Model).


The K-matrix
-
What is K-matrix? It follows from the unitary S-matrix
We can express any unitary operator in terms of an hermitian operator
In terms of the T-matrix


The advantages of K-matrix approach
- It heavily simplifies the formalization of any scattering problem since the unitarity of S is automatically respected.
- For a single-pole problem a K-matrix reduces to the standard BW formula.
- The K-matrix approach can be extended to production processes.


The advantages of K-matrix approach
- K-matrix allows for the inclusion of all the knowledge coming from scattering experiments.
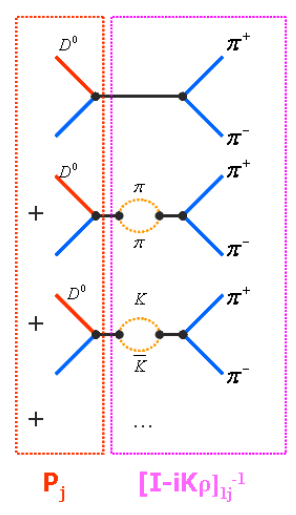
Describes coupling of resonances to D
Comes from scattering data


S-wave scattering parameterization
We take the channels j as
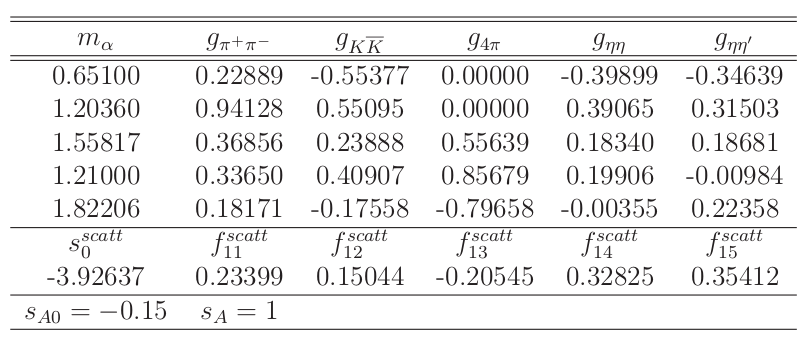
V.V Anisovich and A.V.Sarantsev Eur.Phys.J.A16 (2003) 229


S-wave scattering parameterization
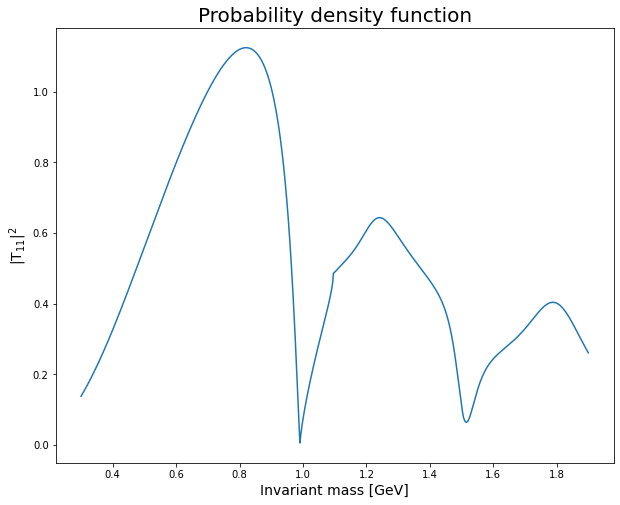
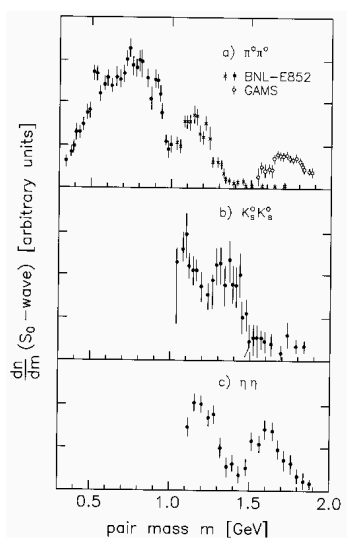


S-wave scattering parameterization



Thank you!
Questions?
K-matrix formalism
By Sebastian Ordoñez
K-matrix formalism
- 913



