The Intertwined Histories of Artificial Intelligence and Education
Shayan Doroudi
AI-ALOE Webinar
February 26, 2025

There have been two major strands with different visions for what AI should like and what education should like.
Why History?
AI research was fundamentally intertwined with education research from the beginning...but that's not so much the case anymore.
There have been two major strands with different visions for what AI should like and what education should like.
Why History in the Age of LLMs?
AI research was fundamentally intertwined with education research from the beginning...but that's not so much the case anymore.
But perhaps LLMs give us a new opportunity to come back to this!
Ironically, LLMs come from a third strand that was largely disconnected from education.
...but, we can attempt to align them to either of these earlier visions!
There‘s more to AI and education than large language models.
1956
Dartmouth Workshop

"Dartmouth Tetrad": Herbert Simon, Allen Newell, Marvin Minsky, & John McCarthy
1956
Dartmouth Workshop
Part I:
The Neats
1956
Herb Simon and Allen Newell create the
Logic Theorist


1956
1970
Simon and Newell publish “Human Problem Solving: The State of the Theory in 1970”
"The theory of problem solving described here gives us a new basis for attacking the psychology of education and the learning process. It allows us to describe in detail the information and programs that the skilled performer possesses, and to show how they permit him to perform successfully."
Establish information-processing psychology (or cognitivism) as dominant learning theory in psychology and education.
Simon and Newell's colleagues conduct decades of work on intelligent tutoring systems.
Herb Simon and Allen Newell create the
Logic Theorist
Simon, H. A., & Newell, A. (1971). Human problem solving: The state of the theory in 1970. American Psychologist, 26(2), 145.
1967
Newell started working on Merlin, an intelligent tutoring system to teach graduate AI!
Simon coined the term "learning engineering"
"the effort transmuted into one of building a program that would understand artificial intelligence"
1996
Simon and colleagues wrote a famous article in Educational Researcher defending cognitivism and arguing against situated learning
1970
Herb Simon and Allen Newell create the
Logic Theorist
Simon and Newell publish “Human Problem Solving: The State of the Theory in 1970”
1956
Simon, H. A. (1967). Job of a college president. Educational Record, 48(1), 68–78.
Moore, J., & Newell, A. (1974). How can Merlin understand? In L. W. Gregg (Ed.), Knowledge and Cognition. Psychology Press.



Part II:
The Scruffies
1956
1967
Newell started working on Merlin
Simon coined the term "learning engineering"
1970
Herb Simon and Allen Newell create the
Logic Theorist
Simon and Newell publish “Human Problem Solving: The State of the Theory in 1970”
Marvin Minsky joins faculty at MIT
Seymour Papert goes to Geneva to study with Jean Piaget
1958


1956
1967
Newell started working on Merlin
Simon coined the term "learning engineering"
1970
Herb Simon and Allen Newell create the
Logic Theorist
Simon and Newell publish “Human Problem Solving: The State of the Theory in 1970”
1964
Marvin Minsky joins faculty at MIT
Seymour Papert goes to Geneva to study with Jean Piaget
1958
Papert joins Minsky at MIT to work on AI from a constructivist
perspective
"I made the transition because I believed that my new world of machines could provide a perspective that might lead to solutions to problems that had eluded us in the old world of children."
Papert, S. (1980). Mindstorms: Children, computers, and powerful ideas. Basic Books, Inc.
1967
Newell started working on Merlin
Simon coined the term "learning engineering"
1970
Herb Simon and Allen Newell create the
Logic Theorist
Simon and Newell publish “Human Problem Solving: The State of the Theory in 1970”
1964
Papert and colleagues create the Logo programming language
Computational Thinking
Microworlds
Scratch
Constructionism
New ways of thinking about learning and education inspired by Piaget and AI
1956
Marvin Minsky joins faculty at MIT
Seymour Papert goes to Geneva to study with Jean Piaget
1958
Papert joins Minsky at MIT to work on AI from a constructivist
perspective
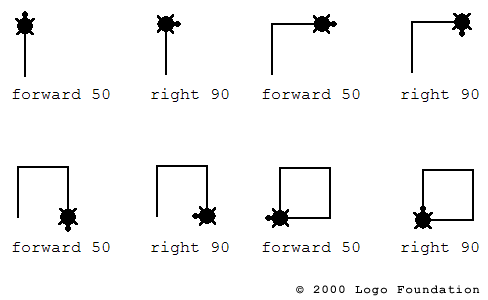
Logo Turtles
for repetition in range(10000): begin_fill() for side in range(4): forward(20) right(60) end_fill() right(random.choice([0, 180]))
for repetition in range(10000): begin_fill() for side in range(4): forward(20) right(60) end_fill() right(random.choice([0, 180]))
1956
Newell started working on Merlin
Simon coined the term "learning engineering"
Herb Simon and Allen Newell create the
Logic Theorist
Marvin Minsky joins faculty at MIT
Seymour Papert goes to Geneva to study with Jean Piaget
1958
Papert and colleagues create the Logo programming language
1967
1985
Second International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Education
"The 1985 conference ended with the exciting prospect of the ‘coming together’ of the two traditional streams of ‘tutoring systems’ and ‘learning environments’ to address common problems in the design of instructional systems from an Artificial Intelligence perspective."
Lawler, R., & Yazdani, M. (1987). Artificial intelligence and education: Learning environments and tutoring systems (Vol. 1). Intellect Books.
1956
Newell started working on Merlin
Simon coined the term "learning engineering"
Herb Simon and Allen Newell create the
Logic Theorist
Marvin Minsky joins faculty at MIT
Seymour Papert goes to Geneva to study with Jean Piaget
1958
1985
Second International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Education
"it was clear that a new interest group had emerged; one which was committed neither primarily to AI nor to education matters, but to matters which fall into the overlap between them. Both subjects show an interest in knowledge acquisition (be it people or machines) and they need a theoretical framework in which to study learning and teaching processes. They can also help each other in many ways."
Yazdani, M., & Lawler, R. W. (1986). Artificial intelligence and education: An overview. Instructional Science, 14(3), 197–206.
1967
Papert and colleagues create the Logo programming language
1956
Newell started working on Merlin
Simon coined the term "learning engineering"
Herb Simon and Allen Newell create the
Logic Theorist
Marvin Minsky joins faculty at MIT
Seymour Papert goes to Geneva to study with Jean Piaget
1958
1985
Second International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Education
1967
Papert and colleagues create the Logo programming language
1956
Newell started working on Merlin
Simon coined the term "learning engineering"
Herb Simon and Allen Newell create the
Logic Theorist
Marvin Minsky joins faculty at MIT
Seymour Papert goes to Geneva to study with Jean Piaget
1958
1985
Second International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Education
1991
The fifth AIED conference gets rebranded as the first International Conference of the Learning Sciences
by Roger Schank — also a leading AI researcher.
1967
Papert and colleagues create the Logo programming language
1956
Newell started working on Merlin
Simon coined the term "learning engineering"
Herb Simon and Allen Newell create the
Logic Theorist
Marvin Minsky joins faculty at MIT
Seymour Papert goes to Geneva to study with Jean Piaget
1958
1985
Second International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Education
1991
The fifth AIED conference gets rebranded as the first International Conference of the Learning Sciences
by Roger Schank — also a leading AI researcher.
Artificial Intelligence in Education (AIED) community
Learning Sciences community
Over time, NEITHER community was concerned with the interdisciplinary study of learning in humans and machines.
1967
Papert and colleagues create the Logo programming language
Two Approaches to AI and Education
| AI | Neat | Scruffy |
| Pedagogy | Instructionism | Constructionism |
| Ed Tech | Tutoring Systems | Microworlds |
| Psychology | Information-Processing | Constructivism |
| Philosophy | Rationalism | Romanticism |
”Education is not the filling of a pail, but the lighting of a fire.”
— Plutarch
Part III:
The Connectionists
1956
Newell started working on MERLIN
Herb Simon and Allen Newell create the
Logic Theorist
1985
Second International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Education
1964
Papert joins Minsky at MIT to work on AI from a constructivist
perspective
The Neats
The Scruffies
Artificial Intelligence in Education (AIED) community
Learning Sciences community
1956
Newell started working on MERLIN
Herb Simon and Allen Newell create the
Logic Theorist
1985
Second International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Education
1943
Warren McCulloch and Walter Pitts describe the
artificial neural network
as a model of computation
1964


Papert joins Minsky at MIT to work on AI from a constructivist
perspective
Artificial Intelligence in Education (AIED) community
Learning Sciences community
Newell started working on MERLIN
1957
1956
Herb Simon and Allen Newell create the
Logic Theorist
1985
Second International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Education
1943
1964
Warren McCulloch and Walter Pitts describe the
artificial neural network
as a model of computation
Papert joins Minsky at MIT to work on AI from a constructivist
perspective
Artificial Intelligence in Education (AIED) community
Learning Sciences community
Frank Rosenblatt develops the perceptron learning algorithm for single-layer neural networks
Newell started working on MERLIN
1957
1956
Herb Simon and Allen Newell create the
Logic Theorist
1985
Second International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Education
1943
1964
Papert joins Minsky and McCulloch at MIT to work on AI from a constructivist
perspective
Warren McCulloch and Walter Pitts describe the
artificial neural network
as a model of computation
Frank Rosenblatt develops the perceptron learning algorithm for single-layer neural networks
Artificial Intelligence in Education (AIED) community
Learning Sciences community
Newell started working on MERLIN
1957
1969
Papert and Minsky publish Perceptrons which showed the limitations of simple neural networks
1956
Herb Simon and Allen Newell create the
Logic Theorist
1985
Second International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Education
1943
1964
Warren McCulloch and Walter Pitts describe the
artificial neural network
as a model of computation
(...and showed what simple neural networks could do!)
Frank Rosenblatt develops the perceptron learning algorithm for single-layer neural networks

Papert joins Minsky and McCulloch at MIT to work on AI from a constructivist
perspective
Artificial Intelligence in Education (AIED) community
Learning Sciences community
Newell started working on MERLIN
1957
1969
1956
Herb Simon and Allen Newell create the
Logic Theorist
1985
Second International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Education
1943
1964
1985
Researchers discover the backpropagation algorithm finally showing the practicality of multilayer neural networks
Papert and Minsky publish Perceptrons which showed the limitations of simple neural networks
(...and showed what simple neural networks could do!)
Warren McCulloch and Walter Pitts describe the
artificial neural network
as a model of computation
Papert joins Minsky and McCulloch at MIT to work on AI from a constructivist
perspective
Artificial Intelligence in Education (AIED) community
Learning Sciences community
Frank Rosenblatt develops the perceptron learning algorithm for single-layer neural networks
Newell started working on MERLIN
1957
1969
1956
Herb Simon and Allen Newell create the
Logic Theorist
1985
Second International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Education
1943
1964
1985
Researchers discover the backpropagation algorithm finally showing the practicality of multilayer neural networks
Artificial Intelligence in Education (AIED) community
Learning Sciences community
Papert and Minsky publish Perceptrons which showed the limitations of simple neural networks
(...and showed what simple neural networks could do!)
Warren McCulloch and Walter Pitts describe the
artificial neural network
as a model of computation
Situated learning emerges as a learning theory in reaction to AI and cognitivism
1987
Papert joins Minsky and McCulloch at MIT to work on AI from a constructivist
perspective

Frank Rosenblatt develops the perceptron learning algorithm for single-layer neural networks
Newell started working on MERLIN
1985
Second International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Education
2012
Deep learning is established
Artificial Intelligence in Education (AIED) community
Learning Sciences community
Researchers discover the backpropagation algorithm finally showing the practicality of multilayer neural networks
Situated learning emerges as a learning theory in reaction to AI and cognitivism
1987
2012
Large language models become popular
2022
Deep learning is established
?
Researchers discover the backpropagation algorithm finally showing the practicality of multilayer neural networks
1985
Second International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Education
Artificial Intelligence in Education (AIED) community
Learning Sciences community
1985
How LLMs Compare to Earlier AI
Unlike earlier AI, LLMs were trained on a LOT of data with no theory of learning or pedagogy in mind.
BUT it does NOT always act like a human!
The resulting pretrained model can be adopted as a model for learning and teaching.
Two Approaches to AI and Education
| AI | Neat | Scruffy |
Connectionist
|
| Pedagogy | Instructionism | Constructionism Situated Learning
|
| Ed Tech | Tutoring Systems | Microworlds |
| Psychology | Information-Processing | Constructivism |
| Philosophy | Rationalism | Romanticism |
Which Approaches Do LLMs Align With?
| AI | Neat | Scruffy |
Connectionist
|
| Pedagogy | Instructionism | Constructionism Situated Learning
|
| Ed Tech | Tutoring Systems | Microworlds |


“Ken Kahn is a pioneer in computing education, reaching back to the first days of the Artificial Intelligence Laboratory at MIT. The Learner’s Apprentice brings this perspective to the latest advances in Generative AI, where student creations result from active collaborations with AI partners.” — Hal Abelson

There have been two major strands with different visions for what AI should like and what education should like.
Why History in the Age of LLMs?
AI research was fundamentally intertwined with education research from the beginning...but that's not so much the case anymore.
But perhaps LLMs give us a new opportunity to come back to this!
Ironically, LLMs come from a third strand that was largely disconnected from education.
...but, we can attempt to align them to either of these earlier visions!
There‘s more to AI and education than large language models.
Further Reading



AI-ALOE Webinar: History of AI and Education
By Shayan Doroudi
AI-ALOE Webinar: History of AI and Education
- 54



