Dynamic vis
06/21/2022
Visualization simplex \(\Delta\)
Static
Interactive
Dynamic
Ref: grammar of animation
no interactivity
controls outside the plotting area
graphic elements as links
tooltips
selections
play, pause, rewind
fading tooltips
Fully static
Always in flux
animation between static stages
(formal) grammar / declarative languages
(formal) specifications / frameworks
interactive vis authoring systems
(i.e. has user interfaces)
UW
Thompson
Thompson
Demiralp et al.
Kindlmann
involves textual programming
no programming
MacKinlay
A Presentation Tool (APT)
Polaris | Tableau
Bostock
Wu et al.
Wilkinson
Wickham
Layered GoG | ggplot
UW
Vega & Vega-Lite
Pedersen
static
dynamic| interactive
Bertin
Semiology of graphics
Ge
Ge
Some guiding questions
- Why dynamic / animated visualization?
- Why formal descriptions of (animated) visualizations?
- What are some existing (formal) models of static visualizations? Of dynamic/animated visualizations?
(Formal) (static) Vis Models
- (Mackinlay 1986)
- 2 criteria: Effectiveness & Expressiveness
- Composition algebra over basis set of graphical primitives (Bertin)
- (Wilkinson 1999) -- Grammar of Graphics (GoG)
- (Demiralp et al. 2014) -- Visual embedding
- (Kindlmann and Scheidegger 2014) -- Algebraic framework of visualization design
- (Wu et al. 2022) -- ComputableViz
- (Tversky, Morrison, and Betrancourt 2002)
- Congruence; Apprehension
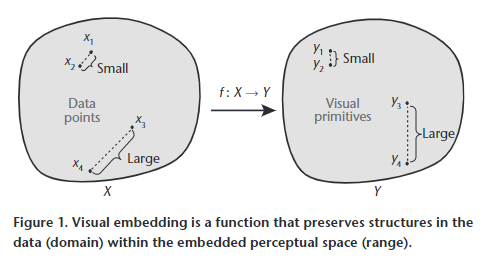
Demiralp et al.
Visualization Embedding
- Optimizing some perceptual goal
- "visualization as a perceptual painting of structure in data"
- Using pairwise distances \(\to\) essentially defining a metric
- Estimate perceptual distance with crowdsourcing
Kindlmann
Algebraic Visualization Design
Three general principles for good visualization design:
- Representation Invariance: data, not spurious details of its representation, should determine the impression of the visualization
- Unambiguous data depiction: make large changes in the data clearly visible
- Visual-Data correspondence: meaningful changes in data should produce meaningful changes in impressions
Formal model:
space of data
space of data representations
💻
space of visualizations
D
R
V
D
R
V
α
ω
data symmetries
visualization symmetries
Dynamic Display!
Kindlmann
Algebraic Visualization Design
Three general principles for good visualization design:
- Representation Invariance: data, not spurious details of its representation, should determine the impression of the visualization
- Unambiguous data depiction: make large changes in the data clearly visible
- Visual-Data correspondence: meaningful changes in data should produce meaningful changes in impressions
Linking this to Tversky's principles about congruence and apprehension:
- Congruence: the visual (external) structure of an explanatory graphic should correspond to the desired structure of the mental (internal) representation in the viewer
- Apprehension: graphics should be readily and accurately perceived and comprehended
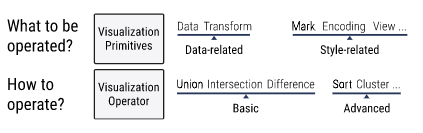
Wu
ComputableViz
- Modeling visualizations as computable data
\(\to\) How?
- Convert visualization specifications to relational database
- Use relational algebra to perform operations such as
- union, intersection, difference
- sort, cluster, ...
Thinking about algebra...
- What is an "algebra"?
- Requires definitions of operator and operand.
- Wilkinson, Grammar of Graphics -- relational algebra
- ComposablzeViz -- relational algebra
- D3 -- relational algebra
- Mackinlay -- composition algebra
- Vega-Lite -- composition algebra
On similarity, sequencing, and searching...
- Given specifications, how do we measure the difference / distance between two graphs?
- What about object matching between "keyframes" in sequencing / dynamic vis?
Dynamic vis
By Sheng Long
Dynamic vis
- 67



